GEOGRAPHY FORM TWO: TOPICAL EXAM.
HUMAN ACTIVITIES
SECTION A:
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS.
1. Choose the most correct answer.
Which of the following is not type of human activity?.
Resource exploitation
Processing of resources.
Buying and selling
Intellectual services.
(ii) Which of the following human activity is not extractive?
Teaching
Fishing
Mining
Hunting and gathering
(iii) Harvesting minerals such as copper from underground is called?
Lumbering
Quarrying
Mining
Extraction
(iv) Acts, functions or occupations executed lawfully by human beings for some purpose is called?
Production.
Human activities
Human occupation
Economic activity.
(v) The backbone of Tanzanias economy is?
Agriculture
Mining
Fishing.
Livestock keeping.
(vi) Which is not and advanced technique in fishing?
Drifting
Trawling
Seining
Barrier trap.
(vii) Stones and sands for building can be facilitated by?
Plumbering
Quarrying
Mining
Extraction.
(viii) Which of the following is not an intellectual activity?
Teaching.
Consulting.
Research
Processing.
(ix) Which of the following processing activity is not in Tanzania?
Car making
Car assembling
Paper making
Coffee pulping.
(x) Growing crops for purpose is termed as _______ farming.
Cash crop
Subsistence
Food crop
Commercial farming
2. Match the items from list A with those in list B.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B:
3. (a) What is human activities?
(b) Describe four types of human activities.
4. Discuss five importances of human activities.
5. With examples, show problems that human activities can cause.
6. (a) What is fishing?
(b) Mention four traditional methods of fishing and four modern methods of fishing.
7. Discuss the social services provided by the government.
8. (a) Mention four intellectual services that can constitute human activities.
(b) Define lumbering? Give importance of lumbering.
SECTION C:
9. Write an essay on human activities carried out in Tanzania.
LEARNINGHUBTZ.CO.TZ Page
TOPICAL QUESTIONS
HUMAN ACTIVITIES
SECTION A:
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
1. What do you understand by the term human activities?
- Are geographical zones occupied by man
- Are ongoing activities all over the country
- Are social cultural activities only
- Are different cultural social and economic activities carried out by man.
2. The most common and perhaps the most important of socio economic activities include:-
- Pastoralism, cultivation and trading activities
- Agriculture, trade and cultural activities.
- Arts, crafts and ceramics
- Recreation, initiation and traditional healing
3. The coastal zone people are involved in which type of human activities?
- Fishing, trading and small scale agriculture
- Lumbering, trading and hand crafts
- Initiation, recreation and social activities.
- Lumbering, mining and small scale agriculture.
4. Cultural practice in economic activities includes the following activities.
- Initiation, arts and ceramics
- Agriculture, fishing and lumbering.
- Crafts, folklore and trading.
- Lumbering, initiation and ceramics
5. The main economic activity for Makonde people is:-
- Carving
- Agricultural activities.
- Lumbering
- Fishing
6. The dominant human activity along the coast is:-
- Fishing
- Mining
- Industrial activities
- Agriculture
7. Human economic activity normally depend on
- Climate and soils
- Nature of people and crops grown
- Types of zones and human interest
- Agriculture and keeping animals
8. Soil is among the factors which determine economic activities together with:-
- Climate
- Type of zone
- Nature of people
- Agricultural activities
9. Agricultural activity is pre dominant in which zones:-
- Southern highland
- Northern zone
- South West zone
- Coastal zone
10. Which one of the following is a primary activity?
- Agriculture
- Transport
- Communication
- Vehicle manufacture
11. Which one of the following does not fit the definition of human activities?
- What people do for a purpose.
- Work done by human being to achieve a certain goal
- Are activities done by people who use resources to produce goods and services.
- These are activities which only affect human beings
12. Which one of the following sets contains secondary activities only?
- Beer making, education, mining, pulping of coffee.
- Paper making, vehicle manufacturing and bread making
- Agriculture, mining, communication and transport.
- Decoration of sisal, glass making and health services.
13. Which one of the following is not a type of primary activities?
- Fishing
- Mining
- Education
- Agriculture.
SECTION B: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS.
14. Briefly explain the meaning of tertiary activity
15. With specific examples differentiate between the following terms.
a) Primary and secondary activities
b) Tertiary and primary activities.
c) Secondary and tertiary activities
16. Briefly explain six (6) importances of human activities.
a) ..
b) ..
c) ..
d) ...
e)
f)
17. Describe seven (7) problems caused by human activities.
a) ..
b) ..
c) ..
d) ..
e) ..
f)
g) .
GEOGRAPHY FORM TWO: TOPICAL EXAM.
AGRICULTURE:
SECTION A:
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS.
1. Choose the most correct answer.
(i) The most important factor that influences Agriculture is?
- Physical factor
- Human factor.
- Economic factor
- Biological factor.
(ii) An agricultural activity which involves crop production in a small piece of land is called?
- Shift cultivation
- Arable farming
- Subsistence farming
- Sedentary farming
(iii) Which is not a problem faced by plantation Agriculture.
- Climatic changes
- Pest and diseases
- Floods
- Price fluctuations
(iv) Intensive production of grapes is called?
- Orchard farming.
- Viticulture
- Fruit farming
- Cereal cultivation.
(v) Which is not a characteristic of mixed farming?
- Moderate farm size
- Involves animals and plants
- Plantation in nature.
- Require substantial capital.
(vi) The largest producer of rice in the world is?
- China
- India
- Indonesia
- Japan.
(vii) The optimal temperature for maize growth is?
- 15
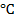 to 20
to 20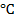
- 14
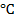
- 18
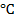 to 27
to 27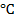
- 20
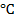 to 25
to 25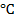
(viii) Tea is harvested after what period in planting?
- 12 15 months.
- 18 24 months.
- 20 26 months
- 20 24 months.
(ix) The world largest producer of cocoa is?
- Ivory coat
- Brazil
- Ghana
- Cameroon.
(x) Which is not problem facing large scale agriculture?
- Poor technology
- Climate
- Competition
- Pests and diseases.
2. Match the items from list A with those in list B.
| LIST A | LIST B |
| (i) Farming carried out in large tracks of land. (ii) Specialized production of a crop in large land piece. (iii) A farmer moves from one land to another after cultivation. (iv) Involves maximum utilization of all the arable or cultivatable land. (v) Growing a wide variety of crops and keeping animals. (vi) Production of grapes. (vii) Requires rainfall of 635 to 1,145MM. (viii) Drying tea in a machine called drier. (ix) Largest sugarcane producer in the world (x) Cash crop commonly found in Arusha. |
|
SECTION B:
3. (a) What is Agriculture?
(b) Briefly explain factors that influence agriculture
4. (a) Mention three forms of small scale agriculture
(b) Discuss six characteristics of small scale agriculture
5. (a) What is plantation agriculture?
(b) Outline advantages and disadvantages of plantation agriculture.
6. (a) Which is world largest producer of Rice?
(b) Describe the growth requirement of rice.
7. Explain the following requirements for maize farming
(i) Requirement for growth
(ii) Farm preparation
(iii) Harvesting
(iv) Processing.
8. Describe cotton farming under the following.
(i) Requirement for growth
(ii) Farm preparations
(iii) Farm maintenance
(iv) Harvesting
(v) Processing.
SECTION C:
9. Discuss problems facing large scale agriculture in Tanzania.
10. Outline problems facing large scale agriculture in U.S.A.
LEARNINGHUBTZ.CO.TZ Page 1
TOPICAL QUESTIONS
AGRICULTURE
SECTION A:
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
1. What is Agriculture?
- Arable farming and domestication of animals
- Crop production and fish farming
- Livestock husbandry only
- Cultivation of crops in a very large piece of land
2. Which one among the following is an importance of agriculture?
- Food production for both people and animals
- Provides raw materials to the growing industrial sector
- Creates unemployment
- Foreign exchange earner
3. One of the following is not a factor influencing agricultural development.
- Climate
- Rainfall
- Temperature variation
- Pressure
4. Intensive farming means:-
- Large amount of capital or labour are applied in a small piece of land
- Large amount of capital is not used for a very large piece of land.
- Very small piece of land is cultivated locally.
- Subsistence farming basically for food supply in the family.
5. Extensive farming can be defined as:-
- Horticulture production in a small piece of land
- Large area of land are worked by a small labour force.
- Commercial farming where production is intended for sale and food.
- Farming whereby people move from one place to another seasonally.
6. Nomadic farming in agricultural activities refers to:-
- Animal keeping through moving from one place to another.
- Permanent cultivation of cash crops
- Keeping animals by zero grazing.
- Crop cultivation of food stuff crops only.
7. Which among the following is not a characteristic of shifting cultivation?
- Sites are selected in the virgin forest
- Simple tools are used like hand hoes.
- Few crops are grown, mostly starchy crops
- Keeping animals and crops cultivation
8. Plantation in agricultural system is referred to as:-
- Small scale agriculture
- Intensive subsistence farming
- Large scale agriculture.
- Sedentary shifting method.
9. Slash and burn agricultural system is also called?
- Shifting cultivation system
- Rotational bush fallowing
- Semi nomadic or semi sedentary
- Commercial mixed farming.
10. The following groups are examples of cash crops except?
- Cotton, tea, pyrethrum and cocoa
- Oil palm, cotton, coffee, tea and cloves
- Wheat, maize, sweet potatoes and yams
- Pyrethrum, cocoa, cotton and tea.
11. Ranching is agriculture means?
- Keeping animals in a large piece of land
- Small number of animals or few cattle kept in a large piece of land.
- Crop cultivation and animal husbandry are practiced.
- Animal keeping in urban areas.
12. Limitations of agriculture in China include:-
- Floods or Great sorrow of China
- Problems of land ownership
- Problem of soil erosion
- Lack of Mechanization.
13. What one lesson has Tanzania learnt from the farming in China?
- Great government involvement in agriculture
- Involvement of the local people
- Development of technology advancement.
- Cooperative associations in the agricultural sector
14. The three major tea growing areas in Tanzania are:-
- Usambara mountains, Southern highlands and West Lake regions.
- Tabora, Mwanza and Usambara.
- Dar es Salaam, Morogoro and Ruvuma.
- Lupembe (Njombe), Dodoma and Musoma.
15. Transhumance in agriculture meanas
- Seasonal movement of people with cattle.
- Permanent keeping of animals in a virgin piece of land.
- Permanent and seasonal crop cultivation.
- Movement of people from one area to another.
16. Commercial livestock farming involves the following except:-
- Extensive, ranches, beef and dairy farming
- Sedentary, Semi normadic and plantations.
- Arable farming, peasants and ranching.
- Semi sedentary, settler, peasant and transhumance.
17. Mixed farming in agriculture means:-
- Keeping animals and growing of crops in the same farm
- Cattle keeping and at the same time growing crops
- Growing more than one crop at the same piece of land (field)
- Keeping more than two types of cattle breeds
SECTION B: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS:
18. Define arable land.
19. Differentiate between shifting cultivation from bush fallowing.
20. Name the areas in Tanzania which are still practicing shifting cultivation and bush fallowing .
21. Define the following terms.
a) Sedentary farming
b) Mixed farming
22. Differentiate between small scale and large scale agriculture.
23. With examples, explain the difference between food crops and cash crops.
24. (a) Explain the effects of rapid population growth on small scale farming.
(b) What are the advantages of small scale agriculture? (Give five (5) points)
25. Citing at least five (5) examples in each case explain what are beverages crops and industrial crops.
26. Briefly explain the term livestock keeping.
27. Name the three (3) major types of livestock keeping systems.
28. Which are the factors that influence the development of livestock keeping in Tanzania.
29. What are the problems facing livestock keeping sector in Tanzania.
30. Briefly explain measures taken by the government of Tanzania in alleviating problems facing livestock keeping.
31. Explain the economic importance of livestock keeping in Tanzania.
TOPICAL QUESTIONS
WATER MANAGEMENT FOR ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT.
SECTION A:
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
1. River development project can be defined as
- Schemes of water supply for various purposes.
- Water management for economic development
- River basin development project
- Construction of dams for controlling floods.
2. The river basin development project is a multipurpose scheme because it is:-
- Aimed at achieving many goals
- Aimed at irrigation
- Aimed at power supply
- Aimed at hydroelectric power supply.
3. Example of river development project in Tanzania include:-
- Kilombero basin, Kagera river basin and Rufiji basin
- Volta river, Akasombo and Orange river project.
- Ganges, Mtera dam, Amazon and Galole scheme
- Galole scheme, Rufiji basin, Gezira scheme.
4. One of the following is not a process in river basin development.
- Construction of the dams
- Dredging of the rivers.
- Widening river channels
- Drying water sources.
5. Below are some of economic importance of river development projects except:-
- Control floods.
- Improvement of irrigation
- Provides water for domestic life
- Deforestation.
6. All the following are the challenges / disadvantages of river basin development project except?
- Unreliable rainfall
- Excessive evaporation
- Water pollution
- A lot of capital is required.
7. One among the following is not associated with aims of river basin development:-
- Control soil erosion
- Control floods
- Improve navigation
- Improve soil fertility.
8. Tennessee river is tributary of:-
- Ohio river in U.S.A
- Akasombo river
- Congo basin
- Zanzibar River.
9. H.E.P is an abbreviation of the following terms:-
- High Elevation project
- Hydro Electric power
- Highly Evolved project
- Hydro electric project
10. A major problem facing river basin development project is:-
- Silting
- Flood
- Diseases
- Land Fragmentation.
11.Which among the alternatives is a problem facing Tennessee River valley Authority (T.R.A) scheme?
- Labour shortage
- Siltation
- Diseases
- Environmental degradation.
12. Kilombero irrigation scheme is situated at:-
- Dar es Salaam
- Tributary of Rufiji
- Great Ruaha river.
- Kilombero river.
13. The main purpose of Kilombero irrigation scheme was:-
- Sugar cane irrigation.
- Water for domestic use
- Water for industrial use
- Cotton irrigation.
SECTION B: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS:
14. What do you understand by the term Water management
15. Mention five different sources of water.
16. Briefly explain five uses of water.
17. (a) What is a river basin development project?
(b) Explain the economic importance of Rufiji. River Basin Development project.
18. (a) What are the benefits of the Tennessee River Valley project (T.R.V.P)?
(b) What are the problems facing Tennessee. River valley Authority (T.R.V.A)
19. (a) Define the term land reclamation
(b) What are the aims of land reclamation
(c) Name the three main methods of land reclamation in Tanzania?
20. (a) What do you understand by the term water resources?
(b) Mention at least four types of water resources
(c) Briefly explain the methods used to extract water resources.
(d) What are the problems caused be extraction of water resources?
21. (a) Briefly explain what is water pollution
(b) Precisely name four main sources of water pollution.
(c) What are the effects of water pollution?
22. (a) Define the term water conservation
(b) How can people conserve water?
TOPICAL QUESTIONS
SUSTAINABLE USE OF FOREST RESOURCES.
SECTION A:
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
1. Timber Industry can be defines as:-
- Activity which involves the production of timber resources.
- Timber is the wood material derived from forests.
- Process which involves individual planting of trees
- Harvesting and replanting trees with proper management.
2. What if timber as used in Geography?
- Is the wood materials derived from the forests.
- Collection of timber products
- Production of forest resources.
- Good management of forest resources.
3. The term forest is defined as:-
- The collection of all varieties of crops
- Collection of trees in an area either natural or artificial
- Activity involving production of timber.
- Process associated with tree production.
4. The process in which an individual plant tree is taken care of until harvest time and after harvesting replaced with another is referred to as:-
- Horticulture
- Silviculture
- Floriculture
- Aquaculture
5. Evergreen rainforest is found in:-
- Tropical climatic condition
- Equatorial climatic condition
- Semi desert region
- Temperate zone climate.
6. The forest occupying the coastal zone is called?
- Mangrove vegetation forest
- Monsoon forest
- Evergreen rainforest
- Tropical forest
7. Which type of forest is composed of hard wood?
- Tropical forests
- Equatorial forests
- Mangrove forests
- Evergreen forests.
8. The following are the hard wood species except?
- Oak, Ash and Beach
- Pines, Far and Spruce
- Oak, Ash and Pines
- Ash, Pines and Cyprus.
9. Major types of forests can be categorized as:-
- Artificial and hardwood forests
- Hardwood and soft wood forests
- Natural and softwood forests
- Natural and Artificial forests.
10. In Geography trees are divided into two major groups. These are:-
- Natural and Manmade trees
- Softwood and hardwood trees
- Tropical and equatorial trees
- Miyombo and Mangrove trees.
11. Main forest products include all the following except?
- Poles, timber, fibres and fruits
- Cotton, ropes and timber
- Tannin, resins and fruits
- Leaves, poles, medicine and skins
12. Which among the following is not an importance of forests?
- Are source of fuel
- Form protective cover to the ground
- Provide habitual to animals
- Are sources of medicine in herb materials.
13. Forestry means?
- Science of managing forest resources for human use.
- Importance of forestry management
- Control and use of forest resources.
- Collection of trees at a very small area.
14. Cutting down trees is known as:-
- Afforestation
- Deforestation
- Reforestation
- Desertification
15. The following are effects of rapid population growth on forest resources apart from:-
- Deforestation for settlement purpose.
- High demand for fuel like firewood, timber and charcoal
- Valuable species are disappearing due to over use or excessive demand.
- Stiff challenge posed by other economic activities.
16. Among the following is the only problem associated with over exploitation of forest resources.
- Desertification
- Low technology
- Poor transport and communication
- Poor capital to be used.
17. What is the meaning of Agro forestry?
- Intercropping trees and crops in the same field
- Science of planting trees
- Poor methods of planting trees and crops
- Refers to collection of vegetation in the forests.
SECTION B: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS.
18. Define the term forest
19. Name two main types of forests
20. What are the importance of forests?
21. What are the problems facing forests in Tanzania?
22. Which methods are used to conserve forests?
23. Point out disadvantages faced by women or girls who walk for a long distance looking for firewood.
24. Give suggestions on how to solve the problems mentioned in question (23) above.
TOPICAL QUESTIONS
SUSTAINABLE MINING
SECTION A:
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
1. Mining is defined as:-
- Extraction of minerals from the ground
- Digging and wetting soils with minerals
- Making holes into soil to find minerals
- Digging method.
2. Major categories of minerals are:-
- Metals and non metals
- Reactants and non reactants.
- Chemicals and non chemicals
- Organic and inorganic minerals
3. Among the following pairs, which one is made of non metals?
- Silt, phosphate and potash
- Nitrate, sulphur, gold and zinc
- Diamond, coal, manganese and oil
- Copper, iron, tin and natural gas.
4. The following are the mining methods except.
- Open cast, strip method and vertical methods.
- Open cast method, underground and placer method
- Digging method, strip method and open cast method
- Cultivation method, strip method and underground methods.
5. Placer method of mining can be defined as:-
- Alluvial minerals by using the pans in river valleys.
- Digging soil with mineral ore along the desert.
- Swirling water in pans through deposit
- Involve digging hole to the lower levels.
6. The following are economic importance of mining except?
- Help to reduce employment
- Lead to development of other sectors like agriculture.
- Encourage development of towns like Mawdui in Shinyanga.
- Lead to diversification of economy.
7. Which of the following is the correct factor for growth in the mining industry?
- Availability of capital
- Absence of labour
- Presence of cities like Dar es Salaam
- Political instability
8. A mining deposit ore refers to:-
- An area with virgin source of minerals
- Extracted area for very long time
- Area without mineral resources
- Forest resource developing minerals source
9. A good government policy on mining helps the mining sector:-
- To strengthen the mining activities
- To decline
- To grow
- To build mineral ores.
10. Decline or exhaustion of the mineral deposit can be referred to as:-
- Problems facing the mining industry in any country
- Factor for mining development in any country
- A name given to the mineral land
- An area expected to have minerals.
11. Which among the following is a problem caused by mining?
- Leads to environmental degradation
- Leads to development of towns
- Increases good services like roads
- Political stability.
12. Which one among the following is Not an environmental effect of mining?
- Environmental pollution
- Destroy nature of land
- Accelerate deforestation
- Increase soil fertility
13. Improving the methods of extraction of mineral is can be referred to as:-
- Suggested way of minimizing effects of mining
- Problems affecting mining in Tanzania.
- Method of gold extraction
- Accelerating mining activities.
14. Which one of the options below is a limitation of mining.
- Labour unrest
- Enough capital
- Good government policy on the mining sector
- Stable transport and communication.
SECTION B: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS.
15. (a) Define the term mining.
(b) Name five types of minerals
16. Mention three major methods of mining.
17. Which are the factors influencing mineral exploitation?
18. What are the problems facing mining industry in Tanzania.
TOPICAL QUESTIONS
TOURISM INDUSTRY
SECTION A:
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
1. Movement of people away from home to another place of interest for leisure or pleasure or studies is called?
- Migration
- Transportation
- Tourism
- Permanent settlement.
2. Tourism is categorized into two types. These are:-
- Domestic and International tourism
- Extensive and intensive tourism
- Internal and domestic tourism
- International and external tourism.
3. In Geography, domestic tourism means:
- People travelling to places within the same country
- People moving from one continent to another continent
- People moving from one country to another country
- All above are correct.
4. International tourism does not involve:-
- Travelling within a county
- Moving across border or across boundaries
- Moving from one country to another
- Moving from one continent to another.
5. All the following are famous tourist attraction sites in Tanzania except.
- Mikumi wildlife, Tarangire and Ruaha reserve
- Serengeti, Mount Kilimanjaro and Mikumi
- Selous reserve, Tarangire and Mikumi parks
- Tsavo, Turkana and Oldonyo Lengai.
6. The following are socio cultural factors influencing tourism except one which is it?
- Historical sites, recreational sites and National parks.
- Pleasant climate, attractive scenery and beaches.
- Available capital, good transport and communication
- Peace of a country, good policy of the government.
7. Among the following is not an importance of tourism:-
- Provides employment to people
- Provides foreign currency to the host country
- Strengthening international relations.
- Eroding of morals and cultural values.
8. The leading country in tourism in the world is said to be:-
- Germany
- U.S.A
- Tanzania
- South Africa.
9. Major problems which are currently hampering the smooth growth of tourism in the world is:-
- Worlds looming terrorism with bombardment
- Increasing the number of attractive sceneries
- Environmental degradation.
- Large capital invested into tourism industry.
10. The following are negative effects of tourism except?
- Leads to environmental pollution
- Leads to spread of disease like AIDS
- Accelerate terrorism.
- Improve culture of a host country.
11. Which among the following is a solution to problems caused by tourism?
- Reducing tourist attraction sites
- Visitors should not be taught the culture of the host country
- Good policy of tourism should be established internationally.
- Very large capital should be used.
12. Eco tourism (Green tourism) means?
- Carrying out tourism without negative impacts.
- Based on disturbing natural environment
- Promotion of environmental degradation
- Conducting tourism with major negative effects.
13. Ecological aspects combined with tourism activities are referred to as:-
- Local tourism
- Eco tourism
- International tourism
- Extensive tourism.
14. Eco tourism is also referred to as:-
- Green tourism
- Blue tourism
- Tourism policy
- Local tourism
SECTION B: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS:
15. (a) Define the term International tourism
(b) What is the main aim of tourism?
16. (a) What are two main types of tourism?
(b) Explain briefly the factors that favour the development of tourism in the world.
(c) How does Tanzania benefit from tourism?
17. Precisely explains the problems facing tourism industry in Tanzania.
TOPICAL QUESTIONS
MANUFACTURING INDUSTRY
SECTION A:
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
1. A manufacturing industry can be defined as:-
- Changing materials to be new products.
- Processing only without changing into new products
- Industries producing simple and new products.
- Processing and changing materials in order to make new products of greater value to man.
2. Industries which produce heavy products in a manufacturing industry are referred to as:-
- Secondary industry
- Primary industry
- Simple products industry
- Complex products industry
3. The production of bulk products like iron, steel, car assembly and ship building is referred to as:-
- Heavy industry
- Simple or light industry
- Secondary industry
- Primary industry
4. Coffee pulping, sisal decortications and cashew nut hollered are activities done under which category of manufacturing industry?
- Processing industry
- Fabrication industry
- Secondary and primary
- Heavy and light
5. Manufacture of plastics, textiles, cosmetics and paper industries can be referred to as:-
- Light industry
- Heavy industry
- Primary and secondary
- Fabrication and primary industry
6. Which among the following is not associated with factors influencing the location of industry.
- Raw material availability
- Availability of fuel and power
- Human resources like labour
- Bad policy of the government.
7. The following are significance of manufacturing industry to the world economy except:-
- Provide employment
- Provide foreign currency
- Stimulate transport and communication
- Discourage improvement of social services.
8. One among the list below is not the effect of manufacturing industries on the environment.
- Land degradation
- Environmental pollution
- Land reclamation
- Cause disappearance of valuable species of plants and animals.
9. The following are types of pollutants produced by the manufacturing industry.
- Gaseous, particulates and liquid maters.
- Solid matters, hard matters and gaseous matters
- Liquid, fluids and gaseous maters
- Dust, particulate and solid matters.
10. Global warming can be defined as:-
- General rise of temperature in the atmosphere
- Great decrease of temperature in the atmosphere
- Minimum addition of temperature into the air
- Melting down of ice caps on the mountains.
11. Gaseous pollutants produce green house effect or gases like:-
- Carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide.
- Oxygen, manganese IV oxide and helium
- Hydrogen peroxide, oxygen gas and carbon gas
- Natural gas and artificial gas.
12. One of the following is not associated with ways of reducing pollutants:-
- Industries should be located far away from residential areas.
- Recycling the waste before dumping
- Avoid nose pollution
- Increase chemical fertilizer in agricultural sector.
13. Importance of iron industry in U.S.A include:-
- Provide employment
- Destroy environment
- Cause soil pollution
- Produce noise pollution.
SECTION B: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS:
14. Briefly define the term Manufacturing industry
15. Give an account of the importance of manufacturing industry in Tanzania
16. Mention five types of manufacturing industries.
17. Name three (3) categories of manufacturing industry.
18. Mr. Sagutinho is an investor from Brazil who wants to start a manufacturing industry in Tanzania. Which are the factors to consider where to locate his manufacturing industry?
19. What are the factors that have influenced the development of car manufacturing industry in Japan?
20. Enumerate problems facing car manufacturing industry in Japan.
TOPICAL QUESTIONS
SUSTAINABLE US OF POWER AND ENERGY RESOURCES
SECTION A:
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
1. The major sources of power can be classified into two main groups namely:-
- Non renewable and new energy resources
- Rewind able and power resources
- Renewable and non renewable resources
- Power resources, energy resources and fuel resources.
2. Inexhaustible power resources include:-
- Hydroelectric power, tidal energy, solar energy and biogas.
- Coal, petroleum, natural gas and fire wood.
- Wood, solar energy, biogas and geothermal
- Nuclear gas, fuel, and solar energy.
3. Challenges encountered when harnessing H.E.P in Africa are:-
- Seasonal fluctuation in volume of rivers
- Excessive evaporation of rivers
- Poor capital used
- Dangerous terrestrial animals
4. Nuclear energy is more economical since:-
- Very small amount of raw material is used
- Produce little amount of waste.
- It is clean and produce fewer green house gases.
- It is very dangerous to the environment
5. Wood fuel can be converted to charcoal by:-
- Hunting the firewood under limited amount of oxygen
- It is provided by burning trees in the open space
- Bush fire occurring suddenly
- Application of fire to a benzene ring.
6. Hydroelectric power is generated under the influence of:-
- Stagnant water
- Fast moving water into the sea or ocean
- Rapids and water falls in the rivers.
- Deposited water sources like wells.
7. Which among the following hydroelectric generating centres are found in Tanzania.
- Mtera dam, Kidatu dam, Kihansi, Hale dam and Rusumo dam.
- Kabora Bossa, Kafue, Kariba dam and Akasombo dam
- Kainji dam, Nyumba ya Mungu dam, H.F verwood dam
- Seven forks dam, Aswan high dam, Owen falls and Nasser dam.
8. Solar energy coming from the sun is referred to as:-
- Renewable energy resource
- Non renewable energy resource
- Tidal power source
- Hydroelectric power.
9. The power produced when water along the coast drive turbine to produce electric power is called?
- Geothermal energy source
- Tidal power source
- Wood fuel power source
- Biogas power source.
10. Wind energy is referred to as:-
- Energy produced by the moving air mass
- Energy produced by biogas resources
- Energy produced by geothermal resources
- Energy produced by nuclear resources.
11. Songo Songo gas field is located in:-
- Zambia copper belt.
- Tanzania Rufiji basin
- Mnazi bay near Mozambique
- U.S.A at Massa chusetts basin.
12. Petroleum which is in its natural state is called?
- Crude oil materials
- Petro chemicals materials
- Coal field resources.
- Gasoline resources.
SECTION B: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS:
13. Define the term power
14. Name two major sources of power
15. What are the factors that favour the development of Hydro electric power (H.E.P)?
16. What is geothermal power?
17. (a) Where is coal derived from?
(b) Name the five groups of coal
(c) Coal is mined using two methods which are
(i) ..
(ii) .
(d) What are the uses of coal?
18. Outline five uses of petroleum.
TOPICAL QUESTIONS
TRANSPORT AND COMMUNICATION
SECTION A:
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
1. Movement of goods, people and services from one place to another is referred to as:-
- Transport
- Trading
- Communication
- Net working
2. The following are economic importance of transport apart from:-
- Make goods available where they are demanded
- Helps supplying raw materials
- Improve trade relations
- Prevent spread of technology
3. There are three main forms of transport, namely:-
- Land, water and air transport
- Human portage, animal transport and pipelines.
- Water, Lakes and rivers
- Oceans, lakes and rivers.
4. Which one of the following sets are forms of land transport?
- Human portage, animals, roads, railways and pipelines
- Water, air, lake, ocean and sea
- Ponds, dams, channels and canals
- Air crafts, aeroplanes, ships and cars
5. Good examples of animal transport include:-
- Camels, donkeys and horses
- Cows, dogs and pigs
- Chicken, cows and cats
- Elephants, rhinos and hippopotamus
6. Road transport equipment involves the following:-
- Vehicles, bicycles, motorcycles and cars
- Donkeys, aeroplanes and trucks
- Elephants, rhinos and hippopotamus
- Motor way, highways and low way.
7. Railway transport refers to:-
- Carrying of goods and passengers to train
- Carrying of goods and passengers by air
- Carrying of goods and passengers by road
- Carrying of goods and passengers by sea.
8. What are the main advantages of railway transport over air transport.
- Cheaper, simple and not affected by weather
- Expensive, quick and affected by weather.
- Carry very small goods and passengers
- Flexible, efficient and quick
9. Which form of transport are more flexible than the others?
- Railway and water
- Road and water
- Water and air
- Animal portage and human portage.
10. Which is the cheapest means of transport?
- Road transport
- Air transport
- Water transport
- Railway transport
11. Water transport is also referred to as:-
- Marine transport
- Sea transport
- River transport
- Lake transport
12. Main pipeline form of transport is categorized as:-
- Road transport
- Land transport
- Animal transport
- Human portage
13. Common equipments associated with air transport include:-
- Airplanes and aircrafts
- Ship building and air crafts
- Car assembling and motor cycles
- Balloon fly and butterfly.
14. Water transport facilities include the following devices.
- Ships, canoes and boats.
- Airplane, local boat and ngalawa
- Sea bus, ferry and air crafts
- Balloon, car assembly and ship building.
15. Which form of transport is most expensive?
- Air transport
- Water transport
- Land transport
- Marine transport.
16. TAZARA transport is associated with:-
- Land transport
- Railway transport
- Water transport
- Air transport
17. Water transport is sub divided into two subtypes namely:-
- Inland water and ocean water
- Sea and ocean
- Ocean and rivers
- Dams and Canals
SECTION B: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS:
18. (a) Define the term transport
(b) Name the three major forms of transport
19. (a) List the advantage and disadvantages of sea transport
(b) Name two lakes used for transport purposes in East Africa
20. What are the importance of transport?
21. What are the advantages and disadvantages of rail transport?
22. How would you compare road transport and with railway transport?
23. List the advantages and disadvantages of air transport.
24. What factors would you keep in mind while choosing a means of transport?
25. Suggest the appropriate form of transport in each of the following cases.
(a) (i) Transport of rice from Mbeya to Dar es Salaam
(ii) Transport of rice from South Africa to Tanzania.
(b) (i) Transport of flowers from Tanzania to U.K.
(ii) Transport of flowers from Arusha to Dar es Salaam
(c) (i) Transport of heavy machine from Japan to Tanzania
(ii) Transport of heavy machine from Dar to Morogoro
(d) (i) Transport of petrol from Iraq to Tanzania.
(ii) Transport of petrol from Dar es Salaam to Zambia.
(e) Transport of copper from Lusaka to Dar es Salaam
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256






