CHAPTER 1
1.0 OXYGEN
1.1 KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTS.
- Combustion- This is the combination of a substance with air such as metals
- Decomposition- this is the break-down of a compound into simpler form
- Catalyst- This is substance that alters the rate of chemical reaction but remains unchanged at the end of reaction.
- Catalytic decomposition- this is the breaking down of a large compound using a catalyst.
- Oxidation- this is the addition of oxygen into a compound
- Reduction- this is the removal of oxygen from a sunstance.
- Oxide- this is a compound formed when oxygen reacts with a metal or a non-metal
- Basic oxide- these are oxides of metals
- Acidic oxides- these are oxides of non-metals.
- Neutrals oxides- these are oxides which do not display acidic or basic characteristics
- Amphoteric oxides- are oxides which displays both basic and acidic properties.
- Aerobic respiration- this is the process by which oxygen is used to break-down foods substances in the body to release energy.
Occurrence:
Oxygen occurs in atmosphere in which occupies 21% it is also found in combined state such as in water and other compounds. Small amounts of oxygen is found dissolved in water.
Discovery:
- The first person to literary prepare oxygen in laboratory was Carl Scheel in the year 1773.
- He heated potassium chlorate compound to form potassium, chloride and oxygen.
- Later on a scientific called John priest prepared oxygen by heating Mercury (I) Oxide.
- However it is was Antoine Lavossier who Performed experiments on the gas and called it oxygen from words oxys and genos.
1.2 Preparation of oxygen
Basically there are two main methods of preparing oxygen in the laboratory these are
- Heating components rich in oxygen
- Catalyst decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
- Heating of Potassium Chlorate in the presence of catalyst.
However in the industry oxygen can be prepared in large scale by fractional distillation of liquid air.
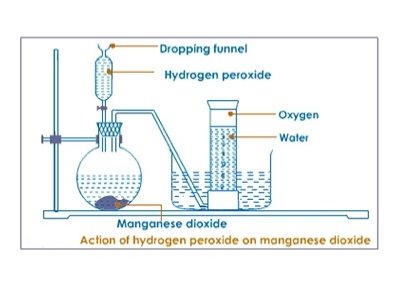
Laboratory preparation of oxygen using catalyst and hydrogen peroxide requirement
- Flat bottom flask
- Beaker
- Stand( complete)
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Delivery tube
- Beehive shelf
- Manganese (IV) oxide
- Water bath
- Water
- Gas
Procedure
- In the flask add 3g of Manganese Oxide.
- Connect your apparatus as shown below.
- Add hydrogen peroxide on the funnel and gradually open the top.
- Allow first few bubbles of the gas to escape before collecting.
- Collect gas jars of oxygen.
Discussion:
- Oxygen is prepared by catalyst decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, Manganese (IV) oxide act as a catalyst. A catalyst is a substance that alters the rate of the rate of chemical reaction but remains unchanged at the end of reaction
- . The first bubbles of gas were not collected because they were mixed by air.
- Oxygen is slightly soluble in water and less denser than air thus it is collected over water.
- The method is called downward displacement of water. The tap should be closed to prevent the oxygen gas from the escaping through funnel.
- The substance that gives oxygen gas is Hydrogen peroxide it can still decompose without catalyst though the reaction will be very slow.
The questions is H2O2 MnO2 → H2O + O2(g).
- Oxygen gas can be tasted by using a glowing splint.
- When glowing splint is introduced in the gas jar fully of the gas jar fully of the gas it will relight. Nitrogen I oxide also relight a glowing splint , however it has no smell which differentiate from oxygen. Nitrogen I oxide is also called a laughing gas.
1.3 Preparing oxygen by heating Potassium chlorate you need.
- Boiling tube
- Stand
- Source of heat
- Potassium chlorate
- Water
- Delivery tube
- Gas jar
- Beehive shelf
- Trough
Procedures.
- Set the experiment as shown below
- Collect several gas jars of the gas.
When oxygen rich compounds are heated, oxygen can be liberated and the compound decomposes. When potassium chlorate the following happens.:
![]() Potassium chlorate heat potassium chloride + oxygen.
Potassium chlorate heat potassium chloride + oxygen.
![]()
![]() KCLO3KCl(S)Solid + O2(g) gas
KCLO3KCl(S)Solid + O2(g) gas
1.4 Physical properties of oxygen
- Oxygen is odorless, colorless and test less
- Boiling point is – 183oc
- Slightly soluble in water
- Its density is 1.1 times that of air
- Its freeze at -2280c
- It is neural to litmus paper
1.5 Chemical properties of oxygen
- Oxygen is used in the process of combustion because it support burning. However oxygen does not it- self burn.
- Oxygen reacts with metals and non metals to form oxides.
- Oxygen react with hydrogen gas to form water
H2(g)+ O2(g)→ H2O(l)
4. Oxygen has no action calcium chloride
Reaction of oxygen with other metals
Sodium
- Metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides can either be base or amphoteric
- Sodium reacts with yellow flame to form metal oxides in the excess oxygen, sodium peroxide is formed. The oxide is white in color.
- Na(s) + O2(g)→Na20(s)white
- Na(s) + O2(g) → Na2O2 (s)
Magnesium
Magnesium reacts with very bright, blinding flame to form white oxide called magnesium oxide.
Mg(s) + O2(g) → MgO(s) white
- When oxides of metals dissolves in water a basic solution is formed , all soluble gases are called alkalis. Alkalis turned litmus paper into blue sodium, Magnesium and calcium oxide are basic.
- The oxide of copper and Iron have no effect or litmus paper and are said to be neutral oxides of aluminum leads and zinc have basic and acid characteristics are said to be amphoteric
Reaction of oxygen with non metal
- Non metals reach with oxygen to form non metal oxides which are acid. Their solution turns blue litmus paper red.
Sulphur.
Burns in oxygen with a yellow flame to form a colorless gas with chocking smell.
Carbon.
Reacts sparks white color producing a colorless gas carbon dioxide
1.6 Uses of oxygen
- Respiration: oxygen is in aerobic respiration, where food is broken down to release energy.
- In hospitals, oxygen is used for people with breathing difficulties and pre mature babies.
- Mountain climbers carry oxygen because the higher you go oxygen concentration decrease.
- Deep sea drivers also used oxygen when swimming down deep in water.
- Extraction of metals- oxygen is used to reduce oxide of metals to corresponding metals during extraction eg. Zinc oxide, iron oxide, aluminum oxide etc.
- Welding: oxygen is combined with a acetylene to form oxyacetylene which is a very high temperature flame (3000c). This is used to melt metal during welding.
- Fuel: oxygen Combine with liquid hydrogen to form a fuel which is used to propel rockets to the atmosphere.
- Explosive in mining a mixture of charcoal or coal, petrol and oxygen (liquid) explode with great force. The explosive used to blast rocks during mining.
SUMMARY.
- Oxygen occurs in atmosphere in which occupies 21% it is also found in combined state such as in water and other compounds.
- The first person to literary prepare oxygen in laboratory was Carl Scheel in the year 1773.
Basically there are two main methods of preparing oxygen in the laboratory these are
- Heating compounds rich in oxygen
- Catalyst decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
- Heating of Potassium Chlorate in the presence of catalyst.
- Oxygen is prepared by catalyst decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, Manganese (IV) oxide act as a catalyst.
- A catalyst is a substance that alters the rate of the rate of chemical reaction but remains unchanged at the end of reaction
- When glowing splint is introduced in the gas jar fully of the gas jar fully of the gas it will relight. This is the test for oxygen gas.
- Physical properties of oxygen;
- Oxygen is odorless, colorless and test less
- Boiling point is – 183oc
- Slightly soluble in water
- Its density is 1.1 times that of air
- Metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides can either be base or amphoteric
- Non metals reach with oxygen to form non metal oxides which are acid. Their solution turns blue litmus paper red.
1.7 END OF TOPIC QUESTIONS.
- Oxygen when it chemically combines with a metallic or non – metallic element what group of compounds would it form?
- Oxides B. Sulphides C. Chlorates D. Hydrides
- ZnO, Al2O3 and PbO2, can react with both acids and alkalis to form salt and water. Which group of oxides will accommodate them?
- Neutral B. Acidic C. Basic D. Amphoteric
- Oxygen when it chemically combines with a metallic or non – metallic element what group of compounds would it form?
- Oxides B. Sulphides C. Chlorates D. Hydrides
- ZnO, Al2O3 and PbO2, can react with both acids and alkalis to form salt and water. Which group of oxides will accommodate them?
- Neutral B. Acidic C. Basic D. Amphoteric
- Which is the right method of manufacturing oxygen in large scale in industries
- Catalytic decomposition of potassium chlorate
- Thermal decomposition of manganese dioxide
- Fractional distillation of liquid air
- Heating hydrogen peroxide using a catalyst
- Which method is suitably used to collect oxygen in the laboratory?
- Downward displacement of water
- Upward delivery
- Upward displacement of air
- Passing it through a dryer
PART II.
- Oxygen is obtained by heating a metal chlorate in the presence of a catalyst.
- Write the formula of the;
- Metal chlorate used ………………………………………….
- The product formed other than oxygen …………………………………………….
- Write the;
- Formula and the IUPAC name of the catalyst used;
Formula …………………………………….
- Word equation of this reaction …………………………………………….
- Draw a large and well labeled diagram for this laboratory preparation of oxygen.
- A magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling flame when inserted in a gas jar of carbon (IV) oxide, forming a white solid and back specks. Name the following:
- The black specks
- The white solid
1.8 SAMPLE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS NECTA ON OXYGEN
- The property of oxygen that can be used for its test is
- It is colorless and odorless
- It is lighter than air
- It relights a glowing splint
- It is slightly soluble in water (1999)
- A gas was tested with a glowing splinter and gave a pop sound the gas was possibly
- Nitrogen
- Oxygen
- Hydrogen
- Chlorine (2000)
- Which of the following sets of processes represent uses of oxygen gas?
- Welding ,ice melting, magnetization
- Mountaineering, sublimation, welding
- Glass cutting, desiccation ,welding
- Diving, welding, mountaineering (2004)
- Oxidation may be defined as
- Loss of hydrogen by a substance
- Gain of hydrogen by a substance
- Reaction in which oxygen is lost
- Reaction in which electrons are increased (2007)
- An important property of oxygen which distinguishes it from other gases is that
- Burns and support combustion
- Burns but does not support combustion
- Neither burns nor support combustion
- Supports combustion but does not burn (2012)
1.8 TOPICALEXAMINATION
CHEMISTRY FORM II
OXYGEN
SECTION A
- Question (i) – (x) are multiple choice items write down the letter of the correct answer:-
- A mixture of two solid substance is commonly heated in the laboratory to produce oxygen such mixture could be that of:-
- Manganese dioxide, hydrogen and magnesium
- Potassium permanganate and magnesium oxide
- Mercury (ii) oxide and hydrogen peroxide
- Potassium chlorate and manganese (iv) oxide
- The sold manganese (iv) oxide which is used in the preparation of oxygen using hydrogen peroxide play the role of :-
- An oxygen producer
- An oxidant
- A catalyst
- A- reducing agent
- When oxygen is prepared in the laboratory it usually collected by
- Downward delivery
- Displacement of air
- Up delivery
- Displacement of water
- Fish and other aquatic organism breathing in oxygen which is
- Combine with water
- Present in the water molecule
- So- plentiful in the air
- Dissolved in water
- The natural process which supplies oxygen to atmosphere is
- Respiration
- Combustion
- Breathing
- Photosynthesis
- The metal known to produce hydrogen from dilute nitric acid is :-
- Magnesium
- Aluminium
- Iron
- Lead
- Which of the following sets of process in present uses of oxygen gas:-
- Welding, ice melting , magnetization
- Mountaineering, sublimation, freezing
- Glass cutting, desiccation, welding
- Diving, welding , mountaineering.
- Hydrogen gas can be collected by downward delivery because
- It burns in air with a pop sound
- It is more soluble than air
- It is lighter than air
- It can fill balloons
- When oxygen combine with metals they
- Form basic oxides
- Form acidic oxide
- Rust
- Sublime
- Which of the following is not true about hydrogen:-
- It is lighter than air
- It burns with blue flame
- It is support combustion
- It is odor less.
SECTION B
- Match each item in list A with response in list B by writing its letter against corresponding item.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION C
- List four (4) chemical properties of oxygen
- Write three (3) common methods of preparations of oxygen in the laboratory
- What is chemical test for oxygen gas?
- List any four (4) uses oxygen gas in our daily life
- Write a word chemical equation to show the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide in the presence of manganese (IV) oxide.
- Why oxygen gas is collected over water?
- Respiration and burning are similar process in some ways and difference process in other ways. Give two differences between them.
- Consider the diagram below and then answer the questions that follows:
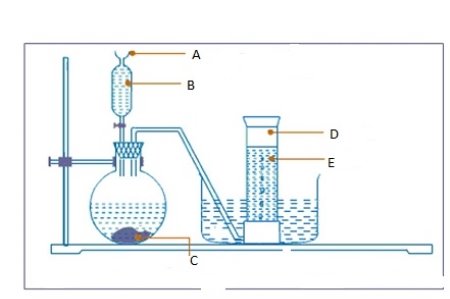
Label parts
- A ………………………………………………………………………………………
- B…………………………………………………………………………………………
- C…………………………………………………………………………………………
- D ………………………………………………………………………………………
- E ……………………………………………………………………………………………..
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania






