CHAPTER 01 : The role of ICT in daily life
| Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about the role of ICT in society transformation. Also, you will learn about the role of ICT in business, agriculture, entertainment, medicine, engineering, data management, employment, cultural interaction and education. The competencies developed in this chapter will enable you to use ICT in daily life activities. |
Think
1. Kind of information you can get using ICT at your school.
2. Advantages of using mobile phones.
ICT and society transformation
The use of modern ICT facilities contributes significantly to socio-economic development, innovation and cultural development globally and nationally. Modern ICT facilities include mobile phones, radio, television, computer, Internet infrastructure as well as services and applications such as social networks and videoconferencing. The use of these facilities improves communication and facilitates economic development on various sectors. For example, nowadays people can do business online, individuals and institutes can conduct online meetings and classes through collaboration tools such as Zoom. In this regards ICT can be used to improve performance in sectors like business, agriculture, entertainment, medicine, engineering, data management, employment, cultural interaction and education.
ICT and business
ICT is widely used in different types and sizes of businesses. For example, many businesses own websites on which they upload information of goods and services they provide. A website can be used to advertise goods and services offered, order these goods and services, pay bills by using credit or debit cards and track the bought goods and services. Also, supermarkets use Point of Sale (POS) terminal machine, and this machine is programmed to read a barcode attached to the item to be sold and relate with the price and hence calculates the total price. The POS terminal is connected to central computer that contains information about stock and price of each item found in the supermarket. Therefore, POS terminal helps not only to calculate the total amount of money the customer is supposed to pay after buying goods, but also it controls the stocks, does inventory, calculates profit gain and prepares financial statements.
In some supermarkets, the terminals also have another machine connected to banks through Internet where you can use your credit or debit card to pay the bill. This reduces the risk of someone carrying a lot of cash for shopping. Such payments, in some cases, are done through mobile money transaction services offered by various cellular phone network providers. In this way, ICT makes the business more efficient, effective and prompt response to customers’ needs. Some other ICT services for business include electronic banking (e-banking), electronic ticketing (e-ticketing) and electronic marketing (e-marketing).
Electronic banking
Electronic banking (e-banking) is a system of banking through which financial transactions are done by an exchange of electronic signals in place of transactions that were formerly done through cash and cherub. Before advancement in technology, people visited banks physically to make their transactions but nowadays technology has advanced and people use their devices anywhere to access bank services such as information about account balance, bank statement, deposits, withdraws and loans. This is achieved via Internet or mobile banking services. Internet banking allows customers to perform financial transactions electronically, mostly using desktop computers, laptops, tablets or smart phones connected to the Internet. An example of Internet banking in the country is the use of banks’ credit or debit card to purchase products or services online. Mobile banking is a service that allows customers to perform banking transactions using a cellular device. An example of mobile banking in the country is when a user who via a mobile phone uses banks’ mobile banking services to pay: utility bills such as water and electricity, Internet services and business licences
ICT and business
ICT is widely used in different types and sizes of businesses. For example, many businesses own websites on which they upload information of goods and services they provide. A website can be used to advertise goods and services offered, order these goods and services, pay bills by using credit or debit cards and track the bought goods and services. Also, supermarkets use Point of Sale (POS) terminal machine, and this machine is programmed to read a barcode attached to the item to be sold and relate with the price and hence calculates the total price. The POS terminal is connected to central computer that contains information about stock and price of each item found in the supermarket. Therefore, POS terminal helps not only to calculate the total amount of money the customer is supposed to pay after buying goods, but also it controls the stocks, does inventory, calculates profit gain and prepares financial statements.
In some supermarkets, the terminals also have another machine connected to banks through Internet where you can use your credit or debit card to pay the bill. This reduces the risk of someone carrying a lot of cash for shopping. Such payments, in some cases, are done through mobile money transaction services offered by various cellular phone network providers. In this way, ICT makes the business more efficient, effective and prompt response to customers’ needs. Some other ICT services for business include electronic banking (e-banking), electronic ticketing(e-ticketing) and electronic marketing (e-marketing).
Electronic banking
Electronic banking (e-banking) is a system of banking through which financial transactions are done by an exchange of electronic signals in place of transactions that were formerly done through cash and cheque. Before advancement in technology, people visited banks physically to make their transactions but nowadays technology has advanced and people use their devices anywhere to access bank services such as information about account balance, bank statement, deposits, withdraws and loans. This is achieved via Internet or mobile banking services. Internet banking allows customers to perform financial transactions electronically, mostly using desktop computers, laptops, tablets or smart phones connected to the Internet. An example of Internet banking in the country is the use of banks’ credit or debit card to purchase products or services online. Mobile banking is a service that allows customers to perform banking transactions using a cellular device. An example of mobile banking in the country is when a user who via a mobile phone uses banks’ mobile banking services to pay: utility bills such as water and electricity, Internet services and business licenses.
Moreover, other common mobile banking services locally available in the country are mobile money transaction services from cellular phone network providers. Generally, these mobile money transaction services are used to transfer funds from one person to another. These funds can be transferred from mobile to bank account and vice versa for paying goods and services. Examples of such services include payments of annual land fees, and a paying small-scale traders.
Electronic ticketing
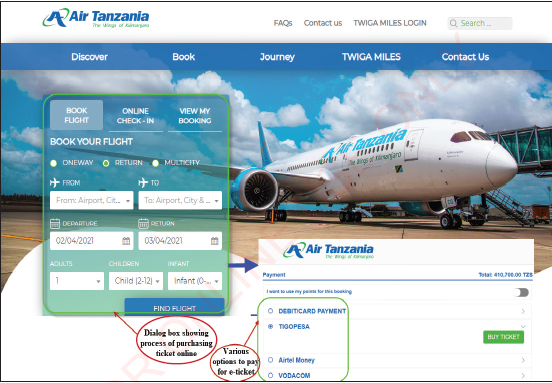
Electronic ticket (e-ticket) is a digital ticket equivalent to a paper ticket. Ticket reservations are increasingly done electronically for paying services such as booking for transport (air, land and marine) and social events (sports and games).Customers use companies’ websites to book and pay for the ticket using e-banking. Examples of e-ticket services in the country are commonly used by Air Tanzania, Azam marine service and football matches. Customers can also pay for their tickets via mobile money services such as M-Pesa and T-Pesa. Figure 1.1(a) shows an example of a process to purchase airline e-ticket via Air Tanzania website.
|
Air Tanzania e-ticketing system with payment options |
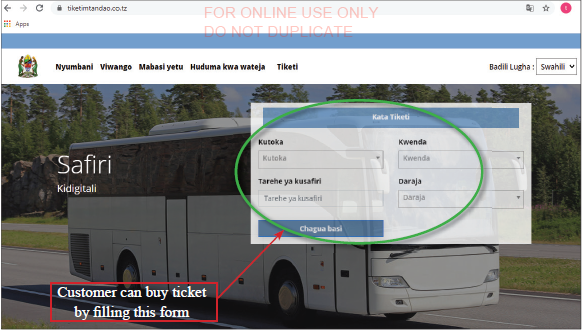
In January 2021, Tanzania through Land Transport Regulatory Authority (LATRA) instructed all public transport bus owners to use e-ticketing system. For bus ticketing system which were proposed by LATRA, see
Figure 1.1(b) that show an e-ticketing system for upcountry buses, where customers can fill the form online for their travel to different locations.
|
LATRA upcountry buses e-ticketing system |
Electronic marketing
Electronic marketing (e-marketing) helps business firms to make use of ICT facilities to market their goods and services. The tools that facilitate e-marketing are such as TV, mobile phones, e-posters, social media, websites, blogs and radio. Every time upon listening to broadcasting media, you will hear business advertisement. This also applies when you visit websites and social media networks.
| Activity 1.1: Searching for an e-marketing platform in Tanzania Use the Internet to search for the electronic marketing platforms in Tanzania that can help business people to market their products |
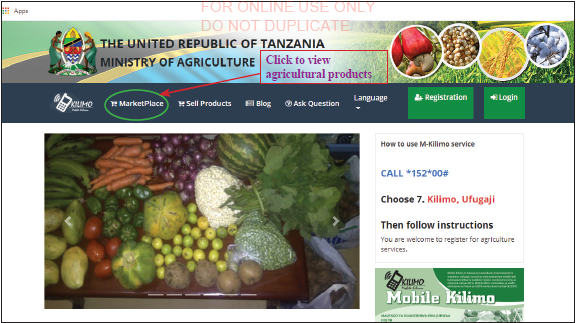
A good example of ICT in doing e-marketing is seen in agriculture when small scale farmers look for markets for their products. Using electronic tools enable farmers to market their products and their promotions reach a wide area within a short time. Figure 1.2(a) shows an example of an e-marketing platform which can help farmers to promote their products.
|
Figure 1.2(a): Government owned agricultural e-marketing platform Source:www.exts.kilimo.go.tz (2021) |
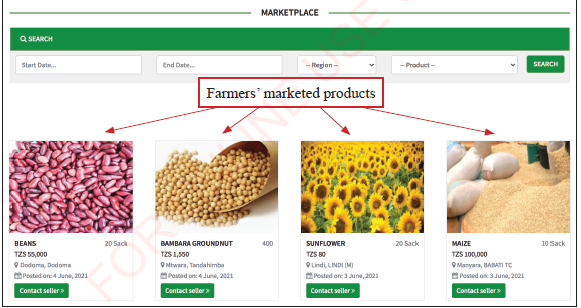
When farmers click the tab written ‘Sell Products’ they will fill information of the products to be sold in a web based form and save it. The information will be linked to a page under the tab ‘Marketplace’ which when clicked, various marketed products will be seen as shown in Figure 1.2(b).
|
Figure 1.2(b): Agricultural products e-marketing place |
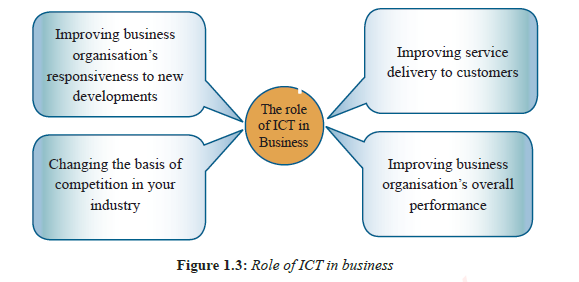
Generally, application of ICT in business can play four major roles, such as improving service delivery to customers, improving business organization's responsiveness to new developments, changing the basis of competition in your industry and improving business organization's overall performance, as shown in
Figure 1.3.
|
|
Improving service delivery to customers
ICT offers tools that help organizations to deliver services efficiently. This is done through integrating the ICT in all forms of service delivery. For example, the use of e-mail or mobile phone to inform customers on the progress of their orders saves time and resources that might have been used for the customers making follow-up. Also, the introduction of e-commerce has been increasingly facilitated by advancement of ICT whereby customers can do online shopping by purchasing and tracking goods or services.
Improving business organization's responsiveness to new developments
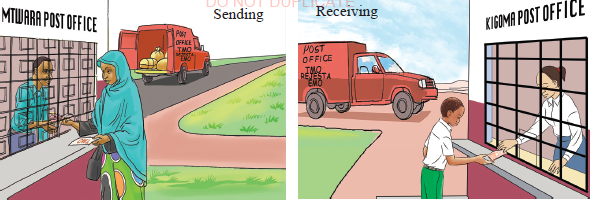
Business organization's responsiveness refers to how organizations react quickly to the changes that occur in a business-related industry to maintain the potential market. The responsiveness includes the efficiency and effectiveness organizations have in the market. ICT can help a business organization to connect with other branches, customers, distributors or business partners to extend services outside the organization. Such use of ICT improves and maintains the customer service in all areas where the organization operates. Figure 1.4(a) illustrates traditional money transaction services such as Telegraph Money Order (TMO) and Express Money Order (EMO) used to send and receive money via public transportation
|
Figure 1.4(a): Traditional money transaction |
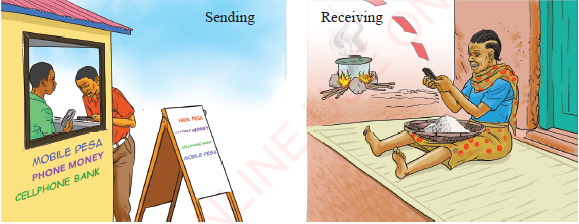
These traditional money transaction services are not very much efficient nowadays. They are addressed by modern money transaction services that are more efficient, secure and can be done in areas with mobile network access even if the areas are not easily reachable by road, as shown in Figure 1.4(b). Modern money transaction is done through cellular phones whereby customers receive money instantly and they are able to transact online using mobile money services.
|
Figure 1.4(b): Modern money transaction |
Changing the basis of competition in your industry
ICT can make a business organization more competitive than others by improving its services and becoming a preferred service provider or quality goods producer. example, an organization can increase the quality of its services or goods with the use of technology. This is possible by increasing the level of automation, thus reducing hired staff and lowering the cost of production and service provision, which in return reduce the price for goods and services. The work or service, which was done by many staff, may be accomplished through technology with improved performance and reduced errors. Also, the products and services can be marketed using ICT to gain more popularity and reach a wider market.
Improving organization's overall performance
The major challenge of a business is to provide quality goods and services. The business that can access new, appropriate and quality technology is usually in a position to attract customers and provide its goods and services efficiently. The introduction of ICT brings changes in business firms that help to restructure
operations and run them efficiently. This includes better use of human, material and financial resources such as having human resource and financial management systems and automating core business processes such as sales and customer handling.
| Exercise 1.1 Answer the following questions: 1. What are other functions of Point of Sale (POS) terminal apart from being used to calculate the total amount of money the customers are supposed to pay after buying goods? 2. Discuss how m-banking can be accessed and used by individuals. 3. With examples, mention and explain four roles of ICT in business. 4. Is e-banking different from m-banking? If yes, how, if no, why? 5. Discuss with your fellow student and report on any other advantage of application of ICT in business within your community and country at large. |
ICT and agriculture
When farmers have to grow crops, raise livestock, or fish, information plays an important role. ICT presents tremendous opportunity for farmers to improve productivity, enhance food security and nutrition, access markets and find employment opportunities in the sector. It also helps in empowering rural people by providing them with better access to natural resources, improved agricultural technologies and effective production strategies. Farmers can now get advice on how to do advanced and productive agriculture using mobile phone technology without having to leave their farms.
Some agriculture specialists sell their consultation services through mobile phone by using Short Message Service (SMS) which assist farmers to do better in agriculture.
Figure 1.5 illustrates some uses of ICT in agriculture by using SMS system to assist farmers in digging and using manures to plant as well as using drones in irrigation
|
Figure 1.5: e-agriculture to improve production. Source: ictworks.org (2021 |
ICT and entertainment
ICT has impacted entertainment industry by enhancing and providing different ways in which you would casually spend your time. With the use of these ICTs, the ways in which you entertain yourself have dramatically increased. For example, by using ICTs, recording and editing music, video and movies have become easier. It is accompanied by easy access through the Internet. This has the advantage that anyone can get access to almost anything from the Internet such as online videos and music from YouTube, see an example in Figure 1.6. You can pay for a music track in an online music store and download it to your computer, laptop, Smartphone or personal mp3 player such as an iPod. Internet is used as a channel for the distribution of music through music download websites. You can also use widespread social networks such as WhatsApp and Face book for entertainment purposes like to communicate and socialize with family members and friends.
|
Figure 1.6: ICT use for entertainment through YouTube Source: YouTube (2021) |
ICT and medicine
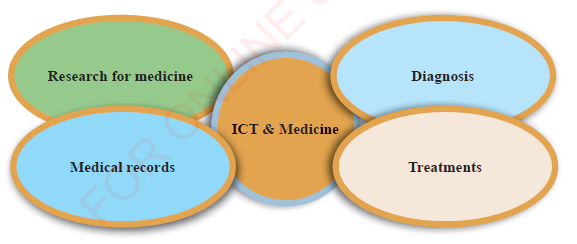
Nowadays, most hospitals are using ICT to improve health services in the process of diagnosing diseases, providing treatment to patients and maintaining proper medical records. Also, medical researchers use ICT as a tool for drugs discovery and finding the causes of diseases. Additionally, via ICT patients can remotely receive services when a doctor and patients are not physically in contact. This situation is called telemedicine. Figure 1.7 summaries various roles of ICT in medicine.
|
Figure 1.7: Various applications of ICT in medicine ICS |
Diagnosis
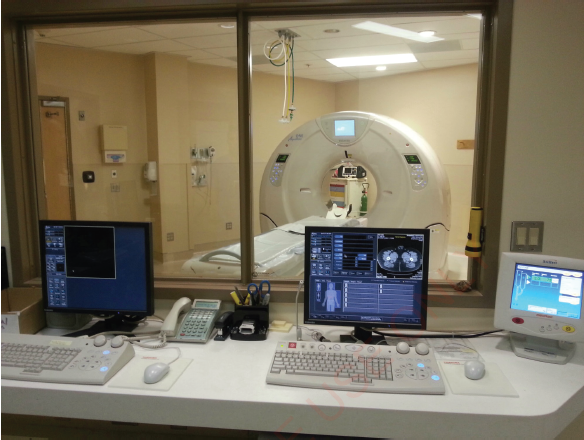
In hospitals, medical experts use ICT-based tools to improve health. Tools like Computerized Tomography (CT) scanners and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are famously used in diagnosing diseases by scanning the whole body of a patient focusing on specific part of interest. Figure 1.8 illustrates CT Scanner
machine which uses ICT application.
|
Figure 1.8: Computer systems in medical diagnosis Source: www.raybar.com (2021) |
Treatments
In hospitals, patients are attended with the assistance of computers. For example, the sensors which are connected to a computer are attached to a patient for recording heart rates. There are other health conditions like blood pressure, brain activity and breathing that are studied by sensors, and the computer sound an alarm when one of the parameters is below the standard level. When the computer is logged in, the data is analyzed to see the changes of a patient’s condition and take action.
Patient medical records
Many hospitals use computerized databases. Databases are used to store medical records of different patients and organize them when a patient has to be transferred to different points of medical services in the hospital. Also, it is used to record the history of patients when they have appointments with doctors. Furthermore, with the hospital’s database, it is possible to make an online booking of medical
services such as ambulatory services.
Research
Health institutions use ICT in research and clinical practices especially in collecting data electronically and storing health knowledge base for medical purposes like clinical decision support systems, which use computers. Also, computers are used to process, record and share health-researched information from one place to another.
| Exercise 1.2 Answer the following questions. 1. What are the applications of ICT in medicine? 2. How is ICT used in medicine? |
ICT and engineering
ICT takes a great role in data capturing, processing, storage and dissemination in engineering from conceptualizing, designing to maintaining. Its application contributes to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of engineering industry. For example, technology enables the industry to save time in operations when producing new products. Also, the quality of products is improved with the application of
advanced technology in the industry.
Think of how engineers and architects use Computer-Aided Design and Computer -Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) applications in their works. CAM refers to the use of computers in all operations in manufacturing plants such as planning, management and storage of information. On the other hand, CAD is the use of computers to aid in the creation, modification, analysis and optimization of a design.
ICT increases productivity and quality of a design through creation of two or three dimensional graphical representation of physical objects as shown in Figure 1.9.
|
Figure 1.9: Use of CAD in mechanical manufacturing engineering design Source: Creative CAD solutions (2021) |
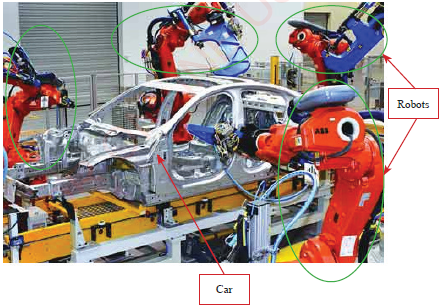
Another example of ICT use in engineering is in motor vehicle manufacturing, whereby scientists have developed software that can help to run a robot. Robot is a complex movement control system that can be used to do several activities. This system is commonly used in heavy industry whereby some activities are too risky to be handled by human beings, for example, in chemical industries, motor vehicle manufacturing and other risky engineering activities. It is also used in areas that need high precision and qualities such as assembling parts of a car during manufacturing. Figures 1.10 shows robotic operations in motor vehicle
manufacturing.
|
Figure 1.10: Robotic operation in motor vehicle manufacturing Source: https://medium.com (2021) |
| Activity 1.2: Searching for ICT use in developing various engineering fields Search information about contribution of ICT in development of any two among the following engineering fields: biomedical, electrical, chemical, mechanical, aerospace, civil, mining and petroleum engineering. Show in detail: (a) The contribution of advancement of ICT in each of the selected engineering fields. (b) The difference in the use of ICT between the two selected engineering fields. |
ICT and data management
Data management refers to the process of acquiring, processing and storing data for easy access and use by beneficiaries. There are various software designed to manage data from individuals to large organization's businesses. This range from general application software such as Microsoft Excel (MS Excel), Statistical
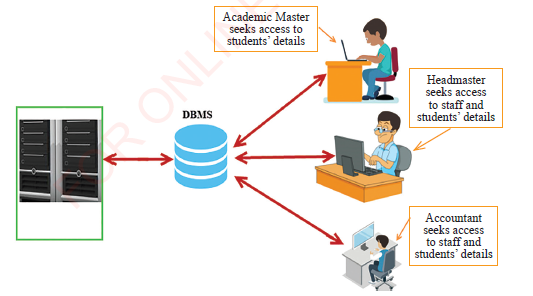
Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) to sophisticated Database Management Systems (DBMS)-based application software such as the Education Management Information System. Most of the organizations run information systems that are centrally organized. These organizations use database management systems that control the movements of the data in and out of the organizations. Data management help organizations to keep their data centrally controlled and hence ease to access, search, edit, analyze and use for decision making. This also applies to data integrity and security improvement as well as reducing data duplication. Figure 1.11 show database provides secured central access of information.
|
Figure 1.11: Administrators access fi les remotely from central database |
Furthermore, the advancement of ICT devices and applications of computing data has led to emergence of data analytics which is the process of analyzing raw data to find trends and answer questions such as what has happened, why it has happened, what will happen in future and what should be done. Its analysis including predictions that are made with the help of tools such as big data and high computing devices.
ICT and employment
ICT includes some of the fastest-growing jobs and careers in Tanzania and worldwide. The range of occupational pathways in ICT continues to be stretched as technologies penetrate more in various aspects in our society. Common areas of work for ICT include software engineering, web and mobile application development; instructional design and learning analytics; systems analysis and design; systems and database administration; general ICT governance and management; multimedia development; network design and administration; data analytics and ICT support.
Employment opportunities for ICT are still growing as the ICT industry did not suffer the effects of global fi nancial crisis as compared to many other industries. Also, ongoing investment in IT infrastructures and applications suggest strong employment growth in the future though with changing skills requirements. ICT skills transfer easily from one country to another, thus experienced ICT professionals can expect to find career opportunities almost anywhere in the world.
ICT careers include job titles such as ICT governance or management specialist, software developer, computer or information systems analyst, data communications analyst, database administrator, desktop or application support specialist, help desk technician and forensic specialist. Others are web and mobile application developer, network and system security specialist, network administrator, software engineer, data analytics specialist, telecom engineer, webmaster and wireless network technician. Figure 1.12 shows a telecom engineer at work.
|
Figure 1.12: Telecomunication expert working at network tower Source: TowerXchange (2021) |
ICT and cultural interaction
ICT has significantly changed the way humans are living. Socio-cultural view of globalization posits that different cultures across the world are continuously evolving to become more integrated and homogeneous. ICT creates awareness in this perspective and it is an important driver of cultural convergence pushing national cultures across the globe to converge towards common cultural values and transparency.
ICT studies track a broad range, and a wider perspective is taken not only by looking at the interaction between human beings and technology but also the interaction among computers or machines themselves. The society has to understand that technology is being made by people, and if it leads to unexpected negative results centrally to our cultural values, people have the right and responsibility to improve
or change the way it is used.
ICT and education
The emergency of ICT has impacted the education sector in many ways. ICT has impacted the processes of teaching, learning, administration and management of education. In general, ICT empowers learners and teachers, promotes changes and increases individual skills. It can help to transform teaching and learning processes from being highly teacher-dominated to learner-centered. This transformation canresult in increased learning gains among learners through developing creativity, life long learning and skills in informational reasoning, communication and ICT (word processing, spreadsheet, and educational software). These skills are necessary for individuals’ employability in the current and future job market. The roles of ICT in education can be summarized in the following key areas:
Facilitating electronic learning (e-learning) or online learning:
ICT in education helps to fi nd new strategies in teaching and learning. E-learning provides opportunities for students to access learning materials in the class when they are at school, at the same time it provides a chance for out of school-compound-students to learn. Figures 1.13(a) and (b) show illustration of online learning.
|
Figure 1.13(a): Students using computers to learn Source:www.theirworld.org |
|
Figure 1.13(b): A child learning through listening to the radio Source:UNICEF/UNI319836/Kanobana |
Promoting inclusive education: The use of ICT in education helps to remove barriers for students with special needs to access essential materials using special ICT tools for their educational needs. For example, the use of non-visual desktop access (NVDA), a free open-source portable screen reader for visually impaired people to use computer. Despite this, ICT opens up new issues related to the ‘digital divide’ and provides access to ICT tools and resources for those who are less fortunate.
ICT Enhances subject learning: The use of ICT in education can improve the competence in literacy and numeracy. In order for students to develop learning through ICT capability, it is helpful to provide them with hands-on activities which reflects on the content learning areas to be developed.
ICT encourages collaboration: ICT encourages cooperation where students or people can interact by sharing and discussing their work or activities. This leads to open ways for communication, thus leading to interpersonal skills.
ICT use motivates learning: Children like to play. Through the use of ICT, computer games related to learning encourage children to play and learn at school and home.
ICT improves engagement and knowledge retention: Integrating ICT in education promotes students to engage more in their learning activities. This is because technology provides a window for learning of the same contents in various ways such as use of simulations and illustrations that improve understanding of difficult concept to be learned.
Helps in school administration and management: ICT provides important contributions in improving the quality of education. Using ICT in administration and management is popular and essential in schools due to the fact that application of ICT helps in data storage, decision making and knowledge management. For example, students’ examinations results, registration and school financial management data are stored in computers by school administrators. This type of data can be used in many administrative and management instances for decisionmaking.
Negative impact of ICT on the society
In spite of the benefits provided by the application of ICT in the society, there are several negative impacts as follows:
Reduced human interaction:
People need some form of social interaction in their daily lives. If they do not get time to communicate, a gap is created and the rate of intimacy between people decreases. For example, in some cases, once parents are back from work, most of the time they are busy with mobile phones and computers. As a result, social interaction with their children is reduced.
Loss of job or reduced employment:
This occurs when manual work is replaced by automated machines and systems like computers, robots, networks, software, and Internet technologies.
Road accidents:
Improper use of ICT devices also contribute to road accidents. For example, the drivers’ distractive behavior including texting and interfacing with navigation and other communication systems while driving, as shown
in Figure 1.14. However, it is not only distraction by drivers that cause problems– texting pedestrians represent an equally big risk, putting themselves and other road users in danger.
|
Figure 1.14: Using ICT (mobile phone) while driving |
| Exercise 1.3 Answer the following questions 1. Explain the role of ICT in the following sectors: (a) Agriculture (b) Medicine (c) Entertainment (d) Engineering (e) Education 2. Discuss how mobile phones can help customers to access bank account. 3. What will happen if ICT is not used in medicine? 4. What is the role of ICT in data management? 5. What is the importance of e-banking in social-economic development of a nation? 6. How have traditional business been transformed by the use of ICT in e-business? |
www.learninghubtz.co.tz
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania