THE OFFICE OF THE PRESIDENT, REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT.
SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES
MARCH 2025
CHEMISTRY FORM FOUR
TIME: 2:30HRS
INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper consists of section A, B and C with total of eleven (11) questions
- Answer all questions in section A and B and two (2) question from section C
- Cellular phones and any unauthorised material are not allowed in the examination room
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s)
- Non programmable calculator may be used
- The following constant may be used Atomic masse:
- H=1, C=12, N=14, O=16, Na=23, S= 32, Ca=40, Cl= 35.5, Cu= 64 and Zn=65 Avogadro’s number = 6.02 x 1023
- GMV at s.t.p = 22. 4 dm3
- 1 faraday = 96,500 coulombs
- Standard pressure = 760 mm Hg
- Starndard tempreture = 273K
- 1 litre = 1 dm3= 1000cm3
SECTION A (16 Marks)
(Answer all questions in this section)
1. For each of the items (i –x) choose the most from the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in the answer sheet (booklet) provided.
(i) When water is added to an acid, the acid becomes
- More acidic and its pH goes down
- More acidic and its pH goes up
- Less acidic and its pH goes down
- Less acidic and its pH goes up
- Neutral and its pH become 7
(ii) 1.4g of potassium hydroxide is dissolved in water to form 250cm3 of Solution.
What is the Molarity of this solution?
- 0.001M
- 0.1M
- 1.4M
- 5.6M
- 6.0M
(iii) An electric current was passed through a concentrated solution of hydrochloric acid using carbon electrodes. The substance liberated at anode was.
- Copper
- Hydrogen
- Oxygen
- Sodium
- Chlorine
(iv) If element Q of group (H) combines with element R of group (IV) what will be the formula of the resulting compound.
- R2Q
- QR6
- R3Q
- R3Q
- Q2R
(v) The IUPAC name of H2SO4 is:
- Sulphuric (IV) acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Sulphuric (V) acid
- Sulphorous acid
- Sulphuric (VI) acid
(vi) Which of the following are the components needed to start fire?
- Match box, fire wood and kerosene
- Match box, fire wood and oxygen
- Oxygen, fuel and heat
- Oxygen, fuel and fire wood
- Heat, match box and oxygen
(vii) Which of the following is NOT a component of the first aid kit?
- Goggles
- A pair of scissors
- Dropper
- Gloves
- Razor blade
(viii) Which among of the following chemical reactions rapidly releases energy in form of light and heat?
- Combustion
- Decomposition
- Displacement
- Neutralization
- Precipitation
(ix) Laboratory Technician prepared a solution containing 26.5g of anhydrous Sodium carbonate in 5 dm3 of the solution and provided to Form Four students to calculate Its Molarity. Which among the following will be the possible answer?
- 0.05
- 0.25
- 1.25
- 5.3
- 0.025
(x) The following reaction 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O (l) is an example of a
- Redox reaction
- Combination reaction
- Esterification
- Neutralization reaction
- Decomposition reaction.
2. Match the item in LIST” A” with the correct response in LIST” B”
| LIST A | LIST B |
| (i) Methyl orange indicator (ii) Calcium hydroxide (iii) pH 2 (iv) Neutralization reaction (v) Sodium hydrogen sulphate |
|
SECTION B (70 MARKS)
3. (a) Write balanced equation of
(i) Sodium hydroxide react with sulphuric acid
(ii) Calcium carbonate decomposed by heat
(b) (i) With aid of a balanced chemical equation name the products formed when nitrates of potassium and zinc decompose by heat
(ii) Suggest why nitrates of zinc and potassium behave differently on heating
4. (a) (i) People suffering from heart burn usually use wood ashes for relief. Mention chacteritics which makes the ashes to be used for heart burn relief.
(ii) Give four compounds found in the laboratory which show the same characteristic as ashes.
(b) How many ions are there in 6.82g of Al2(SO4)3
5. (a) When an acid is reacted with base, it forms salt and water. Using your knowledge of chemistry, explain how will you apply this reaction in your daily life? Give any four points.
(b) Insoluble salts are the salt that does not dissolve in water. Name any three examples of salts that are insoluble in water. (07 Marks)
6. 16.8g of impure potassium hydroxide was dissolved in distilled water to make 1000mls. 20mls of this solution required 28mls of 0.07M sulphuric acid to react. Calculate:
(a) Molarity of KOH
(b) Mass Concentration of pure KOH (07 Marks)
7. a) Mr Mwakatumbula don’t understand the physical properties of water. Teach him by giving three points the main physical properties of water and show the usefulness of each property.
b) Mr Kadinya said that Electrolysis is applied by many areas on the earth. State four industrial application of electrolysis
8. (a) Study the following reaction equation N2(g) + 3H2(g)![]() 2NH3(g) ∆H = - 46.2 kJmol-1
2NH3(g) ∆H = - 46.2 kJmol-1
Use Le-Chatelier’s principle, suggest how you would use temperature and pressure to obtain the highest production of ammonia at equilibrium
(b) The formation of methanol from hydrogen and carbon monoxide can be represented by
CO(g) + 2H2(g) ![]() CH3OH ∆H = 91 kJmol-1
CH3OH ∆H = 91 kJmol-1
What mass of hydrogen would react to cause a heat change of 91 kJ
9. (a) Give the meaning of the following terms
(i) Soil pH (ii) Liming
(b) (i) Explain why sulphur and its compounds are removed from the fuel before they are burned
(ii) By using a reaction equation explain how propane differs from propene
10. (a) In electrolytic production of hydrogen gas, dilute mineral acid is used. Which Method is used in its collection? Give a reason.
(b)Explain the chemical preference of decorating a copper necklace with silver metal by using electrolysis method
(c)During electrolysis of brine, sodium was deposited at cathode and chlorine gas released at anode. If 2.0g of sodium were collected at cathode; find the volume of chlorine gas at s.t.p.
SECTION C.
ANSWER QUESTION 11
11. a)Metals are extracted from the sea and in earth Referring to Tanzania as among the countries in the world extracting metals, explain four stages of extraction of metals.
b). Does the extraction of gold follow all four stages? Give reasons.
FORM FOUR CHEMISTRY EXAM SERIES 204
FORM FOUR CHEMISTRY EXAM SERIES 204
PRESIDENT’S OFFICE, REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES,
MID TERM ONE – MARCH-2024
CHEMISTRY FORM FOUR
Time: 3Hours
Instructions
- This paper consists of sections A, B, and C with a total eleven (11) questions.
- Answer all question in the sections A, B and two (2) questions from section C.
- Section A carries sixteen (16) marks, section B fifty four (54) marks and section C carries thirty (30) marks.
- All writing should be in blue or black pen, except for diagrams that must be drawn in pencil.
- Communication devices and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet (s
SECTION A.
Answer all questions in this section.
- For each of the following items (i-x).Choose the correct answer from given alternatives and writer its letter besides the item number in the answer booklet provided
- An increase in temperature of a gas in enclosed system container caused an increase pressure of the gas. This is because it increases the ;
- Number of gas molecule
- Combination of gas molecule
- Number of collision between gas molecules
- Average velocity of gas molecules
- Kinetic energy of gas particles
- 1.4g of potassium hydroxide is dissolved in water to form 250cm3 of solution. What is the molarity of the solution
- 0.001M
- 0.1M
- 1.4M
- 5.6M
- 6.0M
- When methane undergoes substitution reaction with excess chlorine, What is the final product?
- Chloromethane
- Dichloromethane
- Tetrachloroethane
- Tetrachloromethane
- Monochloromethane
- Ethanol reaction with ethanoic acid to form a group of organic compound called
- Alkynes
- Halo-alkanes
- Esters
- Alkenes
- Alkanes
- Insoluble salts like Barium Sulphate generally can be obtained in laboratory by;
- Evaporation of its concentrated solution
- Crystallization
- Precipitation
- Decomposition
- Displacement
- In a blast fumace carbon monoxide is prepared by passing carbon dioxide over red hot coke. What is the chemical role of carbon dioxide
- An acceleration
- An oxidizing agent
- Reducing agent
- A catalyst
- Oxidized
- What is the oxidation number of Phosphorus in the following compound? H3PO4
- -5
- 0
- +2
- +5
- -3
- Which of the following is not an organic compound?
- CO
- C6H12O6
- CH4
- CH3COOH
- C2H5B1
- A metal Nitrate which will not give a metal oxide on heating is
- Calcium Nitrate
- Silver Nitrate
- Lead Nitrate
- Copper Nitrate
- Zink Nitrate
- What action should be taken immediately after concentrated Sulphuric acid is spilled on the skin
- It should be rinsed off with large amount of water
- It should be neutralized using concentrated NaOH
- The affected area should be wrapped tightly and shown to a medical health provider
- It should be neutralized using solid CaCO3
- It should be neutralized with concentrated KOH
- Match sources of energy in the list A with corresponding description in list B. Write letter of the correct answer beside item number
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B
54 MARKS
Answer all questions
- (a) Study the following reaction equation N2(g)+3H2(g) H = -46.2KJlmo1-1
Use le chateliers Principle, suggest how you would use temperature and pressure to obtain the highest production of ammonium in equilibrium
(b) The formation of methane from hydrogen and carbon monoxide can be represented by:
CO(g) +2H2g CH3OH DH= 91KJ.........
What mass of hydrogen would cause heat change of 91KJ?
- What is the importance of having fume chamber in Chemistry Laboratory
(ii) Why do laboratory doors open outwards?
(b) State the use of following item in first aid
- Cotton wool
- Petroleum jelly
- Pain killers
- Bandage
- Razor blade
- Define the following terms;
- Molecular formula
- Empirical formula
(b) You are provided with compound 22.2%Zuric, 11.6% Sulphur, and 22.3%. Oxygen and the rest water of Crystallization. Calculate the molecular formula of the compound if its molecular mass is 283.
- 16.8g of impure potassium hydroxide was dissolved in distilled water to make 1000mls. 20mls of this solution required 28mls of 0.07M saulphuric acid to react. Calculate :
(a) molarity of KOH
(b) Mass concentration of pure KOH
- (a) The modern periodic law is based modification of Mendeleev periodic law. Explain how the two theories differ from each other.
(b) Comment on the following statement
(i) Lithium has large size than beryllium
(ii) Sodium is smaller than Potassium
(c) gives any four ions whose electronic configuration resemble that of Neon.
- (a) state faradays maw of electrolysis
Using the law state above, derive mathematical expression of Faradays first law of electrolysis.
(b) How many moles of electrons will be transferred is Zinc metal is produced by a current of 14.23A. Supplied for 8.0hrs.
SECTION C
30 MARKS
Answer 2 questions from this section.
- With aid of balanced chemical equation; explain the process that occurs in blast fumace during extraction of irons.
- (a) define the following terms
- Functional group
- Homologous series
- Isomerism
(b) Write down the molecular structure and IUPAC names of the Isomer whose molecular structure is C4H10
(c) By naming reagent, stating conditions whenever possible using a balanced equation describe how Ethane could be converted into
- Ethane
- Chloromethane
- 1,2,- dibromoethane
- Dilute Nitric acid is added to a green solid P.A blue solution R is formed and gas I Precipitate Lime with lime water is formed, the blue solution R is evaporated to dryness in a pyres test tube to give black solid M, brown fumes of gas W and colorless gas which relights a glowing splint was formed.
(a) Identify Substance P, R, I, M, W, and S
(i) Dilute nitric acid and solid P
(ii) Formation of white precipitate with gas I and Lime water.
FORM FOUR CHEMISTRY EXAM SERIES 177
FORM FOUR CHEMISTRY EXAM SERIES 177
PRESIDENT OFFICE REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES
COMPETENCE BASED ASSESSMENT
NEW EXAM FORMAT-2023
032/1 CHEMISTRY FORM FOUR
MID-TERM EXAMS MARCH – 2023
Time: 3:00 Hours
Instructions
- This paper consists of section A, B and C with a total of thirteen (13) questions.
- Answer all questions in this paper
- Calculators, cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s)
- The following constants may be used
- Atomic masses: H=1, C=12, O=16, N=14, Pb=108
- Avogadro’s number = 6.02 x 1023
- GMV at s.t.p = 22.4 dm3
- 1 Faraday = 96,500 coulombs
- Standard pressure = 760 mm Hg
- Standard temperature = 273 K
- 1 litre = 1dm3 = 1000cm3
SECTION A (16 marks)
Answer All Questions
1. For each of items (i) – (x), Choose the correct answer from the alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in answer sheet provided
- Mango Juice from Bakhresa was written, “Shake well before use” What does this mean?
- Suspension
- Solution
- Solute
- Emulsion
- Solvent
- Ammonia gas is collected by which method among the following
- Downward Displacement of water
- Upward delivery
- Downward delivery
- Upward Displacement of air
- The elements are required by adult plant
- What volume of hydrogen gas will be produced. When 1.3g of Zinc granules react completely with excess Dilute Sulphuric acid at S.T.P?
- 223cm3
- 130cm3
- 440cm3
- 220cm3
- 448cm3
- Which of the following substances should not be kept closely to the open bottle containing Carbon-dioxide
- Dilute Nitric acid
- Dilute Hydrochloric acid
- Sodium hydroxide solution
- Sodium Nitrate
- Dilute Suphuric acid
- When Nitrogen gas is formed covalently how many electrons are shared between nitrogen atom
- 2
- 3
- 6
- 5
- 4
- The reasons why white am hydrogen copper II sulphate tums blue when exposed in Atmosphere is that it
- Absorbs water vapour
- Reacts with Oxygen
- Reacts with carbon dioxide
- Becomes Dry
- Release water to the atmosphere
- Which action should be taken immediately after concentrated sulphuric acid is spilled on the skin
- It should be rinsed off with large quantities of running water
- It should be neutralized with concentrated NaOH
- The affected area should be wrapped tightly and shown to a medical health provider
- It should be neutralized with solid CaCO3
- It should be neutralized with concentrated KOH
- The following particles forms the nucleus of an atom
- Proton only
- Neutron and Electron and neutron
- Proton and Electron
- Proton and neutron
- Neutron and Electrons
- What should be done if results Obtained from an experiment do not support the hypothesis
- The results should be left out
- A new problem should be identified
- The experiment should be changed
- Ideas for further testing to find a solution should be given
- The hypothesis should be accepted
- Water exists in three forms, solid, liquid and vapour which among the following are examples of liquid form of water?
- Rain, Snow, hail
- Dew, Rain, Ice
- Mist, Steam, Cloud
- Rain, Hail, Ice
- Rain, Mist, Dew
2. Match the properties of element in List A with respective elements in List B by writing the letter of correct response besides item number in answer sheet provided
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B (54 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section
3. (a) The modern Periodic table law is based on modification of Mendeleev Periodic law. Explain the two theories differ from each other.
(b) Comment on the following statement
- Lithium has large size than Beryllium
- Sodium is smaller than potassium
(c) Give four ions whose electron configuration resembles that of Neon
4. (a) Mr. Mwabashi asked student to prepare all requirements for extraction of sodium metal. Help them describe the use of each of the following
(i) Calcium Chloride (ii)Graphite rod (iii) Steel gauze
(b) Why is sodium collected upward in down cell?
(c) Write electrodes reaction is down cell during extraction of sodium
5. A solution contains 40.3g of substance XOH per liter 250.0cm3 of this solution required 30.0cm3 of 0.3M sulphuric acid for complete neutralization
- Calculate the number of moles of XOH that reacted
- Determine the relative atomic mass of X
6. (a) Differentiate alkanes from alkenes
(b) Study the flow chart below and answer questions that follow;
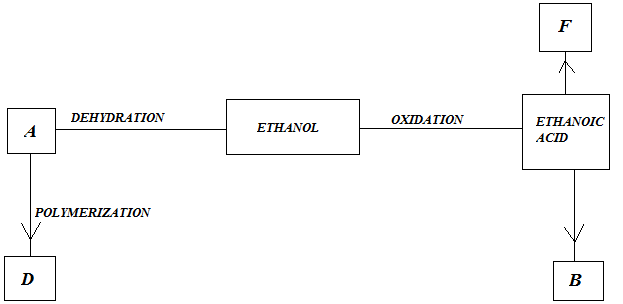 |
- Identify A
- State one Physical Property of B
- Give a reason why D pollutes the environment
- Write equation for formation of F
- Describe an experiment which can be used to distinguish buteno from butanol.
7. (a)A mass of 1.24g of a divalent metal was deposited when a current of 6A was passed through a solution of metal sulphate for 12minutes. Determine the relative atomic mass of the metal (1F = 96,500C)
(b)State two application of Electrolysis
8.(a) What is an alkali?
(b) Aqueous solution of 2M electronic acid and 2m nitric (v) acid were tested for electronic conductivity. Which solution is a better conductor of electricity? Explain
(c) Explain why it is not advisable to prepare a sample of carbon dioxide using barium carbonate and dilute Sulphuric (VI) acid
SECTION C (30 Marks)
Answer any two questions in this section
9. (a) What is Isomerism?
(b) Using illustration differentiate chain Isomerism from position Isomerism
(c) Alkenes are saturated, why alkenes are unsaturated explain
10. (a)Explain the following terms
- Reversible reaction
- Dynamic equilibrium
(b)The industrial Oxidation of sulphur dioxide is summarized as follows
2So2(g) + O2(g) → 2SO3(g) DH= -94.9 KJ/Mol
What will be the effect of each of the following on production of sulphur Trioxide?
- Increase in moles of sulphur dioxide
- Increase in pressure
- Decrease of temperature
- Decrease of moles of sulphur dioxide
(c)Briefly explain how each of the following factors affects the rate of a chemical reaction
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Concentration
- Catalyst
- Surface area
(d) Give one good reason for the following
- Fruits ripe faster during summer than during winter
- Steel wire get rust faster than iron nails
11. (a)Using Iron filling, describe an experiment that can be conducted to show that Oxygen is present in air
(b)Element U has atomic number 12 while element V gas atomic number 16. How do the melting points of elements compare
(c) In haber process, nitrogen reacts with hydrogen according to the following equation;
3H2(g) + N2(g) → 2NH3(g) DH= -92KJ/Mol
- What would be the effect of adding catalyst to the position of equilibrium
- Explain why it is not advisable to use a temperature higher than 773K in haber process
FORM FOUR CHEMISTRY EXAM SERIES 141
FORM FOUR CHEMISTRY EXAM SERIES 141
THE PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION, REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
COMPETENCE BASED SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES
CHEMISTRY MID TERM EXAMINATION
FORM FOUR-MARCH/APRIL-2022
Time: 3Hours
Instructions.
- This paper consists of section A, B and C with a total of 14 questions
- Answer all questions in section A and B and ONE (1) question from section C.
- Section A and C carries 15 marks, while section B 70 marks
- Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Non programmable calculators may be used.
- Write your number on every page of your answer booklet.
- Where necessary the following constants may be used;
Atomic masses; H=1, C=12, N=14,O=16, Na=23, S,=32, Ca =40, Cl =35.5, Cu=64, Zn=65.
Avogadro’s number = 6.02 x 1023
GMV at s.t.p = 22.4dm3
1 faraday = 96,500 coulombs.
Standard temperature = 273K
Standard pressure = 760mmHg.
1 Litre = 1 dm3 = 1000cm3
SECTION A (15 Marks)
Answer All questions in this section.
- The method of collecting hydrogen chloride gas in a class experiment is known as:
- Downward displacement of water
- Downward displacement of air
- Upward displacement of air
- Fountain
- Condensation
- The only metal which does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid is:-
- Magnesium
- Copper
- Zinc
- Sodium
- calcium
- Which among the following equations correctly shows the reaction between chlorine gas and water?
- C l2(g) + H20(1)→CI2(g)
B 2C12(g) + 2H20(1)→ 4C1-1(aq) + 02(g) + 2H2(s)
- Cl2(g) + H20(1)→HCl + HOCI(aq)
- 2Cl2(g) + 2H20(I) →2H0C1 +H2(g)
- 2C12(g)+ 3H200) → C12 (.0 + 2H30+
- A gas which when exposed to air forms white fumes is likely to be:
- Nitrogen
- Chlorine
- Ammonia
- Hydrogen chloride
- Sulphur.
v. Which is not true about hydrogen chloride?
- It supports combustion
- It is a very soluble gas
- It forms white fumes with ammonia
- It is acidic in nature
- When exposed to air forms white fumes
- Sea water contains various salts. Which salt is present in the largest proportion?
A. Magnesium sulphate
B. Sodium chloride
C. Calcium sulphate
D. Magnesium chloride
- Study the chemical equations below: which can remove temporary and permanent hardness?
a. Ca(HCO3)2(aq) → CaCO3(g) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
b. Ca(HO)2(aq) + Ca(HCO3)2(aq) → CaCO3(g) + 2H2O(l)
c. Ca2+(aq) + CO2-(aq) → CaCO3(g)
d. Ca2+(aq) + Na2Z(aq) → 2Na+(aq) + CaZ(g)
- Hard water which is softened just by boiling contains dissolved;
A. Calcium carbonate
B. Calcium chloride
C. Sodium carbonate
D. Magnesium sulphate
E. Calcium hydrogen carbonate
- Which of the above equations (vii) removes temporary hardness of water only?
A. a and b
B. b and c
C. c and d
D. d and a.
- Which set of compounds when in water cause hardness easily removed by boiling addition of Na2CO3 or use of ion exchange?
A. Ca(HCO3)2, Mg(HCO3)2
B. CaCl2, MgSO4
C. Fe(NO3), Ca(NO3)2
D. mgCl2, FeCl2
2. Match the physical processes represented by arrows (i) - (v) in List A with the corresponding terms in List B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number in the answer booklet provided.
| LIST A | LIST B |
| i) Water that easily forms lather with soap ii) Water that does not form lather with soap iii) Water that contains dissolved calcium and magnesium hydrogen carbonate iv) Water that contains dissolved sulphates of calcium and magnesium v) An element whose complex ion is used in softening water
| A. Plaster of Paris B. Gypsum C. Nitrogen dioxide D. Carbon dioxide E. Calcium F. Phosphorous G. Soft water H. Hard water I. Permanent hard water J. Temporary hard water K. Scum L. Stain M. Fur N. Coating O. Sodium P. Potassium Q. magnesium |
3. Figure 1 below represents the laboratory preparation of hydrogen chloride gas.
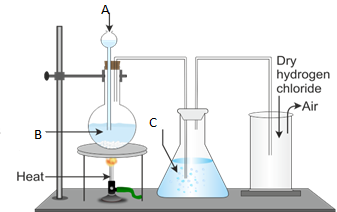
(a) Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D.
(b) (i) Do you think the gas can be collected over water? Give reasons for your answer.
- Explain the test for the gas.
- What is the function of C?
- Name the method used to collect the gas.
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place during the preparation of hydrogen chloride gas.
(c) Write chemical equations for the reaction between:
(i) Ammonia gas and hydrogen chloride.
(ii) Hydrogen chloride gas and water.
4. Write equation for reaction between
- Chlorine and Magnesium
- Chlorine and phosphorous
- Chlorine and copper
- Chlorine and hydrogen sulphate
5. Explain what happens when a stream of Hydrogen chloride gas is passed over
- Ammonia gas
- Iron II solution.
6. Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow
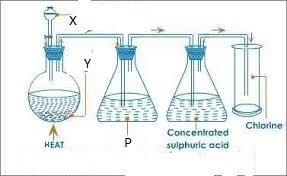
The apparatus above are used to prepare chlorine
- State substance
Y
X
P
- What is the use of conc. Sulphuric acid?
- State the use of p.
- Write equation for reaction occurring at the flask.
- How can you show that test tube used for collection of chlorine is full?
- Name the method of collection
- Give two uses of chlorine
- State 2 compounds of chlorine that pollute the environment.
7. Write down the chemical equations used when softening water of the
(a) Temporary hardness through (i) boiling water (one question) (ii) use of chemicals (two equations)
(b) Permanent hardness through (i) use of chemicals (one equation) (ii) iron exchange (one equation)
8. Define the following terms;
(e) Soft water
(f) Hard water
(g) Permanent hardness of water (h) Temporary hardness of water
9. a) What is the hardness of water?
b) Briefly explain types of hard of water.
c) State the causes of hardness of water for each type mention in (b) above.
d) Explain how you would remove the hardness of water according to its type.
e) Give three (3) advantages and three (3) disadvantages of the hard water.
10. Balance the following equations:
(i)Ca + H3PO4→ Ca3(PO4)2 + H2
- Cu + HNO3 → Cu (NO3 )2 + NO2 +H20
- SnCi2+FeC13→SnC14+FeCI
11. Give the name of the types of reaction represented by each of the following chemical equations.
- C3H8(g) +50,(0)→ 3CO2 + 4H20(1)
- 2Pb (N 03),(,)→2Pb0(,) + 4NO2 +02(g)
(iii)Zn(s)+CuS04(aq) —>ZnSO4(aq) +CU(S)
12. Complete the following equations and determine the type of chemical reaction involved in each case.
(i) Zn(s)+ H2SO4(aq)→
(i) AgN 03(aq) + NaCl(aq)→
(iii) N2(g) + H2(g) →
FORM FOUR CHEMISTRY EXAM SERIES 74
FORM FOUR CHEMISTRY EXAM SERIES 74
THE PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION, REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES
CHEMISTRY 1 MID TERM EXAMINATION
FORM FOUR-2021
Time: 3Hours
Instructions.
- This paper consists of section A, B and C with a total of 14 questions
- Answer all questions in section A and B and ONE (1) question from section C.
- Section A and C carries 15 marks, while section B 70 marks
- Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Non programmable calculators may be used.
- Write your number on every page of your answer booklet.
- Where necessary the following constants may be used;
Atomic masses; H=1, C=12, N=14,O=16, Na=23, S,=32, Ca =40, Cl =35.5, Cu=64, Zn=65.
Avogadro’s number = 6.02 x 1023
GMV at s.t.p = 22.4dm3
1 faraday = 96,500 coulombs.
Standard temperature = 273K
Standard pressure = 760mmHg.
1 Litre = 1 dm3 = 1000cm3
SECTION A (20 Marks)
Answer All questions in this section.
1. For each of the items (i)-(xv), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in the answer booklet provided.
- Most salts have comparatively high melting points because they have;
- Crystalline structure
- Low pressure
- High specific heat
- Strong electronic attractions between ions
- Strong covalent bond
- A magnesium atom and a magnesium ion have the same;
- Electron configuration
- Number of electrons
- Chemical properties
- Number of protons
- What mass of pure sulphuric acid is found in 400cm3 of its 0.1M?
- 2.45gm B. 9.80gm C. 3.92gm D. 4.90gm
- The volume of 18M concentrated sulphuric acid that must be diluted with distilled water to prepare 10 litres of 0.125M sulphuric acid is;
- 69.44cm3 B. 22500cm3 C. 225cm3 D. 4440cm3
- If two jars labelled W and Z contain 22.4dm3 of oxygen gas and 22.4dm3 of nitrogen gas at STP respectively, then it is true that;
- There were 6.02 x 1023 oxygen molecules in jar W and 6.02 x 1023 nitrogen molecules in jar Z.
- 6.02 x 1023 oxygen atoms were in jar W and 6.02 x 1023 atoms of nitrogen in jar Z.
- There were 12.4 x 1023 molecules of oxygen and nitrogen in the gas jars W and Z.
- 6.02 x 1023 molecules of oxygen and nitrogen were in the two jars W and Z.
- Sodium metal is kept in the oil or kerosene because it;
- Sinks in oil but floats on water
- is very alkaline
- Reacts vigorously with water
- Forms a protective coat of sodium oxide with oil
- The following is one of the characteristics properties of non – metals;
- They are electronegative in nature
- They behave as reducing agents
- They form cations by gaining electrons
- They form anion by loss of electrons
- One of the disadvantages of hard water is that is;
- Causes corrosion of water pipes
- Causes increased tooth decay
- Requires more soap for washing
- Contains minerals that are harmful
- When dilute solutions of calcium chloride and sodium carbonate are mixed;
- A white precipitate of sodium chloride is formed
- A white precipitates of calcium carbonate is formed
- A colourless solution of calcium carbonate and sodium chloride are formed
- A mixture of precipitates of sodium chloride and calcium carbonate are formed.
- A solution of sodium carbonate was prepared in order to get a 2M solution. 200cm3 of this solution was used in a titration experiment. The number of moles present in 200cm3 of 2M solution used in the titration will be;
- 4.0 B. 0.04 C. 0.40 D. 0.045
- Match the responses in list B with the word or phrases in list A by writing a letter of the correct response in the table provided below;
2. (a) Match the items from list A with those in list B.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
3. Figure 1 below represents the laboratory preparation of hydrogen chloride gas.
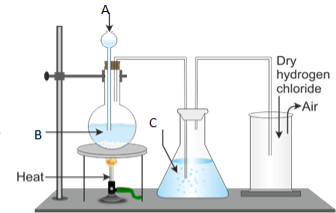
(a) Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D.
(b) (i) Do you think the gas can be collected over water? Give reasons for your answer.
- Explain the test for the gas.
- What is the function of C?
- Name the method used to collect the gas.
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place during the preparation of hydrogen chloride gas.
(c) Write chemical equations for the reaction between:
(i) Ammonia gas and hydrogen chloride.
(ii) Hydrogen chloride gas and water.
4. (a) 1.4gm of potassium hydroxide is dissolved in water to form 250m3 of solution. What is the
molarity of this solution?
(b) What is the molar concentration of a solution containing 1.75 moles of the solute in 3
litres (dm3)?
5. (a) How many molar volumes of 132.0g of CO2 are there at STP?
(b) Determine the number of molecules in 0.25 moles of lead (II) nitrate.
6. (a) What mass in grams of hydrated sodium carbonate (Na2CO3 . 10H2O) in 65cm3 of 0.2M
solution?
(b) What volume of carbon dioxide would be evolved at STP when 6.2g of copper (II)
carbonate is reacted with Suphuric acid?
7. You are given the following symbols of metals’ Zn, Na, Cu, Ag, Mg
- State the metal in each case;
- Which reacts vigorously with cold water?
- Which reacts strongly with steam but not with cold water?
- The metal whose carbonate doesn’t decompose on heating.
- The metal whose nitrate decomposes leaving a metallic residue.
- Write equation for reactions in (a) (i) and (ii).
- Arrange the above metals in order of increasing activity.
8. (a) Give the chemical formula for each of the following;
- Potassium carbonate
- Sodium nitrate (III)
- Iron (III) nitrate
- Aluminum oxide
(b) Complete the following equations and balance them.
- AgNO3(s) heat →
- ZnCO3(s) heat→
- KOH(aq) + H2SO4(aq) →
- CuSO4 . 5H2O(s) heat →
9. (a) What is meant by Dilution?
(b) Determine the litres of water that must be added to 30cm3 of 12M HCl to get a solution
which is exactly 0.25M.
10. (a) State two advantages of hard water.
(b) State two disadvantages of hard water.
(c) Give two methods of softening temporary hardness of water.
11. (a) Define the terms Molecular formula.
(b) Substance X contains 52.2% carbon, 13.0% hydrogen, the rest being oxygen. Calculate the empirical formula of X.
(c) If the density of X is 23, calculate the Molecular formula of X.
SECTION C: 15 MARKS
Answer the questions from this section and include the necessary details.
13. (a) (i) With the aid of a well labelled diagram, explain how you can prepare hydrogen gas
from the laboratory, using zinc metal and dilute hydrochloric acid.
(ii) Write a balanced chemical for the reaction taking place.
(b) (i) What is observed which hydrogen is passed over red hot copper (II) Oxide?
(ii) Write equation for the reaction that takes place in b(i) above.
(c) Which method would you use to prepare big crystals of sodium nitrate in the laboratory?
Explain briefly.
14. 25cm3 of potassium hydroxide were placed in a flask and a few drops of phenolphthalein indicator were added. Dilute hydrochloric acid was added until the indicator changed colour. It was found in the 21cm3 of acid were used.
From above information answer the following questions;
- (i) What piece of apparatus should be used to measure out accurately 25cm3 of sodium
hydroxide solution?
(ii) What colour was the solution in the flask at the start of the titration?
(iii) What colour did it turn when the alkali had been neutralized?
- (i) Was the acid more concentrated or less concentrated than the alkali?
(ii) Name the salt formed in the neutralization.
(iii) Write an equation for the reaction.
(iv) Is the salt, normal or acidic salt? Give reasons for your answer.
FORM FOUR CHEMISTRY EXAM SERIES 46
FORM FOUR CHEMISTRY EXAM SERIES 46
THE PRESIDENT�S OFFICE
THE MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND VOCATIONAL TRAINING
MID TERM EXAMINATIONS-MARCH 2020
032 CHEMISTRY- FORM FOUR
Duration: 2:30 Hours
INSTRUCTIONS:-
1.This paper consists of sections A,B and C
2.Answer all questions in all sections
3.Whenever necessary, the following constructs may be used.
Atomic masses: C=12 O=16, H=1, Mg = 24, Na=23, Cl= 35.5, Ca= 40, Cu= 63.5.
Avogadro�s constant = 6.02 x 1023 particles
Molar volume of gas at S.T.P = 22.4dm3mol -1 or 22400cm3 mol -1
SECTION A (15MARKS)
- .Question (i) � (x) are multiple choice items, choose among the given alternatives and write its letter into the answer sheet provided:-
- It compound contain 26.7% carbon, 2.2% hydrogen and the rest is oxygen what is its empirical formula?
- CHO
- C2H2
- CH2O
- CHO2
- The solution are mixed in a beaker and the mass of the beaker and contents is recorded at various times after mixing.
The graph shows the results.
Mass of beaker
And contents
| | |
| | |
Time
The two solutions could be:-
- Aqueous copper (II) sulphate and aqueous ammonia
- Aqueous sodium carbonate and dilute nitric acid
- Aqueous potassium hydroxide and aqueous zinc sulphate
- Aqueous sodium hydroxide and dilute hydro � chloric acid
- A student does an experiment in which three test � tubes containing hydrochloric acid.
The diagram below show the test- tubes containing the experiments. Which metal is placed in each test � tube?
|
| Test tube 1 | Test tube 2 | Test tube 3 |
| A | Iron | Silver | Magnesium |
| B | Iron | Magnesium | Silver |
| C | Magnesium | Silver | Iron |
| D | Silver | Iron | Magnesium |
- A Student decomposes aqueous hydrogen peroxide using manganese (iv) oxide MnO2 as catalyst
The question for the reactions is
2H2O2 Mno2 2H2O+O2
(aq) (l) (g)
- 100 cm3 of hydrogen peroxide is allowed to completely decompose and 120cm3 of oxygen is produced (one mole of a gas occupies 22400cm3 at room temperature and pressure). The concentration of the hydrogen peroxide is :-
- 0.01mol/dm3
- 0.10mol/dm3
- 0.05mol/dm3
- 0.50mol/dm3
- A student was given a sample of a carbonate, M2Co3 where M is a metal. He was asked to find the mass of M2Co3, the mass of M2Co3 and beaker was 7.69g and mass of beaker was 5.99g from this ,the mass of M2Co3 is:-
- 1.71g
- 5.21g
- 7.69g
- 1.70g
- The moles of sodium chloride in 250cm3 of 0.5M sodium chloride are:-
- 0.250Mol
- 0.125Mol
- 2Mol
- 1.25Mol
- Which of the following properties generally increases down the group?
- Ionization energy
- Atomic size
- Electronegativity
- Sodium and zinc
- Which of the following combination is not likely to form covalent bond?
- Magnesium and oxygen
- Nitrogen and oxygen
- Sulphur and fluorine
- Sodium and zinc
- One mole of water corresponds to:-
- 6.02 x 1023 atoms of hydrogen and 6.02 x1023 oxygen atoms
- 22.4dm3 at 1atom and 250c
- 1g
- 18g
- Neutrons are present in all atoms except
- H
- He
- C
- Ne
- Match each item in list A with response in list B by writing its correct letter to the number of corresponding item in the answer sheet(s) provided.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B:70 MARKS
Answer ALL questions
- An industrialist has approached you for information on the distillation of crude oil .What advice would you offer as regards the followings:-
- __ Separation of crude oil into fractions
- __ The main fractions of crude oil
- __ Uses of fractions of crude oil
- __ Uses of fractions of crude oil
- __ A schematic representation of the industrial process of fractional distillation of crude oil.
(10 marks)
- (i) Explain the following terms:-
- Standard solution
- The end point of a titration
- 25cm3 of 0.059M sodium hydroxide solution reacted with 23.5cm3 of dibasic acid, H2C2O4. XH2O containing 3.8gdm-3. Given that the ionic equation for the reaction is ;
-Calculate;
i)The molar concentration of the acid
ii)The value of x
d) Write down balanced chemical equation for the reaction involved. (C=12,H=1,0=16)
(10 marks)
- (i) Study the structures below the allotropes of carbon and answer the questions that follows:-
- Identify the allotropes S and R
- Which of the two allotropes is a good conductor of electricity? Explain
- Explain the following
- Carbon dioxide is used as refrigerant
- Carbon dioxide is used as a fire extinguisher (10 marks)
- (i) A weak base containing a few drops of methylorange indicator was titrated with a strong acid and the curve below was obtained.
| | |
| | |
14
pH
12 A
10
8
6 B
4
2
0 Volume of hydrochloric acid added(cm3)
- What will the colour of the indicator at (i) A (ii) B
- Explain why the pH value decreases
- Write down the equations for the reaction, if any, that takes place between dilute hydrochloric acid and each of the following:-
- Copper(II) (b) Lead(II) (c) Zinc (d) Sodium hydroxide (e) calcium hydrogen carbonate.
(10marks)
- A part of periodic table below. The elements are represented by letters which are not the real symbols of the elements.
| 1A |
|
| |||||||
| 3B | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8C | 9 | 10E | ||
| 11M | 12 | 13X | 14L | 15W | 16H | 17 | 18Z | ||
| 19F | 20 G |
| |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | |
- Write the electronic configuration of the following elements: E,X, L and H.
- Which pair of elements from ions by gaining two electrons?
- Which element is the most reactive metal?
- Which two element when reacted form a liquid which freezes at 00c and boils at 1000c?
- Give the formulae of the oxide and chlorides of elements A,G,X and W.(10marks)
- 7.5g of calcium carbonate was placed in a conical flask containing 50cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid. The flask was kept at constant temperature and the volume of carbondioxide gas evolved was measured at 20minutes intervals.
- Not all the calcium carbonate was used a during the reaction. The results were recorded in the table below.
| Time from start of reaction (min) | Volume of Co2 evolved(cm3) |
| 0 | 0 |
| 20 | 550 |
| 40 | 810 |
| 60 | 965 |
| 80 | 1000 |
| 100 | 1020 |
| 120 | 1020 |
- Write equation for the reaction between which carbonate and hydrochloric acid
- Plot a graph of volume of carbondioxide (cm3) against time (min)
- What volumes of carbondioxide where evolved during the second 20minutes internal? (20-40)
- Calculate the mass of 11.2cm3 of carbondioxide gas evolved at S.T.P (molar gas volume = 22.4dm3 at S.T.P).
- Determine the mass of calcium carbonate which had reacted after 20minutes. (Ca = 40, O= 16, C= 12) (10marks)
- (a) Explain the changes take place in the solution of concentrated sodium chloride with carbon anode and a mercury cathode.
- Two electrolytic cells for solutions of sodium chloride with carbon and a mercury cathode and aqueous copper (II) sulphate with inert electrodes were connected in series. A current of 1.5A was passed for 600seconds. The first cell contained aqueous sodium chloride with a little sodium hydroxide had copper electrodes and reddish brown precipitate formed.
- Why was there as change in the appearance of the electrolyte in the first cell?
- Why was a small amount of sodium hydroxide added to aqueous sodium chloride in the second cell?
- Name the reddish brown precipitate formed.
- Write an ionic equation for the formation of the substance in (iii)?
- Calculate
- The value for the faraday constant
- The charge on the electrode
- A hydrocarbon has a molecular mass of 56. On combustion 0.28g of hydrocarbon gave 0.88g of carbon dioxide and 0.36g of water
- Calculate the empirical formula of the hydrocarbon
- Draw a structural formula of the hydrocarbon
- To which group of hydrocarbons does the compound belong?
11. The diagram below represents an assembly of the apparatus used to prepare ethene from an alkanol X.
- Name the substances labeled X and Z
- Name substance Y
- Name the conditions under which ethene is prepared from the alkanol X.
10. Zinc metal and hydrochloric acid reacts according to the equation below;
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
3.12g of Zn metal were reacted with 200cm3 of 0.1M hydrochloric acid
(i) Determine the reagent that was in excess
(ii) Calculate the total volume of hydrogen gas liberated at standard temperature and pressure.( Z=65.4, Molar gas volume = 22.4 litres at S.T.P)
12. (a) State Le- chatelier�s principle
(b) The industrial preparation of ammonia in the Haber process is represented by the following equation:
N2(g) + 3H2(g) catalyst 2NH3(g) H= -46.2KJ/mol
| | |
| | |
Study the equation carefully then answer the questions that follow:
What will happen to the position of equilibrium if:
- The temperature of the equilibrium mixture is increased?
- More Nitrogen gas is added to the equilibrium mixture?
- The formed ammonia is removed from the equilibrium mixture?
(c ) What is the use of catalyst in the reaction in 10(b) above?
(d) What is the meaning of the negative sign against the value of heat change -46.2KJ/mol in the chemical reaction given in 10(b) above?
(e) Sketch an energy profile diagram against reaction in 10(b) above.
SECTION C: (15 MARKS)
Answer ALL questions
13. a)Explain what is meant by the following terms:
i) A homologous series
ii) Unsaturated hydrocarbons
iii) Isomerism
b) Write and name all possible isomers of C5H12
c) Write the structures of the following:
i) 2,3-dimethylbutane
ii) 2,3,4-trimethylpent-2-ene
14. Your village is rich in the raw materials for generation biogas: your DDC seeks advice form you as regards:-
- The raw materials.
- The suitability of sitting the biogas plant in the village
- The physical and chemical principle involved
- Economic importance of biogas.
FORM FOUR CHEMISTRY EXAM SERIES 8
FORM FOUR CHEMISTRY EXAM SERIES 8
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256







