
FORM FOUR PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 219
FORM FOUR PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 219
PRESIDENT’S OFFICE, REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES,
PRE MOCK EXAMINATION
PHYSICS FORM FOUR
Time: 3Hours
Instructions
- This paper consists of sections A, B, and C with a total eleven (11) questions.
- Answer all question in the sections A, B and two (2) questions from section C.
- Section A carries sixteen (16) marks, section B fifty four (54) marks and section C carries thirty (30) marks.
- All writing should be in blue or black pen, except for diagrams that must be drawn in pencil.
- Communication devices and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet (s
- The SI unit of acceleration is:
A) Meter (m)
B) Kilogram (kg)
C) Second (s)
D) Meter per second (m/s)
E) Meter per second squared (m/s²)
- According to Newton's Second Law of Motion, force (F) is equal to:
A) Mass (m)
B) Mass x Acceleration (ma)
C) Acceleration (a)
D) Weight (mg)
E) Work (W)
- An object submerged in a fluid experiences an apparent buoyant force equal to:
A) Its weight in air
B) The volume of fluid displaced by the object
C) The weight of the fluid displaced by the object
D) The density of the object
E) The density of the fluid
- Opposite poles of magnets attract each other, while like poles repel each other. This principle is the foundation of:
A) Electromagnetism
B) Electrostatic force
C) Nuclear force
D) Gravitational force
E) Strong force
- A changing magnetic field can induce an electric current in a nearby conductor. This phenomenon is described by:
A) Ohm's Law
B) Kirchhoff's Laws
C) Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction
D) Lenz's Law
E) Coulomb's Law
- A car accelerates uniformly from rest to a speed of 20 m/s in 5 seconds. What is the car's acceleration?
A) 1 m/s²
B) 4 m/s²
C) 5 m/s²
D) 10 m/s²
E) 20 m/s²
- Most materials expand when heated and contract when cooled. This phenomenon is primarily due to:
A) Phase change
B) Increased atomic mass
C) Increased intermolecular spacing
D) Decrease in density
E) Change in chemical composition
- A convex lens can be used to:
A) Magnify objects (act as a converging lens)
B) Diverge light rays (act as a diverging lens)
C) Measure distance
D) Detect electric current
E) Separate colors of light (act as a prism)
- The speed of a mechanical wave depends on:
A) Its amplitude only
B) Its frequency only
C) The properties of the medium it travels through
D) The color of the wave (for light waves)
E) All of the above
- A diode allows current to flow through it in:
A) Both directions
B) One direction only (forward bias)
C) One direction only (reverse bias)
D) Proportion to the applied voltage
E) Independent of the applied voltage
2. Match the following geophysics terms in LIST A with corresponding description in LIST B.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
3. (a) What is the refractive index for a certain medium, if the light in air enters the medium at an angle of 30° and refracted at 22°?
(b) A vertical object 10 cm high is placed 20 cm away from a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. using a ray diagram, determine
(i) Image distance
(ii) The height of the image formed
(iii) The magnification of the image
4. (a) Describe how a lens camera operates the same as human eye. Give three points
(b) Briefly explain how conduction of heat can be applied in your daily life (three reasons)
5. (a) NYAMWERU was at home cultivating. He had two hoes, sharp and blunt hoe. Blunt hoe was not cutting well as how sharp hoe did. Explain to him why sharp hoe cuts well than blunt hoe. (b) A cube of sides 2cm is completely submerged in water so that the bottom of the cube is at a depth of 10cm. find:
- Difference in pressure between bottom and top of the cube.
- Different of force between bottom and top of the cube.
6.(a) Explain why does a solid weigh more in air than when immersed in a liquid?
- By using a help of diagram explain what happen to the two parallel straight conductors when current is moving in the same direction and in opposite direction.
- A block of wood of mass 5kg is placed on a rough inclined plane, at 60° to the horizontal. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the wood and the plane is 0.3, determine the acceleration of the wood down the plane.
7. A metal rod has a length of 2.00 meters at room temperature (20°C). When heated to 100°C, the rod expands by 1.6 mm.
a) Calculate the linear expansivity of the metal.
b) Predict the length of the rod if it is cooled down to -10°C.
c) Explain why bridges often have expansion joints built into their structure.
8. A car of mass 1200kg is accelerating on a straight track. The grapg below shows how the force acting on the car varies with time.
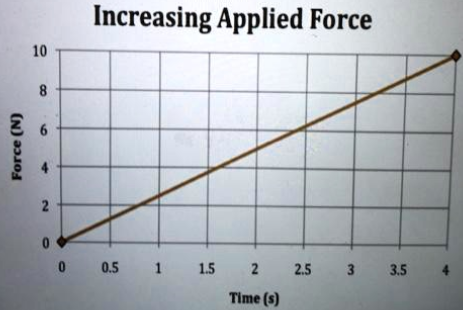
- Describe how the acceleration of the car will change over time.
- Calculate the aceleration of the car when the force is 3000 N
- Explain why the force needed to acelerate the car increases over time.
9. (a) George Ohm observed that as the current flows through the circuit, it encounters some opposition. This opposition determines the amount of current flowing in electric device depending to the particular material
(i) State the law that Mr. George formulate.
(ii) Briefly explain factors affecting resistance of a conductor observed by Mr. George Ohm to sum up his observation.
(b) (i) Distinguish between the concept of conductors, semiconductor and insulators in term of energy bands
(ii) Give out one structural difference between A.C and D.C generators.
10. (a) Students of form four in Uganda were not taught about electronics. Suppose you were invited to speak to them, using a labelled diagram explain how full-wave rectification can be achieved by using two diodes and centre-tapped transformer.
(b) (i) Electrical energy is distributed in all parts of Tanzania by the National Grid
System which transmits a.c at very high voltage. Why is an a.c and not a d.c used?
(ii) Six cells each having an emf of 2V and internal resistance of negligible resistance, a 1.4Ω resistor and a metal-filament lamp. The ammeter reads 3A, what readings would you expect from a high resistance voltammeter connected across the battery terminals?
11. (a) When a simple pendulum displaced at a small angle swings to and fro, in this motion potential energy and kinetic energy changes by alternating each other. With the aid of diagram verify the alternation of these energies.
(b) A 50kg girl runs up a staircase of 50 steps each step is 15cm in height in 5s. Find Work done against gravity by the girl and Power she use to run.
FORM FOUR PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 190
FORM FOUR PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 190
PRESIDENT OFFICE REGIONAL ADMNISTRATION
AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES
COMPETENCE BASED ASSEMENT
PHYSICS FORM FOUR
TERMINAL EXAMS MAY – 2023
031/1
TIME: 3HOURS
INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper consists of session A, B and C
- Answer all questions from section A and B and only two questions from section C
- Any unauthorized materials are not allowed in examination room.
- Write an examination number on every page of your answer sheets
- Where necessary, the following constant may be used:
- Acceleration due to gravity g=10m/s2
- S.T.P, 760mmHg, 273K
SECTION A (16 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section
- For each of items (i) – (x) choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter the item number in the answer sheets provided.
- The multiple reflection of the sound produced when its travels in an enclosed room refers as
- Sound waves
- Transverse waves
- Resonance
- Echo
- Reverberation
- The phenomenon that causes the dispersion white light into spectrum prism:
- Refraction
- Deflation
- Reflection
- Absorption
- Interference
- The death of deep seas creatures is when brought shallow water. This happens because of:
- Their pressure inside bodies is greater to the surrounded pressure of water.
- Their pressure made inside bodies is less than that surrounded pressure of water
- The density of dead body is equal to that of water
- Volume of body displaced is equal to volume of water
- Pressure of dead body is equal to that of atmospheric pressure.
- Aluminum is used in making motor engines pistons and cylinders due to its
- Low density and high thermal conductivity
- Low density and low thermal conductivity
- Its good conductor of heat than copper
- Thermal expansivity is high
- It’s stronger enough to maintain high temperature.
- One of the assumptions made when demonstrating how to determine specific heat capacity of substance by the mixture method is that:
- No heat lost to the surrounding, heat absorption by apparatus
- Heat lost to the surrounding, heat absorption by apparatus
- No heat lost to the surrounding, heat absorption by apparatus
- Heat lost to the surrounding, no heat absorption by the apparatus
- Calorimeter is apparatus for demonstrating.
- The phenomenon of melting under pressure and re-freezing when pressure reduced is called:
- Ebullition
- Triple point of water
- Regelation
- Depression
- Equilibrium
- Sweeting uses the cooling effects caused by
- Osmosis
- Diffusion
- Freezing
- Evaporation
- Saturated water
- A lens camera of focal length 15cm is used to take a picture of a man of height 1.8M, if a man is standing 10M ahead of the camera, what is magnification of the image:
- 1.8
- 1.5
- 0.00152
- 0.00142
- 0.005
- Mercury from Spheroid drops when split on a wooden bench because:
- Its velocity is very high
- It has relative density
- It has high cohesive force
- It has low surface tension
- It is subjected to high atmospheric pressure.
- A device consists of a coil rotating in an external magnetic field to produce electricity refers as
- Transformer
- Electric bell
- Spark coil
- Generator
- Galvanometer
- Match the items in List A with the responses in List B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number of the answer sheets provided.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B (54 MARKS)
Answer all questions from this section
- (a)Give out six differences between lens camera and human eyes.
(b)Optometrist and Ophltholmegist prescribe lenses measure in diopters, what is the power of the lens if the local lengths of the length 2M?
- (a)Why the overhead power cables more likely to break and fall during the cold season of the year than warm season of the year, even though they carry the same weight all the year around.
(b) 250cm3 of a gas are collected at 25°C and 750mmHg; calculate the volume of gas at STP?
- (a) What is the meaning and functions of the following electrical devices:
(b)A cell supplies a current of 0.6A through a 2Ω through a 7Ω resistors, calculate the emf and inter resistance of a cell
- (a)Why does the sky appear blue while being observed from the earth and black when you are on moon
(b)A solid of mass 26g absorbs 800J of heat when heated. If the initial temperature to the body is 30°C, find its final temperature.
- (a)The handle of a screw jack is 35cm and the pitch of a screw is 0.5cm if the efficiency of the jack is 55% calculate the force required to be applied at the end of the handle to lift a load of 2300N.
(b)(i) State the factors in which pressure in liquid and solids depends on.
(ii)In a hydraulic press the area of the piston to which the effort is applied is 5cm2. If the press can raise a weight of 2KN when an effort of 400N is applied, what is the area of the piston under the load?
- (a)A certain sample with half-life of 8days contains 16g of iodine-131.
- Write an expression to show the decay process of the sample
- Use an expression in (a)(i) to sketch the graph then estimate the mass of sample which will remain undecayed after 20 days
(b) Describe the mode of action of Geiger-Muller (G-M) tube in detecting nuclear radiations
SECTION C (30 MARKS)
Answer only two questions in this section
- (a)What is sonometer, state why guitars have string vary (thickness and thinnest) which produce the biggest frequency
(b)The frequency obtained from a plucked string 800Hz when tension is 8N. Calculate frequency when tension doubled and tension when frequency is halved?
(c)Distinguish the concepts of conductors, semiconductors and insulators in terms of their energy bands.
- (a)Explain briefly how the concept of wave is applied in:
(i)Medicine (ii) Communication (iii) Scientific Research
(b)The diagram below shows displacement time graph of wave with velocity of 2m/s
Calculate
(i)the amplitude (ii)Frequency (iii)Wavelength
(c)A circuit in a house is protected by a 10A fuse. The circuit is connected to the 240V main. The following appliances are connected to the circuit:
| Appliance | Power Rating |
| Bulb 1 | 100W |
| Bulb 2 | 7300W |
| TV | 5W |
| Heater | 1500W |
Determine whether the fuse will blow on or off if all appliances are turned on
- (a)In production of x-rays what are roles of
(i)Low voltage (ii)High voltage (iii)Tungsten target
(b)Describe four (5) applications of friction in daily life.
(c)State laws of electromagnetic induction
FORM FOUR PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 150
FORM FOUR PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 150
THE PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION, REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
COMPETENCE BASED SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES
PHYSICS TERMINAL EXAMINATION
FORM FOUR-2022
INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper consists of sections A, B and C with a total of eleven (11) questions.
- Answer all questions in sections A and B and two (2) questions from section C.
- Cellular phones and any unauthorised materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Non-programmable calculators may be used.
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
- Where necessary the following constants may be used:
- Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s 2
- Density of water = I .0 g/cm 3
- Pie= 3.14.
- Coefficient of linear expansivity of the brick 1.2 x 10 -5 K -1
- Speed of light in air = 3 x 108 m/s.
- Speed of sound in air = 340 m/s.
SECTION A (15 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
1. For each of the items (i) - (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in the answer booklet provided.
- High voltage is used for transmitting electricity on the National Grid. This is because high voltage
- is needed everywhere
- means high current would be used
- needs transformers for conversion
- would minimize electrical energy losses by using low current.
- would facilitate power distribution to customers.
- Polarization is
- the cell defect caused by impurities in zinc plate
- the formation of hydrogen gas around the positive plate of an electric cell
- the formation of tiny cells around zinc plate
- the cell defect that can easily be corrected by amalgamation
- the process of giving polarity
- A transistor is a device which
- amplifies alternating current or voltage
- amplifies direct current or voltage
- rectifies direct current or voltage
- amplifies and rectifies alternating current or voltage
- Rectifies alternating current or voltage.
- What causes water tides in the sea?
- Rotation of the earth about the sun
- Rotation of the moon about the earth
- Rotation of the earth about its axis
- Gravitational force due to the earth on the sea
- Gravitational force due to the moon on the sea
- Which is an incorrect statement about the solar planets?
- They are always moving in space
- They are all non luminous
- They all revolve round the sun as their centre
- They all have at least one moon
- The brightest planet as observed from the earth is venus.
- Which of the following are inner planets?
- Mercury and Venus
- Jupiter and Mars
- Saturn and Venus
- Neptune and Uranus
- Pluto and Mars.
- One use of gamma rays (?rays) is to
- treat neurotics
- treat black spots
- heal fractures
- kill cancer cells
- join broken hands.
- The conduction in a semi conductor material is due to
- doping
- extrinsic conduction
- intrinsic conduction
- motion of charges
- movement of holes and electrons.
- Compared to cool air, warm air can hold
- more water vapour
- less water vapour
- the same amount of water vapour
- no water vapour
- more or less the same amount of water vapour.
- Which of the following is correct about a capacitor?
- Does not need an insulator between its plates
- Has very high capacitance when air is between its plates
- Must have metal plates to store a charge
- Has capacitance defined by C = V/Q
- Has no voltage across it when working in a radio receiver.
2. Match the items in list A with the responses in list B by writing the letter of the correct response
beside the item number.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
3. (A) Define the terms
(i) Half life (ii) atomic number
(b) Name the three fundamental particles of which atoms of an element are composed. How are these particles distributed in the atom of an element whose atomic number is 3 and mass
number7?
(c) A radioactive nucleus is denoted by the symbol 88X226
Write down the compositions of the nucleus at the end of the following stages of disintegration
(i) Emission of an alpha (∝) particle
(ii) Further emission of beta (β) particle
(iii) Further emission of a gamma radiation
4. (a) (i) Distinguish between mechanical and electromagnetic waves
(ii) Explain why a duck remains floating at the same place as a wave passes by the water in a lake
(b) (i) What are ultrasonic vibrations?
(ii) An FM radio station broadcasts electromagnetic waves at frequency of 125 M Hz. The radio waves have a wavelength of 2.4 metres. Calculate the speed of the radio waves
(c) Gamma ray busters are objects in the universe that emit pulses of gamma rays with high energies. The frequency of the most enegetic bursts has been measured at round 3.0 x 1021 Hz.
(i)What is the wavelength of these gamma rays?
(ii)What could be their period?
5. (a) A body projected vertically with a velocity of 40m/s from the ground, comes to rest momentarily at the top most position and returns to the ground. Calculate; (i) The maximum height reached by the body (ii) The total time of flight
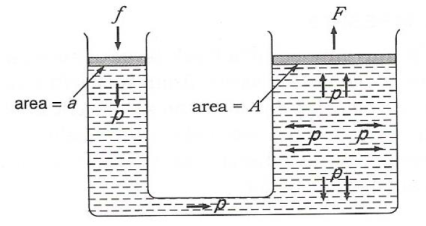
(b) In figure below, a force of 100N acts on the smaller piston of area 2cm2. Calculate the upward force acting on the large piston of area 900 cm2.
(c) A body of mass 400g falls freely from a tower and reaches the ground after 4s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the mass as it hits the ground. (Take g= 10m/s2)
6. (a) A machine is used to lift a load of 400N with an effort of 80N.
Calculate
- The mechanical advantage of the machine,
- The efficiency of the machine, if the velocity ratio of the machine is 8
(b)A spiral spring produces an extension of 4cm when a force of 2N is applied to it. Calculate the spring constant for a system when two such identical springs are arranged in (a) series (b) parallel
(c)A metal block of density 7 800kg/m3 weighs 117N in air and 105N in a liquid when wholly immersed wholly immersed. Calculate the density of the liquid.
7. (a) Name two objects in space which are the earth’s nearest neighbours
(b) What are the real names of objects in the sky which are commonly known by the following names?
(i) An evening star
(ii) A morning star
(iii) A shooting star
(c) The earth appears to be stationary, but it is always in motion. Calculate the unnoticed speed of a man along
the equator, in km/h,due to
(i). Rotational motion of the earth about its axis
(ii). Revolution of the earth around the sun
Take 1 year = 365 days
8.(a) Define the following terms.
(i) Capacitor
(ii) Semi-conductor
(iii) Transistor
(b) What are the differences between a conductor, a semiconductor and an insulator in terms of their conductivity?
(c) An output of transformer is connected in series with semiconductor diode
(i) Draw the sketch of the expected variation of electromotive force against time.
(ii) Give reasons whether this device is suitable or not for use in a radio.
9. (a) Sketch the magnetic field patterns due to a current passing through
(i) a long straight wire (ii) a circular coil (iiii) a long solenoid
Indicate clearly the direction of current and magnetic field.
(b) Explain briefly how the domain theory of magnetism is used to differentiate a magnetic material from a magnet
(c) (i) Describe how sounds are transmitted by telephones,explaining the actions of both transmitter and receiver.
(ii) What additional equipment is needed to ensure good communication over long distance?
SECTION C (10 Marks)
Answer one (1) question from this section.
10. (a) Using Newton’s second law of motion, state two quantities which vary with net force
applied on a body. (02)
(b) Write an equation obtained by combining the force and the two quantities you have
mentioned. (02)
(c) Evaluate the proportionality constant if your equation is used to define the unit of force,
the Newton, while taking a unit of each variable in your equation. (01)
(d) A certain force gives a mass m 1 an acceleration of 12.0 m/s 2 . What acceleration will the
same force give the two masses when they are joined together? (04)
11. (a) (i)Use the kinetic theory to explain why solids expand when heated.
(ii)Mention two experiments which can be done in the laboratory to verify thermal expansion of solids.
(b) Explain how each of the following works:
(i) a bimetallic thermostat.
(ii)a bimetallic thermometer.
(c) (i) What is an induction coil?
(ii) Describe the structure of an induction coil and briefly explain its mode of action.
FORM FOUR PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 87
FORM FOUR PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 87
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256







