CHAPTER 01: WORD PROCESSING
Starting and Ending a Wording Processing Program
The Meaning of Word Processing
- Explain the Meaning of Word Processing
Word processing is the process of creating, editing, storing and printing typed documents. One is able to write text, store it electronically, display it on a screen, modify it by entering commands and characters from the keyboard, and print it.
The Importance of Word Processing
- Explain the Importance of Word Processing
The importance of word processing are as following:
- Saves time— Word processing helps teachers use preparation time more efficiently by letting them modify materials instead of creating new ones. Writers can also make corrections to word processing documents more quickly than they could on a typewriter or by hand.
- Enhances document appearance— Materials created with word processing software look more polished and professional than handwritten or typed materials do.
- Allows sharing of documents— Word processing allows materials to be shared easily among writers. Teachers can exchange lesson plans, worksheets, or other materials on disk and modify them to fit their needs. Students can also share ideas and products among themselves.
- Allows collaboration of documents— Especially since the release of Google Docs, teachers and students can now create, edit, and share documents synchronously.
Start and End a Word Processing Program
STARTING MICROSOFT WORD
- There are two alternatives.
- Alternative 1, Using start button
- Click start button, the menu will appear
- Start all programs
- Select Microsoft office, the group menu will appear.
- Double click Microsoft word 2003-2016 the window will appear
- Alternative 2,Using keyboard
- Press window log key.
- Select all programs for double click on Microsoft word 2003-2016
- NOTE:If you select all programs follows procedure 3 and 4 above other wise
- The window will appear.
Create a Word Processing File
CREATING DOCUMENT USING MICROSOFT WORD
- Microsoft word, commonly referred to as word, is the most common word processor. The five commonly used versions of word 97, 2000, 2002(XP), 2003, 2007, 2010, 2013 and 2016. While word 97-2003 look alike and are compatible, word 2007 radically divorces from these in the look and manually out, there is no file menu and once text is highlighted a float formatting tool bar is displayed above the selected text. More over document saved in 2007 format cannot be opened in previous version unless you saved the file in compatibility mode for consistency: we shall use the word processing software called Microsoft word 2003.
- Typing text: When typing, once the cursor reaches the end of the current line automatically jump to the next line. If one word does not in current line automatically wraps at the beginning of the next line. This is referred as word wrap.
Save a Word Processing File
Saving file
- On the menu, click the “save as” command
- Select the storage location from the “save in” list box
- Type the name of the file in the “file name” box the click “ok”
Editing and Formatting
EDITING A DOCUMENT
- Making changes or modifying an existing document is called editing, some editing operations includes;
Deleting text
- To delete a character, a word or a block of text
- Highlight the text to be deleted
- Press the “delete” key or the “backspace” key
Find and replace
- Find and replace is used to locate a word or a phrase and replace the target word or phrase.
Spelling and grammar checker
- Spelling and grammar checker automatically locate misspelled words and grammatical mistakes
- Check a document spelling and grammar
- On tools menu bar click spelling and grammar or press F7
- In the spelling and grammar dialog bar. Misplace words are shown in red while grammatically incorrect phrases are in green.
- From the suggestion list, select the correct spelling and grammar.
- Click change (all) button. To ignore, click the ignore (all) button.
LIMITATION OF SPELL CHECKER
- Names of people and places are not usually included.
- The same two words in a row may not be deleted
- If a word is spelled incorrectly but used in the wrong context it will not be deleted
- Quality of dictionaries can vary
Thesaurus
- The thesaurus allow the user to automatically find the words or phrases with similar meaning (synonyms) or opposite meaning (antonyms) to the one deleted.
To use the thesaurus
- On the insert menu, point to auto text and then click auto text command.
- Click the auto correct or auto text tab and type the auto correct or auto text.
- Click to apply and close the dialog box.
Undo and Redo
- Undo reverses the most recently command while redo reverts back to the cancelled action.
- Click the edit menu, click undo or redo. Alternatively, press ctrl + Z to undo or ctrl + Y to redo
Format a Word Document
Formatting refers to enhancing the appearance of the document. You format text, paragraphs, pages, or the entire document.
Text formatting
- We format text by applying different font types, style, size, color and another attributes.
Text font
- To format text font
- Highlight the text to be formatted
- On the format menu, click font
- In the font dialog box, select the font, style, size and color
- Apply other font attributes then click ok
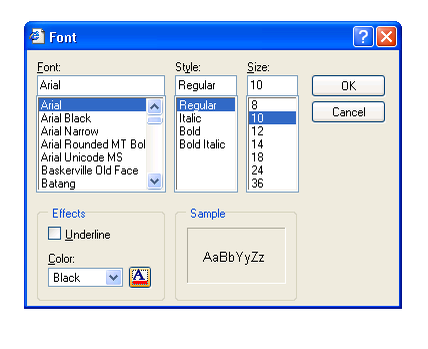
Font Dialog Box
Case
- The cases applied to text are: lower case, upper case, sentence case, title case and toggle. The use of case in these sentences is deliberate
To change case
- Highlight the text
- On the format menu, click change case
- In the change case dialog box, select case then click ok
Superscript and subscript
- Superscript appears just above the rest of the character as in cm2 superscript.Subscript appears just below other characters as in H2O subscript
To make text superscript or subscript
- Highlight characters
- On the format menu click font
- On the font dialog box check superscript or subscript
Paragraph of formatting
- A paragraph is a separate block of text dealing with a single theme and starting on a new line or what. Some of the formatting features you can apply in to a paragraph include alignment, setting tabs and indents, drop cap, bullets and numbering, line, spacing, inserting column and page breaks.
- Alignment is the arrangement of text relative to the left margin, Center of the page or the right or the right margin. The five major alignment options available are the left, center, right, justified and forced justified.
To align text
- Highlight the text
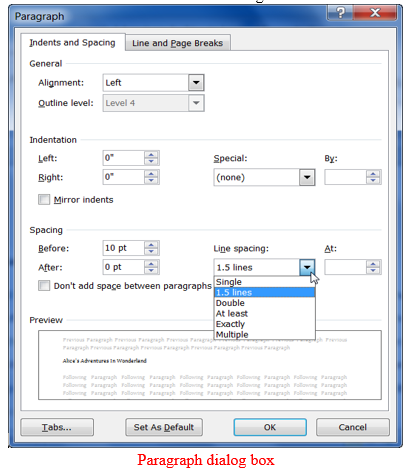
- On the format menu click paragraph.
- In the dialog box, select the alignment option then click ok
Note: you can apply alignment by simply clicking any of the five alignment buttons on the formatting toolbar
Line spacing
- You can set the space between line, paragraphs or blocks of text
To space line
- Highlight the lines of text
- On the format menu, click paragraphs dialog box.
- In the paragraph dialog box, select the line spacing option from the line spacing list box then click ok button
Setting tabs and indents
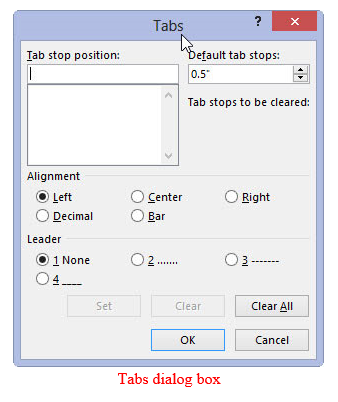
- Tab refers to definite cursor stop when the tab key is pressed. Indenting is moving a sentences or block of text away from the margin using the tab key.
To set tabs and indents
- On the format menu click tabs
- In the dialog box, set the tab stop, alignment and leading then click ok
- Press the tab key to increase or the space bar to decrease the indent.
- Alternatively click the increase/decrease indent buttons on the formatting tool bar.
