Chapter 02 : Energy
In Chapter One, you Learned about exploration of the environment. In our environment, there are different objects which produce energy. Energy is the ability to do work. Energy is obtained from objects such as a whistle, a stove and a torch. Such objects produce various forms of energy. In this chapter, you will learn about three forms of energy. These are sound energy, heat energy and light energy. You will also learn how these types of energy are used in daily life.
Sound energy
Sound energy is the energy produced by vibrating sound waves.
There are two sources of sound.
1. Natural sources of sound
2. Man-made sources of sound
Natural sources of sound are animals, wind, streams and volcanoes.
Man—made sources of sound are also called artificial sources of sound. Artificial sources of sound are airplanes, helicopters, trains, explosions, factories and home appliances such as vacuum cleaners and fans.
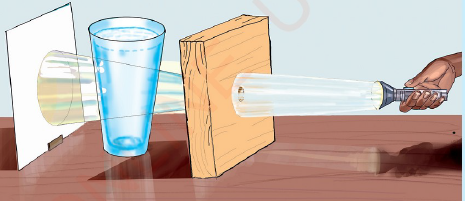
Look at the following pictures and then read the description that follows.
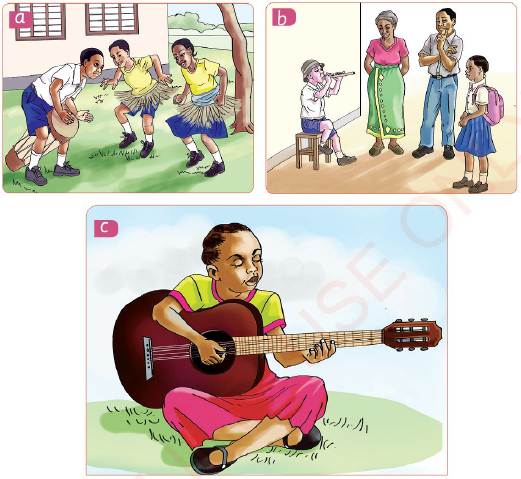 |
| Figure 1 Activities producing sound energy |
Sound is a form of energy produced from vibrations of various things. It is a means of communication. Sound spreads from its source to all directions. Playing a drum, a whistle or a guitar produces sound. When people talk to each other, they produce sound. Also, when a hen is calling its chicks, it produces sound. Some of the sources of sound energy include a flute, a piano, a trumpet, a whistle, a drum, a guitar and a bell. We hear sounds through our ears.
Activity 1 To investigate how sound travels in the air
| Materials a bell and a piece of iron Procedure
|
When the bell rings, sound waves spread in all directions. Pupils hear the sound and assemble from all directions. The sound travels by spreading in air through waves.
Uses of sound energy
- For communication as in talking, calling and crying.
- For entertainment such as listening to music.
- For alarm or alert such as ambulance, police, fire and horns.
- Used by bats to navigate and find food.
Reflection of sound
Sound bounces back when it meets an obstacle or a solid body. This is a reflection of sound. A solid body can be a wall or a rock. A reflected sound is called an echo.
Activity 2 To produce an echo
| Material Empty room Procedure
|
When you shout "hello" in an empty room, the sound is reflected. In a few seconds, you hear the word "hello" again. This is an echo.
Activity 3 To investigate whether sound travels in water
| Materials Basin, water and a small stone Procedure
|
 |
| Figure 2 Transfer of sound waves |
When you drop anything in water, sound and waves are produced. Water waves reflect how sound moves in water. Therefore, sound travels in water in a similar way it does in the air.
In Figure 2, the boy drops a stone into a basin full of water. Water waves show how sound waves travel by spreading.
| Activity 4 To examine the way sound travels through cotton string |
Materials Hard paper, glue and a cotton string
Procedure
- Fold the paper to form two speaker shapes by using glue.
- Join the two speakers using a long cotton string.
- Tell your friend to call you from one end of the speaker.
- Hold one speaker on your ear while your friend is calling.
- Can you hear the sound through the cotton string?
- Please write what you hear.
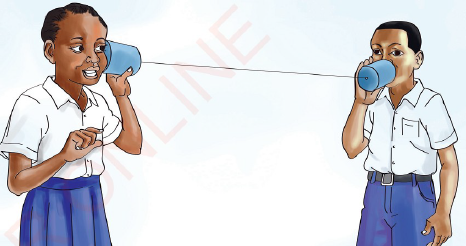 |
| Figure 3 Transfer of sound through a string |
When one pupil calls from one speaker, another pupil hears the sound that passes through the cotton string. This shows that sound travels through a cotton string.
Study the following picture and investigate how sound travels through the iron rod.
 |
| Figure 4 Transfer of sound through the iron rod |
Figure 4 shows a girl hitting an iron rod. The boy is listening from the other end.
| Activity 5 Investigate how sound travels through an iron rod |
| Materials A piece of iron rod, a table and a ruler Procedure
|
We have seen that air, water, cotton string and an iron rod transmit sound. Therefore, sound can be transferred in solid objects, liquids, and air.
| Exercise 1. What is energy? 2. Write three forms of energy. 3. What is sound energy? 4. Mention two sources of sound. 5. Mention three natural sources of sound. 6. Mention three artificial sources of sound. 7. List uses of sound. 8. A reflected sound is called ___________ |
Heat energy
Heat is a form of energy. Heat energy can pass through solids, liquids and gases. For example, heat travels in iron, water and air. This shows that solids, liquids and gases can transfer heat.
Look at the following pictures to study different sources of heat.
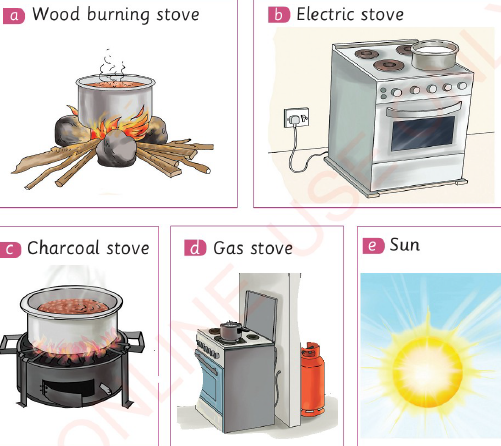 |
| Figure 5 Sources of heat energy |
Heat energy can be produced by various sources. These include wood burning stoves, electric stoves, charcoal stoves and gas stoves. It can also be produced by the sun. The sun is one of the natural sources of heat.
Activity 6 To produce heat energy
| Materials A piece of stick and a piece of wood Procedure
|
When you rub your palms, they become hot. Therefore, friction causes heat.
| Activity 7 To investigate objects which allow heat to pass through |
| Materials Hot water, aluminium cup, plastic cup and large wooden spoon Procedure
|
The transfer of heat differs from one object to another. Some solid objects like aluminium and iron allow heat to pass very fast. Objects like these are called good conductors of heat. Solid objects like wood and plastic do not allow heat to pass easily due to their nature. These objects are called insulators or poor conductors of heat.
Heat transfer methods
Heat always moves from a warm to a cool place. For example, hot objects in a cool room will cool to a room temperature. Also, cold objects in a warm room will heat up to the room temperature.
Three ways of heat transfer
- Conduction, is the transfer of heat through solid objects. When a metal strip is heated at an end, the heat travels to the other end.
- Convection is the transfer of heat through liquid substances such as water.
- Radiation is the transfer of heat through the air.
Look at the following pictures to study different uses of heat.
 |
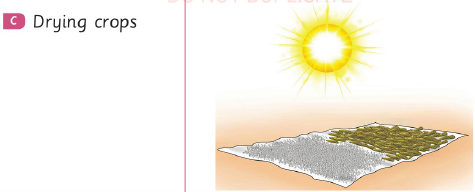 |
| Figure 6 Uses of heat |
Heat energy is also used for cooking food and drying clothes. Other uses of heat energy are boiling water for drinking and bathing, hatching chicks and grilling.
Light energy
Look at the following pictures and then read the description that follows.
 Kerosene lamp |  The sun |
 A torch | |
| Figure 7 Sources of light energy | |
The pictures in Figure 6 show some sources of Light. There are two main sources of Light, namely natural and artificial sources. The sun is the main natural source of light. Artificial sources of Light include candles, kerosine lamps and torches.
Characteristics of Light energy
Activity 8 To investigate how light travels in the air
Procedure
(i) Stand outside early in the morning when the sun rises.
(ii) What do you see?
(iii) Write down what you see.
When the sun rises in the morning, you see light rays. These rays travel in straight Lines. Light is a form of energy. This energy helps us to see. Sunlight is also important for the growth of plants.
Activity 9 To examine materials which allow light to pass through and those which do not
| Materials Glass, white paper, cardboard with a hole, a book, torch and water Procedure
(v) When the sun rises in the morning, put a book in the direction of the sun. What do you see? |
Light rays from the torch pass through a hole, a glass and water. Then, the rays pass through glass to the paper. Therefore, light can pass through water, glass and paper. Light cannot pass through objects such as a book. The dark area behind the book is called a shadow. The shadow is found behind the object that does not allow light to pass through.
Reflection of light
Light rays can strike on a shining surface and go in a different direction. This action is called reflection of light. A mirror is a better light reflector than a shining plate. When you look at yourself in the mirror, you see your image. This is because the light rays from your face are reflected.
Any smooth and shining surface reflects light and forms an image. When you look into water, your image will appear. This is because the water surface is smooth and can reflect light. Objects which are neither smooth nor shiny do not reflect light. Examples of these are pieces of paper, board and soil.
Therefore, the general characteristics of light are as follows.
1. Light travels in a straight line.
2. Light is reflected when it strikes on a smooth or shiny surface.
3. Light bends when it passes from one medium to another. This bending of light is called refraction. For example, when you take a ruler and hold it in the air, it looks straight. But when you put it in water it looks bent.
Exercise
Match the words in group A and B to make the correct meanings.
Example. Fire — G
| Group A | Group B |
| (i) Reflection (ii) Sun(iii) Drum, bell and trumpet (iv) Heat travels in (v) Shadow(vi) Fire |
|
2. Answer the following questions.
- Light energy travels in a ______
- Mention objects that allow light to pass through them.
- Explain the importance of heat energy at home.
3. Explain why a frying part handle is made of wood or plastic.
4. Write TRUE or FALSE.
- There are two forms of energy. ___
- The sun is an artificial source of heat. ___
- Drums, bells, flutes and pianos produce sound. ________
- Heat can be transferred through an iron. __________
- Sound energy is caused by vibration of things. _______
- Friction causes heat. ___________________________
Vocabulary
Assemble coming or getting together
Grilling to cook food directly over or under high heat
Hole an opening through part of something
Image a physical likeness or representation
Insulator an object which does not allow heat to pass through
Kerosene lamp lamp that uses kerosene to burn
Reflect to bounce or throw back light rays or sound waves
www.learninghubtz.co.tz
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania