Chapter 01 : Environment
In this chapter, you will learn how to explore the environment.You will also identify living and non-living things in the environment. Environment is everything that surrounds us such as soil, plants, buildings, animals, air and water.
 Environment |
Exploring the environment
We identify things In the environment using parts of the body. These parts include eyes, nose, ears, tongue and skin. The eyes are used to see and identify things. The nose is used to detect good or bad smells. The ears are used for hearing and differentiating sounds. These sounds arise from different things such as cars, aeroplanes and music. The skin helps us to touch and feel things. The skin can detect hot, cold, hard, soft and rough objects when we touch them. The skin can also sense heat when we get closer to hot objects. It also senses cold when we stand next to cold things. The tongue is used to taste different foods, fruits and drinks. The eyes, tongue, ears, nose and skin are sense organs.
We should be careful when exploring things in the environment. Some things are poisonous, itchy, hot, stinky and sharp. You should not taste anything that you do not know.
Exercise 1
Answer the following questions.
1. The part of the body used to smell is called
2. The part of the body used to hear different sounds is called
3. The part of the body used to sense heat or cold is called
4. What is an environment?
5. Which part of the body is used to identify different colours of things?
6. Mention five things which are found in your school environment.
7. Which part of the body is used to taste honey?
Living and non-living things
Living things are things that have life. Living things can breathe, eat, grow, move, reproduce and die.
Non-living things are things which have no life.
Activity I Explore the school environment. Mention living and non-living things you have seen, touched and heard.
Look at the following pictures and answer the questions after them.
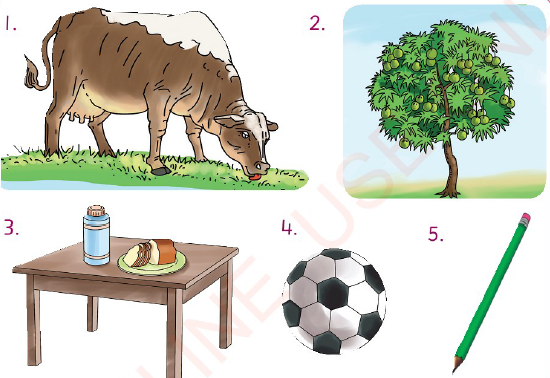 |
| Figure 2 living and non-living things |
The pictures in Figure 2 show a cow grazing on grass, a mango tree, a table with pieces of bread on a plate, and a thermos. They also show a pencil and a ball.
Question
Mention the living and non-living things found in Figure 2.
Exercise 2
Answer the following question.
Mention five living things and five non-living things.
Characteristics of living things
| Activity 2 To observe the difference between a grasshopper, a cockroach and a stone in a bottle. Materials Three bottles with small holes, a stone, live specimens of a grasshopper and a cockroach Procedure
|
In the bottle, the grasshopper will be seen jumping. The cockroach will be seen crawling. lumping and crawling are types of movement. Movement helps them to get their basic needs like food or safety from enemies. Small holes in the bottles help the grasshopper and the cockroach to get air. Without food and air they would die.
Characteristics of living things
All living things breathe, reproduce, grow and die. They also move, feed and excrete. These characteristics are briefly described below.
Breathing
Breathing is the process of taking air into and out of the lungs. Lack of fresh air causes organisms to die.
Reproducing
Living organisms increase in number through reproduction. Living things produce young beings which are similar to them. For example, a human being gives birth to a baby while a cow reproduces a calf. Plants reproduce seeds from which young plants grow.
 |
| Figure 3 Reproduction in animals |
Growing
Living organisms grow to different heights and sizes. If you sow a seed, after some time, it will grow into a seedling and later into a mature plant.
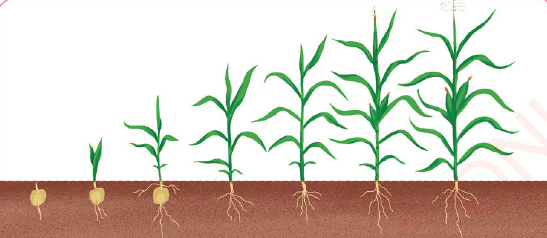 |
| Figure 4 Growth stages of plants |
Human beings, like other animals, increase in height and mass. They pass through different stages of development. The stages are infancy, childhood, teenage, adulthood and late adulthood(elderly).
Figure 5 Stages of human development
 |
Movement
Living organisms move. Animals move from one point to another. For example, grasshoppers jump and snakes slither from one place to another.
Plants move through the growth process. Leaves and branches move by growing towards light. Roots move downward and sideways to absorb water.
Feeding
Living organisms need food. Animals eat plants and other animals. For example, goats eat plants. Plants make their own food.
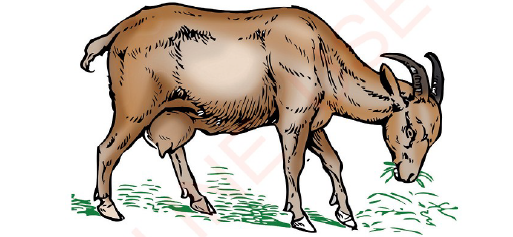 |
| Figure 6 A goat grazing on grass |
Excretion
Living organisms remove waste products from their bodies. The removal of waste products from the body is known as excretion. Examples of waste products are urine, sweat and carbon dioxide.
Waste products are harmful to the body. They must be removed to enable living things to be healthy.
| Exercise Answer the following question. Indicate whether the things are living or non-living things. Put a tick (✓) in the appropriate column. |
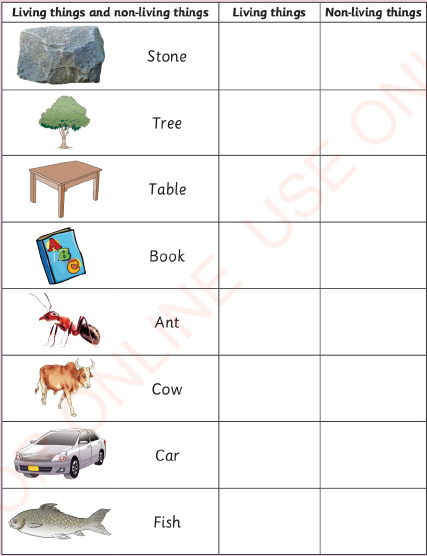 |
Valuing living things
Living things need to be protected and kept in a safe environment. They also need sufficient food. Hence, it is necessary to protect the environment. Doing so allows living things to reproduce, grow and live safely.
| Study the following picture and answer the questions that follow.  Figure 7 Activities for protecting environment Questions 1.From Figure 1, identify two ways used to protect the environment. 2. Mention two other ways of valuing animals and plants |
Taking precautions and safety measures
Dangerous living things
In the environment, some living things are dangerous. This type can harm or kill human beings or other animals. Examples of dangerous organisms are snakes, scorpions, bees, street dogs, lions and hyenas.
Do not therefore, play in bushes because snakes and others can harm you. Do not disturb dangerous animals like street dogs. Also, keep the environment clean and safe.
 |
| Figure 8 Dangerous living things |
Dangerous non-living things
Some of the non-living things in our environment are dangerous. These things can cause pain, injury or harm to a human being and other animals. Examples of dangerous non-living things are needles, knives, broken glasses, rusted nails and tins.
Therefore, be careful when you use needles and knives in daily activities. Also, make sure broken glasses, rusted tins and nails are disposed of properly. Ensure your environment is safe and clean.
 |
| Figure 9 Dangerous non—living things |
Read the following story and then answer the questions that follow.
Daima and Dinia are pupils at Kilimahewa Primary School. One day, they talked to their teacher while they were cleaning the school environment. The teacher told them the environment had dangerous living and non-living things. What follows is a dialogue between the teacher, Daima and Dinia.
| Teacher | Have you ever seen dangerous things? |
| Daima | Yes, teacher. I have seen some dangerous things in our environment. |
| Teacher | Good Daima! What are they? |
| Daima | I have seen a knife, a razor blade, a needle and fire. |
| Teacher | Which one has hurt you? |
| Daima | The knife cut my finger when I was cutting an orange. |
 |
| Figure 10 A child has cut himself while cutting an orange. |
Teacher Sorry Daima. A knife is dangerous, but it is very useful. It is used for peeling fruits and cutting various things.
Daima Thank you, teacher. When I was with Dinia, our guardian showed us how to hold and use knives carefully.
 |
| Figure 11 Holding a knife carefully |
Teacher Very good, Dinia. You have been listening to us for a while. Can you explain to me what your guardian told you?
Dinia Yes, I can. He told me that whenever I give someone a knife, both of us must hold it by the handle.
Teacher Alright Dinia. Have you ever been hurt by anything dangerous?
Dinia Yes, teacher. I was stung by bees.
Teacher Bees are dangerous organisms. We should not disturb them
 |
| Figure 12 Children being chased by bees |
Dinia Okay, teacher. Also, one day mosquitoes bit me. I suffered from malaria after that.
Teacher Oooh, I am very sorry! Mosquitoes are dangerous too. Other dangerous organisms include lions, scorpions, snakes, spiders and centipedes. Be careful while you are exploring the environment. You should not play in shrubs and rubbish pits because they are not safe places.
| Questions 1. Mention two dangerous organisms that hurt Dinia. 2. Why did Dinia suffer from malaria? 3. Why did the teacher advise Dinia and Daima not to play in rubbish pits? |
| Exercise A: Fill in the blanks. I. We use_________ to identify the sound of drums. 2. Living things that move by flying are________ and__________ 3. List two examples of living organisms which can swing. 4. Examples of living things that move by crawling are __________ and . . . . . . . . . B: Answer the following questions. 1. Mention 3 dangerous non-living things that you know. 2. What happens if a living thing is placed in a room without fresh air? 3. Explain why living things move. 4. What precautions should be taken in using sharp objects? 5. Mention the characteristics of living things. 6. Explain how you can protect living things. C. Choose the correct answer to complete each sentence. 1. Living things will _________ if they do not get air. (a) live (b) die (c) grow 2. Which of the following is the most poisonous insect?(a) Butterfly (b) Cockroach (c) Bee 3. An organism that spreads malaria is called _ (a) mosquito (b) housefty (c) flea 4. Living things increase in number by _______ (a) hiding (b) reproducing (c) playing |
Vocabulary
Danger the possibility that someone may be harmed or killed
Explore to search through or to study closely
Grazing to feed on growing grass
Human development the process of growth and change that takes place between birth and maturity
Investigation a way of finding out information or experimentation
Living organism anything that is living
Locomote move or displace from one point or place to another
Reproduce to produce babies, eggs and seeds
Slither to move smoothly, quietly, or secretely, like a snake
Specimen a real organism to observe or experiment on
www.learninghubtz.co.tz
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania






