CHAPTER TWO
ENERGY
KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTS.
- Current- this is the flow of electron through a conductor
- Voltage- this is the force that causes charges to move in an electric conductor.
- Resistance-this is the opposition to the flow of electric current through an electric conductor.
- Ohms law- This is used to express the relationship between voltage, resistance and current.
- Power surge- sudden increase in amount of electric voltage
- Fuse- a device made of thin wire which overheats and breaks a circuit in case of too much current.
- Circuit breaker- is a device that is found near the main switch in a house or a building and switches off automatically when current increases.
- Renewable energy- This is energy which does not get depleted and can be regenerated.
- Solar energy- is a form of energy that comes from the sun
- Biomas- This is energy from plant materials
- Global warming- This is increase of world temperature.
- A machine- this is a device that makes work easier.
Electric energy
Basic measurements of electricity
The basic measurements used in electricity are:
(1) Current (ii) Voltage (iii) Resistance
Current
Current is the flow of electrons through a conductor.The symbol for current is I and the SI unit for measuring current is Ampere (A).
Voltage
Voltage is the force that causes charges to move in an electric conductor. The other name for voltage is electromotive force (e.m.f.) or potential difference (p.d.). The symbol for voltage is V and the SI unit for measuring voltage is Volt (v).
Resistance
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current through an electric conductor. The symbol for resistance is R and the SI unit for measuring resistance is Ohm (0). Examples of electric devices with resistance are bulbs, loud speakers and heaters among others.
Ohm's Law
The relationship between Voltage, Resistance and Current is called Ohm's law. By using a simple experiment, we can show this relationship clearly.
How to verify ohms law.
Ohms law states that for any conductor such as wire, the amount of electric current which flows through it is directly proportional to the voltage applied and inversely proportional to the resistance.
That is I = V/R.
We can verify ohms law as follows;
Materials- voltmeter, ammeter, dry cells, bulbs. And connecting wires.
Steps.
- Connect the circuit as shown below
- The ammeter should be connected in series with the bulb
- Connect the voltmeter across the bulb
The set-up is as follows.
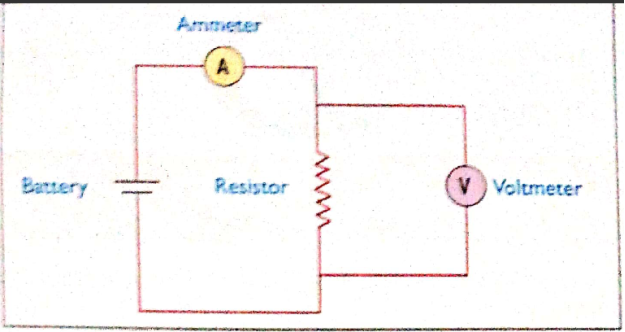
The results of the experiment can be seen as follows;
| Cells | Cell 1 | Cell 2 | Cell 3 | Cell 4 | Cell 5 |
| Voltage V | V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 |
| Current I | I1 | I2 | I3 | I4 | I5 |
| Resistance R | V1/I1 | V2/I2 | V3/I3 | V4/I4 | V5/I5 |
Use one cell, two cells, upto five cells and record voltage across the bulb and the current in the circuit. In each case, find the ratio of voltage across the bulb to the current flowing through the circuit.
You should note that the ratio of voltage across the bulb to the current flowing through the circuit is constant.
Observations.
The ratio gives us the resistance. Since the same bulb (resistance) is used throughout experiment, then the ratio should be the same, thus verifying the Ohm's law which -,1;.ate.g.; that for any conductor (such as a wire), the amount of electric current which flows through it is directly proportional to the voltage applied and inversely proportional to the
That is I = V/R
Therefore, the formula for calculating voltage is;
Voltage = Current x Resistance
(V = I x R)
Resistance (R)= V/I
Worked examples
Example I
A machine has a resistance of 8 Ohms and requires a current of 5 Amperes. Calculate the Voltage of the battery that will be required to operate it.
Solution:
R 8 Ohms, 1 = 5 Amperes,
V= IxR
V = 5A x80
V = 40V
Example 2
A battery of 18V is connected in a circuit. What amount of current flows in the wire if the resistance is 1.50?
Solution:
V = 18 volts, R = 1.5 Ohms
I=V/R
1= 18V
1.50
I = I2A
Example 3
A machine with a voltage of 84V produces a current of 12k Calculate total resistance produced by the machine.
Solution:
V = IR;
R =V
V = 100 l = 25A
84V
Hence R= 84V/12A
R = 7 Ohms
Total resistance in a circuit
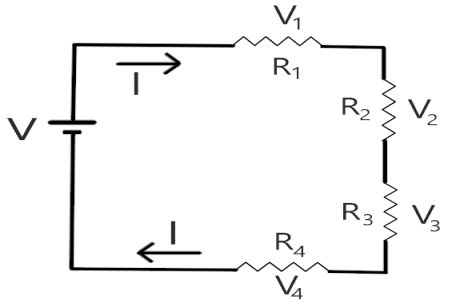
Resistors in series
The resistors R1 R2 and R3 are in series.
Their total resistance RI is obtained by adding all the resistances. RT = RI + R2+ R3
Resistors in parallel
Now R1, R2 and R3 are in parallel. The reciprocal of the total resistance 1/RT is obtained by adding the reciprocal of individual resistances.
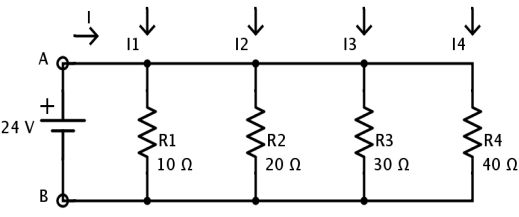
I/R =1/R1+1/R2+1/R3.
Therefore RT = (R1R2R3)/(R1R2+R1R3+R2R3)
Example 1.
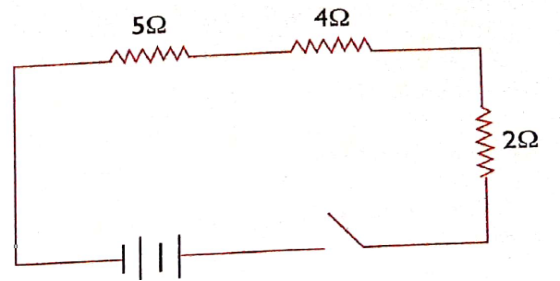
Find the total resistance in the circuit below.
Solution;
RT =R1+R2+R3
RT=5ῼ+4 ῼ+2 ῼ
RT = 11 ῼ
Example 2.
Calculate the resistance in the circuit below
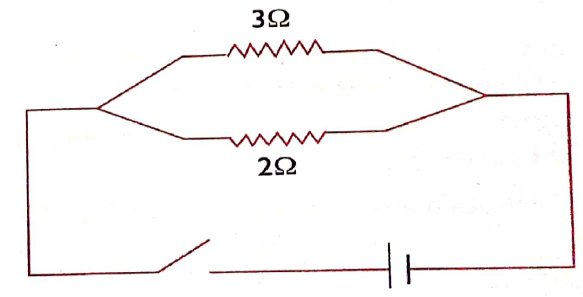
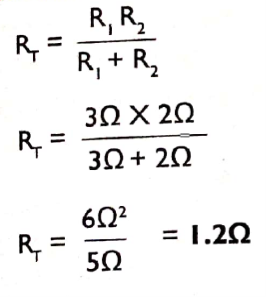
Example 3.
Given that R1=2ῼ, R2=2ῼ and R3 =1ῼ
Calculate the total resistance in the circuit below;
Solution;
Protecting buildings from power surges and lightning
Power surges are caused by a sudden increase in amount of electric voltage. Power surges may cause damage to electrical appliances or buildings. It can also lead to fire accidents and even death. Lightning on the other hand is caused by clouds of different charges rubbing onto each other. This produces a strong charge which descends downwards towards the earth. Lightning can destroys buildings and other structures found on its path. It can destroy them if not well protected. It can also strike plants and animals on its path, causing their death.
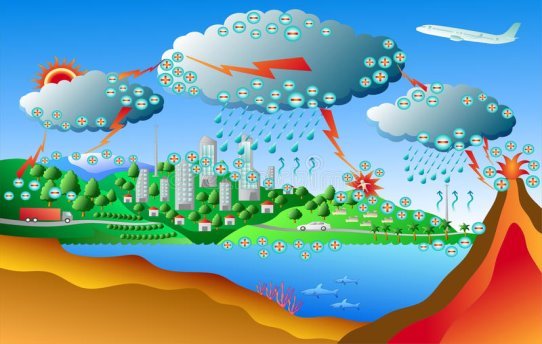
Inorder to prevent these damages we use devices like fuses, circuit breakers, earth wire and lighting arrestors.
(a) fuse
A fuse is a short thins wire which overheats, melts and breaks the circuit in case of too much current. Fuse are found in the main switch, plugs or in sockets. Fuses are rated according to the current required in a particular appliance.

Fuse.
The circuit breaker
A circuit breaker k a device that is fitted near the main switch in a house or building. Circuit breaker switches off automatically in case of a sudden increase in current How When the circuit breaker trips, It shows there is a problem and should be resolved before switching it on.

Circuit Breaker.
(c) Lightning arrestor
A lightning arrestor is a sharp rod made from a good conductor of electricity such as copper. Lightning arrestor is fitted at the highest point of a building and is connected to the ground. Lightning charges flow through the arrestor all the way to the ground where the charge is neutralized.This prevents destruction of the building.

Earth wire
The earth wire is found on the cable that distributes electricity to our buildings and different electric appliances. This cable has Neutral, Live and the Earth wires.
The earth wire is connected to the ground and drains unwanted electricity such as lightning or excess electrons to the ground. The earth wire is necessary because it prevents the electrical appliances from damage and absorbs the excess electricity from appliances. Earth wires should be included in a home's electrical system to protect from electric shock, short circuits, power surges, and fire.
Renewable energy
There are two main forms of energy namely Renewable energyand Non-renewable energy.
Renewable energyis a type of energy derived from sources that are never-ending and can be replenished time after time. Examples are sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat.
Non -renewable energyis a type of energy that gets used up and completely becomes exhausted with time. Examples of non-renewable energy are the fossil fuels(oil, coal and natural gas).
The most widespread sources of renewable energy include:
1. Wind energy: Wind is air in motion. The movement of the wind is caused by differences of temperature at the Earth's surface due to varying temperatures of the Earth's surface due to the sun's heat. Wind energy can be used to generate
electricity or pump water from wind mills.

Wind Power.
2. Solar energy: This is a form of energy harnessed from the Sun.This energy can be collected and converted into different forms such as electric or heat energy.

Solar energy
- Solar energy can be used in solar water heaters with solar collectors to produce heat that heats up water.
- Direct conversion of sunlight to electrical energy using mirrors and boilers or photovoltaic cells. The electrical energy produced can be used for heating, lighting and for commercial purposes.
4. Hydropower energy: This is a form of energy tapped from running water. Moving running or fast flowing water creates high energy that can be harnessed and moving water can be utilized to drive generator turbines turned into power. The moving to produce electricity.
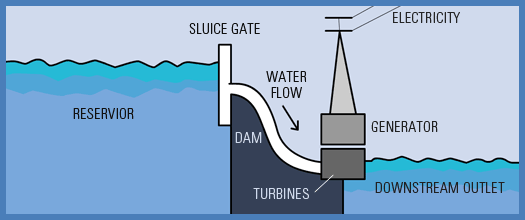
Hydro-electric power plant.
5. Biomass energy: Biomass is the energy from plants. The most common forms of biomass energy include:
Fire wood and charcoal from trees burned to produce heat for cooking and warm thing. This process releases carbon dioxide gases into the atmosphere and is a major contributor to air pollution in many areas.
Methane generated from animal and plant wastes used to generate electricity, heat and light energy.
Production of alcohol for automobile fuel and fueling electric power engines.
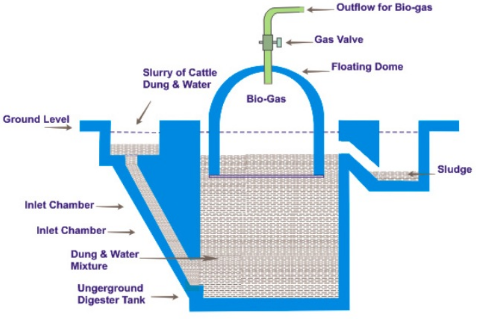
Biogas power-plant
Geothermal energy: Geothermal energy is produced from hot water found deep down the earth's surface which produce steam under high pressure. The steam under high pressure can be used to rotate generator turbines hence generate electricity.

Geothermal PowerPlants.
Advantages of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is eco-friendly. It is a clean source of energy, meaning, it has low or zero carbon emission as compared to fossil fuels which emit high levels of carbon dioxide, which are greatly responsible for global warming and climate change. Solar and wind power are considered eco-friendly because they emit zero toxic gases to the environment.
It is a renewable resource: This means that they do not get exhausted or run out. Sources of energy like fossil fuels (coal, gas, and oil) are said to be limited resources and there is a possibility that they will run out in the near future.
Renewable energy is a reliable source of energy: Solar and wind plants if well distributed over a large geographical area, there can provide a guaranteed supply of electricity.
Renewable energy is cheaper compared to most traditional sources of energy. Disadvantages of Renewable Energy
The electricity generation capacity is low when compared to traditional forms of energy generation like fossil fuel. Renewable energy technology generate low power and therefore it can't be solely relied upon to power the whole nation.
Renewable energy technology is unreliable since it totally depends on the weather especially sun and wind, to be able to generate energy. In case the weather conditions are not good enough, renewable energy technologies would not be able to generate any electricity.
Generating electricity
Energy comes from various sources. Examples are such as water, wind, plant and animal waste and the sun,
Generating electricity using biogas
Biogas is a promising renewable source of energy produced from a mixture of animals waste and water. It is produced in a container called biogas digester. The reactions in the digester produce the biogas. Biogas is a mixture of methane, carbon dioxide and nitrogen. Methane gas is what is collected and used as fuel for combustion engines. Which convert it to mechanical energy, powering an electric generator to produce electricity. It can also be directly converted into electrical power for example in a fuel cell. It can also be burnt to release heat at high
temperature for cooking.
Generating electricity using solar energy
The word solar means from the sun. Solar energy is obtained from the sun.
Solar energy from the sun is converted to electrical energy using solar panels.
A solar panel is a sheet or plate that is used to trap and convert light energy to electrical energy.
Solar panels are put on rooftops of buildings in order to trap light well. Solar energy is trapped and then stored in batteries for domestic use. The batteries are connected to an inverter which converts the direct current(D.C) to alternating current (AC). The energy produced can be used by bulbs and other electrical appliances.
Solar panels are friendly to the environment since no harmful gas or water is produced.
Generating electricity using water (Hydroelectric power - H.E.P)
This happens in hydroelectric power generation stations. In these stations, water electricity by rotating the turbines. Moving water has kinetic is used to produce energy. Kinetic energy is the energy in motion.
When the turbines rotate they produce current electricity. Therefore, kinetic energy in moving water is converted into electric energy. Electrical energy produced is transmitted through wires to various places, for example, homes, industries, schools and hospitals.
Generating electricity from wind
Wind is moving air. Moving air can be used to generate electricity using special equipment called windmills. Strong winds are used to rotate the propellers of the windmills. Propellers are made of blades. These propellers are then connected to generators through shafts. The generators produce electricity which is then connected to the national grid for supply to various places
Windmills are usually placed in open field where there is no obstruction to the flow of wind.
Machines
Complex machines
A machine is any device used to make work easier. Examples of simple machines are levers, wheel and axle, wedges, screws, slope or inclined planes and pulleys. A complex machine consists of two or more simple machines which are combined to do work together as a single device. Combining simple machines increases the speed and efficiency of the machine. Example of complex machines are bicycles, sewing machines, motorcycles, computer, typewriters, wood plane and vehicles.
Bicycle
A bicycle contains a number of simple machines put together. Examples are levers, inclined planes (pedals), wheels, axle and screws. '
Sewing machine
A sewing machine is used to make clothes. It contains simple machines such as wheel and axle, lever, screws, wedges and inclined planes.
A wood plane
A wood plane is made up of an inclined plane and a lever (handle). It is used to smoothen wooden surfaces.
CHAPTER SUMMARY.
- Energy is the ability to do work
- Electricity is a form of energy
- The basic measurements of energy are current, voltage and resistance.
- The relationship between voltage, resistance and current is expressed using ohms law.
- Resistors can be in parallel or in series
- A sudden increase in electric voltage is called power surge
- Power surges can be managed using fuse, circuit breaker lighting arrestor or earth wire.
- Renewable energy is a form of energy derived from sources that are never ending and can be replenished over time.
- Non-renewable energy is a type of energy that gets used up and cannot be regenerated.
- Examples of renewable energy sources includes, solar energy, wind energy, biomass energy etc.
- Electricity can be generated using biogas, solar panels hydroelectric power and wind.
- A device that makes work easier is called a machine.
www.learninghubtz.co.tz
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania






