THE PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
PHYSICS FORM TWO PRE- MOCK EXAMINATION
CODE 031
TIME: 2:30 HOURS
INSTRUCTIONS.
- This paper consists of section A, B and C with the total number of ten(10) questions
- Answer all questions in each section
- Section A carries (15) marks, section B (70) marks and section C carries (15) marks
- All writing must be in blue/black ink except drawing which must be in pencil
- Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the assessment room.
SECTION A (15 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section
1. For each of the items (i) – (x) choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in the answer sheet provided
- Physics is the study of:
- Living organisms and their interactions
- The composition of matter and its changes
- Matter, energy, and the interactions between them
- The history of Earth and its rocks
- If someone in the lab spills a flammable liquid on their clothes that ignites, your immediate action should be to:
- Find a fire extinguisher
- Yell for help and stop the person from moving
- Direct them to the safety shower or help them use a fire blanket
- Throw water on them
- The SI unit for length is the:
- kilogram (kg)
- second (s)
- meter (m)
- gram (g)
- What is the net force required to keep an object moving at a constant velocity?
- Zero
- Equal to the object's weight
- Dependent on the object's speed
- More force is always needed
- If you double the area over which a force is applied, the pressure will:
- Double
- Stay the same
- Be halved
- Increase by four times
- A lever is a simple machine that can be used to:
- Increase the force applied
- Increase the speed of an object
- Change the direction of a force
- All of the above
- An object with a density less than water will:
- Sink immediately
- Float
- Dissolve
- None of the above
- The buoyant force on a submerged object is equal to:
- The weight of the object
- The weight of the fluid it displaces
- The volume of the object
- The density of the object
- Opposite poles of two magnets will:
- Repel each other
- Attract each other
- Have no effect on each other
- It depends on the type of magnet
- The flow of electrons in a circuit is called:
- Resistance
- Voltage
- Current
- Power
2. Match the terms related to magnetism on the left to the correct description on the right.
| Column A | Column B |
|
|
SECTION B: 70 Marks
- (a)Explain briefly the first aid measure that should be taken in case of
- Cut
- Poisoning
- State any five laboratory safety rules
- (i) Define physics.
- State any five branches of physics
- State any five career opportunities in physics
(a) Name any 4 items contained in the first Aid kit found in the laboratory
- Briefly explain how physics is related to biology
- State any three effects of a force
- (a) Describe the method you would use to measure the circumference of a cylinder using a thread and a meter rule
- A sphere of diameter 3.0 cm is mounted into a thin uniform wire of diameter 0.2mm calculate the length of the wire in meters
- (a) State any three differences between mass and weight
| Mass | Weight |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
- The mass of 25cm3 of ivory was found to be 0.045kg. Calculate the density of ivory in SI units
- 300 cm3 of fresh water of density 1000kg/m3 is mixed with 100cm3 of sea water density 1030kg/m3.calculate the density of mixture
8.(a) Explain how you would measure the volume of irregularly shaped object using the displacement method.
(b) Distinguish between a fundamental and derived quantity giving an example of each (c) Define force and state its SI unit
- State any 4 types of force
- (a) Distinguish between a scalar and vector quantity giving an example of each
- State any 3 applications of capillary action
- State any two factors affecting the surface tension
- A man has a mass of 70kg. Calculate
SECTION C: 15 Marks
10 (I) (a)His weight on earth where the gravitational strength is 10 N/kg
- His weight on moon where the gravitational strength is 1.7 N/kg
- Explain briefly why water wets the glass while mercury does not
- Differentiate between cohesive and adhesive forces
- A body weighs 400N in water. If the up thrust force is 20N.calculate its weight in air
- Explain briefly why a razor blade floats in water and when soap solution is carefully added to the water it sinks
(II) Explain the following behavior of molecules.
- When it is raining it is advisable not to touch a canvas tent from inside
(ii)Water rises up in harrow tubes but Mercury which is also a liquid falls in narrow tubes to level below the outside surface?
FORM TWO PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 180
FORM TWO PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 180
THE PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
PHYSICS FORM TWO MID TERM 1 EXAMINATION
CODE 031
TIME: 2:30 HOURS
INSTRUCTIONS.
- This paper consists of section A, B and C with the total number of ten(10) questions
- Answer all questions in each section
- Section A carries (15) marks, section B (70) marks and section C carries (15) marks
- All writing must be in blue/black ink except drawing which must be in pencil
- Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the assessment room.
SECTION A (15 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section
- A student sets up a simple circuit with a battery, wires, and a lightbulb. Which change will increase the brightness of the lightbulb?
(A) Adding another lightbulb in series
(B) Using a battery with a higher voltage
(C) Using thinner wires
(D) Making the wires longer
- A circuit has a current of 2 amps and a resistance of 4 ohms. What is the voltage of the power source?
(A) 0.5 volts
(B) 2 volts
(C) 6 volts
(D) 8 volts
- Two balloons are rubbed with wool and then hung near each other. The balloons push each other apart. What can you conclude?
(A) Both balloons have a negative charge
(B) Both balloons have a positive charge
(C) One balloon is charged, the other is neutral
(D) The balloons have a mixture of positive and negative charges
- A student places a bar magnet on a sheet of paper and sprinkles iron filings around it. Which of these diagrams best represents the pattern the iron filings will form?
(A) Straight lines radiating out from the magnet in all directions
(B) Circles around the magnet
(C) Lines flowing out of one end of the magnet and into the other end
(D) Random clumps throughout the paper
- A large, heavy box and a small, light box exert the same amount of pressure on a table. Which statement explains this?
(A) The large box has a higher density
(B) The small box has a smaller area in contact with the table
(C) The force of gravity is stronger on the large box
(D) The pressure depends on the material the boxes are made of
- A 50 Newton force is applied to move a 10 kg box across a rough floor. If the box accelerates at 2 m/s², what is the force of friction acting on the box?
(A) 30 N
(B) 20 N
(C) 10 N
(D) 5 N
- A ramp is used to help load a heavy crate into a truck. The ramp is an example of which type of simple machine?
(A) Pulley
(B) Inclined plane
(C) Wedge
(D) Lever
- Which of these correctly describes the difference between heat and temperature?
(A) Temperature is a form of energy, heat is the amount of energy transferred
(B) Heat is a form of energy, temperature is the measure of the average kinetic energy of particles
(C) Temperature depends on the substance, heat is the same for all substances
(D) None of the above are correct
- A solid metal cube sinks when placed in water. What can you conclude about the cube?
(A) The cube's weight is greater than the buoyant force acting on it
(B) The cube's weight is equal to the buoyant force acting on it
(C) The cube's density is less than the density of water
(D) The buoyant force only depends on the shape of the object
- A student accidentally splashes a small amount of acid on their hand. What should they do first?
(A) Apply a strong base to the area
(B) Notify the teacher and flush the area with water
(C) Wrap the hand tightly with a bandage
(D) Go to the school nurse immediately
2. Match the term that describes a property of a Magnet in LIST A with the correct MEANING of the term in LIST B
| Column A | Column B |
|
|
SECTION B: 70 Marks
3. a) Use the concept of pressure to explain why during construction of a railway, wide wooden or concrete sleepers are placed below the railway tracks?
b) i) What are the three factors does pressure in liquid depend on? (3marks)
ii) Calculate the pressure exerted on a diver at a depth of 20m below the surface of water in the sea.
4. a) i) The passengers sitting in a moving bus tend to fall forward when the bus suddenly stops. Explain why?
ii) State the law governing the phenomenon happened in 5(a)(i) above.
b) Differentiate elastic collision from inelastic collision by considering the way billiard balls collide on the pool table game.
- (a). State the Archimedes principle
(b). List down three conditions necessary for a body to float
(c). An object of weight 18 N when immersed in the water it experiences an up thrust of 2N. Calculate the following
- Real weight
- Relative density
- Density of the object in Kg/m3
6. (a) Differentiate ferromagnetic materials From paramagnetic materials by giving two typical examples of each.
(b) As a student who has the knowledge of magnets, how can you advice a person who is doing the business of selling magnets the three appropriate ways of storing magnets so that they can last longer.
7. (a) (i) When the pulling force is applied to the handle of the door, the hinge acts as the axis of rotation, and the door turns about. What do you understand by the term turning effect?
(ii) When forces are in equilibrium, it means that there is no net force to cause any movement. Describe conditions for parallel forces to be in equilibrium.
(b) A heavy uniform metal beam AB weighting 500kg is supported at its ends. The beam carries a weight of 3000kg at a distance of 1.5m from end A. If the beam is 4m long, determine the thrusts on the supports A and B.
8. (a) When the metal can that containing hot water is closed, and the cold water is poured on it, the can collapses. Why?
(b) In an experiment using Hare’s apparatus, the lengths of methanol and water columns were found to be 16 cm and 12.8 cm respectively
(i) What is the relative density of methanol?
(ii) If the length of methanol column was altered to 21.5 cm what would be the new height of the water column?
9.a) Explain why efficiency of machines is always less than 100%?
b) An object weight in air is 6.0N and 4.0N when immersed in water. What will be its:
i. Up thrust in water
ii. Relative density
iii. Density
c). Give reason why a ship can move on surface of water without sinking?
SECTION C: 15 Marks
Answer question eleven.
10.
10.(a) Explain briefly why:
(i)Water tanks have their outlets fixed at the bottom?
(ii)A tractor with wide tyres cannot easily get stuck in muddy places as compared to vehicles with narrow tyres.
(b) ![]()
![]() Calculate the maximum pressure exerted by a block of mass 150kg and surface dimensions of 4m by 6m by 8m resting on the table.
Calculate the maximum pressure exerted by a block of mass 150kg and surface dimensions of 4m by 6m by 8m resting on the table.
FORM TWO PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 179
FORM TWO PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 179
PRESIDENT OFFICE REGIONAL ADMNISTRATION
AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES
COMPETENCE BASED ASSEMENT
PHYSICS FORM TWO
TERMINAL EXAMS-MAY – 2023
031
Time: 2:30Hours
Instructions
- This paper consists of sections A, B and C with a total of ten (10) questions.
- Answer all questions
- Sections A and C carry fifteen (15) marks each and section B carries seventy (70) marks
- All answers must be written in the space provided
- All writing must be in blue or black ink except drawings which must be in pencil
- All communication devices, calculators and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the assessment room.
- Where necessary the following constants may be used:
- Acceleration due to gravity, g=10m/s2
- π = 3.14
SECTION A. 15 MARKS
- For each of the items (i) – (x) Choose the correct answer among the given alternatives write its letter in box provided
- A cooking oil was mixed with water and poured into a measuring cylinder and allowed to settle for three minutes, which one will be the observed phenomenon?
- Cooking oil floats over water
- Meniscus of water appeared convex in shape at the surface
- Water floating on the oil.
- Water and oil completely mixed up.
- If two cars are both travelling at 50Km/h and they collide head on, the effect is similar to a car colliding with a wall at what velocity?
- 0 km/h
- 10 km/h
- 50 km/h
- 100 km/h
- A house building contractor fitted window glass panes which someone cannot see through, but the rooms are fully illuminated with light. These types of glass pane materials are said to be:
- Dim
- Opaque
- Translucent
- Transparent
- The substance which is lighter has low density and less affected by gravitational force. In comparison with water, the number of times a substance is denser than water is termed as?
- Density
- Relative density
- Volume
- Mass
- Which phenomenon explain ability of some small insects to walk over a water surface?
- Capillarity
- Adhesion
- Surface Tension
- Osmosis
- Which of the following instruments work under the Pascal’s principle of pressure transmission
- Spring balance
- Single fixed pulley
- Inclined plane
- Hydraulic press
- The process whereby materials recover the original length after removing the load or force is described as.
- Plasticity
- Deformation
- Elasticity
- Elastic limit
- The quantity obtained by taking the ratio of mass per unit volume of a substance is described as:
- Relative density
- Density
- Matter
- Volume
- Materials can be twisted into different shapes. Which among the following forces causes twisting of elastic materials?
- Restoring force
- Compressional force
- Stretching force
- Torsional force
- A machine with effort between load and fulcrum belong to which class of lever?
- First class lever
- Third class lever
- Second class lever
- Fourth class lever
2. Match the description of electric terms in list A with the correct electric terms in list B by writing a letter of the correct response below the corresponding item number in the table provided
|
| List B |
| (i) The flowing of charge per unit time (ii) The instrument which used to measure current in wire (iii) A potential difference across the cell terminal as when no power delivered (iv) Is the instrument which used supply electric energy (v) Is a continuous path through which electric charge flows |
|
SECTION B. 70 MARKS
ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS FROM THIS SECTION
3
a) state laws of reflection
b) Explain the behavior of light when it encounters translucent, transparent and opaque materials
c) Calculate number of images when the angle between two plane mirrors is: i. 600 ii. 00
d) How the number of images formed by plane mirrors related to the angle between two plane mirrors?
4. a) State conditions for a body to be in equilibrium.
(b)By using the principle of Moment determine unknown Weight (W) on the fig below.
(c)A machine having velocity ratio (V.R) of 5 need an effort of 240N to raise a load of 720N. How much
i. mechanical advantage
ii. Efficiency (e)
5.a) Explain why efficiency of machines is always less than 100%?
b) An object weight in air is 6.0N and 4.0N when immersed in water. What will be its:
i. Up thrust in water
ii. Relative density
iii. Density
c) Give reason why a ship can move on surface of water without sinking?
6. a) Kinetic energy potential energy are forms of mechanical energy. Give comparison and differences between them
b) A car of mass 4tones travels at velocity of 4m/s .How much kinetic energy developed?
c) How much power developed when a crane lifts a container of mass 500kg through a height of 5m in 10sec ?
7. (a) When the metal can that containing hot water is closed, and the cold water is poured on it, the can collapses. Why?
(b) In an experiment using Hare’s apparatus, the lengths of methanol and water columns were found to be 16 cm and 12.8 cm respectively
(i) What is the relative density of methanol?
(ii) If the length of methanol column was altered to 21.5 cm what would be the new height of the water column?
8. (a) When water and mercury were in two separate measuring cylinders, the teacher asked student to observe the reading in both cylinders. Why does mercury form downward meniscus while that of water forms upward meniscus?
(b) A force of 4 N causes a certain copper wire to extend to 1.0 mm. Find the load that will cause a 3.2 mm extension on the same wire.
9. (a) Write down three equations of uniform acceleration of motion and explain the meaning of each symbol used in the equation.
(b)The football P of mass 0.5 kg was kicked by a goalkeeper at 12 m/s and collides with another football Q of mass 0.45 kg which was at rest. After the collision both balls move off together at 10 m/s. Calculate:
(i) The momentum of ball P before collision
(ii) The momentum of ball P after collision
SECTION C. 15 MARKS
ANSWER QUESTION 10
10. Three resistors of 2 ?, 4 ? and 6 ? are connected in series to a battery of e.m.f 24 V and have negligible internal resistance.
(a) Draw the circuit diagram including the battery, ammeter, switch and the three resistors.
(b) Find the current flowing in the circuit drawn in 10 (a) above.
(c) Find the potential difference at the ends of each resistor in 10 (a).
FORM TWO PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 149
FORM TWO PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 149
THE PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION, REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES
PHYSICS TERMINAL EXAMINATIONS MAY
FORM TWO-2022
Time: 2:30Hours
INSTRUCTIONS.
- This paper consists of section A, B and C with a total of 10 questions
- Answer all questions.
- Section A carries 30 marks, section B 50 marks and section C 20 Marks
- All answers should be written in the spaces provided.
- All communication devices, calculators and any unauthorized material are not allowed in examination room.
- Write your number on every page of your answer booklet.
- Where necessary, the following constants may be used;
- Acceleration due to gravity, g=10m/s2
- Density of water= 1g/cm3 or 1000kg/m3
SECTION A (30 Marks)
Answer All questions in this section.
1. For each of items (i-xx) choose the correct its letter in the box provided
(i)The formed by a plane mirror is always
- Smaller than the object
- Virtual
- Large that the object
- Real
(ii)A body which gains excess electrons becomes
- Negatively charged
- Positively charge
- Electrified
- Both A and B are correct
(iii)Which of the following is not a form of energy?
- Light
- Friction
- Magnetism
- Electrons
(iv)A person in a bus which starts to move forward tends to fall backwards. This is because he/she is obeying:
- The Principle of moment
- The Newton’s third law of motion
- The Newton’s second law of motion
- The Newton’s first law of motion
(v)When a body floats in water
- It displaces its own volume of water
- The mass of the water displaced by the body is equal to its own mass
- It weights the same as in air
- The downthrust is more than the upthrust
(vi)The velocity-time graph has a slope which represents
- Displacement
- Acceleration
- Velocity
- Speed
(vii)Work and energy have the same SI unit of
- Calorie
- Joule
- Walt
- Pascal
(viii)Heat energy is transferred from the sun to the earth by the process of
- Convection
- Radiation
- Conduction
- None of the above
(ix)A wheelbarrow is an example of
- First class lever
- Third class lever
- Complex machine
- Second class lever
(x)When charging a body by rubbing with either fur or skill the particles which are transferred are
- Protons and electrons
- Protons
- Electrons
- Nuclei
(xi)current electricity can be measured in
- Ohms
- Coulomb
- Volt
- Milliampere
(xii)A piece of metal of volume 10cm3 has a mass of 65.5kg. The density of metal is
- 65.5kg/m3
- 6.55kg/m3
- 655kg/m3
- 0.655kg/m3
(xiii)Umbra refers to
- Partial shadow
- Midnight
- Total shadow
- Moon
(xiv)When a narrow glass tube is dipped into mercury
- The adhesion of molecules of mercury is stronger than the cohesion of molecules of mercury
- The meniscus of mercury in a glass vessel curves upwards.
- Mercury experiences a downwards force equal to its weight.
- The level of mercury in the tube drops below that of the surrounding
(xv)A piece of metal of volume 0.24cm3 and mass 0.72 has a relative density (R.D) of
- 3.0g/cm3
- 3.0
- 3.0kgm3
- 0.3
(xvi)A body which sinks in water has its density
- Less than that of water
- Larger than that of water
- Equal to that of water
- Less or equal to that of water
(xvii)The mechanical advantage of a machine is 4. Find the effort needed to operate a machine of the load 1000N.
- 40N
- 2800N
- 250N
- 1999N
(xviii)A force exerted by a pressure of 20N/m2 acting over an area of 2m2 is
- 10N
- 18N
- 22N
- 40N
(xix)What is the acceleration of a body of mass 30kg when constant force of 150N is applied on it?
- 50m/s2
- 0.5m/s2
- 5.0m/s2
- 0.05m/s2
(xx)As the balloon goes up, the weight of air displaced becomes less and less. This means that the upthrust
- Is increased
- Is reduce
- Is exactly equal to its weight
- Remains constant
2.Match the items in List A with a correct response in List B by writing a letter of the correct response below the number of the corresponding item in List A in the table provided.
| LIST A | LIST B | |
|
| |
3.
- The Fundamental law of electrostatics charge state (i)______ (ii)_____
- Substance which allows electricity pass through are called ___________
- A point at which the resistant of Magnetic flux density is zero is called
- Water wets glass but mercury does not we because _______
- Lubricant are applied in machine in order to _______
4.(a)Differentiate between real weight and apparent weight of an object as applied in physics
(b)A solid weighs 64N in air and 48N when totally immersed in a liquid of density 0.8g/cm3 calculate
- The upthrust on the solid
- The volume of the solid
- The density of the solid
5(a)The two uses of a gold leaf electroscope are …………….
(b)In verification of Ohm’s law the following circuit was used during the experiment
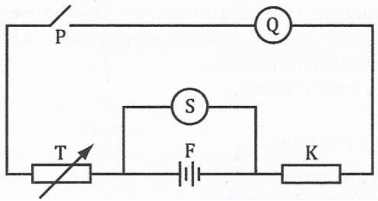
- P: represents ……………………...
- Q: represents ……………………...
- S represents ……………………...
- T: represents ……………………...
- F: represents ……………………...
- K: represents ……………………...
6(a) mention two examples of magnetic materials
(b)Name the materials which when rubbed with a dry cloth become
- Negatively charged
- Positively charged
(c)State two conditions for a body to be in equilibrium:
7(a)Distinguish between upthrust and apparent weight.
(b)The apparent weight of a body is 6.4N. If the weight of liquid displaced is 4.7N, what is the weight of the body in air?
8(a)A car with a velocity of 90m/s is uniformly retarded and brought to rest after 10seconds. Calculate its deceleration
(b)State the fundamental law of static electricity
(c)Explain what is wrong in the circuit diagram shown below.
9(a)Mention the type of mechanical energy
(b)A body of mass 10kg is raised to a height of 4 metres above the ground in 2 seconds
- Find the energy possessed by the body after raising it
- What is the type of energy possessed by the body?
10.The mass of an empty density bottle was 50g. When filled with a certain liquid of volume 20cm3 its mass became 75g. Find the
- Density of the liquid
- Relative density of the liquid
FORM TWO PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 100
FORM TWO PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 100
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256







