CHAPTER 01 : WORD PROCESSING
Introduction
In the past, documents were processed manually and in hardcopies, either handwritten or by a typewriter. Nowadays, documents can be created using a computer system through application programs for word processing. In this chapter, you will learn the concept of word processing; working with MS Word program and files; editing and formatting a word document; printing a word document; and using the help facility. The competencies developed will enable you to prepare documents of good quality
Concept of word processing
Word processing is an art of creating, editing, formatting, saving and printing of text-based documents. The documents processed can be letters, memos, reports, manuals, books and almost all documents required for different uses. Word processing is done through a computer in which an application program or software known as word processor has been installed.
Word processor
A word processor is an application software for manipulating electronic text-based documents. This software allows a text to move around and to be manipulated in different ways. For example, a word processing software allows correction of misspelled words throughout the document by means of a single command of spelling and automatic grammar check. Such commands alert a user to correct spelling, punctuation, and syntax errors. The document format, layout, and font type and sizes can be changed repeatedly until a satisfactory appearance is produced. Since all editing, ideally, occurs on screen, word processing can result in decreased paper usage, simplified editing, and neat varieties of the same work in good quality formats. When the final draft is ready, the document can be printed out in multiple copies if necessary, sent as an attachment through e-mail, shared on a computer network, or simply stored as an electronic file.
Most word processors have powerful sets of programs, which can produce a combination of images, graphics and text. Moreover, these word processors offer facilities for document formatting such as font changes, page layout, and paragraph indentations. There are different examples of word processors such as WordPerfect, WordStar, Microsoft Word (MS word), Google Docs, Open Office writer, and Write Pro. Microsoft Word, in particular, has different versions such as MS word 2003, MS Word 2007, MS Word 2010, MS Word 2013, MS Word 2016 and MS Word 2019. However, at this level, you will learn about MS Word 2016.
Features of electronic word processors
All electronic word processors have some common features such as:
(a) Creating and editing features;
(b) Formatting features;
(c) Spelling and grammar check features;
(d) Word wrap;
(e) Mail merge; and
(f) What You See Is What You Get (WYSIWYG) features.
Importance of using a word processor
Word processor enables a user to:
(a) Easily correct mistakes in a document;
(b) Store document electronically for future use;
(c) Create good quality documents since it has many formatting features such as borders, text layout, bullet styles, line and paragraph spacing, indentation shading, bold underline, etc;
(d) Automatically check spelling since it is full of useful tools such as a grammar checker available to improve the quality of user’s work;
(e) Use a plenty of good quality document templates available online; and
(f) Import data from a data file and use it to create mail merge.
| Activity 1.1: Studying the significance of a word processor Using library or Internet resources, collect two documents, one that was prepared using a typewriter and another one prepared using a word processor. Compare the two documents and summarise in your own words the significance of a word processor program. |
Working with MS Word program and files
Starting MS Word program
There are different ways of starting MS Word 2016 program on a computer. The type of operating system you are using and how the computer is configured cause these differences. The commonly used way to start MS Word 2016 is clicking the shortcut for MS Word icon on the task bar or start menu as shown in Figure 1.1, or on a desktop screen.
|
Figure 1.1: Task bar with options for starting MS Word |
Key:
1 = Start button
2 = Shortcut for MS Word
If you are using a start menu, the following activity can help you to load the program.
| Activity 1.2: Starting MS Word (i) Click on the Start button on the task bar for Windows 8 or Windows 10: Start pop up menu will appear. (ii) Scroll down and click on MS Word 2016: Different MS Word templates will appear. (iii) Choose the Blank document template: MS Word program window will open. |
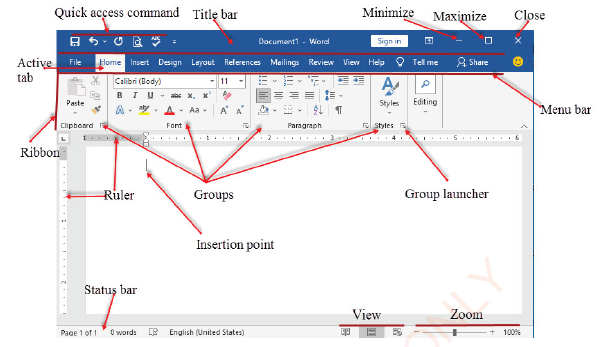
Parts of MS Word window
MS Word window has several parts, including Title bar, Menu Bar, Ruler, Working area and Status bar. Figure 1.2 shows different parts of MS Word 2016.
|
Figure 1.2: Parts of MS Word 2016 |
Title bar
The title bar displays the program name and the name of the current document you are working on, as it appears in Figure 1.3.
|
Figure 1.3: Title bar |
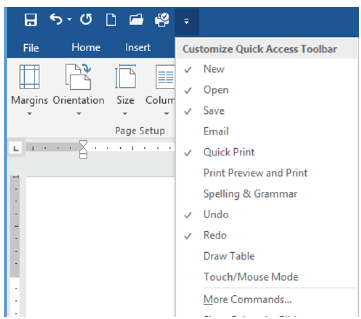
By default, when you open MS Word for the first time, the title bar will display a blank Document 1-Word. Usually, the bar also displays quick access bar commands. The Quick Access commands allow you to access common commands regardless of the selected tab. The common quick access commands are Save, Undo, and Redo, but one can customise quick access commands to suit his/her needs. Activity 1.3 will help you to customise the quick access toolbar.
| Activity 1.3: Customizing the quick access toolbar (i) Click the drop-down arrow to the right of the quick access bar, (ii) Click on the command you want from the pop-up menu as shown in Figure 1.4, (iii) An icon for the selected command will appear on the quick access bar |
|
Figure 1.4: Quick access pop menu |
Menu bar
MS Word menu bar has different tabs including File, Home, Insert, Design, Layout, References, Mailing, Review, and View, as shown in Figure 1.5.
|
Figure 1.5: Menu bar |
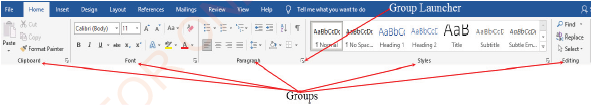
Each tab has a ribbon that displays a list of commands in groups. For example, a ribbon for Home tab contains command groups such as Clipboard and Font as shown in Figure 1.6.
|
Figure 1.6: Groups of commands in the Home ribbon |
Note: This combination of icons and tabs, which is known as the Ribbon interface,also appears in other programs like MS PowerPoint, MS Excel, MS Outlook, and
MS Access.
| Activity 1.4: Exploring different tabs Navigate each tab to display a ribbon with different groups of commands. |
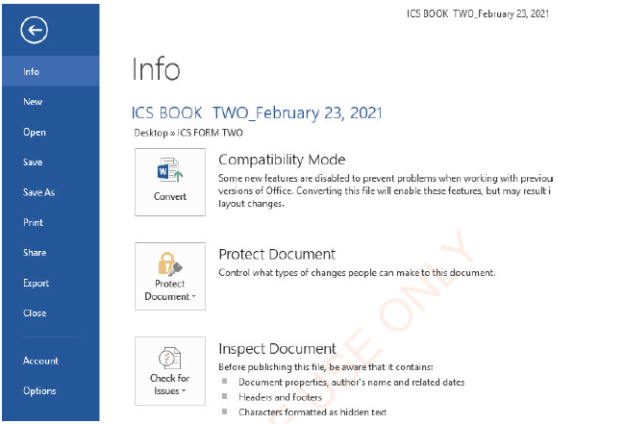
File tab
File tab appears at the left topmost corner of all tabs. When open, it displays the menu for actions such as Info, New, Open, Save, Save As, Print, Share, Export, Close, Account, and Options, as
|
Figure 1.7: File menu |
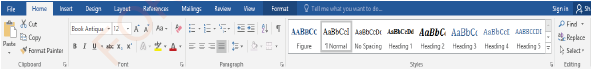
Home tab
Home tab displays a ribbon with different groups of commands such as Clipboard, Font, Paragraph, Style, and Editing, as shown in Figure 1.8.
|
Figure 1.8: Home ribbon |
Insert tab
Insert tab displays a ribbon with various groups of commands such as Pages, Tables, Illustrations, Add-ins, Media, Links, Comments, Header & Footer, Text, and Symbols, as shown in Figure 1.9.
|
Figure 1.9: Insert ribbon |
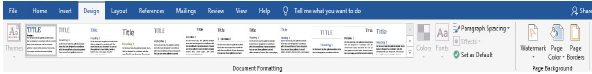
Design tab
Design tab displays a ribbon with Document Formatting and Page Background as shown in Figure 1.10.
|
Figure 1.10: Design ribbon |
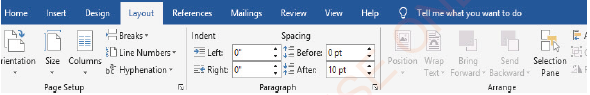
Layout tab
Layout tab displays a ribbon with options for page setup, paragraph setup and word arrangement, as shown in Figure 1.11.
|
Figure 1.11: Layout ribbon |
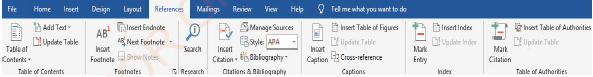
References tab
Reference tab displays a ribbon with groups of commands such as Table of Contents, Footnotes, Citation and Bibliography, Captions, Index, and Table of Authorities, as shown in Figure 1.12.
|
Figure 1.12: References ribbon |
Mailings tab
Mailings tab displays a ribbon with different groups of commands that include Create, Start Mail Merge, Write & Insert Fields, Preview Results, and Finish as shown in Figure 1.13.
|
Figure 1.13: Mailings ribbon |
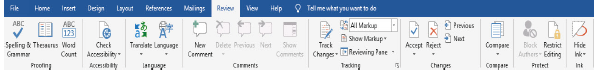
Review tab
Review tab displays a ribbon with groups of command that include Proofread, Accessibility, Language, Comments, Tracking, Changes, Compare and Protect documents as shown in Figure 1.14.
|
Figure 1.14: Review ribbon |
View tab
View tab shows different groups of options for document view such as Show, Zoom, Window, and Macros, as shown in Figure 1.15.
|
Figure 1.15: View ribbon |
Ruler
Ruler displays the left and right margins, tab settings, and indentation, as shown in Figure 1.16. You may use a ruler to change the default left and right margins, and create indentation and tabulations.
|
Figure 1.16: Ruler |
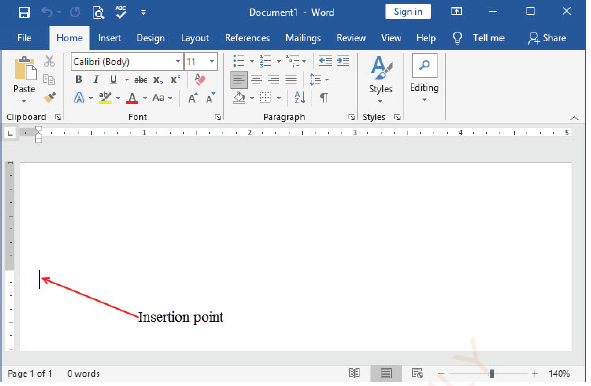
Working area
Working area looks like a white paper on which a text can be written. The blinking vertical line in the upper left corner of the sheet area is called Insertion Point. The insertion point indicates the position where the character typed will appear in the sheet as shown in Figure 1.17. As you type a character, you will notice the insertion point moving to indicate where the next character you type will appear.
|
Figure 1.17: Working area |
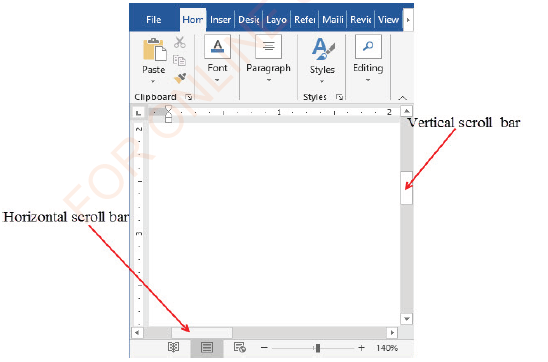
The working area also contains vertical and horizontal scroll bars. These bars represent the current relative location of an insertion point in the document. A scroll bar allows you to move right or left and down or up the window as shown in Figure 1.18.
|
Figure 1.18: Vertical and horizontal scroll bars |
You can scroll a document window in several ways. For instance, if you need to scroll only a short vertical distance, click continuously up or down the vertical scroll bar. Likewise, you can jump to the next page or previous page by clicking the next or previous page arrows. Also, you can use a mouse to scroll faster up or down by holding and dragging down vertical scroll bars.
Status bar
Status bar appears at the bottom of the screen and provides information such as current page, current section, total number of pages, total number of words, the language used, current line number, and current column number. For example, in Figure 1.19, the status bar shows that the current opened document is on page 11 out of 152 pages and the document contain 24532 words.
|
Figure 1.19: Status bar |
Usually, the status bar contains commands that show how the document can be viewed and zoomed. In MS Word, you can display your document in one of the following views: Read Mode, Print Layout, or Web Layout.
Read Mode: Read Mode view formats your screen to make reading your document more comfortable.
Print Layout: The Print Layout view shows how the document will look like when printed.
Web Layout: Web Layout view enables you to view your document, as it would appear in a browser such as Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox, or Google Chrome.
| Activity 1.5: Changing document view You can change the document view to suit your needs. For example, you can change word screen view into read mode by following these steps: (i) Click View tab, (ii) The icon next to Read Mode is Print Layout with a box around it, (iii) Click Read Mode. You are now in Read Mode. (iv) Press escape key on the keyboard to return to print preview mode. |
Closing MS Word program
When you have completed working with MS Word program, you will be required to close the program. In most cases, you would save your work before closing.
| Activity 1.6: Closing MS Word file and program (i) Click File tab, (ii) Click Close button, (iii) If you have entered a text that is not yet saved, you will be prompted to save changes. If you click “Yes”, you will be prompted to save a document by giving a file name and specifying the location. If the changes are in an existing file, click “Save”, and the changes will be saved. (iv) If you click “No”, the document will be discarded. If you click “Cancel”, closing will be cancelled and you will be allowed to work further on the document. To close a document without exiting MS Word: (i) Click the File tab, (ii) Then click Close button, or (iii) Press Ctrl+W. |
Creating MS Word file
Inserting a text
When entering a text, you must first position the insertion point where you want to insert the text, either to the left or right of an existing character. Text is inserted into the MS Word document in various ways such as:
(a) Typing via a keyboard;
(b) Copying/cutting a text from other documents and pasting it into a word processing document;
(c) Scanning printed documents and using Optical Character Recognition (OCR) software to convert the scanned documents into text characters;
(d) Using voice recognition software to convert spoken words into text characters and vice versa; or
(e) Importing files such as tables, pictures, and databases from storage media or other sources.
In this chapter, you will mainly use options (a) and (b) in creating a word document. When beginning a new project in MS Word, you will often want to start with a new blank document. In order to create a new document, do the following:
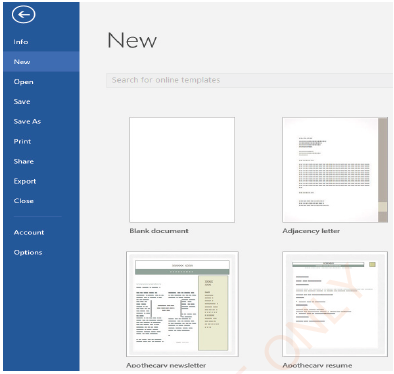
Click File tab: Backstage view will appear.
(ii) Click New tab: a window which looks like that of Figure 1.20 will display different templates.
(iii) Click Blank Document, the blank document will appear
|
Figure 1.20: Creating new document |
| Activity 1.7: Type the following passage in MS Word Electronic word processing enables a user to edit and format documents easily. It makes possible sharing of information quickly and getting feedback. Teachers may be in a good position of using electronic word processor for preparing lessonnnotes, schemes of work, lesson plans and other word documents. |
Navigating a document using a keyboard
The easiest way to move the insertion point by short distances is to use the arrow keys. You can also use additional keys to move the insertion point by longer distances.
Procedures
(i) Press [Ctrl+Home] to move the insertion point to the beginning of the document.
(ii) Press Down Arrow key [ ]to move the insertion point down one line.
(iii) Press Up Arrowkey [ ] to move the insertion point up one line.
(iv) PressRight Arrow key [ ] to move the insertion point one character to the right.
(v) Press Left Arrow key [ ] to move the insertion point one character to the left.
(vi) Press [End] to move the insertion point to the end of the current line.
(vii) Press [Home] to move the insertion point to the beginning of the current line.
(viii) Press [Ctrl+ ] to move the insertion point to the next word.
(ix) Press [Ctrl+ ] to move the insertion point to the previous word.
(x) Press [Page Down] to move the insertion point down one screen.
(xi) Press [Page Up] to move the insertion point up one screen.
(xii) Press [Ctrl+Page Down] to move the insertion point to the top of the next page.
(xiii) Press [Ctrl+Page Up] to move the insertion point to the top of the previous page.
(xiv) Press [Ctrl+End] to move the insertion point to the end of the document.
Saving MS Word document
Saving MS Word document for the first time
After you have typed your text, you should store it in your computer for future use. Steps to save the typed document for the first time include the following:
(i) From File menu tab, Click Save As, a Save As window will appear.
(ii) Select the location by clicking Browse and choose the location (for example, Removable Disk, Documents, or Desktop).
(iii) Write the file name (the name should either reflect the content of the document, for example ICS notes or any other name that can be easily remembered).
(iv)Choose file format like Word document (.docx), Plain Text (.txt) or Rich Text Format (.rtf).
(v) Click Save.
Saving changes while working on an MS Word document
You should continue saving the document when the work is in progress to avoid loss of content in case of problems like power failure. In this case, you may use a shortcut for Save , or Click File menu then click Save command, or press Ctrl+S.
Saving MS Word document as PDF
PDF stands for Portable Document Format. The format is used for saving files in such a way that they cannot be easily modified but still can be shared and printed.
In most MS Word versions, you can convert an MS Word document into a PDF file type by following these steps:
(i) Open an existing MS Word document or create a new MS Word document,
(ii) Click File tab option at the top-left of the MS Word program window,
(iii) Click Save As option in the menu,
(iv)On Save As window, click Browse to select a location on your computer where you want to save the file,
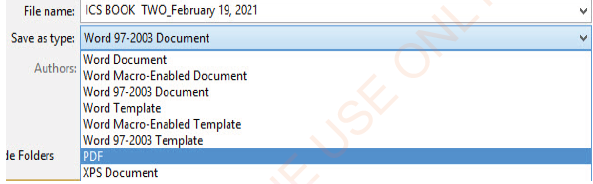
(v) In the Save as type drop-down list, select the PDF option as shown in Figure 1.21.
|
Figure 1.21: Saving MS Word document as PDF |
(vi) Click Save button to save the MS Word document as PDF.
Saving MS Word document in external storage
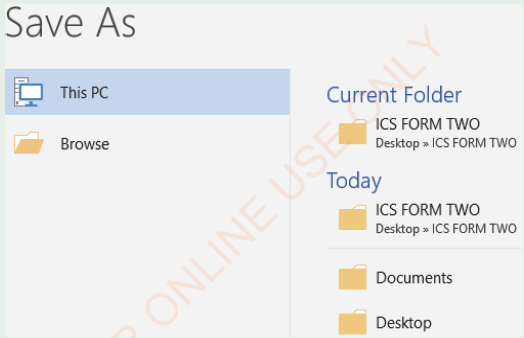
External storage devices such as flash disks can usually store the file created by a word processor. Follow the steps in Activity 1.8 to save a document in a flash disk.
| Activity1.8: Saving an MS Word document in a flash disk or any other external storage Device Steps: (i) Open an existing MS word document or create a new MS word document, (ii) Insert the flash disk in the computer as shown in Figure 1.22,
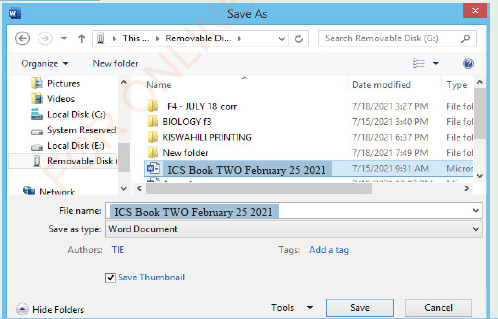
(iii) Click File tab: File menu options will appear, (iv) Click Save As: The window for Save As will appear as in Figure 1.23,
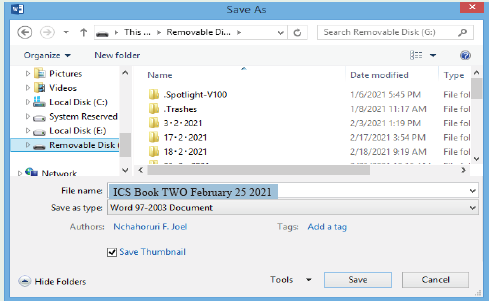
(v) Click Browse: Save As dialog box will open as in Figure 1.24
(vi) Type the name of the file, example “ICS Book TWO February 25 2021” in the File Name (See Figure 1.24), (vii) Scroll on the left-hand side of the menu to find the flash disk or removable disk, (viii) Click on the Flash disk or on Removable Disk: the flash disk or removable disk will open as in Figure 1.25. (ix) Click Save.
|
Opening an existing MS Word document
Opening a document stored in a computer
When a document is saved in a computer, it can be opened at anytime when it is needed as MS Word program allows a user to open an existing document. To open an already saved document, do the following:
(i) Click File tab,
(ii) Click Open: the open dialog box will appear, giving you the option to choose the file from the location where it is stored.
(iii) Choose the file,
(iv) ClickOpen: The file will be opened.
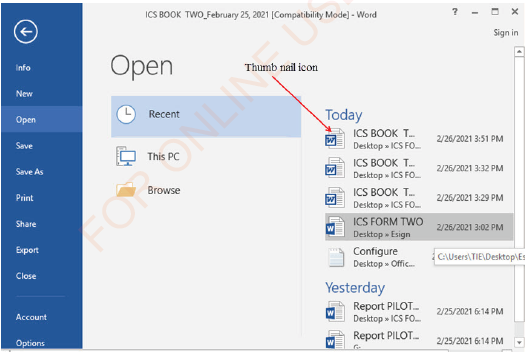
Alternatively, you can use the shortcut for opening (Ctrl + O); this will display the open dialog box as shown in Figure 1.26. You can also open an existing document by double clicking the file. or
NOTE: If the document you want to open is in the Recent Documents list, click its File name or Thumb nail icon (see Figure 1.26) to open it. The window like what is seen in Figure 1.27 will be opened.
|
Figure 1.26: Opening a file from a recent document |
|
Figure 1.27: Opened MS Word document |
Opening a file saved in external storage
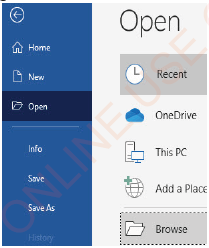
Sometimes, a word document is saved in external storage devices such as flash disk. To open the file saved in an external storage, follow these steps:
(i) Click on File tab,
(ii) Click on Open,
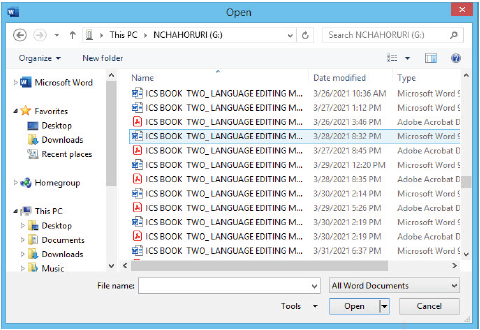
(iii) Click Browse as shown in Figure 1.28. The Open dialog box will appear as shown in Figure 1.29.
|
Figure 1.28: Window for file browsing |
|
Figure 1.29: Opening a file from a removable disk |
(i) Scroll in left column window to find the removable disk option,
(ii) Select the file you want to open,
(iii) Click on Open button. The file will be opened.
| Exercise 1.1 1. Outline the steps for opening, creating, saving, and closing a word document. 2. Why should you save your working document before closing it? 3. What is the use of Ruler in MS Word? 4. What is the importance of using a word processing program? |
Editing and formatting a document
The word processor offers different facilities for correcting mistakes like spelling and grammar errors in a document. It also gives a room to decorate a document in a format that you want using features such as font type, font size, page layout, and paragraph indentation. This section describes how you can edit and format a word document.
Editing an MS Word document
Editing is the process of correcting mistakes and errors or removing unwanted content. After a document is created, it may contain mistakes, errors, unrequired content or missing some content. This creates the need of editing the text. Editing
may involve adding or removing a text, or moving a text from one place to another.
This section covers some basic tasks done during editing such as selecting, deleting, copying, moving a text, undoing and redoing changes.
Selecting a text
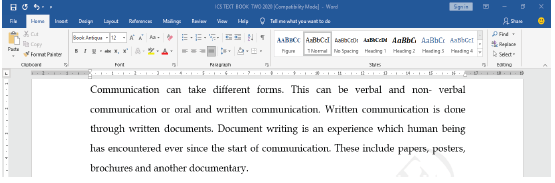
Before making any change or editing a text, you must first select the text that you want to edit. You can use the mouse or the keyboard to select the text. The selected text appears highlighted on the screen, as it is shown in Figure 1.30.
|
Figure 1.30: Selected text |
To select a text, do the following:
(i) To select a word, double-click anywhere in the word.
(ii) To select a sentence, hold the Ctrl key and click anywhere in the sentence.
(iii) To select a paragraph, triple-click anywhere in the paragraph.
(iv)To select the entire document, press Ctrl+A.
(v)To select adjacent words, lines, or paragraphs, drag the mouse pointer over the text; or click at the beginning of the text, and then hold the Shift key and click at the end of the text.
(vi)To select non-adjacent words, lines, or paragraphs, make the first selection, and then hold down the Ctrl key and make the second selection.
NOTE: To deselect the text, click anywhere in the document.
Deleting a text in MS Word document
If you wrongly insert a text or an object in a word processor, you can remove the text or the object that has been mistakenly written. This is done by the use of backspace key and the delete key on the keyboard. To delete a character at a time,
position the insertion point in front of the character then press the backspace key; or place the insertion point at the beginning of the character, then press the delete key. The delete key removes characters to the right of the insertion point, while the backspace key removes characters to the left of the insertion point. To delete a word, sentence, paragraph or block of text, select it then press the delete key.
Copying and moving a text
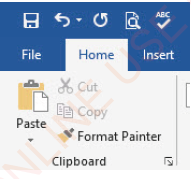
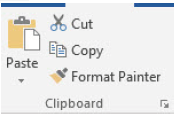
When editing a document, you may want to duplicate a text in another location, or you may want to remove a text from its original location and place it in a new location. Copy is a command used to create a duplicate of a text, while Cut is a command for moving a text. The shortcuts for the two commands appear in the Clipboard group of the Home ribbon as in Figure 1.31.
|
Figure 1.31: Commands for copying and cutting a text |
Copying a text
To copy a text, you must first select the text, then click on the icon or command Copy. Alternatively, you can copy a text by pressing the Control key (Ctrl) and C key on the keyboard. Copying can also be done through the following procedure: select the text, hold the Ctrl key and place the cursor over the selected text, press and hold the left mouse button, drag to the desired location and lastly, release the mouse button to paste.
Cutting a text
Cut is one of the useful commands in a word processor. When editing a document, you may realise that some text needs to move from the present location to a new
ocation. The word processor provides a solution to that through Cut command. To cut a text, do the following:
(i) Select the text you want to move,
(ii) Right click on the selected text,
(iii) From the popup menu, click the Cut shortcut ,
(iv) Move the insertion point to the place where you want the text to appear,
(v) Right click and click Paste shortcut from the popup menu.
Alternatively, you can move the text by dragging and dropping the selected text by following these steps:
(i) Select the text you want to move,
(ii) Click and hold the mouse then drag the text to a location where you want it to appear. The cursor will have a rectangular shape under it to indicate that you are moving the text,
(iii) Release the mouse button, and the text will appear.
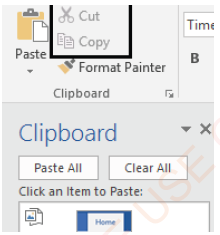
NOTE: The cut or copied text is stored on the Clipboard. The Clipboard is a temporary storage area. Figure 1.32 shows a Home tab and Clipboard group. Every time a new text or any other object is copied or cut, the clipboard content is replaced with the new one.
|
Figure 1.32: Clipboard |
Pasting a text
Paste command helps you to shift the text you have copied or cut to another place. To paste a text, locate a place where you want to insert the text, then click the paste icon or use a keyboard shortcut Ctrl + V.
Undo and Redo command
Sometimes, you may make mistakes when entering a text in the word processor. Whenever you make a mistake, you can easily reverse it with the Undo command. After you have undone one
or more actions, the Redo command becomes active and allows you to restore the undone actions. Table 1.1 shows the procedures to
Undo and Redo actions.
Table 1.1: Undo and Redo actions
| To undo an action: | To redo an action: |
| On the Quick Access toolbar, click the Undo button , or press Ctrl+Z. | On the Quick Access toolbar, click the Redo button , or press Ctrl+Y. |
Spelling and grammar check
You can check the spelling and grammar in the file all at once, or you can let the spelling and grammar checkers suggest corrections automatically while you work. The word processor offers a dictionary of standard grammar and spellings, but they are not comprehensive. To customize these features, do the following:
(i) Choose the language for which you want to check the spelling and grammar,
(ii) Use custom dictionaries to add words to the spelling checker,
(iii) Use exclusion dictionaries to specify a preferred spelling for a word,
(iv)Check spelling and grammar in a different language.
Checking all spellings and grammar in a file at the same time is useful when you want to proofread a text. You can check for possible mistakes and then confirm each suggested correction. You can resolve each error that the program finds in different ways: Select the word in the suggestions list, and then click Change or
(i)Select the word in Dictionary check box,
(ii) Edit the word,
(iii) Click Change.
If you want MS Word to recognise the word and not treat it as a misspelling, click Addor Add to Dictionary. If you want to ignore a misspelled word and move on
to the next misspelled word, Click Ignore Once. If you want to ignore all instances of a misspelled word and move on to the next misspelled word, Click Ignore All. Alternatively:
(i) Open MS Word document,
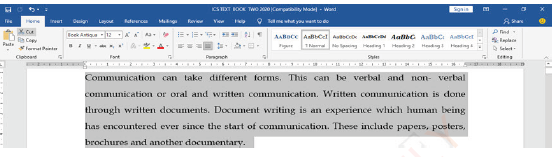
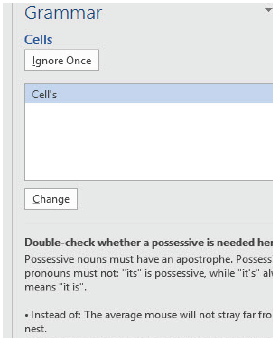
(ii) Click on proofing error icon on the status bar: the grammar check window will open as shown in Figure 1.33.
(iii) Select the correct word in the Search Box,
(iv)Click Change.
|
Figure 1.33: Error and grammar check window |
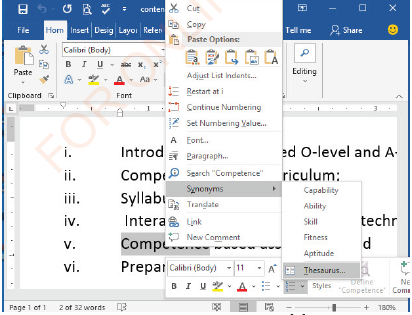
Synonyms and thesaurus
The word processor has features that help the user to get alternative words. The user can see words with similar meaning by right clicking the mouse button on the word he/she wants to look for alternatives. Figure 1.34 displays the window which gives an option to choose the synonyms of that word or find the thesaurus.
|
Figure 1.34: Synonyms and thesaurus |
| Activity 1.9: Changing the word using Synonyms and Thesaurus Steps (i) On the working area, type the word “desired”, (ii) Right click the word “desired”, (iii) On the drop down menu, choose the preferred word, (iv) Click Insert. Or (i) Type any word on the working area, (ii) On the Review tab, click Thesaurus, (iii) See alternative words in thesaurus, (iv) Type the word in your text. |
Using drag-and-drop action
Drag-and-drop editing allows you to use a mouse to copy and move a text by dragging a text to the desired location. The results are the same as cutting or copying and pasting, except that the cut or copied items are not saved to the Clipboard. This feature is most useful when the text you want to cut or copy and the destination location are both visible in the document area.
CUT
(i)Select the text you want to move,
(ii)Point to the selected text and drag it to the desired location.
COPY
(i) Select the text you want to copy.
(ii) Hold control key (Ctrl), point to the selected text, and drag it to the desired location.
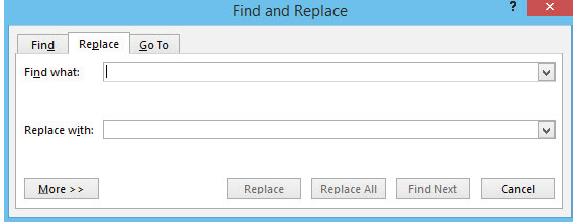
Find and replace
Find and replace gives a chance to find a word and replace it with a new one. This editing feature can help you to correct a wrong word that might have appeared several times in your document.
Steps:
(i) On the Editing group of the Home ribbon, click Replace: the window for find and replace will appear as shown in Figure 1.35,
|
Figure 1.35: Find and replace window |
(ii) Write the word you want to find,
(iii) Write the replacing word,
(iv)Click Replace if you want to find and replace one occurrence of a word:
Click Replace all if you want to replace all occurrences of the found word.
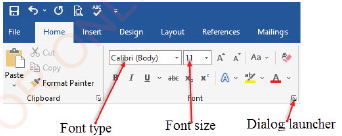
Formatting MS Word document
Formatting helps you to change the appearance of a document so that it can look neater and of good quality. Text formatting includes font type, font size, font colour, font style, page setup, etc. The font group on the Home ribbon contains the commonly used text formatting commands. You can also format a text using the font dialog box, which is opened by clicking the dialog box launcher in the Font group as shown in Figure 1.36.
|
Figure 1.36: Formatting commands |
Changing font type and font size
A font is the style of text lettering, and it defines the overall appearance of a text.
Examples of font types are such as Times New Roman, Arial, Calibri Light, and
Calibri extra. The default font in MS Word 2016 documents is Calibri (bold).
Changing font style
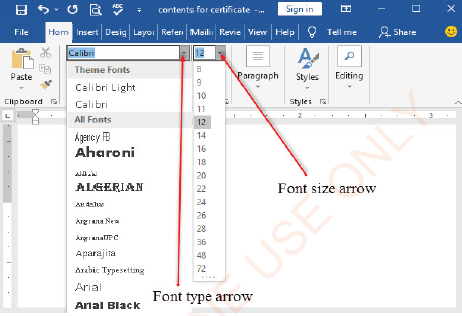
Changing the font of a text can be done through the following steps:
(i) Select the text that you want to format,
(ii) On the Home ribbon, in the Font group, click the Font style arrow and choose the desired font from the list (see Figure 1.37).
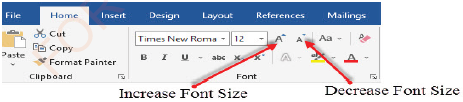
Changing font size
Click on the Font Size arrow and select the desired font size from the list on the Home ribbon in the Font group (see figure 1.37). If a font size of your choice is not listed in the Font Size list, click in the Font Size box , type the desired number, and then press the Enter key.
|
Figure 1.37 (a): Font type and size |
NOTE: The Font size can also be changed by clicking on the Increase Font Size
button to increase or Decrease Font Size button to decrease the
font (see Figure 1.37(b)).
|
Figure 1.37(b): Buttons to increase and decrease font size |
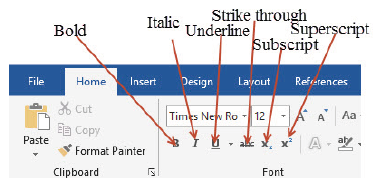
Applying font attributes
Formatting attributes such as bold, italic, or underline call the attention of readers to particular parts of your text. Figure 1.38 shows different formatting attributes,in a font group.
|
Figure 1.38: Formatting attributes |
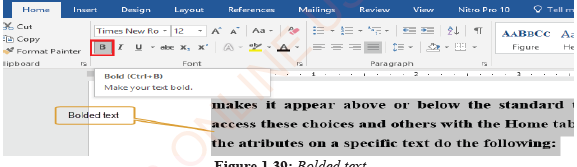
Additionally, you can assign a superscript or subscript notation to any text that makes it appear above or below the standard text. Subscript is the character such as a number or a letter that is slightly below the normal line (baseline). For example, in H2O, 2 is a subscript. Superscript is a character such as a number or a letter that is set slightly above the baseline. For example, in x3, 3 is a superscript. These attributes and others are found on the Home ribbon. In order to apply the attributes on a specific text, do the following:
(i)Select the text where the attributes will be applied,
(ii) Point and click on the attribute you want to apply, for example, Bold as shown in Figure 1.39.
|
Figure 1.39: Bolded |
Changing font colour and highlighting text
Font colour is used to emphasise some text in the document. If the document has a text that needs to get special attention from the reader, its colour can be changed or highlighted.
Changing font colour
To change the font colour, follow the following steps:
(i) Select the text you want to change,
(ii) Click the down arrow next to the colouricon . It is usually displayed as letter Aunderlined with some colour as shown in Figure 1.40.
| Figure 1.40: Font colour |
After clicking on the down arrow for the colour, select the colour you want for your text.
Highlighting a text
To highlight a text, the following steps are used:
(i) Click the Home tab,
(ii) In the Font group, click the text highlight button arrow to select the colour,
(iii) Drag the mouse over the text you want to highlight. The text becomes highlighted just like using a highlighter on a regular paper, but far neater as shown in Figure 1.41.
| Figure 1.41: Highlighting text with colour |
(iv)Click the text highlight button to return the mouse to normal operation.
Text alignment
MS Word program has a feature that allows the user to either align a text to the left, right, centre, or justify. By default, MS Word aligns a text to the left margin of thedocument. However, there may be times when you want to adjust text alignmentto the centre, right, or justify. To align a text, do the following:
(i) Select the text you want to align,
(ii) On the Home ribbon, select one of the four alignment options from the
Paragraph group. Figure 1.42 shows the alignment options in Paragraph group.
| Figure 1.42: Text alignment |
NOTE: Alignment is, therefore, the act of arranging your text in different positions based on choice or the purpose of the text. There are four kinds of text alignment namely left, right, centre and justify.
Left alignment
Left alignment means that each line will start from the left margin. Left alignment is commonly used for body text and make the document easier to read.
Right alignment
Right alignment means that each line will finish on the right hand margin. The starting position of each line will be different based on the length of the line. Right alignment is used for small sections of content, such as text in header and footer.
Centre alignment
Centre alignment means that each line will be displayed with equal spacing on either side. This setting is mostly used to print title, header and quotes of any text.
Justify alignment
Justify alignment means that each line will start on the left side and finish exactly on the right margin. The extra space will be adjusted among the words. Justified text looks neat as words are evenly distributed to both sides of the page.
NOTE: If you want to change the alignment of a paragraph, select the text and then place the cursor on the alignment style you want, then click on it.
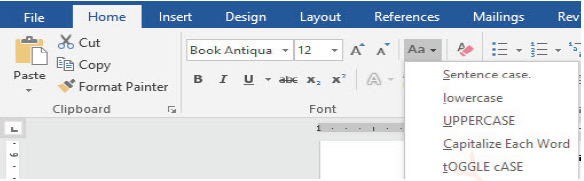
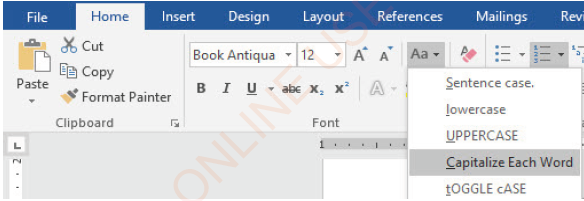
Changing text case
There is a time when text cases need to be changed. The Change Case command helps to change case, instead of deleting and retyping a text. To change the text case, follow these steps:
(i) Select the text you want to modify,
(ii) On the Home ribbon, in the Font group, click the Change Case command arrow. A drop-down menu will appear as in Figure 1.43.
|
Figure 1.43: Text case |
(iii) Click the desired case option from the menu, like “Capitalise Each
Word”, as shown in Figure 1.44.
|
Figure 1.44: Capitalisation of each word |
| Activity 1.10: Formatting a text (i) Type the names of the subjects you learnt in primary school. (ii) The title of text should be “PRIMARY SCHOOL SUBJECTS”. (iii) Bold the title. (iv) Increase the size of the title to 24 points. (v) Change the colour of the first subject to blue. (vi) Change one of the subject names to Italic style. (vii) Change the remaining subject names to bold and italic style. (viii) Save the file as “my primary school subjects”. |
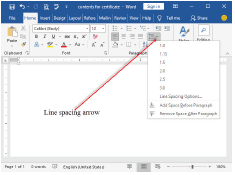
Line spacing
The space between each line of a paragraph is called line spacing. It is set to 1 by default in MS Word. It can also be set to 1.5, 2, or to other values. Spacing enables easy reading of the text. Use the paragraph spacing button on the Home ribbon to change the line spacing.
(i) Click on line spacing drop-down arrow as shown in Figure 1.45,
|
Figure 1.45: Line spacing options |
(ii) Move your cursor over each of the built-in spacing options, and notice how the line spacing changes. Figure 1.45 indicates the drop-down menu of the line spacing command.
(iii) Click the option you want.
Bulleting and numbering
In MS Word, bulleted lists and numbered lists can be applied to a text whenever listing of items is needed. Numbered lists can be created using commands in Paragraph group of the Home ribbon, as shown in Figure 1.46.
|
Figure 1.46: Bullet and number |
Listing items using bullets
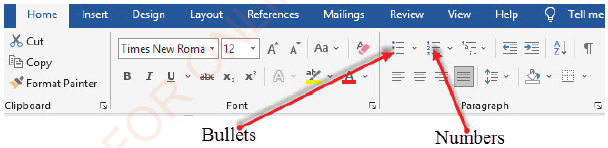
As mentioned earlier, bullets can be added to a text whenever listing of items is needed. To add a bullet to a text, do the following:
- Select the text you want to be in bullets,
- (ii) On the Home ribbon, in the Paragraph group, click the Bullets button
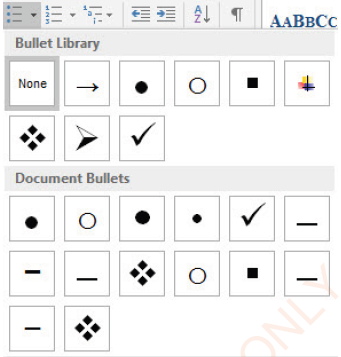
- arrow : the window like that in Figure 1.47 will appear,
- (iii) Click the bullet type of your choice.
|
Figure 1.47: Bullets types |
- Listing items using numbers
- As mentioned earlier, numbers can be added to the text whenever listing of items
- is needed. To add a number to a text, do the following:
- (i) Select the text you want to be numbered,
- (ii) On the Home ribbon, in the Paragraph group, click the Numbering
- button arrow ,
(iii) Click the numbering type you want from the list as shown in Figur1.48
|
Figure 1.48: Numbering type |
Copying formats
A format of a specific text can be copied and applied to other text in the MS Word document. This feature helps a user to save time and effort when more than one format has been applied to a text and you want to format an additional text with existing formats.
To copy a format, follow these steps:
(i) Select the text that has the format you want to copy.
(ii) On the Home ribbon, in the Clipboard group, click the Format Painterbutton as shown in Figure 1.49.
|
Figure 1.49: Format painter |
(iii) The mouse pointer changes to a paint brush with an I-beam .
(iv)Select the text to which you want to apply the copied format.
NOTE: If the copied format needs to be applied to more than one area, doubleclick the Format Painter button. This keeps the Format Painter active until you press the Esc key or click the format printer once again.
Drop cap
There are two types of drop cap, dropped and in-Margin. To apply the Drop cap,
follow the steps in Activity1.11.
| Activity 1.11: Applying drop cap Type the text “Education is an endless process, that someone get in and never lives unless he/she dies” Make the first letter as In-margin drop cap by following these steps: (i) Select the first letter, (ii) Click on Insert tab, (iii) In the Text group of the Insert ribbon, click Drop Cap, and then selectIn margin drop cap style. |
Results
|
|
Use the same steps to apply dropped drop cap style to a text.
Page break
Page break enables you to separate sections of a document so that they can appear as separate pages at the time of printing.
| Activity 1.12: Inserting page break Steps: (i) Click where you want to insert a page break, (ii) Click Insert tab, (iii) In the Pages group of the Insert ribbon, Click Page Break. |
Page numbering
MS Word allows you to insert page numbers in your document. There are different options you can use to insert page numbers. By default, numbering starts from 1 onwards. But you may use other numbering formats instead of the default one, or use different numbering styles in one document.
Inserting page numbers
Steps:
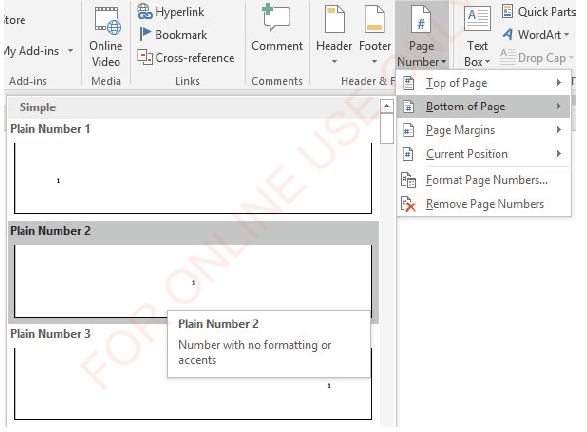
(i) Click on the page you want to insert a number,
(ii) Click Insert tab,
(iii) In Header and Footer group, click the Page Number arrow ,
(iv)Select the position you want your numbers to appear (top or bottom) as shown in Figure 1.50.
(v) Choose alignment (left, centre or right) and number style.
|
Figure 1.50: Inserting page number |
Inserting different numbering formats in the same document
Before you insert different numbering formats in the same document, insert section break in the pages you want to put different numbering formats.
Inserting section break
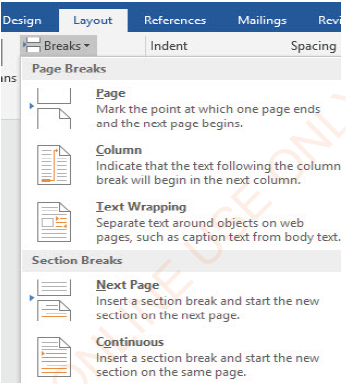
Steps:
(i) Position a cursor to the bottom of the page you want to separate,
(ii) Click on Layout tab,
(iii) In the Page Setup group of the Layout ribbon, Click Breaks: the window like that in Figure 1.51 will appear,
(iv)On Section Breaks, click Next Page.
|
Figure1.51: Inserting section break |
Inserting new style of numbers
Steps:
(i) In the Header & Footer group of the Insert ribbon, click the Page
Number arrow,
(ii) Click Format Page Numbers,
(iii) On the Page Number Format pane, set the number format and specify where and how you want the numbering to start, as shown in Figure 1.52.
| Figure 1.52: Page number format pane |
(iv) ClickOK,
(v) Go back to the Page Number menu,
(vi)Select the position of a page number,
(vii) Click.
Header and footer
Headers and footers identify a text in printed documents. Usually, headers and footers include text or graphics such as page numbers, company logo, document title, file name, or author’s name. A header appears at the top margin, while a footer appears at the bottom margin. MS Word gives an option of using the same header or footer throughout the document, or using different headers and footers at different parts of a document. You can also use different headers and footers on odd and even pages or certain parts of the document.
Footer insertion
To insert the footer, follow these steps:
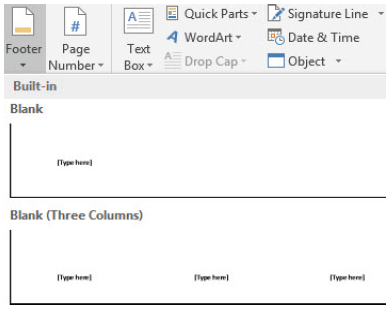
(i) Click Insert tab,
(ii) In Header and Footer group of the Insert ribbon, click Footer arrow to insert footer (see Figure 1.53),
(iii) Select the position (Left, Centre or Right) and style of the footer,
(iv)Click,
(v) Type the text for the footer,
(vi)Click the Close button.
|
Figure 1.53: Footer insertion |
Header insertion
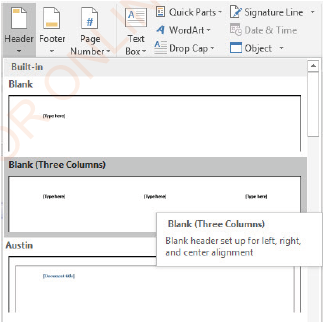
To insert the header, follow these steps:
(i)Click Insert tab,
(ii) On Header and Footer group of the Insert ribbon, click Header arrow to insert header,
(iii) Select the position (Left, Centre or Right) and the style of header as, shown in Figure 1.54,
(iv) Click,
(v) Type the text for the header.
|
Figure 1.54: Header insertion |
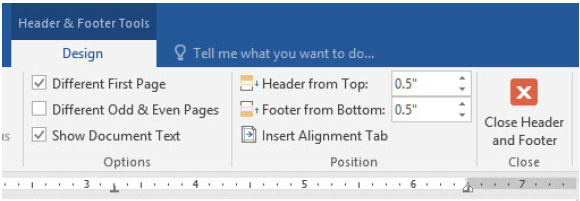
NOTE: After inserting the header and/or footer, click on Close Header and
Footer button, as shown in Figure 1.55, to close the header and footer window.
|
Figure 1.55: Closing the header and footer window |
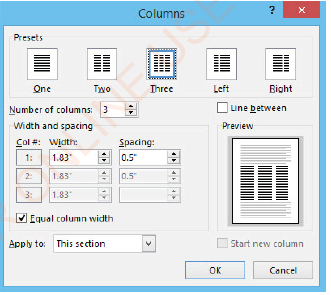
Column
MS Word provides tools that can help you to type your document or set it into columns. There are different styles of text columns. For example, you can have a one-column text, two-column text, and three-column text, which can either be aligned to the left or to the right as shown in Figure 1.56. The command also gives an option to insert a line between the divided text.
|
Figure 1.56: Column window |
To insert a column, follow these steps:
(i) Select the text you want to divide into columns,
(ii) Click Layout tab,
(iii) In the Page Setup group of Layout ribbon, Click the Columns arrow,
(iv)Click the style of the column one, two, or three columns
Table creation
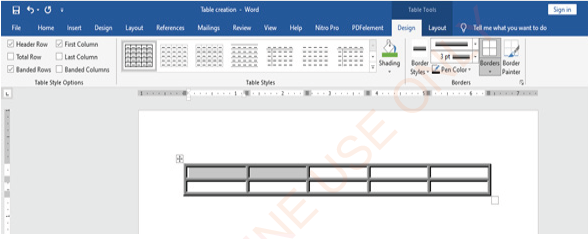
MS Word gives powerful tools to organise text in a table. A table is made of rows and columns. You can create a table by inserting it using the Table command on the Insert ribbon.
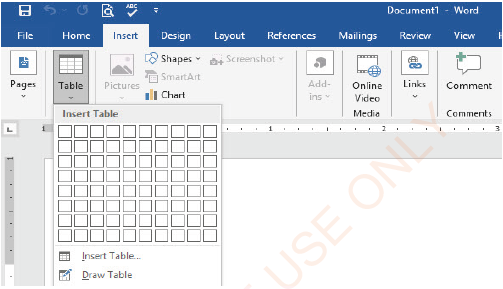
Inserting a table
To insert a table, follow these steps:
(i) Click on Insert tab,
(ii) Choose a Table command: the window similar to Figure 1.57 will appear.
(iii) Select the number of rows and columns.
|
Figure 1.57: Inserting a table by selecting the number of rows and columns |
Or
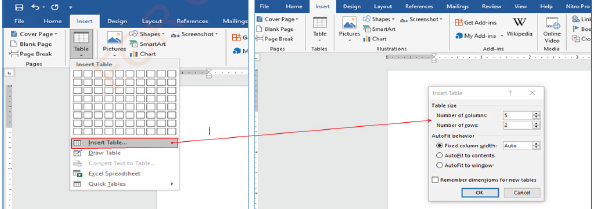
(i) Select the Insert Table option as shown in Figure 1.58(a), and
(ii) Specify the number of rows and columns, like 2 and 5 respectively, as shown
in figure 1.58(b).
|
(a) Inserting table (b) Specifying column and row |
Figure 1.58: Inserting a table by specifying the number of rows and column
(iii) Click OK: the table will be created as shown in Figure 1.59.
|
Figure 1.59: New table displayed after pressing OK button |
Editing and formatting of tables
Editing and formatting tables involve different attributes like introducing borders, merging cells, inserting rows or columns, deleting rows or columns, aligning text within cells, repeating heading rows, shading, and changing text direction.
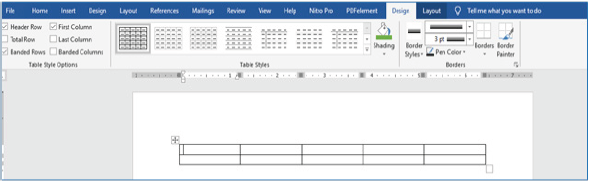
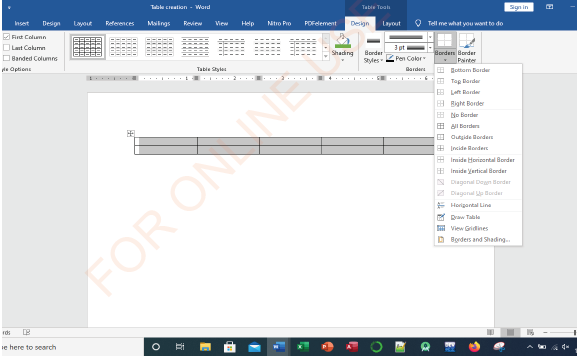
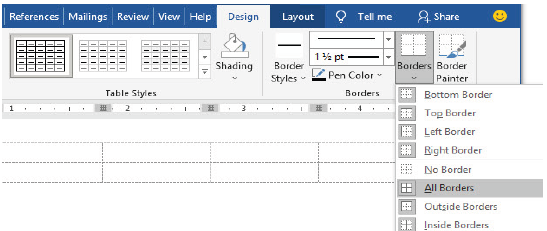
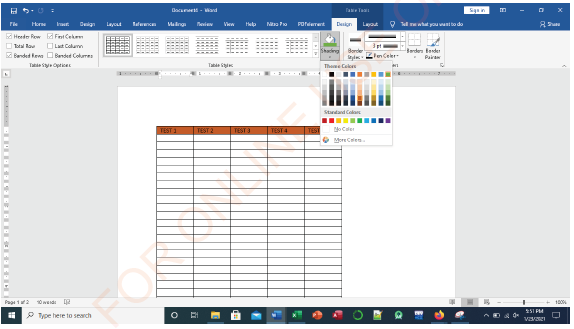
Introducing borders
(i) Select the cells to which you want to introduce borders,
(ii) On the Design ribbon, as shown in Figure 1.60, click the Borders command arrow,
|
Figure 1.60: Borders insertion menu |
(iii) Choose the type of border you want to apply to your table. In this case, All Borders, as shown in Figure 1.61, has been selected.
|
Figure 1.61: Inserting borders |
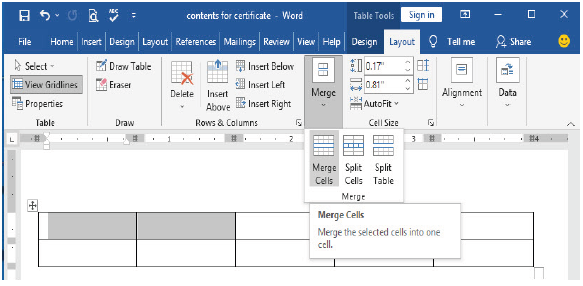
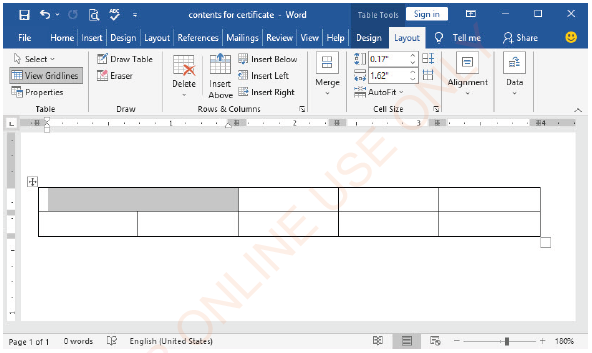
Merging cells
(i) Select the cells you want to merge like what is shown in Figure 1.62,
|
Figure 1.62: Cell selection |
(ii) Select the Layout tab under Table tools,
(iii) Choose merge cells as illustrated in Figure 1.63(a) and Figure 1.63(
|
Figure 1.63(a): Merging table cells |
|
Figure 1.63(b): Merged table cells |
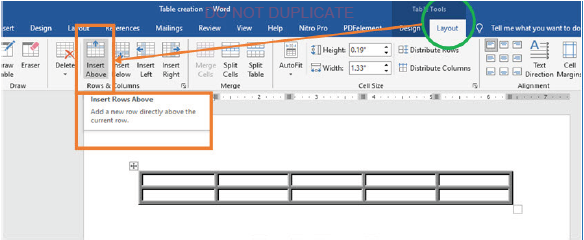
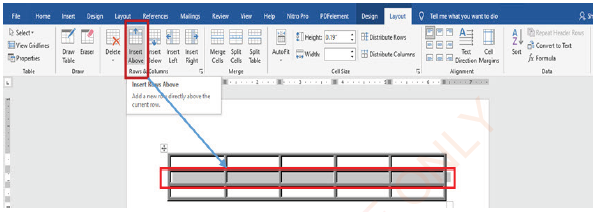
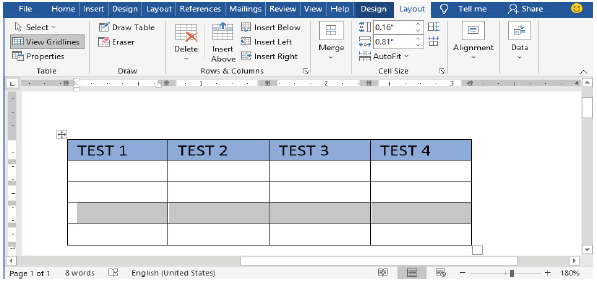
Inserting rows
(i) Select the row above which you want to insert a row, as shown in Figure 1.64(a),
(ii) Click Layout tab under Table tools,
(iii) Click either Insert Above or Insert Below. The new row is inserted as shown in Figures 1.64(b).
|
Figure 1.64(a): Inserting a row above the selected row |
|
Figure 1.64(b): View of inserted row |
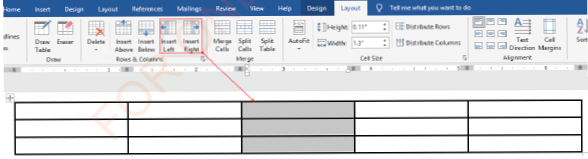
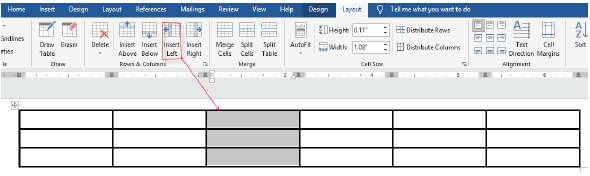
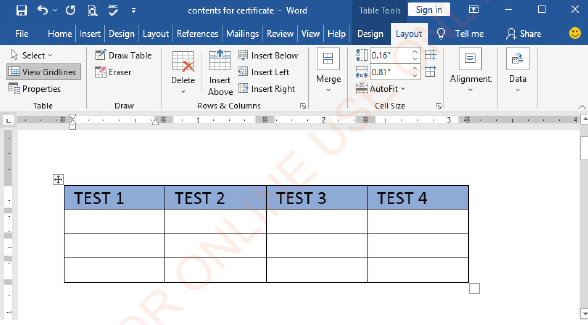
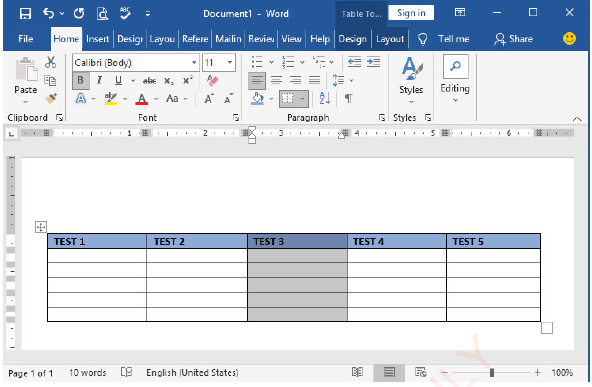
Inserting column
(i) Select the column after (or before) which you want to insert a column,
(ii) Click Layout tab under Table Tools,
(iii) Click either Insert Left or Insert Right as shown in Figure 1.65,
|
Figure 1.65: Inserting a column left or right |
(iv)The number of columns is increased by one as shown in Figure 1.66.
|
Figure 1.66: View of table column insertion |
Aligning text within the cells
Steps:
(i) Create the table,
(ii) Insert a text in the cell,
(iii) Select the text, as shown in Figure 1.67,
(iv) ClickLayout tab from Table Tools,
(v) Choose your desired text alignment as shown in Figure 1.68.
|
Figure 1.67: Text selection in table cells |
|
Figure 1.68: Text alignment in table cells |
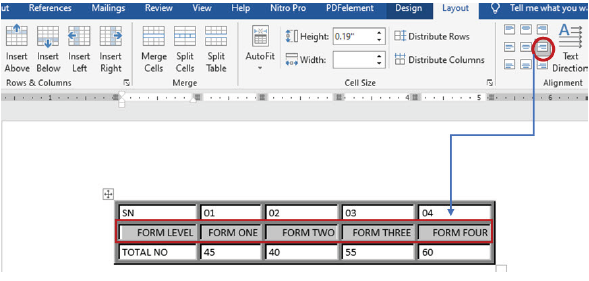
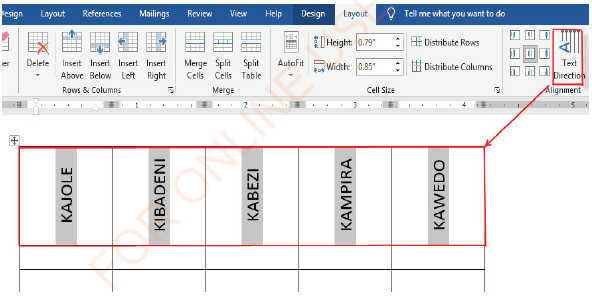
Changing text direction
Steps for changing text direction:
(i) Select the cells containing the text which direction you want to change,
(ii) Click Layout tab under Table Tools,
(iii) Click the text direction option of your choice as shown in Figure 1.69.
|
Figure 1.69: Text direction |
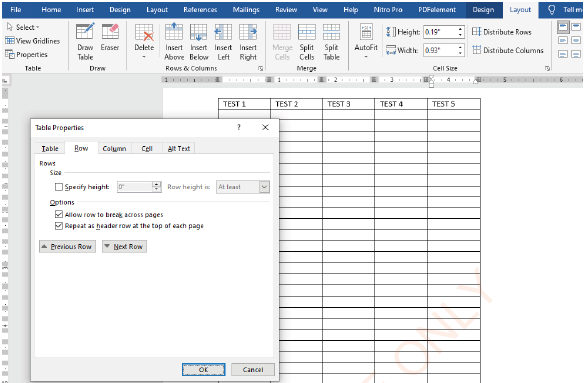
Repeating heading rows
Steps:
(i) Select the Heading row,
(ii) Click Layout tab under Table Tools,
(iii) Click Properties command under Table group to display table properties
options as shown in Figure 1.70,
(iv) ChooseRepeat as header row at the top of each page,
(v) Click OK.
|
Figure 1.70: Repeating the heading row |
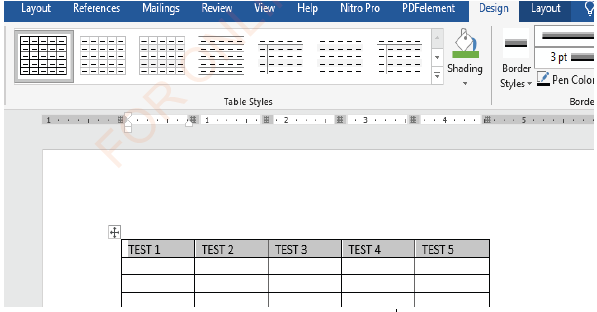
Text shading
(i) Select the row containing the text you want to shade as shown in Figure
1.71,
|
Figure 1.71: Row text selection |
(ii) On the Design ribbon, in Table Tools, select the shading option (see Figure 1.72),
| Figure 1.72: Shading selection |
(iii) Shade the text with the colour of your choice as in Figure 1.73.
|
Figure 1.73: Colour shading selection |
Deleting rows
Steps:
(i) Select the rows you want to delete,
(ii) Click the Layout tab under Table Tools,
(iii) Click Delete to access various options,
(iv) ClickDelete Rows from the drop down menu, as seen in Figure
1.74(a). A row will be deleted, reducing the number of rows, as seen in table 1.74(b).
(v)
|
Figure 1.74(a): Before row deletion |
|
Figure 1.74(b): After row deletion |
Deleting a column
Steps:
(i) Select the column you want to be deleted, as seen in Figure 1.75(a),
(ii) Click the Layout tab under Table Tools,
(iii) Click Delete to access various options,
(iv)Select Delete Columns from the drop-down menu. A column will be deleted, reducing the number of column, as seen in Figure 1.75(b).
|
Figure 1.75(a): Before column deletion |
|
Figure 1.75(b): After column deletion |
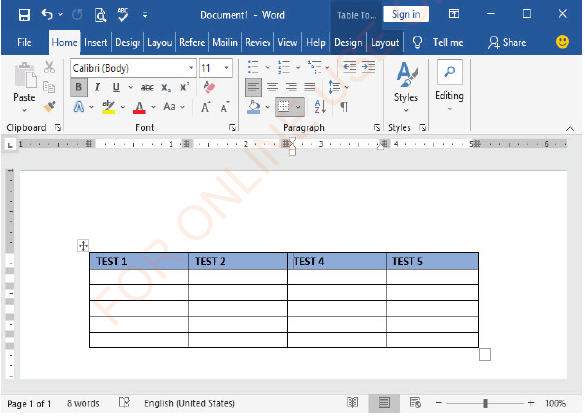
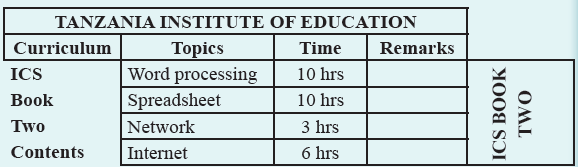
| Exercise 1.2 1. By using Microsoft Word, draw the following table
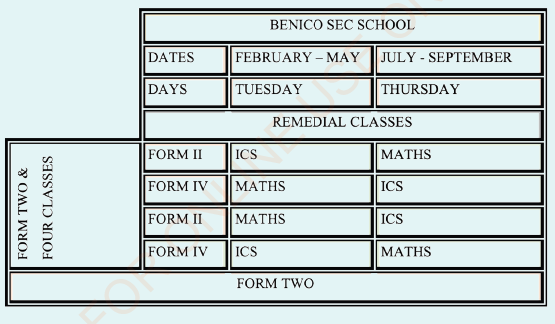
(a) Align the text direction in the column “Curriculum” to point downward (b) Change the style of the border (c) Merge the cells under the “Remarks” column (d) Type “Learning the use of technology” in the Remarks column (e) Save your work as ICS timetable 2. Use MS Word to create the following table:
3. Type the following text, separate it into two columns, have a line in between, and apply justify alignment. “Editing and Formatting of tables involve different attributes like introducing borders, merging cells, inserting rows or column, deleting rows or columns, aligning text within the cells, repeating heading rows, shading and changing text direction.” |
Printing a document
Page setup
MS Word automatically helps you to set the way you want your document to appear when printed. It involves setting orientation and margins. There are two types of orientation namely portrait and landscape.
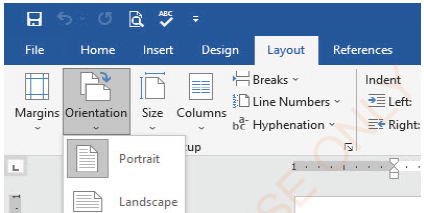
Setting orientation
Steps:
(i) Click Layout tab,
(ii) In the Page Setup group of the Layout ribbon, click the Orientation command arrow,
(iii) Choose the orientation you want as shown in Figure 1.76(a).
|
Figure 1.76(a): Orientation options |
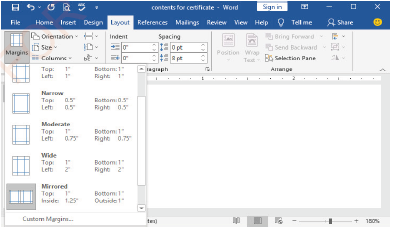
Setting margins
Steps:
(i) Click Layout tab,
(ii) In the Page Setup group of the Layout ribbon, click the Margins command,
(iii) Click on the margin of your choice as shown in Figure 1.76(b).
|
Figure 1.76(b): Setting page margin |
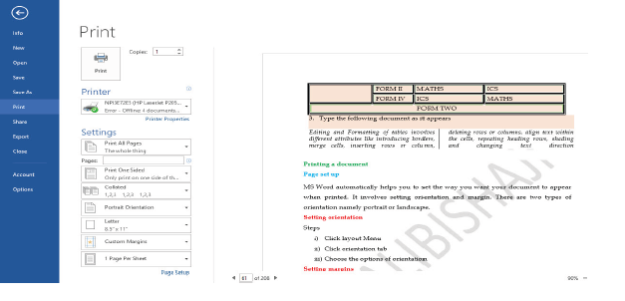
Previewing a document
Before printing the document, you can preview it to see how it will look like when printed. You can view one or more pages at a time, increase or reduce the size of the page on the screen, and check page breaks.
To preview a document before printing, follow these steps:
(i) Click on File tab,
(ii) Click the Print Command on the Backstageview. Figure 1.77 shows how a previewed page looks like.
|
Figure 1.77: A previewed document |
Printing a document
To print a document, a computer needs to be connected to a printer. To print a word document, follow these steps:
(i) Click File tab,
(ii) Click Print command on the Backstage view,
(iii) Choose the printer connected to your computer,
(iv)Under settings, choose how you prefer your printed document to appear,
(v) Select the number of copies you want to print,
(vi) If you are satisfied with the appearance of your previewed document, click the Print command to print your document as shown in Figure
|
Figure 1.78: Printing a document |
Using MS Word help facility
MS Word Help is a collection of tools and files which help to answer questions, offer tips, and provide help on all MS Word features. MS Office Help tools assist you when you need more information about a particular task or feature. Accessing the help facility in MS Word can be performed using the following steps:
(i) Open a blank MS Word document,
(ii) Press F1 key on the keyboard: A help window will open as shown in
Figure 1.79.
|
Figure 1.79: Word help pane (Offline) |
| Activity 1.13: MS Word individual project Imagine that you are a shop owner offering a range of products and services including stationeries, mobile money such as M-pesa, TigoPesa, Airtel money, T-pesa, Halopesa, Easy Pesa, and banking such as CRDB, NMB and NBC agents. Write a 2-page MS Word report required by the trading office in your area on quarterly basis by doing the following: (i) Write two paragraphs briefing your business history and operations. (ii) Using a roman numbered list, list all items sold in the shop. (iii) Bold the items which are most preferred by customers. (iv) Add a table showing sales records for three months. (v) Add borders to your table. (vi) Add a drop-cap style in the first paragraph. (vii) Add page numbers, header and footer in the report. (viii) Write a concluding paragraph of the report. (ix) Save the file on the Desktop as Myshop. |
| Exercise 1.3 Review Questions A. Multiple choice questions Choose the letter of the most correct answer and write it in the provided box 1. The _____ defines the appearance and shape of letters, numbers, and special characters. (a) font type (b) font size (c) insertion point (d) paragraph formatting 2. The scroll box on the vertical scroll bar indicates the _____. (a) position of the insertion point from the top of the page (b) distance of the insertion point from the left margin (c) current relative location of a document portion displayed in the window (d) distance of the insertion point from the right margin 3. _____ is the process of changing the way letters, numbers, punctuation marks, and symbols appear on the screen and in print. (a) printing document (b) editing character (c) formatting a document (d) shading text 4. To save an existing document with a different file name, click _____. (a) the Save button on the Standard toolbar (b) Save on the File menu (c) the Save As button on the Standard toolbar (d) Save As on the File menu 5. To erase a character to the right of the insertion point, press the _____ key. (a) cancel (b) backspace (c) delete (d) enter B: Filling in the blanks Write a correct word or statement to complete each of the following sentences 1. ………………………is one of the software used for word processing. 2. The spelling checker can find and flag some ………………………spelling errors. 3. A style of text that makes a letter or word darker and thicker to stand out in a document is called …………………. 4. .……………………………. text is very important as it identifies which text in a document you want to modify. 5. The type of alignment for ensuring the text starts on the left margin and ends exactly on the right margin is called ……………………… C: Short answer questions Answer the following questions 1Briefly explain the applications of word processing in your school and community. 2. Explain how the use of word processors has reduced the use of typewriters. 3. Explain the advantages of MS Word as a word processing application. 4. Describe in details the functions of the Vertical and Horizontal Scrollbars. 5. Baraka has finished typing the letter. Print Preview shows that it is more than one-page long. State two ways in which the letter could be made to fit on one page. 6. (a) A form two student is asked to write an essay about his/her school. Unfortunately, the word “school” has been typed several times as “schol”in the document. It is possible to change the misspelled word throughout the document in one operation. Name the feature which would enable this to be done. (b) The first word in the following sentence has been typed as “their”instead of “there”. “Their will be coffee served on entrance”. This has been shown as an error on the document. Which feature of the word processing package detects this kind of error? 7. Explain two different types of section breaks and how they are used. 8. How do page setup margins control the text flow in a document? 9. Explain the difference between spelling errors and grammatical errors, as they appear in the Spelling and Grammar checker. 10. Explain the difference between: (a) Save and Save As (b) Copy and Paste (c) Copy and Cut 11. Explain why you need to preview a document before printing. 12. What is the function of the following combination of keys? (a) Ctrl + A (b) Ctrl + Page Up (c) Ctrl + Home (d) Ctrl + B (e) Ctrl + E (f) Ctrl + Z (g) Ctrl + F (h) Ctrl + V (i) Ctrl + X (j) Ctrl + SHIFT + HOME 13. Explain the use of the following features in MS Word: (a) Find and Replace (b) Undo and Redo (c) Thesaurus (d) AutoCorrect 14. Differentiate between selecting and highlighting a text. 15. List the steps you would follow to correct wrongly spelled words in a document. 16. Explain the meaning of the following terms as used in word processing: (a) Word wrap (b) Italicising a text (c) Page Break (d) Header (e) Footer (f) Indenting (g) Alignment (h) Bullets 17. (a) What is document formatting? (b) List any five document formatting features. (c) Differentiate between ‘Superscript’ and ‘Subscript’ in a word processor. (d) State one function of Drop Cap in a document. 18. (a) Explain the importance of page numbers in a document. (b) Explain how you can give different page numbering styles to different pages in a multi-page document. (c) Give four uses of the Horizontal ruler in MS Word. |
www.learninghubtz.co.tz
| Exercise 1.3 Review Questions A. Multiple choice questions Choose the letter of the most correct answer and write it in the provided box 1. The _____ defines the appearance and shape of letters, numbers, and special characters. (a) font type (b) font size (c) insertion point (d) paragraph formatting 2. The scroll box on the vertical scroll bar indicates the _____. (a) position of the insertion point from the top of the page (b) distance of the insertion point from the left margin (c) current relative location of a document portion displayed in the window (d) distance of the insertion point from the right margin 3. _____ is the process of changing the way letters, numbers, punctuation marks, and symbols appear on the screen and in print. (a) printing document (b) editing character (c) formatting a document (d) shading text 4. To save an existing document with a different file name, click _____. (a) the Save button on the Standard toolbar (b) Save on the File menu (c) the Save As button on the Standard toolbar (d) Save As on the File menu 5. To erase a character to the right of the insertion point, press the _____ key. (a) cancel (b) backspace (c) delete (d) enter B: Filling in the blanks Write a correct word or statement to complete each of the following sentences 1. ………………………is one of the software used for word processing. 2. The spelling checker can find and flag some ………………………spelling errors. 3. A style of text that makes a letter or word darker and thicker to stand out in a document is called …………………. 4. .……………………………. text is very important as it identifies which text in a document you want to modify. 5. The type of alignment for ensuring the text starts on the left margin and ends exactly on the right margin is called ……………………… C: Short answer questions Answer the following questions 1Briefly explain the applications of word processing in your school and community. 2. Explain how the use of word processors has reduced the use of typewriters. 3. Explain the advantages of MS Word as a word processing application. 4. Describe in details the functions of the Vertical and Horizontal Scrollbars. 5. Baraka has finished typing the letter. Print Preview shows that it is more than one-page long. State two ways in which the letter could be made to fit on one page. 6. (a) A form two student is asked to write an essay about his/her school. Unfortunately, the word “school” has been typed several times as “schol”in the document. It is possible to change the misspelled word throughout the document in one operation. Name the feature which would enable this to be done. (b) The first word in the following sentence has been typed as “their”instead of “there”. “Their will be coffee served on entrance”. This has been shown as an error on the document. Which feature of the word processing package detects this kind of error? 7. Explain two different types of section breaks and how they are used. 8. How do page setup margins control the text flow in a document? 9. Explain the difference between spelling errors and grammatical errors, as they appear in the Spelling and Grammar checker. 10. Explain the difference between: (a) Save and Save As (b) Copy and Paste (c) Copy and Cut 11. Explain why you need to preview a document before printing. 12. What is the function of the following combination of keys? (a) Ctrl + A (b) Ctrl + Page Up (c) Ctrl + Home (d) Ctrl + B (e) Ctrl + E (f) Ctrl + Z (g) Ctrl + F (h) Ctrl + V (i) Ctrl + X (j) Ctrl + SHIFT + HOME 13. Explain the use of the following features in MS Word: (a) Find and Replace (b) Undo and Redo (c) Thesaurus (d) AutoCorrect 14. Differentiate between selecting and highlighting a text. 15. List the steps you would follow to correct wrongly spelled words in a document. 16. Explain the meaning of the following terms as used in word processing: (a) Word wrap (b) Italicising a text (c) Page Break (d) Header (e) Footer (f) Indenting (g) Alignment (h) Bullets 17. (a) What is document formatting? (b) List any five document formatting features. (c) Differentiate between ‘Superscript’ and ‘Subscript’ in a word processor. (d) State one function of Drop Cap in a document. 18. (a) Explain the importance of page numbers in a document. (b) Explain how you can give different page numbering styles to different pages in a multi-page document. (c) Give four uses of the Horizontal ruler in MS Word. |
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania