TAXATION
Meaning of Taxation
TOPIC OBJECTIVES
The student should be able to:
1. Define taxation
2. Explain the purposes of Taxation,
3. Mention the principles of Taxation.
4. Identify types of Taxation (Direct and Indirect).
5. Distinguish between the different systems of Taxation.
6. Define progres- sive, proportio- nal and regres sive taxation.
7. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of Direct and Indirect Tax.
KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTS
The principle of simplicity: This is Ability of the taxpayer to understand.
The principle of convenience: This principle emphasizes that both time and manner in which payments are executed should be convenient to the taxpayer.
The principle of certainty: According to Adam Smith, there should be certainty in taxation because uncertainty creates favourable climate for tax evasion hence compromising with the Taxation objectives
The principle of Equality: Taxes should be allocated among individuals fairly and reasonably.
Direct Tax; A direct tax is the one, which is paid by the person or entity on whom it is legally imposed.
Indirect Tax; An indirect tax is the one, which is imposed to one person or entity but paid partly or fully by others.
Value Added Tax (VAT);Value added tax is the tax levied on value added on the price of the product at each stage of production, and or distribution activities.
Estate taxes are imposed on the transfer of property upon the death of the owner.
Property tax, sometimes known as an ad valorem tax, is imposed on the value of real estate or other personal property.
A regressive tax structure results in low-income individuals paying a higher percentage of their income on taxes than high-income individuals.
A progressive tax structure is the opposite of a regressive tax structure. In a progressive tax system, taxpayers making more money pay higher tax rates than those making less money.
- Taxation refers to the practice of government collecting money from its citizens to pay for public services.
- It is a means by which governments finance their expenditure by imposing charges on citizens and entities. Without taxation, there would be no public Expenditures. One of the most frequently debated political topics is taxation.
- Taxation is the practice of collecting taxes (money) from citizens based on their earnings and property. The money raised from taxation supports the government and allows it to fund police and courts, have a military, build and maintain roads, along with many other services.
- Taxation is the price of being a citizen, though politicians and citizens often argue about how much taxation is too little or too much.
The Purpose of Taxation
What are the objectives of Tax
The concept of tax was initiated with a view to generate government revenue in its very beginning stage. In course of time it has been utilized for various purposes.
To raise government revenue for development and welfare programmes in the country.
To maintain economic equalities by imposing tax to the income earners and improving the economic condition of the general people.
To encourage the production and distribution of the products of basic needs and discourage the production and harmful ones.
To discourage import trade and protect the national industries
The Principle of Taxation
If the major objectives of taxation are to be achieved, taxes should conform to certain criteria. These are summarized in the following principles:
1. The principle of simplicity: This is Ability of the taxpayer to understand. The principle of simplicity is one of principles of taxation and it advocates that Tax system should be plain, simple to understand by the common taxpayers.
- It should not be complicated to understand how to calculate and ultimately ascertain how much to be paid. This principle of taxation is so important in that it helps in avoiding corruption as well as exploitation by the taxing Authority
2. The principle of convenience: This principle emphasizes that both time and manner in which payments are executed should be convenient to the taxpayer. An Economist by Names of Adam Smith said that `Every Tax ought to be levied at the time or in the manner in which it is most likely to be convenient for the contributor to pay. For instance the payment of Value Added Tax and Excise duty by the consumer is very convenient because the consumer pays the Tax when he buys the commodities at the time when he has the means to buy the product. Furthermore, the manner of payment is also convenient because these Taxes are inclusive in the prices of the commodities
3.The principle of certainty: According to Adam Smith, there should be certainty in taxation because uncertainty creates favourable climate for tax evasion hence compromising with the Taxation objectives. By this principle, it means that, the tax which each individual taxpayer is bound to pay should be certain. The time, the manner of payment and the amount to be paid must be clear to the taxpayer. Thus, this requires that there should be no element of arbitrariness in a tax. It should be in relation to ascertaining as to when, what and where the tax is to be paid.
3.The principle of Equality: Taxes should be allocated among individuals fairly and reasonably. In taxation systems, the principle of equality is considered as the most important. As Adam smith put it forward `The subjects of every state ought to contribute towards the support of the government as nearly as possible in proportion to their respective abilities. This implies that every person should pay the tax according to his ability and not the same amount. It further means that every taxpayer should not pay at the same rate; rather every taxpayer should pay the tax proportion to his income of the taxpayer.
Types of Taxation
There are two types of taxation, direct and indirect taxation
Direct Tax; A direct tax is the one, which is paid by the person or entity on whom it is legally imposed. It is collected from the persons or entities on the income they have earned exceeding a certain specified limit. Tax is generally calculated at a certain percentage on the income. Income tax, corporate tax, land revenue tax etc. are the examples of direct tax.
Indirect Tax; An indirect tax is the one, which is imposed to one person or entity but paid partly or fully by others. It is transferable to others. The tax is collected from customers by including it in the price of the goods or services they have purchased. The producers collect such a tax from wholesalers the wholesalers from retailers and the retailers from the final consumers. Excise duty, custom duty, VAT etc. are some of the examples of indirect tax.
Value Added Tax (VAT);Value added tax is the tax levied on value added on the price of the product at each stage of production, and or distribution activities. Value added is the difference between sales values and purchase value or the conversion cost plus profit. Conversion cost means the expenses on rent, depreciation, maintenance, insurance, salary etc. It is imposed on the goods at import, production and selling stages.
Difference between the Different Systems of Taxation
Difference between direct and indirect Tax
| Direct Tax | Indirect Tax |
|
|
|
SYSTEM OF TAXATION
Taxes on Income
The federal government, 43 states and many local municipalities levy income taxes on personal and business revenue and interest income. In most cases, income tax brackets are progressive, meaning that the greater the income, the higher the rate of taxation. Federal rates for the 2013 tax year range from 10 to 39.6 percent. State and city rates are generally much lower. In addition, many systems allow individuals to trim their tax bill with various credits, deductions and allowances. Businesses pay taxes on their net income, that amount can be taken as an above-the-line business deduction on a person‘s income tax return.
Capital gains taxes are those paid on any profits made from the sale of an asset and are usually applied to stock and bond transactions. The capital gains tax rate has recently been raised from 15 to 20 percent. Profits made from the sale of real estate are also subject to a capital gains tax. Single homeowners may exclude up to TSH 250,000 of capital gain on the sale of a home, as long as the home was a principal residence for at least two of the five years before the sale; married couples filing jointly can exclude up to TSH500,000.
Estate taxes are imposed on the transfer of property upon the death of the owner. They were created to prevent the perpetuation of tax-free wealth within the country‘s most affluent families. Since the tax exempts the first $5.43 million of an estate‘s worth, estate taxes only affects about 1 percent of the citizenry. The maximum top estate tax rate is 40 percent. Many states also impose their own estate tax, sometimes known as an inheritance tax. Opponents of these types of taxes believe that they are an unfair confiscation of wealth passed on to an heir and call them ―death taxes. A tax related to the estate tax, and assessed in a similar manner, is the gift tax, levied on a transfer of wealth during a person‘s lifetime. The first $14,000 of a gift is excluded from the tax.
Taxes on Property
Property tax, sometimes known as an ad valorem tax, is imposed on the value of real estate or other personal property. Property taxes are usually imposed by local governments and charged on a recurring basis. For example, homeowners will generally pay their real estate taxes either once a year or as a monthly fee as part of their mortgage payments.
Real estate taxes are often subject to fluctuation based upon a jurisdiction‘s assessment of the worth of a property based on its condition, location and market value, and/or changes to the amounts apportioned to various recipients of the tax. For example, if residents of a community have voted to increase the millage rate (the amount per $1,000 that is used to calculate taxes) for a school system, homeowners could see an increase in the tax levied on their properties. Conversely, if property values have fallen due to adverse economic circumstances, home taxes may decrease.
Other items that may be subject to a property tax are automobiles, boats, recreational vehicles and airplanes. Some states also tax other types of business property such as factories, wharves, etc.
Taxes on Goods and Services
The sales tax is most often used as a method for states and local governments to raise revenue. Purchases made at the retail level are assessed a percentage of the sales price of a particular item. Rates vary between jurisdictions and the type of item bought. For example, a pair of shoes may be taxed at one rate, restaurant food at another, while some items, like staple commodities bought at a grocery store, may not be taxed at all. Also, the same shoes may be taxed at a different rate if sold in a different state or county.
Some believe that sales taxes are the most equitable form of taxation, since they are essentially voluntary and they extract more money from those who consume more. Others believe that they are the most regressive form of taxation, since poorer people wind up paying a larger portion of their income in sales taxes than wealthier individuals do.
Excise taxes are based on the quantity of an item and not on its value. For example, the federal government imposes an excise tax of 18.4 cents on every gallon of gas purchased, regardless of the price charged by the seller. States often add an additional excise tax on each gallon of fuel.
User fees are taxes that are assessed on a wide variety of services, including airline tickets, rental cars, toll roads, utilities, hotel rooms, licenses, financial transactions and many others. Depending upon where someone lives, a cell phone, for example, may have as many as six separate user taxes, running up the monthly bill by as much as 20 percent.
So-called sin taxes are imposed on items like cigarettes and alcohol. Luxury taxes are imposed on certain items, such as expensive cars or jewelry.
Types of Tax Structures
There are three general ways that a government can apply tax rates. Taxes can be levied on a regressive basis, a progressive basis or proportional basis. Lets take a closer look at each of these tax structures.
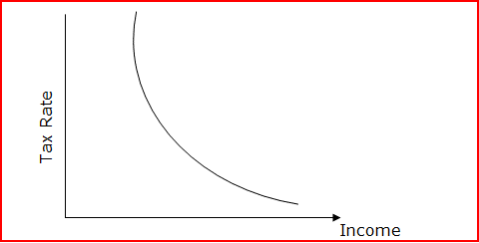
Regressive Tax Structure
A regressive tax structure results in low-income individuals paying a higher percentage of their income on taxes than high-income individuals. A regressive tax structure tends to shift the burden of taxation to the poor.
How a government defines the income subject to a particular tax rate or schedule is also important. For example, the United States government treats earned income differently than investment income and gives investment income a preferential tax rate. In other words, the government imposes a higher rate of tax on income earned through wages and salary than on income earned on investments. Thats why Warren Buffett pays a lower rate of income tax than the average American household - most of his income is from investment activities, not from his labor.
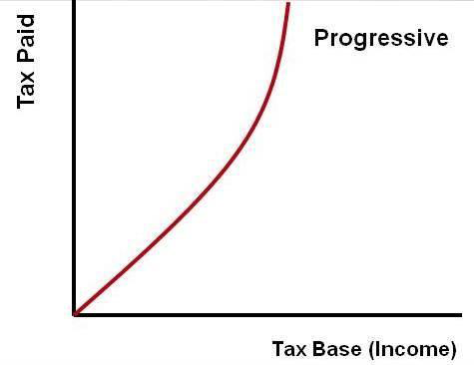
Progressive Tax Structure
A progressive tax structure is the opposite of a regressive tax structure. In a progressive tax system, taxpayers making more money pay higher tax rates than those making less money. The United States uses a progressive income tax structure because it taxes earned income at progressively higher rates as earned income increases. A progressive tax structure tends to shift the burden of taxation to the wealthy.
Proportional Tax Structure
- In a proportional tax structure, the tax rate does not depend upon the relative income level of the taxpayer. You can think of a proportional tax rate as a flat tax. A common example of a flat tax in the United States is a sales tax. The poorest member of society pays the same sales tax on a television as the richest. A proportional tax system theoretically should create an equal tax burden for all taxpayers, but some argue it doesnt.

The Advantages and Disadvantages of Direct and Indirect Tax
SOURCES OF GOVERNMENT REVENUE
Government revenue refer to the income generated by the government through various income sources inside and outside the particular government, As to any other person one will be eager to know where government earn money to finance its activity as well as expenditure of the government. The following are the source of revenue of various government including united republic of Tanzania (URT) :-
TAXATION
Like we have discussed in the previous tutorial that taxation is a compulsory levy imposed by the government whereby no direct benefit citizen will receive from the government,The levy is usually payable by citizen at different rate depending on the nature of economic activity conducted by an individual or firm the obtained amount is the revenue for the government and is used to meet various expenditure causing taxation to be the first source of government revenue.
FEES
These are payment made by users of public services on government cost sharing in health and education,That is to say the payment made by user of public services i.e health and education is not the actual cost that they were required to pay rather than contribution on cost already payable government.
FINES
Refer to the penalties imposed by government against law breaches,i.e any person or firm which had been proved guilt by law must be exposed to specific fine as the compensation for the destruction made by a person or firm and the collected amount being the revenue for the government
GRANTS
Refer to non-payable money provided by the government to another government with the aim of helping such government either to improve or to start a project which are of great importance.to the society of such government.
FOREIGN INVESTMENT
Sometime government may decide to invest beyond its boundary provided there is a proof for sustainable and profitable cash flow,the obtained amount after operation being the revenue for particular government.
Advantages Of Direct Tax
- Direct tax is equitable as it is imposed on person as per the property or income.
- Time, procedure and amount of tax paid to be paid is known with certainty.
- Direct tax is elastic. The government can change tax rate with the change in the level of property or income.
- Direct tax enhances the consciousness of the citizens. Taxpayers feel burden of tax and so they can insist the government to spend their contributions for the welfare of the community.
Disadvantages Of Direct Tax
Direct tax gives mental pinch to the taxpayers as they have to curtail their income to pay to the government.
- Taxpayers feel inconvenience as the government impose tax progressively.
- Tendency to evade tax may increase to avoid tax burden.
- It is expensive for the government to collect tax individually
2. Indirect Tax
FINES,
Refer to the penalties imposed by government against law breaches,i.e any person or firm which had been proved guilt by law must be exposed to specific fine as the compensation for the destruction made by a person or firm and the collected amount being the revenue for the government
GRANTS,
Refer to non-payable money provided by the government to another government with the aim of helping such government either to improve or to start a project which are of great importance.to the society of such government.
FOREIGN INVESTMENT
Sometime government may decide to invest beyond its boundary provided there is a proof for sustainable and profitable cash flow,the obtained amount after operation being the revenue for particular government.
Advantages Of Direct Tax
- Direct tax is equitable as it is imposed on person as per the property or income.
- Time, procedure and amount of tax paid to be paid is known with certainty.
- Direct tax is elastic. The government can change tax rate with the change in the level of property or income.
- Direct tax enhances the consciousness of the citizens. Taxpayers feel burden of tax and so they can insist the government to spend their contributions for the welfare of the community.
Disadvantages Of Direct Tax
- Direct tax gives mental pinch to the taxpayers as they have to curtail their income to pay to the government.
- Taxpayers feel inconvenience as the government impose tax progressively.
- Tendency to evade tax may increase to avoid tax burden.
- It is expensive for the government to collect tax individually
2. Indirect Tax
An indirect tax is a tax imposed on one person but partly or wholly paid by another. In indirect tax, the person paying and bearing tax is different. It is the tax on consumption or expenditures. Examples of indirect taxes are:
- VAT
- Entertainment Tax
- Excise Duty
- Sales Tax
- Hotel Tax
- Import And Export Duty etc.
Advantages Of Indirect Tax
- Indirect tax is convenient as the taxpayer does not have to pay a lump sum amount for tax.
- There is mass participation. Each and every person getting goods or services has to pay tax.
- There is a less chance of tax evasion as the taxpayers pay the tax collected from consumers.
- The government can check on the consumption of harmful goods by imposing higher taxes.
Disadvantages Of Indirect Tax
- Indirect tax is uncertain. As demand fluctuates, tax will also fluctuate.
- It is regretful as the tax burden to the rich and poor is same.
- Indirect tax has bad effect on consumption, production and employment. Higher taxes will reduce all of the above.
www.learninghubtz.co.tz
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania






