TOPICAL QUESTIONS: FORM ONE.
INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS:
SECTION A:
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS.
1. For each of the item below, choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number.
The branch of science which deals with the study of the relationship between matter and energy is:-
Civics
Chemistry
Pshology
Physics
(ii) Physicist is a person whose occupation specializes in the science of:-
Biology
Physics
Mathematics
Chemistry
(iii) Matter is________________
Anything which has got mass and occupy a space.
Anything which contains mass and volume
Scientific study of energy.
A science which deals with the study of nature and physical properties.
(iv) The ability or capacity of doing work is known as:
Mass
Matter
Pressure.
Energy.
(v) The following is the fundamental subjects which other subjects use its application.
Physics
Chemistry
Biology
Mathematics.
2. Complete each the following statement by writing the correct answer in the space provided.
__________ is a scientific study of matter in relation to energy.
Energy is ability or capacity of doing________________
_______________ is anything which has got mass and occupies a space.
There are _______________ states of matter.
A person who study Physics is called_______________
3. Define the following terms.
Physics
Physicist
Science
Technology
4. List any three importance of studying Physics.
5. List any five areas where Physics is applied in real life.
6. Mention five subjects which relates with Physics.
LEARNINGHUBTZ.CO.TZ Page
TOPICAL QUESTIONS: FORM ONE.
INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS:
SECTION A:
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS.
1. For each of the item below, choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number.
(i) The branch of science which deals with the study of the relationship between matter and energy is:-
- Civics
- Chemistry
- Pshology
- Physics
(ii) Physicist is a person whose occupation specializes in the science of:-
- Biology
- Physics
- Mathematics
- Chemistry
(iii) Matter is________________
- Anything which has got mass and occupy a space.
- Anything which contains mass and volume
- Scientific study of energy.
- A science which deals with the study of nature and physical properties.
(iv) The ability or capacity of doing work is known as:
- Mass
- Matter
- Pressure.
- Energy.
(v) The following is the fundamental subjects which other subjects use its application.
- Physics
- Chemistry
- Biology
- Mathematics.
2. Complete each the following statement by writing the correct answer in the space provided.
(i) __________ is a scientific study of matter in relation to energy.
(ii) Energy is ability or capacity of doing________________
(iii) _______________ is anything which has got mass and occupies a space.
(iv) There are _______________ states of matter.
(v) A person who study Physics is called_______________
3. Define the following terms.
(i) Physics
(ii) Physicist
(iii) Science
(iv) Technology
4. List any three importance of studying Physics.
5. List any five areas where Physics is applied in real life.
6. Mention five subjects which relates with Physics.
LEARNINGHUBTZ.CO.TZ Page 1
FORM ONE, TOPICAL EXAMS
INTRODUCTION TO LABORATORY PRACTICE
PHYSICS:
SECTION A:
Answer all Questions in this section
1. For each of items (i) – (ii) choose the correct answer among the given alternatives and write its letter in box provided.
(i) When of fire hazard from an electric fault erupts in house:
- Cut off all connecting wires
- Switch of the main switch
- Break the main switch.
- Switch off the switch sockets.
(ii) Laboratory rules are useful in:-
- Making students enjoy science subject
- Making students conduct experiments freely
- Ensuring safety while in the laboratory
- Ensuring good communication with other students and the teachers.
(iii) A student gets an electric shock and falls down unconscious in a physics laboratory. Which of the following would you do first to help the victim?
- Administer breathing exercise
- Call the physics teacher
- Call other students
- Call a medical doctor
(iv) Which of the following used to stop fire?
- Matches
- Extinguishers
- Fuels
- Brushes
(v) Which of the following is safety precaution in the Physics laboratory?
- Doing experiment in the laboratory
- Handling of apparatus in the laboratory
- Use equipment with care in the laboratory
- Do anything in the laboratory
(vi) A set of techniques used by scientists to investigate a problem refers to:-
- Data interpretation
- Scientific method
- Performing an experiment
- Data presentation
(vii) First aid is an immediate assistance or care given to a sick person or an accident victim before getting:-
- Help from nearby people
- Professional medical help
- Relatives and friends’ assistance
- Traditional medical care
(viii) Special room that have been designed and equipped for carrying out scientific experiments is called?
- Class room
- Staff room
- Bed room
- Laboratory
(ix) Which of the following is a feature of modern laboratory?
- Well illuminated
- Two doors open inward
- Kerosene stoves as source of heat
- With no windows.
(x) Wire gauze used for
- Providing a plat form for heating stability
- Demonstrating thermal expansion
- Providing equal distribution of heat while burning
- As a source of heat.
2. Match each item in List A with response in List B by writing its letter below the number of the corresponding item in the table provided.
| LIST A | LIST B |
| (i) The condition in the laboratory where physicist protected from danger, risk or injury. (ii) Preventing direct contact with victim’s body fluids (iii) A situation where by victim is weak and unable to stand which caused by too much heat and congestion (iv) The symbol established to ensure safety in the laboratory and in other field like goods or commodities (v) Symbol which means that the substance can speed up the rate of burning (vi) The test of whether hypothesis is true or false (vii) It involves the use of mathematics concept such as pie charts, graphs and formulae. (viii) Cause laboratory accident (ix) It prevents the victim’s condition from becoming worse (x) The special tools and instruments commonly used to carry out the experiments in the laboratory. |
|
3. Complete each the following statements by writing answers in the space provided.
(i) Laboratory can be defined as______________________________________
(ii) ___________________ used for measuring volume of liquids.
(iii) The se of regulation governing physicist to conduct experiment and maintain the laboratory is known as___________________________
(iv) The substance has high voltage which should not be touch is represented by symbol called_____
(v) Scientific investigation or scientific procedure is also called_____________________
(vi) Fire triangle can be defined as______________________________
(vii) Dry powder, foam or foam extinguisher is suitable for class_________________ fire.
(viii) The burning cooking appliances with oils and fats at high temperature is class___________ fire
(ix) The first procedure to help the fainted victim is_________________
(x) Petroleum jelly used for _______________________________
SECTION B:
Answer all questions)
4. (a) Laboratory rules can be defined as____________________________________
(b) Mention any four laboratory rules.
(c) List five laboratory apparatus used for measuring volume of liquids in the laboratory.
5. (a) First aid kit can be defined as________________________________
(b) Complete the table below by filling the blanks.
| Item | Uses |
| (i) | Covering wounds to protect the victim from dirty and germs. |
| Antiseptic solution | (ii) |
| (iii) | For reducing muscular pain |
| Thermometer | (iv) |
| (v) | For cutting dressing materials. |
6. (a) Laboratory safety is____________________________
(b) Mention four laboratory safety procedures.
(c) Mention five causes of laboratory accident.
7. (a) Mention five importance of first Aid
(b) List five procedures to help a victim with small cut or wound.
8. (a) Mention four causes of laboratory fire.
(b) Give examples of materials of each of the following classes of fire.
(i) Class A:____________________
(ii) Class B:_____________________
(iii) Class C: ____________________
(iv) Class D: ____________________
(v) Class E: ____________________
(vi) Class F: ____________________
9. (a) Warning signs can be defined as________________________________
(b) Give one example of each of the following warning sign.
(i) Flammable: ______________
(ii) Harmful: ________________
(iii) Explosive: _______________
(c) Draw diagram of each of the following warning sign.
(i) Radioactive
(ii) Corrosive
10. (a) List steps of scientific investigation chronologically
(b) Mention three types of variable as applied in scientific research.
TOPICAL EXAMINATIONS
MEASUREMENT:
SECTION A. 20 Marks.
1. Multiple choice questions.
(i) Measurement is defined as;
- Assigning numbers
- Assigning values
- Precise description
- Making observations.
(ii) Which is not a basic quantity?
- Mass
- Time
- Length
- Second
(iii) Advantage of metric system is that:
- It is universally accepted
- It is decimal based system
- One can convert from one unit to another
- Units of measurement are small.
(iv) SI – Unit of length is
- Centimeter
- Kilometer
- Meter
- Millimeter.
(v) Diameter of a wire can be measured using
- Venier caliper
- Micrometer screw gauge
- Meter Ruler
- Beam balance
(vi) Which is not a derived quantity?
- Volume
- Speed
- Area
- Distance
(vii) Accurate volume of a liquid can be measure by using
- Volumetric flask
- Pipette
- Burette
- Cylinder.
(viii) A factor which affect sinking or floating is
- Volume
- Density
- Mass
- Surface area.
(ix) A box block with rectangular shape, measuring 10cm, by 5cm by 5cm by 2cm has a density of given mass is 200g;
- 4g/cm3
- 2g/cm3
- 1g/cm3
- 100g/cm3
(x) Which is not true about relative density?
- Pure water is used in its calculation
- Relative density is calculated by comparing its density with water
- Pure water has density of 1000kg/m3
- Relative density has no unit.
2. Match the following items.
| List A | List B |
| (i) Used to measure density of liquid (ii) Use in measuring density of irregular substance (iii) Used to prepare volume of correct solution (iv) Suitable to measure thickness of a wire (v) Characteristics which can be measured by an instrument. |
|
SECTION B
3. Fill the gaps below
(i) Process of assigning numbers to observation or events__________________
(ii) _________________ is a characteristic which can be measured by instrument
(iii) A quantity that cannot be derived from another is___________
(iv) ______________ is SI – unit of length
(v) Two scales of venier caliper are ___________________ and ________________
(vi) Amount of matter in a substance is _______________
(vii) Mass is measured by using__________________
(viii) Are quantity that depend on other quantities_________________
(ix) Used to measure fuel volume of a liquid____________
4. (a) Define density
(b) A block of metal of volume 25cm3 was dropped in water and volume raised to 65cm3. Find initial volume of water.
5. (a) Define relative density
(b) A clean dry beaker has a mass of 400g. 112cm3 Kerosene is poured into the beaker with help of burette, if the mass of beaker and kerosene is 500g, find density of kerosene.
6. (a) Define volume of a substance.
(b) Mention three apparatus used to measure volume of substance.
7. An empty petrol tin has a mass of 0.75kg. When full of petrol, the tin and petrol has a mass of 7.75kg. If the density of petrol is 700kg/m3, find volume of petrol in tin.
8. Identity areas in daily life you can find application of density.
TOPICAL EXAMINATION
ARCHIMEDES PRINCIPLE AND LAW OF FLOTATION
SECTION A:
1. Multiple choice questions.
(i) What principle did Archimedes discover?
- Principle of volume
- Principle of density
- Principle of buoyancy
- Principle of gravity.
(ii) The term buoyant mean
- Float
- Push
- Flying
- Sink
(iii) An ice – cake is pushed to the top of glass of water by
- Buoyant force
- Density
- Compressed air
- Sinking object
(iv) Which of these gives correct formula of density?
- D = mass
 volume
volume - D = mass + volume
- D = mass – volume
- D = mass
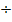 volume.
volume.
(v) Amount of matter in a substance is called
- Volume
- Density
- Mass
- Length.
(vi) What happens when you heat a gas?
- It gains mass
- It loses mass
- It increases volume
- It decreases volume
(vii) The mass of an object on earth is 6kg. What will be the mass on moon?
- 6kg
- 0kg
- 1kg
- 13kg
(viii) Archimedes principle states that:-
- Buoyant force acting on an object equal volume of liquid displaced by object.
- The buoyant force acting on an object equals the weight of fluid displaced.
- The buoyant force acting on an object will always be equal
- Water displaced is equal to weight of an object.
(ix) Has a weight of 15N and a buoyant force of 18N.
- Sinking object
- Floating object
- Buoyed up object
- Light object.
(x) ________ is pumped into sub – marine ballast tank to decrease density.
- Oil
- Compressed air
- Nitrogen
- Water
2. Match the following
| List A | List B |
| (i) Upward push when object is in water. (ii) Indicates safety limit of loading (iii) Instrument used to measure density of liquid (iv) Discovered relationship between weight of body and up thrust (v) A gas used in Balloons |
|
SECTION B
3. (a) What is buoyancy
(b) Explain why a ship floats in water.
4. (a) State the law of floatation
(b) What condition are required for body to float?
5. (a) What is up thrust?
(b) State Archimedes Principle
6. (a) Distinguish between
(i) Floating and sinking
(ii) Weight and up thrust
(b) Why does hydrometer have wide bulb and Narrow stem.
7. When a body is totally immersed in fluid, its weight is found to be 45N the weight of liquid displace is 2.5N. Find weight of body in air.
8. (a) What is apparent weight?
(b) Describe a simple experiment to determine apparent weight of an object.
9. Given that weight of an object in air = 125N, apparent loss in weight = 50N. Determine apparent weight of the body.
TOPICAL EXAMINATIONS
FORCE
SECTION A
1. Multiple choice questions:
(i) Which is not work done by force?
- Cause a body to move
- Change body direction
- Increase volume of a body
- Stops a body in motion
(ii) Force responsible for elongation and restoration of body
- Torsional force
- Stretching and restoring force
- Repulsive force
- Attractive force
(iii) The SI –Unit of force is
- Newton
- Gravity
- Meter per second
- Meter squared.
(iv) Force used to squeeze or press together
- Compressional force
- Frictional force
- Repulsive force
- Tensional force.
(v) Force exhibited by magnet is called.
- Torsional force
- Attractive force
- Frictional force
- Stretching force
2. Match the following items.
| List A | List B |
| (i) Force exerted by earth (ii) Quantity of matter in substance (iii) Results in extending of a body (iv) Cause twisting of material (v) Stretching force |
|
SECTION B
3. (a) Mention at least seven types of force.
(b) What is stretching and restoring force?
4. Explain what type of a force you apply to stretch a rubber.
5. How can one make attractive force useful?
6. Give four usefulness of frictional forces in our daily life
7. (a) Define force
(b) Give two example of force that are result of bending or stretching object.
8. Explain a simple experiment to demonstrate repulsive forces.
9. Why is a body which weigh 60N on earth’s surface only. Weighs 10N on the surface of moon.
10. Give advantages and disadvantages of friction .
11. Mention differences between mass and weight.
TOPICAL EXAMINATIONS
PRESSURE
SECTION A
1. Multiple choice questions
(i) The SI – Unit of pressure is
- Ohms
- Paschal
- Joule
- Watts
(ii) A girl of mass 40kg wears heels with an area of 1cm2 in contact with ground, pressure on ground will be:-
- 4
 10-5
10-5 - 4
 104
104 - 4
 105
105 - 4
 105
105
(iii) Pressure is equal to
- A/F
- F/A
- d/F
- F/d
(iv) Formula of pressure in liquids is
- P = hPg
- P = Pg/h
- P = hg/P
- P = hP/g
(v) Atmospheric pressure is calculated by the
- Height of water column is barometer
- Height of mercury column in barometer
- Height of lime column in barometer
- Height of oil column in barometer.
(vi) Amount of pressure in liquid decrease with
- Volume
- Base area
- Mass
- Depth.
(vii) In a typical hydraulic press, a force of 20N is exerted on small piston of area 0.050m2, force exerted by large. Piston on load if it has an area of 0.50m2 will be
- 200N
- 100N
- 50N
- 10N
(viii) In a weather map, lines joining all those regions with same atmospheric pressure are called.
- Bars
- Mill bars
- Isobars
- None of above
(ix) If pressure of a liquid is 1000Pc and height of liquid is 20cm, then density of liquid is:-
- 50g cm-1
- 5g cm-
- 100g cm-1
- 0.2g cm-1
(x) We may feel internal injury of altitude sickness at higher or lower altitudes than sea level because.
- The pressure of our body remains the same
- Our body adjusts the pressure slowly
- Our body experience high pressure
- Our body experience low pressure.
2. Match the following.
| List A | List B |
| (i) SI – Unit of pressure (ii) Pressure in liquids (iii) Used to measure pressure (iv) Pressure on liquids depends on (v) One application of pressure. |
|
SECTION B
3. Fill the gaps
(i) Pressure in solids depends on __________
(ii) Pressure in liquid depends on____________
(iii) When pressure is applied on non – viscom liquid it is transmitted ________ in all directions
(iv) Atmosphere exerts a pressure of approximately ________________Nm2 on earth’s surface.
(v) The two types of barometer are _______________ and __________________
(vi) An example of device that uses atmospheric pressure________________
4. (a) Define pressure and state SI – Unit.
(b) Calculate the pressure at bottom of pond 10m deep if the density of water is 1000kg/m3 and acceleration of gravity is 10m/s2.
5. (a) State two factors which pressure in liquids depends
(b) Explain why
(i) Sharp knife cuts easily than blunt knife
(ii) An elephant cannot easily sink in mud
(iii) Tyres of a tractor are wide
6. A glass slab of density 2500kg/m3 measures 20cm ![]() 10cm
10cm ![]() 50cm, find:-
50cm, find:-
(i) Maximum
(ii) Minimum pressure exerted on flat horizontal surface.
7. Explain principles of lift pump.
8. How does a bicycle pump work?
TOPICAL EXAMINATIONS
PROPERTIES OF MATTER
SECTION A
1. Multiple choice questions
(i) Which is a characteristic of a gas?
- Conducts electricity
- Does not have definite shape or volume
- Has definite volume but not shape
- Has both fixed volume and shape.
(ii) Which is not example of a compound?
- Limestone
- Hydrogen
- Salt
- Water
(iii) Tiny particle that makes matter are called
- Molecules
- Element
- Atoms
- Electrons
(iv) Atoms in solid are closely packed together due to:-
- Cohesive force
- Adhesive force
- Capillarity
- Bond
(v) Which of the following has the highest density?
- Liquid
- Gas
- Solid
- Plasma
(vi) An insect called pond skater can walk on water because of:
- Elasticity
- Surface Tension
- Hooke’s law
- Buoyancy
(vii) Water is able to move in narrow vessels because of:
- Surface Tension
- Adhesion force
- Cohesion force
- Capillarity action.
(viii) Which of the following is not application of capillarity?
- Oil raise in wicks of lamps
- Absorption of water by towel
- Water raise in soil
- Uptake of water by xylem.
(ix) An example of semi – permeable membrane is
- Potato
- Cell wall
- Cell membrane
- Vacuole
(x) The property of a body to return to its original position is called.
- Inelasticity
- Elasticity
- Stretching
- Compression
2. Match the following.
| List A | List B |
| (i) Allows only some particles to enter and prevents others. (ii) Ability of liquid act as stretched elastic skin (iii) Raise of liquids in Narrow tubes (iv) Law which govern elasticity (v) Matter is made of small particles in continuous motion. |
|
SECTION B
3. (a) What is matter
(b) Mention three states of matter.
(c) Using diagram explain arrangement of particles in gas, solid and liquid.
4. Define the following:
(i) Cohesion
(ii) Adhesion
(iii) Capillarity
(iv) Surface tension
5. (a) State Hooke’s law
(b) Identify applications o elasticity in everyday life.
6. (a) What is surface Tension
(b) Explain why some insects can walk on water.
7. (a) Define the term Osmosis
(b) Explain application of Osmosis in daily life
8. (a) What is the difference between elastic and plastic materials?
(b) State application of capillarity in daily life.
TOPICAL EXAMINATIONS
LIGHT
SECTION A
1. Multiple choice questions.
(i) Which of these is a luminous body?
- Moon
- Mirror
- Star
- Earth
(ii) Path taken by light is called?
- Ray
- Beam
- Transit
- Rays
(iii) Which is not true?
- Light can bent
- Light travel in straight line
- Opaque object do not allow light to pass.
- Glass is transparent.
(iv) A part of shadow which receives no light from source is called?
- Shadow
- Eclipse
- Penumbra
- Umbra
(v) When Earth is between the Sun and the Moon, we get?
- Earth eclipse
- Moon eclipse
- Solar eclipse
- Venus eclipse.
(vi) Angle between incident ray and normal ray is called?
- Normal angle
- Incidence ray
- Angle of incidence
- Angle of reflection
(vii) If left side of object appear as its right side and vice versa the image is said to be:-
- Normal
- Reversed
- Lateral
- Multiple
(viii) Which is not application of reflection
- Formation of periscope
- Car mirror
(ix) The properties of images by plane mirror are
- Virtual and normal
- Inverted and normal
- Lateral inverted virtual
- Normal and multiple
(x) Which of these does not produce reflection?
- Mirror
- Polished cooking utensils
- Cobble stone road
- Silvered iron sheets.
2. Match the following items.
| List A | List B |
| (i) Produce own light (ii) Stream of light rays (iii) Allow small amount of light to pass (iv) Shadowing of one heavenly body in the shadow of another (v) Earth is between the sun and the moon.
|
|
SECTION B
3. State laws of reflection.
4. What is reflection of light? Distinguish between angle of incidence and the angle of reflection.
5. List characteristics of an image formed on a plane mirror
6. Discuss the application of periscope
7. Define with examples the terms opaque, transparent and translucent as used in light.
8. Explain the formation of multiple images in mirror inclined at 90 ![]()
9. What is reflection of light? Distinguish between the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection.
TOPICAL EXAMINATIONS
WORK, ENERGY AND POWER.
SECTION A
1. Multiple choice questions
(i) The formula of work done is
- Force
 displacement
displacement - Force
 velocity
velocity - Pressure
 displacement
displacement - Mass
 acceleration
acceleration
(ii) An object of mass 200g moving with velocity 50cm/s. What is its kinetic energy?
- 2.1
 105, erg
105, erg - 2.0
 105, erg
105, erg - 2.8
 105, erg
105, erg - 2.5
 105, erg.
105, erg.
(iii) A machines do a work of 100 Joule is 20 seconds, what is its power?
- 120 watt
- 80 watt
- 5 watt
- 2000 watt
(iv) The unit of power is?
- Watt
- Newton
- Joule
- Newton – meter
(v) The rate of change of work is_________
- Power
- Force
- Momentum
- Energy
(vi) What happens to its potential energy when object is taken to high attitude?
- Its potential energy increases
- Its potential energy decrease
- Its potential energy remains same
- None of the above.
(vii) What is the formula of potential energy?
- Mv2
- mgh
- mgh2
- pgh.
(viii) The formula of kinetic energy is
- (
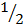 ) mv2
) mv2 - Mv2
- mgh
- P?dv
(ix) A pump raise 100kg of water steadily through a height of 30m in 10s, what is the power developed by the pump?
- 300J/s
- 1000W
- 3000W
- 1200W.
(x) A particle is thrown upward with some kinetic energy. What happened to its kinetic energy at the highest point or height it reaches?
- Its kinetic energy is lost
- It’s all kinetic energy is absorbed by air
- It’s all kinetic energy is converted to potential energy
- Its kinetic energy remains the same.
2. Match items below:
| List A | List B |
| (i) Ability is do work (ii) Force (iii) Device used to transform energy from one form to another (iv) S. I for power (v) Energy possessed by body in motion |
|
SECTION B
3. (a) State law of conservation of energy
(b) A stone of mass 2kg is released from height of 2m above the ground. Find the potential energy of stone when it is at height of 0.5m above the ground.
4. (a) What is power?
(b) A ball of mass 0.2kg is dropped from a height of 20m. On impact with ground it loses 30j of energy. Calculate the height it reaches on the rebound.
5. (a) Distinguish between potential and kinetic energy.
(b) Distinguish between work and power. Define unit of joule watt (W) and horse power (h.p)
6. Calculate the power of water pump which can lift 1000kg of water through a vertical height of 5m in 2seconds.
7. A 50kg girl runs up a staircase of 50 steps each. Steps in 15cm in height, in 5 second.
a) Find work done against gravity by the girl
b) At what power is she running
8. Name one device which converts:-
a) Heat energy into electrical energy
b) Mechanical energy into electrical energy
c) Electrical energy into heat
d) Electrical energy into sound energy
9. A ball is thrown vertically upward. At position is its kinetic energy maximum.
10. A body of mass 0.5kg is projected vertically upwards such that it attains a height of 40m. What is the potential energy at its highest point?
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256