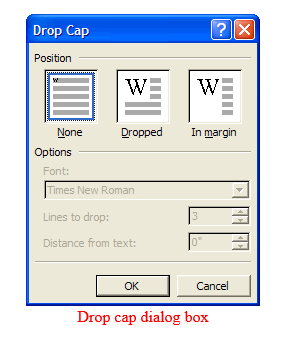
Drop cap
- A drop cap is a large character in a paragraph that occupies more than one line down.
To create a dropped cap
- Highlight the paragraph you want to begin with drop cap
- On the format menu, click drop cap
- Click dropped or in margin
- Specify the number of lines & other options then click ok
BULLETS AND NUMBERING
- Bullets and numbers are used to create ordered list
To add bullets or numbers.
- Highlight the text
- On the format menu, click columns
- In the columns dialog box enter the number of columns, set the column width then click ok
PAGE AND COLUMN BREAKS
- Page, section and column breaks are to force the cursor to a new page section or column even before the end of the current.
To insert a break.
- Position the insertion pointer where you back want to create a break
- On the insert menu, click break
- In the break dialog, set the break type the ok
PAGE SETUP
- Page setup options let you define the paper size, margins and operations.
To set up a page
- On the file menu, click page setup
- In the page setup dialog box
- Click any of the following; Margins tab to set up page margins,Paper tab to specify the paper type and orientation and Layout tab to specify the page content layout relative to the margins
- Click to apply the setting
PAGE NUMBERING
- Page numbers are used to organize a large document for case of reference
To insert page numbers
- On the start menu, click page numbers
- In the position box, specify whether to place the page numbers at the top of page (header) or at the bottom of the page (footer)
- In the alignment box-specify whether to align page numbers to the left, center or right of the page
- If you don’t what a number on the first page, clear the show number on the first page check the box then click ok
- Note: click on the format button to specify other page options such as numbering type and font.
HEADER AND FOOTER
- Header are lines of text that appear at the top margin every page or selected pages while footer appear at the bottom margin
To insert header and footer
- On the view menu, click header and footer
- To create a header, enter text or graphical object in the header area
- To create footer, click inside the footer area and enter the text or graphical object
- Click CLOSE on the header and footer tool bar
FOOT NOTES AND END NOTES
- Footnotes and endnotes are used in large documents to explain, comment or provide reference for text in a document. Footnotes appear at the bottom of the page while endnotes appear at the end of a section or a document.
To insert footnote or endnote
- On the insert menu, point to reference and click footnote. A dialog box is displayed.
- In the location section, click footnotes or endnotes and specify the location of the footnotes or endnote
- In the format section, specify the number type start and continuity.
- Click insert.
CREATE AND MANIPULATING TABLES
- A table is made up of rows and column of cells. It is used to organize and present information in rows and columns
To create a table
- Click where you want to insert the table
- From the table menu, point to insert and then click table
- In the dialog box, set the number of the column and rows
- Specify the auto format option if needed to be
To delete rows or columns
- Select the row
- On the table menu, point to delete then click row/column
To insert rows or columns
- Click the insertion pointer where you want to insert the row/column
- On the table menu, point to insert then click/column
To merge cells
- Highlight the cells
- On the table menu, click merge cells
To split cells
- Highlight the cell to spilt
- On the menu, click split cell
- Enter number of rows or columns
Performing calculations in a table
- To calculate numerical values in a table, use cell references. A cell is a cross-section of rows and column. Column is represented by letter A, B, C. while rows are represented by 1, 2, 3…….as shown below
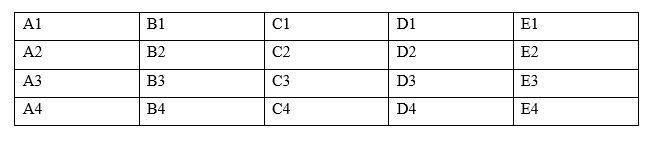
- Place the insertion pointer to where you want the result to be displayed
- On the table menu, click formula
- Type a formula in the formula box e.g. = (A1 , E1)
- Click ok
- Note: you can select a formula from past function list and ABOVE and LEFT instead of typing a formula and using cell references respectively
Printing a Document
Word processing is not complete without producing a hard copy
A hard copy (or "hardcopy") is a printed copy of information from a computer
Sometimes referred to as a printout , a hard copy is so-called because it exists as a physical object. The same information, viewed on a computer display or sent as an e-mail attachment, is sometimes referred to as a soft copy.
To print a document
- Preview it by click “print preview” on the file menu
- Click print from the file menu
- Select the printer range, number of copies and other options then the dialog box
Help Facility
Help Facility
Use Help Facility
The help facility has been included in the Windows operating system since Windows 95, the help files are installed as part of the installation. It looks different in every version of Windows but the basic idea is the same. You can usually press the “F1” key to access help regarding your current program.
Microsoft Word is a great word processing program but help button differ depending on which version you uses.
- Some users who upgrade from Word 2003/XP (2002)/2000 to 2007/2010/2013/2016 will find it hard to get the Help button, because all the buttons are relocated and organized in a new way. This article focuses on how to find out the Help button
Help Menu
Use help Menu
Just take Microsoft Word 2010 for example. With Classic Menu for Word 2007/2010/2013/2016 installed, you can click Menus tab to get back the classic style interface. The Help menu lies in the right most of the toolbar. 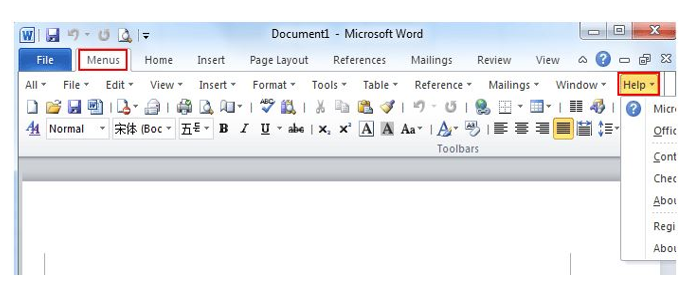
If you have no Classic Menu for word installed
Method 1:
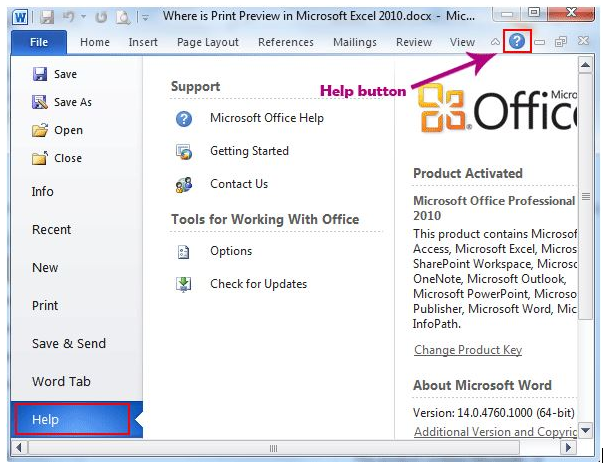
- The Help button in Word is too small that will be easily ignored. Actually the Help button stays in the top right corner of the window. The button looks like a question mark surrounded by a circle. The following picture shows its position. Or you can use the shortcut key F1 to enable the Help window.
Method 2:
- The Help menu has been added into the Word 2010 backstage. Click File, and you can find Help in the pane.
Classic Menu for Office
- Classic Menu for Office is the software designed for the people who are accustomed to the old interface of Microsoft Office 2003, XP (2002) and 2000. It brings back the classic menus and toolbars to Microsoft Office (includes Word) 2007, 2010, 2013 and 2016. The classic view helps the people to smoothly upgrade to the latest version of Office, and work with Office 2007/2010/2013/2016 as if it were Office 2003 (and 2002, 2000).
www.learninghubtz.co.tz
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania






