CHAPTER 01 : INFORMATION
By end of this topic, you should be able to:-
- Develop skills of using information and communication media
- To define data and able to relate data and information
- To identify sources of information and to apply skills of using different accessories of the computer to process data and information.
- To state the importance of information and list the traditional ways and modern ways of disseminating Information
- Compare and contrast modern and traditional ways of disseminating information
- Describe the communication media and use communication media equipment
The meaning of Data
Data and information are used interchangeably but they are quite different.
Consider this example: when a student is admitted at school he/she fills a form with details such as parents names, date of birth, place of domicile , address ,phone number and so on, those details are referred as data. When such data are used by the school authority then the school get the information about a particular student.
Data can be defined as facts about something that can be used in calculating, reasoning or planning.
Data (Input) is a collection of unprocessed items, which can include text, numbers, images, audio, and video which are later processed into information
Information conveys meaning to users , it is also known as processed data (output)
Data is any collection of numbers, characters or other symbols that has been coded into a format that can be input into a computer and processed.
Data on its own has no meaning or context.
It is only after processing by a computer that data takes on a context and becomes information.
Therefore information is an organized data which give meaningful sentence or statement.
Relationship of Data and Information
Relate Data and Information
Data and Information are closely interrelated to each other.
SIMILARITIES BETWEEN DATA AND INFORMATION
- Both data and Information can be presented in alphabets
- Both data and information can be Presented in numerals
- Both data and Information can be presented in symbols
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN DATA AND INFORMATION
| DATA | INFORMATION |
| i) data is a row fact which is unprocessed. | i) information is data that has been processed |
| ii) data is the lower level of knowledge | ii) Information is the second level of knowledge |
| iii) observation and recording are done to obtain data | iii) Analysis is done to obtain information |
The sources of Information
Identify sources of Information
What is the source of information?
An information source is a person, thing, or place from which information comes, arises, or is obtained. That source might then inform a person about something or provide knowledge about it. Information sources are divided into separate distinct categories, primary, secondary, tertiary, and so on.In simple words source of information means the origination of the message.
A) PRIMARY SOURCES OF INFORMATION
- Primary source of information allow learners to access original and unedited information. Primary source requires the learner to interact with the sources and extract information.
- Examples: personal interview, E-mail, discussion, debate, meeting, survey, observation etc.
B) SECONDARY SOURCES
- Secondary sources are edited primary sources, second hand versions. They represent someone else's thinking.
- Example Books, Encyclopedia, DVD's magazines, news paper, video tape, audiotape, TV, internet, website.etc.
C) TERTIARY SOURCES
- These sources are intermediate between primary and secondary sources .
- Example someone may read a news paper and pass the information to others through various means.
The importance of Information
Computers were originally used by scientists for calculating numbers, and have gradually become useful in offices and industries. In recent times, simplified models that can be used by almost everybody have become common in schools and homes for accomplishing many varied tasks and applications.
Lists the uses that computers are now commonly put to: writing letters, and reports, printing books, newspapers, and magazines, drawing pictures and diagrams, doing statistics, mathematics and handling financial records, controlling traffic lights, flying aeroplanes, making and playing music and video, sending messages anywhere in the world.
Internet The Internet is a global collection of many types of computers and computer networks that are linked together. It is increasingly becoming the solution to many information, problems, information exchange, and marketing describes the Internet as a mixture of many services with the two most commonly used being electronic mail (e-mail for short) and the World Wide Web (www). It plays a significant role in education, health, political processes, agriculture, economy, businesses and newsgroups.
With Internet connectivity, one can do business all over the world without physical contact with the buyer or the need for a business intermediary. E-mail Electronic mail (e-mail) is the exchange of text messages and computer files transmitted via communications networks such as the Internet .
The e-mail system as the equivalent of postal mailing services, with the biggest difference being the time and cost involved. And not only written data, but all sorts of information in the form of video, audio, or photographs, can be sent via e-mail.
E-mail as an increasing popular method of communication, especially in the workplace. Mobile phones is a telephone system that can move or be moved easily and quickly from place to place. Mobile phones were once the tool of rich and busy executives who could afford both the luxury. Mobile phones are now the ICT that is reshaping and revolutionizing the communications globally. Its impact on the economic activities of nations, businesses, and small entrepreneurs is phenomenal.
The availability of this new technology has been reshaping the material basis of the society as well as bringing about a profound restructuring of economic, political, and cultural relations among states.
In summary information is important because:
- It creates awareness.
- It educates people.
- It alerts people when there is danger.
- Information gives instructions.
- Information helps in decision making.
- Information can be used in advertising goods.
Information dissemination
WAYS OF DISSEMINATING INFORMATION
- i) Traditional Ways
- ii) Modern Ways.
Information dissemination is the process of spreading or distributing information using various ways from one individual to another. or Information dissemination is the process of making the information known to the general public.
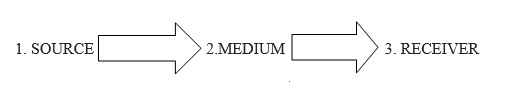
- SOURCE: This is the origin of the message. the source can be direct or indirect
- MEDIUM : This is the means or channel of spreading information such as newspaper , signs, magazines radio television telephone internet etc.
- RECEIVER : These are the intended audience to receive the message or information.
Traditional ways of disseminating Information
List the traditional ways of disseminating information
Uses traditional tools to spread information example songs, drums, poems whistle.
The modern ways of disseminating Information
List the Modern ways of disseminating Information
Uses modern tools to spread information example Internet, TV, Radio stations, magazines, posters, burners, fliers, websites, Social media like WhatsApp, Facebook, tango, immo, Instagram, tweeter etc.
The comparison of modern and traditional ways of disseminating Information
Compare modern and traditional ways of disseminating Information
THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN TRADIONAL AND MODERN WAYS
| TRADIONAL WAYS | MODERN WAYS |
| Slow in disseminating information | Quick and faster to disseminate information |
| Most of them are manually operated | They are electrically equipped |
| Message can be sent within short distance | They can cover a great distance |
| The information reaches few people | so many people can get information at a time. |
| The cost of sending the message is too high | The cost of sending message is very low |
Contrast modern and traditional ways of disseminating information
Contrast modern and traditional ways of disseminating information
THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN TRADITIONAL AND MODERN WAYS
| TRADITIONAL WAYS | MODERN WAYS |
| Slow in disseminating information | Quick and faster to disseminate information |
| Most of them are manually operated | They are electrically equipped |
| Message can be sent within short distance | They can cover a great distance |
| The cost of sending the message is too high | The cost of sending message is very low |
| The information reaches few people | Many people can get information at a time. |
The communication media
Communication media refers to the means of delivering and receiving data or information
Communication media can be classified into 2 categories
- guided media: the messages (data) are guided along a physical path. example of guided media include phone lines, twisted pair cables, coaxial cables and optical fiber
- unguided media: are media that allow the transmission of data without the use of physical means to define the path it takes(wireless). examples, Bluetooth, radio wave, microwave, infrared, Wi-Fi etc.
www.learninghubtz.co.tz
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania






