CHAPTER 1
1.0NUTRITION
1.1 KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTS.
- Nutrients- these are molecules which are required for growth, maintenance and repair
- Macro-nutrients- are nutrients that are required in very large quantities
- Micro-nutrients- these are nutrients which are needed in very small amounts
- Auto-trophic nutrition- this is the process by which organisms manufacture their own food from simple inorganic substances like carbon and hydrogen.
- Heterotrophic nutrition- this is a process by which living organisms get nutrients by eating other organisms.
- Holozoic nutrition- this is taking complex food substances, digesting them, assimilating them in their bodies.
- Saprophytism- is a relationship in which organisms obtain nutrients from dead decaying matter.
- Symbiosis- this is a feeding relationship between two organism
- Commensalism- this is a feeding relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected.
- Mutualism- this is type of symbiosis in which both organisms benefits from the relationship
- Parasitism-is a feeding relationship in which one organism benefits while the other one is harmed.
- Balanced diet- this is a food substance that contains all nutrients in correct proportions
- Obesity- is a nutritional disorder in which an individual has excess weight.
- Anorexia nervosa- this is a disease in which an adolescent girl starves oneself by refusing to take enough food.
- Monosaccharide’s- are simple sugars made up of simple sugars and sweet tasting.
- Polysaccharides- are formed by condensation involving combination of two monosaccharides
- Condensation- this is the process by which two or more monosaccharides combines to form disaccharides.
- Polysaccharides- are formed by condensation involving several monosaccharides
- Essential amino acids-these are amino acids which need to be provided in diet because the body cannot synthesize.
- Non-essentially amino-acids- these are amino-acids which the body is capable of synthesizing and need not be provided in diet.
1.2 INTRODUCTION
- Nutrition is the process by which living things obtain nutrients assimilate and use them in their bodies.
- Organism can obtain nutrients by two ways, making their own food or obtaining from other organisms.
- Therefore we have two types of nutrition, heterotrophic and autotrophic nutrition.
- Organisms need nutrients in order to grow and survive. These nutrients are obtained from food.
- Food substance includes carbohydrates, Lipids, proteins, vitamins and mineral salts.
- The building blocks of our bodies are called nutrients.
- Nutrients can be macronutrients which are required in large scale or micronutrients, which the body does not require in large amount.
- Nutrition is therefore one of the most important characteristics of living things.
Significance of nutrition
- Organisms can obtain nutrients for growth.
- Nutrients are required to replace, repair damaged tissues.
- New impulse transmission is possible through the process of nutrition where energy is obtained.
- Homeostasis and regulation is made possible because of nutrition which provides required energy.
- Some organism such as glowing worms and fireflies need nutrients to produce light.
1.3 Forms of nutrition
Basically we have two main forms of nutrition
- Autotrophic this is main form of nutrition in which organisms synthesizes food from simple organic compounds.
- This is carried out by plants and some bacteria. Plants use photosynthesis, while bacteria use chemosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants make food using carbon dioxide, water and sunlight.
- Photosynthesis mostly occurs in leaves.
- Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition where by living organism takes in already manufactured food substances such as carbohydrate, proteins and fats.
- Organism which obtain food this way are called heterotrophy.
- Heterotrophy mainly consists of animals.
Forms of heterotrophicnutrition
- Holozoic nutrition this involves taking of complex food substances, digesting them and assimilating nutrients. This form of nutrition is divided into three groups.
- Carnivorous feeding: is mode of feeding whereby organisms feed on meat only. Organisms which feed on meet are calledcarnivores
- Herbivorous mode of feeding: is a mode of feeding where organisms feed on plants only. These organisms are called herbivores
- Omnivorous mode of feeding: is a made of feeding where organisms feed on both plant and animals.
- Saprophytism is a feeding relationship in which an organism absorbs nutrients from dead organic matter. Most fungi are saprophytes.
- Symbiosis is a close feeding relation between two species.
Forms of symbiosis
- Mutualism: this is a feeding relationships relationship where by both organisms’ benefits from the relationships. Examples are bacteria on part of ruminants and bacteria on root nodules of leguminous plants.
- Commensalism is a type of symbiosis where one organism benefits while the other remain unaffected by relationship. Examples, small plants growing on large tree.
- Parasitism: one species benefits from the relationship, while the other on is harmed examples ticks on cows.
1.4 Human nutrition
Types and functions of food substances that help the body in growth. These are outlined below.
Proteins
Sources
The food substance includes beef. Chicken, fish, termiles, milk, eggs, lenticels, mushrooms e.t.c.
Composition
Protein is made up of smaller molecules called amino acid which are linked together by peptide bond. Many amino acid join together to form protein
Classes of protein
Protein are two types, first class protein, which are obtained from animals and second class protein, which is obtained from plants. First class protein contain all essential amino acids, second class protein lacks one or more amino acids, which are essentials. Amino acids can be essential or non essential. Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the body and has to be supplied on diet.
Non essential amino acids can be synthesized by the body and need not be supplied in diet.
Functions of proteins
- Proteins help in growth and repair of the body. Most cells are made of protein.
- Defense and protection of the body
- Antigens and antibodies are made of made of protein. Antibodies help the body destroy diseases causing micro organisms.
- Sources of energy in times of starvation, proteins can be broken down to release energy.
- Structural components
- Many body organisms and tissues are made of protein. These structures include muscles fibre, hooves, nail hair, feather among other.
- Structural functions
Many components in our body are made of protein. These includes anzymes, haemoglobin, hormones, and fibrinogen.
Properties of protein
- Dissolve in water forming colloid a suspension. In this type of solution, sold particles remain separated in solution.
- Protein are affected by high temperature when heated above a certain temperature, they become denatured.
- Protein are amphoteric in nature. They can react with both acids and bases.
| Protein | Functions | Comments |
| Structural proteins
| Makes hair Forms tendons and ligaments Forms muscles tissue | Found in hair Found in tendons and ligaments Founds in muscles |
| Functional proteins
| Speed up chemical reaction Transport of oxygen Regulates life process Help in blood clotting | Control reaction like respiration Found in red blood cells Secreted by endocrine glands Found in body and body fluid |
| Storage proteins
| Source of protein for young animals. Source of protein for embryo | Found in milk Found in white eggs |
| Food protein
| Cannot be synthesized by the body. Can be synthesized by the body | They form first class protein since have all amino acids Form second class protein since they lack some amino acids |
Carbohydrates
Sources
Maize, wheat, cassava, rice and chapatti, sugar, sucrose, bread.
Composition
Made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in ratio of 1: 2: 1. They are called energy giving food.
Groups of carbohydrates
Monosaccharides.
Are simple sugars, with chemical formula CnH2nOn
Example include glucose, fructose and galactose.
Properties of Monosaccharides
- Are sweet tasting
- Are soluble in water
- They are crystallized
- Are reducing sugar that is they can reduce copper II sulphate into copper I oxide
- Monosaccharide can be combined to form disaccharides by a process called condensation where water molecule is lost, glucose + glucose→ Maltose + Water
b) Disaccharides
Formed by linking two monosaccharide by the process of condensation. They can be broken into their constituent monosaccharide by a process known as hydrolysis.
Water is used in this process
Maltose + ![]() Glucose + Glucose
Glucose + Glucose
Examples includes sucrose, maltose and lactose
Sucrose ![]() glucose + fructose
glucose + fructose
Lactose ![]() glucose + galactose
glucose + galactose
Propertiesofdisaccharides.
- Are soluble in water
- They are crystalline in nature
- Are non- reducing sugars.
c) Polysaccharides.
Formed when many monosaccharide’s combine together. They are then said to be complex in nature. Examples of polysaccharides include starch, cellulose and glycogen.
Properties
- Are not sweet tasting
- Are insoluble in water
- Are uncrystallined.
Examples of polysaccharides, sources and functions.
| Polysaccharides | Where found | Functions |
| Starch | Plant cells | Storage of carbohydrate. |
| Cellulose | Cell wall |
|
| Glycogen | Animal cell |
|
Lipids
These are composed of fats and oils. They contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. They are insoluble in water.
Fats are sold at room temperature. Oils are liquids at room temperature. Fats acids can be essential or non essential fats acids. The body is not able to produce essential fats acids.
Sources
- Oily fish
- Nuts
- Oil seeds
- Avocado
- Olives
Functions of Lipids
- They are sources of energy. They produce more energy than carbohydrates. They however need a lot of oxygen to be broken down.
- They are important components of cell membrane.
- They are source of metabolic water. When broken down, fats are able to release a lot of water.
- Lipids protect sensitive organs of the body such are kidney and heart where they act as shock absorber.
- They provide insulation to the body against cold weather.
- They are sources of vitamin A, D, E, and K which are soluble in fats.
Vitamins
Are complex organic micro nutrients that are essential for growth and survival. Vitamins can be, fat- soluble can be stored in body and need not be consumed daily. Examples are vitamin A, D, K and E.
Water soluble: vitamins are not stored in the body. They are thus consumed daily. Vitamins B and C are water soluble.
The table below shows types of Vitamins, use sources and deficiency disease.
| Vitamin | Use | Source | Deficiency disorder |
| A(Retinol) | Night vision Protects skin | Vegetable, kale, spinach. Milk, liver, Eggs, carrots | Night blindness Poor vision |
| B2 | Cells metabolism and energy release. | Liver, meat, unpolished grains. | Cracks and sores in mouth, visual problems. |
| B1(Thiamine) | Proper growth Cell respiration | Egg York, kidney Beans unpolished cereals | Beri- beri |
| B3(Niacin) | Need for enzyme action | Nuts, fish, meat, yeast extracts, unpolished rice | Pellagra. |
| B6 (Pyridoxine) | Need in protein metabolism | Meat, vegetables yeast, extracts, whole grains | Nerve irritability sore in mouth anemia. |
| B12(Cynocobalamin) | Form red blood cells build genetic material | Fish, meat, egg, milk liver. | Anemia, nerve damage. |
| Vit C (ascorbic Acid) | Antioxidant. Improves absorption of energy, college synthesis | Citrus fruits refresh green, vegetables liver. | Muscles weakness easily bruising, bleeding gun infections. |
| Vit D Calciferol | Egg yolk, milk, oil fish and liver | Build and maintain teeth and bone. | Rickets in children. osteoporosis in adult. |
| Vit. E. Tocopheral | Antioxidant prevent cell damage and membranes damage | Corn or sunflower, butter, brown rice peanuts. | Nerve abnormalities infertility in rats. |
| Vit. K. | Needed for Normal blood clothing | Green vegetables and liver | Defective blood coagulation resulting in excessive bleeding. |
Table 1.1
1.5 MineralElements.
Plants obtain elements from soil through absorption. Human’s and Mammals obtained obtain elements from food they eat.
Minerals elements are need for body growth, repair and protection against diseases. They take part in various chemical reactions in the boy. The table below summaries sources and function of minerals.
| Element | Source | Function |
| Potassium (K) | Most foods | Muscular contraction Nerve transmission. |
| Calcium (Ca) | Milk and its products green vegetables | Strong bones and teeth, muscle contraction nerve impulse, clothing. |
| Phosphorus (P) | Milk, meat, fish, eggs nuts. | Bone and teeth building Muscles and nerve impulse. |
| Sodium (Na) | Table salt, green vegetable | Muscular contraction, tissue fluid balance, nerve transmission. |
| Sulphur (S) | Amino acid and methionine in animals protein. | Synthesis of proteins. |
| Chlorine (Cl) | Table salt, sea foods | Maintenance of tissue fluids blood and lymph. |
| Iodine I | Ground water, sea food, table salt. | Synthesis of thyroids hormone |
| Iron (Fe ) | Liver, green, vegetable yeast, eggs | Hemoglobin formation |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Green vegetables | Health bone and teeth, muscle contraction. |
| Nitrogen (N) | Protein food | ATP formation, protein synthesis healthy bones and teeth. |
Table 1.2
Mineral elements can be grouped into categories, Macronutrient – are nutrients required in large quantities. Examples include nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus potassium calcium, magnesium and carbon.
Micro nutrients: Are those required in small quantities e.g copper, zinc, manganese Boron. They are also referred to as trace elements.
Water
All chemical reaction in our body takes place on water medium. About 90% of the body cells are made of water.
Properties of water
- Can dissolve many substances.
- Has high heating capacity
- Has very high surface tension
Function of water
- Transportation of materials occur in water medium
- Water assists in cooling of the body.
- Being transparent, it allows light to pass supporting aquatic life.
- It is within water in which most of chemical reactions take places.
- Water is needed in the process of digestion of food. Correct level of water should be maintained because inadequate amount of water leads to thirst, dehydration and constipation. Loss of more 10% of water in body can result into death.
Roughage
This is obtained from indigestible part of plants. Roughages has no nutritional values, but helps in passage of food and feces through the gut.
Sources of roughage include whole grain cereals, fruits, beans, cabbage, spinach, cassava and baked potatoes.
1.6 Balance diet.
This is a meal that contains all types of food types including carbohydrate, proteins, lipids, water, mineral salts vitamins and roughage. The food should be taken in correct quantity and proportions. Avoid foods which lead to life style diseases such as red meat. Take enough fruits, vegetables and poultry products.

Figure 1.1 Balance diet.
1.7 Nutritional requirements for different group of people.
The amount type, quantity and quality of food taken will depended on several factors include body size, age, sex state of health and occupation.
The following groups of people need different nutrients,
- Manual workers
Are laborers who do hard manual work, for example in quarries, and construct sites. These people need a lot of energy giving foods such as ugali, cassava, and chapati.

Figure 1.2 Manual worker
- Expectant and lactating mothers.
Are mothers who are expecting to have a baby and those who are breast feeding. Their food should contain;
- High amount of protein- for growth and development of foetus, and milk production.
- Balance diet -they need food for themselves and the baby.
- Mineral salts such as Zinc and calcium for proper progression of labour and fetus bone development.
- Lactating mother need enough water for milk production
- They should avoid alcohol and cigarette smoking.

Figure 1.3 Pregnant woman
- Young children
- They need a balanced diet with high proportion protein.
- Vitamins – to prevent them from disease and infections.
- Mineral salts for proper growth of bones and teeth.
- Vitamins B12 for formation of red blood cells and vitamin to help children build their immunity.
- Energy giving food because they are active than adults.
- The elderly
-They are less active they need less food.
-They need with high level of vitamins to help fight infections.
-They also need protein to build and repair their bodies.
- Their food should also contain fiber in order to prevent constipation.
-Mineral salts such as zinc is needed for healthy immune system and increasing healing of wounds. Calcium helps to strengthen bones.
- They need easy to chew foods because their teeth have problems.

Figure 1.4 The elderly
- The sick
- Their food should have high proportion of vitamins and proteins to protect the body and repair it.
- They need exercise to ensure that symptoms are kept at bay.
- Take plenty of fruits and water.
- Sedentary worker
- Are people who stay in one place, for a long period of time while performing daily activities.
- Examples are secretaries, cleaners, receptionist doctors, and tailors.
- They are more prone to lifestyle diseases such as obesity.
- They need food which do not contain a lot of carbohydrate and lipids.
- Their food should contain vitamins, fruits and they should do exercises.

Figure 1.5 Sedentary worker.
1.8 Nutritional deficiencies and disorders in human beings
Are disorders which occur when the body is not getting enough nutrients, or is getting enough nutrients, or is getting nutrients in excess. The following are some of nutritional disorders.
1) Marasmus
Is a form of malnutrition common in children. It is caused by lack of adequate amount of food.
Signs of symptoms
- Loss of weight
- Slowed growth (stunted growth)
- Decreased activity and lack of energy
- Wrinkled skin
- Irritable and extreme hunger.
- Eating a lot food when available
- Weak muscles.
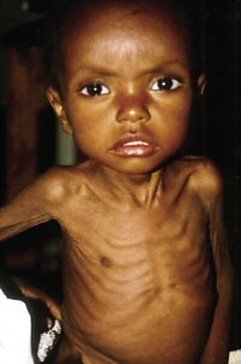
Figure 1.6 A Victim of marasmus
Treatment
Give the child adequate amount of food in correct proportions.
2) Kwashiorkor
Is a nutritional disorder caused by deficiency of proteins in diet. Affects children especially after stopping breast feeding
Symptoms.
- Protruding stomach
- Wasting of muscles
- Dry, flaky and rough skin
- Reddish brown hair which falls easily
- Child becomes anemic and weak.
- Stunted growth and lack of appetite
- Weakened immunity and diarrhea.
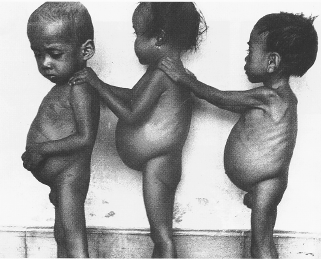
Figure 1.7 Victims of Kwashiokor
Treatment
Provide the child with a diet having adequate amount of proteins.
Rickets.
- Caused by lack of vitamin D which is associated with calcium and phosphrous intake.
- These minerals are required for health formation of bones.
- Lack of vitamin D causes weak bones which cannot support the rest of the body leading to bow-leggedness, commonly in children.
- This condition can also affect adults where already hardened bones soften due to withdraw of calcium.
- Women can also loose calcium to their foetus during pregnancy. Once calcium is withdrawn, the bones become susceptible to fracture a condition called Osteomalacia.
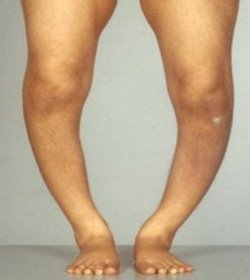
Figure 1.8 A child with rickets
Signs and Symptoms.
- Skeletal deformation such as bow-legs, knock knees and odd shaped skull
- Pain in bones
- Dental problems such as weak teeth or delayed formation
- Weak muscles
- Bones are easily fractured.
Prevention.
- Increase amount of vitamin D, phosphate and calcium in diet
- Ensure exposure to sufficient amounts of sunlight
Obesity
Results from imbalance between intake, storage and use of energy. It is common to people who takes a lot of carbohydrate and do not exercise.
1.9 SUMMARY
- Nutrition is a process by which an organism takes in food to substances and uses them to sustain life.
- Nutrition is important for growth, development, repair of damaged parts, immunity, warmth and reproduction.
- The human diet should have proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, fiber and water.
- Proteins are obtained from milk, meat, beans, peas, lentils, nuts, mushrooms and seafood. They are important for growth, repair, and formation of cell membranes, muscle function, production of human protein and as a source of energy.
- Lipids are obtained from various fats and oils. Lipids are essential sources of energy; provide cushioning of internal organs, insulation, storage of fat soluble vitamins, formation of cell membranes and control of the blood pressure and immune response.
- Sources of carbohydrates include cassava, maize, potatoes, bananas, rice and wheat. Carbohydrates are a major source of energy and also aid in the formation of cell membranes.
- Vitamins are either fat soluble (vitamins A, D, E and K) or water soluble (the B and C vitamins). They boost the immunity of the body against diseases.
- The human body requires minerals such as calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, iron, zinc, sodium, chlorine, iodine, fluorine, manganese and copper.
- Dietary fiber or roughage is indigestible but it helps in the passage of food in the digestive tract.
- Water is important in the formation of body fluids and cell cytoplasm, maintenance of the body’s shape, digestion, lubrication and cooling of the body.
- A balance diet constituents all necessary nutrients in the amounts.
- Nutritional requirements vary depending on age, sex and general body condition of a person. For example, expectant and lactating mothers need a diet that has adequate nutrients to maintain their bodies and help their babies and fetuses to grow and to develop.
- Malnutrition results from eating too little or eating the wrong foods.
Examples of nutritional disorders are:
Obesity: being excessively overweight.
Anorexia nervosa: self starvation in order to reduce weight.
Bulimia nervosa: eating a lot then forcefully removing the food from the body immediately. Examples of nutritional deficiency diseases are:
Marasmus: lack of adequate amounts of enough vitamins D, calcium and phosphorus.
- Food tests are used to determine the nutrients that are in a certain food substance.
- There are three types of carbohydrates: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
- Monosaccharides are reducing sugars. They dissolve in water to form sweet solutions.
Disaccharides are reducing sugars while others are non reducing sugars.
On the other hand, polysaccharides are formed by the condensation of several mono saccharides to form a long chain. They are all non reducing sugars. They do not dissolve in water.
- Proteins are made of long chains of amino acids. Amino acids contain both acidic carboxyl groups so they can react with both bases with both bases and acids. Proteins form colloids instead of true solutions they are also denatured by PH and strong heat.
To test for proteins, millions test or biuret test is used.
- Lipids are made up of glycerol and fatty acids. Lipids are insoluble in water but dissolve in organic solvents. The grease spot test, Sudan III test and emulsion test are used to test, for lipids.
1.10 END OF TOPIC QUESTIONS.
- (a) What is Nutrition?
(b) Mention two type of Nutrition?
1. …………………………………………..
2. …………………………………………..
( c ) List down six importance of Nutrition.
- …………………………………………
- ……………………………………………..
- …………………………………………….
- …………………………………………..
- ………………………………………….
- ………………………………………….
- (a) Define the following
- Saprophyte
- Commensalism
- Parasitism
- Mutualism
- Symbiosis
(b) List down fine (5) classes of food Nutrients.
i. …………………………………………….
ii………………………………………………
iii………………………………………………
iv………………………………………………
v……………………………………………..
- State one difference between each of the following pairs
- Anaemia and marasmas
- Micro nutrients and macro nutrients
- Ingestion and egestion
- List five factors contributing to back of balanced diet
- _____________________________________________________
- _____________________________________________________
- _____________________________________________________
- _____________________________________________________
- _____________________________________________________
- Give the meaning of the following
- Balance diet
- Malnutrition
- Assimilation
- Give the smallest unit of the following
- Carbohydrate _______________________
- Protein _______________________
- Lipid _______________________
- The table below shows various elements their function and their deficiency disorder in the body. Fill in the blanks to complete the table
| ELEMENT | FUNCTION | DEFICIENCY DISORDER |
| Eg. Calcium (Ca) (i) Potassium (K) | Formation of bone and teeth Nerve muscle action | Brittle teeth and bones |
| (ii) | Formation of thyroxin hormone | |
| (iii) Iron (Fe) | ||
| (iv) Phosphorus (p) | ||
| (v) | Formation of acidic medium in the stomach |
END OF TOPIC QUESTIONS
NUTRITION AND FOOD NUTRIENT
SECTION A. 20MARKS.
1. Choose the correct answer from the alternatives given.
- Lipids
- Proteins
- Carbohydrates
- Vitamins
2. Vitamin D deficiency in a diet will lead to a disease know as
- Beriberi
- Goiter
- Scurvy
- Rickets
3. The chemical reagents used to test reducing sugar is……
- Lactose
- Galactose
- Sucrose
- Maltose
4. Match the items in List A with the correct responses in list B.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. Write True for correct statements and False for incorrect statements.
- Heterotrophy produces their own food.
- All parasites obtain their nutrients by sucking the blood of their hosts.
- Animals which eat plants are called omnivores
- Disaccharides are sugar which made up only one molecule.
- Glucose, galactose and sucrose are example s of monosaccharides.
6. Mention the vitamin (s) responsible for each of the following:
- A vitamin that helps you read properly by improving your vision.
- A vitamin that strengthens your teeth, gums and bones.
- A vitamin that makes your blood clot after you accidently cut yourself.
- A vitamin that helps your body to stop bleeding.
- A vitamin that protects your body to produce blood.
- A vitamin that protects your body against diseases and infections.
7. Define the following terms:
- Nutrition
- Parasite
- Autotrophic nutrition
8. The body needs nutrients for good health. Name any 5 diseases caused by lack of specific nutrients.
9. Write short notes on the various types of nutrition.
10. Explain why:
- Vitamins B and C need to be taken regularly.
- We should include roughage in our diets even though it is not a nutrient.
- We should take adequate amounts of water.
11. Doto bought a kilogram each of beans, potatoes, and coconuts. She bought oranges and green vegetables. Mention the food nutrients found in each food substance substance she bought. Explain the functions of each nutrient to the body.
12. Select any three foods bought by Doto and explain how you would carry out food test for each.
1.11 TOPICAL EXAMINATION
BIOLOGY FORM 2
NUTRITION.
SECTION A.
- Multiple Choice questions.
- Below are some of diets taken in East Africa, which one of them could easily cause kwashiorkor in children when taken for quite a long period?
- Millet with fish
- Cassava with beans
- Rice with meat
- Bananas with green vegetables
- A person whose diet lacks iodine is likely to develop a nutritional disorder knownas
A. beriberi
B. rickets
C. night blindness
D. goitre.
- A person with a deficiency of vitamin C is likely to become a victim of
A. beriberi
B. rickets
C. night blindness
D. scurvy.
iv)A secretion containing enzymes which digest protein and carbohydrate is;
- Bile
- Gastric Juice
- Pancreatic Juice
- Hydrochloric acid
- A food sample which was tested by boiling with Benedict's or Fehling's solution gave an orange precipitate. This showed that the food sample contained
A. Reducing sugar
B. Fats
C. Protein
D. Sucrose.
- Pregnant mothers need food that is rich in;
A. Protein
B. vitamins
C. Minerals
D. Carbohydrate
vii) Which part of a leaf has a large surface area for absorption of sunlight?
- Petiole
- Lamina
- Stomach
- Apex
viii) Which of the following is not a traditional method of food preservation?
- Canning
- Curing
- Drying
- Smoking
- The first site of digestion of protein is in the,
- Mouth
- Oesophagus
- Stomach
- Small intestine
- Bile is produced in the
- Pancreas
- Stomach
- Gall bladder
- Liver
- Matching items questions.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B.
3. (a) Explain briefly how you would carry out the following tests
- Millions test
- Reducing sugar
- Starch
(b) Give the properties of the following food substance?
i) Monosaccharides
ii) Disaccharides
- Polysaccharides
4. (a) Outline the adaptation of ileum in digestion and absorption of food.
(b) Mention the role of the following in digestion,
i) Hydrochloric acids
ii) Bile
iii) Saliva
5. (a) Distinguish between;
i) Food preservation and food storage
ii) Refrigeration and freezing
iii) Curing and smoking
(b) Explain how the following methods can be used to preserve food
i) Smoking
ii) Pasteurization
iii) Using additives
6. (a)Name at least fivevitamin deficiency diseases.
(b) i)What is a balanced diet?
ii) List sixcomponents of a balanced diet.
7. (a)Name the threeelements that form carbohydrates.
(b) Briefly state two properties of polysaccharides.
8. (a) What are the building blocks of proteins?
- Distinguish between first class proteins and second class proteins.
- State fourfunctions of lipids in the human body.
9.A team of researchers went to a village near Tukuyu, Mbeya and found a five year old boy with the following symptoms:
- The stomach was protruding. • The skin was dry, flaky and rough.
- The hair was reddish and fell off easily. • The boy had no appetite.
(a) (1) Name the disease that the boy was suffering from.
- What deficiency caused the disease?
- Mention other disorders the boy was likely to be having.
- What advice would you expect the researchers gave to the parents of the boy?
(b) Suggest the type of diet, which the boy may have been eating.
10. (a) List two functions of digestive system
(b) Distinguish between mechanical and chemical digestion
(c) Which enzymes completes the digestion of protein in the ileum
1.12 NUTRITION QUESTION FOR NECTA
- A leaf is decolorized by boiling in ethanol before testing for starch because
- It make starch more reactive
- It prevent masking of the colour change
- The starch gains show up more easily
- It breaks down other sugar
- It is very soft (2007)
- A secretion containing enzymes which digest protein and carbohydrate is
- Bile
- Gastric juice
- Pancreatic juice
- Saliva
- Hydrochloric acid (2007)
- Green plants in a community are ecologically referred to as
- Consumers
- Decomposers
- Ecosystem
- Primary consumer
- Producers (2008)
- A food sample X turned blue-black when it was mixed with iodine solution . This concludes that sample X contained
- Fats and oil
- Non reducing sugar
- Proteins
- Reducing sugar
- Starch (2008)
- Which of the following sets of enzymes is responsible for protein digestion?
- Amylase and maltase
- Amylase and rennin
- Maltase and pepsin
- Maltase and lipase
- Pepsin and rennin (2010)
- Rickets in children and osteomalacia in adult are conditions caused by lack of?
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D (2011)
- Food sample turned blue-black when mixed with iodine solutions this includes that the sample contained
- Fat
- Protein
- Reducing sugar
- Starch (2012)
- A person who takes too much carbohydrate and lipids develops
- Giantism
- Kwashiorkor
- Marasmus
- Obesity (2013)
- The whole process of taking in food digesting it to provide energy for living aand material for growth is known as
- Catabolism
- Metabolism
- Nutrition
- Respiration (2013)
- The structure on the wall of the ileum responsible for absorption of digested food are called
- Alveoli
- Villi
- Mesophyll
- Epiglottis (2014)
- In the human digestive system the stomach is known as
- A tissue
- A cell
- An organ
- An organism (2015)
- The end product of fat/liquids in digestion process is called
- Amino acid
- Peptide
- Glucose
- Fatty acid and glycerol (2015)
- A secretion containing enzymes which digest both protein and carbohydrate is known as
- Bile
- Mucus
- Pancreatic juice
- Saliva (2016)
www.learninghubtz.co.tz
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania






