PRESIDENT'S OFFICE REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
FORM THREE ANNUAL EXAMINATION
031/1 PHYSICS
TIME: 3:00 Hours November, 2025
INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper consists of sections A, B and C with eleven (11) questions.
- Answer ALL questions in section A and B and any two (2) from section C
- Section A carries 16 marks, section B 54 marks and section C 30 marks.
- Non-programmable calculator may be used
- Where necessary the following constants may be used
- Acceleration due to gravity =10ms-2
- Gravitation force g = 10N/kg
- Density of water = 1000kg/m3 or 1g/cm3.
SECTION A (16 marks)
Answer all questions from this section
1. For each of the items (i) –(x) choose the correct answer from among given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in the booklet provided. (10 marks)
(i) An object immersed in a liquid in a tank experiences an up - thrust. What is the physical phenomena that causes the up - thrust?
- The density of the body differs from that of the liquid
- The density of the liquid increases with depth
- The pressure in the liquid increases with depth
- The value of g in the liquid increases with depth
(ii) One of the following does not affect surface tension. It is ;
- Impurities
- Detergents
- Temperature
- Volume of the liquid
(iii) A Form Three student did an experiment to demonstrate electrostatic attraction between water and charged comb through rubbing it with hair. The charged comb was brought to a slow stream of water coming from the tap as seen in figure below. The result of the experiment found the water particle were attracted to the comb causing the stream of water to bend. This means that the charge on the comb

- Is the same with that in water
- Is less than that in water
- Is opposite to that in water
- Is larger than that in water
(iv) If a small displacement of a system from the rest position (after getting some energy) results in a small bounded motion about the equilibrium position , then the system is in :
- Neutral equilibrium
- Unstable equilibrium
- Stable equilibrium
- Natural equilibrium
(v) Which of the following groups of machines represent first class lever?
- Wheel barrow and bottle opener
- Fishing rod and sugar tongs
- Crowbar and claw harmer
- Nut crackers and pair of scissors
(vi) Whenever the surfaces in contact tend to move or move with respect to each other , the force of friction comes into play
- Only if objects are solid
- Only if one of the two objects is liquid
- Only if one of the two objects is gaseous
- Irrespective of whether the objects are solid, liquid or gaseous
(vii) In tropical countries shinny bright roofing materials are more preferred compared to dull brown tiles because;
- shinny bright roofing materials are more attractive than dull brown tiles
- shiny bright roofing materials are more durable than dull brown tiles
- shinny bright roofing reflects the sun’s radiant heat more than dull brown tiles
- shinny bright roofing materials are lighter than dull brown tiles
(viii) At normal temperature due to a puncture the compressed air inside the tube of a car wheel suddenly starts coming out. Then the air inside the tube
- Starts becoming hotter
- Starts becoming cooler
- Remains at the same temperature
- May become hotter or cooler depending on the amount of water vapour present in air
(ix) If the e.m.f and internal resistance of a battery are 1.5V and 0.4Ω respectively, the current that this battery will supply a resistor of 14.6Ω will be :
- 15A
- 10A
- 1.0A
- 0.1A
(x) A block of mass 10kg is lying at the front desk of a classroom. The coefficient of static friction is 0.5. A force of 40N is applied to the book. The book will

- Move
- Not move
- Move up and down
- Slide
2. Match the items in list A with the corresponding items in list B (6marks)
| List A | List B |
|
|
SECTION B (54marks)
Answer all questions
3. (a) Explain the following pair of words Fog and Smog (3marks)
(b) Tanzania meteorological agency (TMA) recorded dew point for temperature and dew point in four towns 12 noon as shown in table below.
| City | Dew point |
| Arusha | 1 |
| Morogoro | 12 |
| Zanzibar | 5 |
| Dar es Salaam | 4 |
Assume that all cities have their air temperature of 220C
- In which town is the relative humidity the highest? (2.5marks)
- In which town is the relative humidity the slowest? (2.5marks)
4. (a) Name, draw and mention one use of the three different types of diverging lenses (3marks)
(b) Why does the swimming pool appear much shallower than its actual depth? (2marks)
(c) A converging lens produces an upright image four times the object height. If the focal length is 25cm, find the object distance. (4marks)
5. (a) Why an iron ball sinks in water? (3marks)
(b) A crown made of gold and silver has a volume of 60cm3 and mass of 1. 05kg.Find the mass of gold contained in the crown. (Density of silver = 10.5g/cm3 and density of gold = 19.3g/cm3) (6marks)
6. (a) State two ways that can be used to improve the efficiency of the machine (3marks)
(b) A certain first class lever of length 2.5m has a velocity ratio of 12 and an efficiency of 85%
- How far from the fulcrum is the effort force applied? (3marks)
- What effort is required to lift the load weighing 75N? (3marks)
7. (a) State parallelogram law of force. (4marks)
(b) A metal sphere weighing 60N is suspended from a beam by a thin string. What horizontal force must be applied to the weight to keep the string at an angle of 380 to the vertical? What is the tension in the string? (5marks)

8. (a) Give two difference between elastic collision and inelastic collision (3marks)
(b) A 4kg object is moving to the right at 2m/s when it collides elastically head-on with a stationary 6kg object. After collision, the velocity of the 6kg object is 1.6m/s to the right.
- What is the velocity of the 4kg object after the collision? (3marks)
- What is the total kinetic energy before and after collision? (3mark)
SECTION C (30marks)
Answer ONLY two questions
9. (a) i) Explain how the efficiency of the vacuum flask would be affected if the double walled glass bottle was replaced with a double-walled metal bottle. (4marks)
(ii) Why do you feel warmer during cloudy night than during clear sky night? (4marks)
(iii) The diagram below show a bimetallic thermostat used to regulate a cooler and heat in a class room. Given Linear expansivity of brass = 18.9 × 10−4𝐾−1 and Linear expansivity of iron = 10.2 × 10−4𝐾−1 . To keep the temperature in the room constant, which of the two devices A or B should be the heater? Explain your answer (2marks)

(b) A hollow metal sphere of mass 5kg is tied to the bottom of the sea –bed by a rope. The tension in the rope is 60N. Calculate the volume of the sphere. (5marks)
10. (a) i) How can a simple electric cell be constructed? (2marks) ii) Sketch a diagram of the simple electric cell and locate the anode and cathode (3marks) iii) Write the chemical reactions taking place at each electrode and within the electrolyte (4marks)
(b) Study the circuit below and then answer the questions that follows.

Calculate the current passing through the circuit when:
- Switch k1 is closed (2marks)
- Switches k1 and k2 are both closed (2marks)
- Switch k1 is open and k2 is closed (2marks)
11. (a) In which part of a fridge or a microwave oven do magnetic strips installed? Why? (5marks)
(b) White and light coloured clothes are more suitable in hot seasons. Explain (4marks)
(c) A plastic tray weighing 48g and containing 200g of water at 200C is put in a refrigerator which abstract heat at a uniform rate of 2100J/min. Calculate the;
- The time taken for the tray and water to reach at 00C (3marks)
- Total time taken to freeze all the water to ice at 00C. (3marks)
Given specific heat capacity of plastic = 1050J/kgK; specific latent heat of fusion of water = 335000J/kg.
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 250
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 250


FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 239
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 239
THE PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
FORM THREE PHYSICS ANNUAL EXAMINATION
PHYSICS
TIME: 3 HOURS OCTOBER, 2024
Instructions
1. This paper consists of three sections A, B and C with a total of eleven (11) questions.
2. Answers all questions in sections A and B and two (2) questions in section C.
3. Read each question carefully before you start answering it.
4. Non-programmable calculators and mathematical tables may be used.
5. Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
6. Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s) provided.
7. Wherever necessary you may use the following:
(i) Acceleration due to gravity = 10m/s2
(ii) Pie π![]()
(iii) Density of water = 1.0g/cm3 or 1000kg/m3
(iv) Density of sea water = 1.3g/cm3 or 1300kg/m3
(v) Specific heat capacity of ice = 2100J/kg°C
(vi) Specific heat capacity of Copper = 420J/kg°C
(vii) Specific heat capacity of water = 4200J/kg°C
(viii) Coefficient of limiting friction force = 0.61
(ix) Coefficient of dynamic friction force = 0.42
SECTION A (16 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section
1. For each of the items (i) – (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in answer booklet(s) provided.
SECTION A. (16 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
1. For each of the items [i] – [x], choose the correct answer from the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number
(i) The SI unit of acceleration is:
A) Meter (m)
B) Kilogram (kg)
C) Second (s)
D) Meter per second (m/s)
E) Meter per second squared (m/s²)
(ii) According to Newton's Second Law of Motion, force (F) is equal to:
A) Mass (m)
B) Mass x Acceleration (ma)
C) Acceleration (a)
D) Weight (mg)
E) Work (W)
(iii) An object submerged in a fluid experiences an apparent buoyant force equal to:
A) Its weight in air
B) The volume of fluid displaced by the object
C) The weight of the fluid displaced by the object
D) The density of the object
E) The density of the fluid
(iv) Opposite poles of magnets attract each other, while like poles repel each other.
This principle is the foundation of:
A) Electromagnetism
B) Electrostatic force
C) Nuclear force
D) Gravitational force
E) Strong force
(v) A changing magnetic field can induce an electric current in a nearby conductor.
This phenomenon is described by:
A) Ohm's Law
B) Kirchhoff's Laws
C) Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction
D) Lenz's Law
E) Coulomb's Law
(vi) A car accelerates uniformly from rest to a speed of 20 m/s in 5 seconds. What is the car's acceleration?
A) 1 m/s²
B) 4 m/s²
C) 5 m/s²
D) 10 m/s²
E) 20 m/s²
(vii) Most materials expand when heated and contract when cooled. This
phenomenon is primarily due to:
A) Phase change
B) Increased atomic mass
C) Increased intermolecular spacing
D) Decrease in density
E) Change in chemical composition
(viii) A convex lens can be used to:
A) Magnify objects (act as a converging lens)
B) Diverge light rays (act as a diverging lens)
C) Measure distance
D) Detect electric current
E) Separate colors of light (act as a prism)
(ix) When a plastic pen was rubbed against dry hair seriously, the pen was able to attract small pieces of paper. This meant that _______________
A. Hair become negatively charged
B. Hair become positively charged
C. Hair gain electrons
D. Paper loses electrons
E. Both hair and paper are positively charged
(x) A block of wood rests on the horizontal surface. A form three student says that the friction between the block and the surface depends on;
1. Surface area in contact
2. Nature of the surface
3. Weight of the block
Which of A, B, C, D and E is correct?
A. 1, 2 and 3
B. 2 and 3
C. 1 and 2
D. 1 and 3
E. 2 only
2. Match the items in LIST A with corresponding response in LIST B by writing the letter of correct answer beside item number in answer sheet provided.
| LIST A | LIST B |
| i. It depends on the nature of surfaces of bodies in contact ii. It supports an object which is in contact with another body iii. It acts on a small range of about 0.01fm to 0.001 fm iv. It is short range force(operates in a distance ranging from 0.7fm to 2.5 fm) v. It is a central force vi. Comes into operation when an elastic body is twisted. | A. Strong force B. Force of gravity C. Frictional force D. Torsion force E. Electromagnetism F. Tension force G. Normal force H. Weak force I. Buoyant force J. Viscous force
|
SECTION B 54 MARKS
Answer all questions
3. (a) What is the refractive index for a certain medium, if the light in air enters the medium at an angle of 30° and refracted at 22°?
(b) A vertical object 10 cm high is placed 20 cm away from a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. using a ray diagram, determine
(i) Image distance
(ii) The height of the image formed
(iii) The magnification of the image
4. (a) Describe how a lens camera operates the same as human eye. Give three points
(b) Briefly explain how conduction of heat can be applied in your daily life (three reasons)
5. (a) NYAMWERU was at home cultivating. He had two hoes, sharp and blunt hoe. Blunt hoe was not cutting well as how sharp hoe did. Explain to him why sharp hoe cuts well than blunt hoe.
(b) A cube of sides 2cm is completely submerged in water so that the bottom of the cube is at a depth of 10cm. find:
i. Difference in pressure between bottom and top of the cube.
ii. Different of force between bottom and top of the cube.
6. (a) Explain why does a solid weigh more in air than when immersed in a liquid?
(b) By using a help of diagram explain what happen to the two parallel straight conductors when current is moving in the same direction and in opposite direction.
(c) A block of wood of mass 5kg is placed on a rough inclined plane, at 60° to the horizontal. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the wood and the plane is 0.3, determine the acceleration of the wood down the plane.
7. A metal rod has a length of 2.00 meters at room temperature (20°C). When heated to 100°C, the rod expands by 1.6 mm.
a) Calculate the linear expansivity of the metal.
b) Predict the length of the rod if it is cooled down to -10°C.
c) Explain why bridges often have expansion joints built into their structure.
8. A car of mass 1200kg is accelerating on a straight track. The graph below shows how the force acting on the car varies with time.
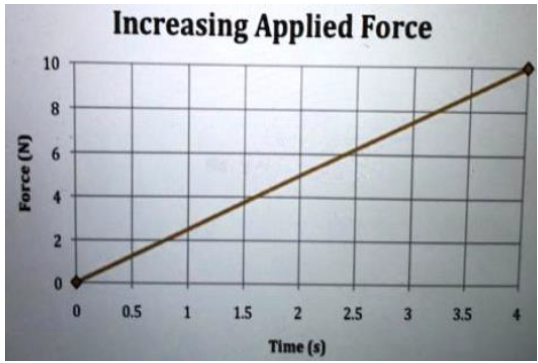
(a) Describe how the acceleration of the car will change over time.
(b) Calculate the acceleration of the car when the force is 3000 N
(c) Explain why the force needed to accelerate the car increases over time.
SECTION C. 30 MARKS
Answer any two questions
9. (a) George Ohm observed that as the current flows through the circuit, it
encounters some opposition. This opposition determines the amount of current flowing in electric device depending to the particular material
i. State the law that Mr. George formulate.
ii. Briefly explain factors affecting resistance of a conductor observed by Mr. George Ohm to sum up his observation.
(b) (i) Distinguish between the concept of conductors, semiconductor and insulators in term of energy bands
(ii) Give out one structural difference between A.C and D.C generators.
10. (a) After a long flight a plane may be charged
(i) What causes a charge?
(ii) Why is passenger in a plane not charged but an attended who immediately opens the door from outside after landing of the plane is at risk?
(b) (i) Explain how submarine can either float or sink.
(ii) A piece of cork with a volume of 100cm3 is floating on water. If the density of the cork is 0.25g/cm3. Calculate the volume of cork immersed in water and the force needed to immerse the cork completely. (Assuming mass of 1g has a weight of 0.001N)
11. (a) When a simple pendulum displaced at a small angle swings to and fro, in this motion potential energy and kinetic energy changes by alternating each other.
With the aid of diagram verify the alternation of these energies.
(b) A 50kg girl runs up a staircase of 50 steps each step is 15cm in height in 5s.
Find Work done against gravity by the girl and Power she use to run.
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 184
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 184
PRESIDENT’S OFFICE REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
COMPETENCY BASED EXAMS
SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES
FORM THREE ANNUAL EXAMINATION
031 PHYSICS
TIME: 3HRS NOVEMBER, 2023
INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper consists of section A, B, and C with a total of eleven (11) questions
- Answer all questions in section A and B and any two (2) questions from section C
- Show clearly your work
- Section A carries fifteen (15)marks, section B sixty (60) marks and section C carries twenty five (25) marks
- All writing should be in blue or black pen except for diagrams that must be drawn in pencil.
- Non-programmable calculator may be used
- Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Write your examination number on each page of your answer sheet(s)
- Where necessary, use the following constants
- Acceleration due to gravity(g) = 10m/s2
- Density of water = 1g/cm3 or 1000kg/m3
SECTION A (16 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section
1. For each of items (i) – (ix), choose the most correct answer from among given alternatives and write its letter beside item number in answer sheet provided
- A bus carrying heavy load on its top carries is likely to overturn because.
- It runs faster
- Its center of gravity is low
- Its center of gravity is high
- Its equilibrium is neutral
- It is at stable equilibrium
- Which of the following conditions must be satisfied for a body to float?
- Apparent weight is equal to weight of the fluid displaced
- Real weight of the body equals to its upthrust
- Upthrust equal to weight of fluid displaced
- Apparent weight is equal to product of real weight of the body and its upthrust
- Density of a body is equal to density of surrounding fluid
- In an experiment, A simple pendulum showings between A and B. The amplitude of Oscillation is
- Distance A to B
- Half the distance A to B
- Distance A to B and Back
- Twice the distance A to B
- The distance from A in one direction
- From four students were discussing on properties of matter, where one of them said that solid has define shape and all member of group agreed. Which one could be the reason behind for solid to have definite shape?
- It has high adhesive force
- It has high surface tension
- It has low viscosity
- It has high cohesive force
- It has low adhesive force
- Angle was in a car, she tried to look at her friend who were outside of car through glass window, but she did not see well. You as a form as a form four student, what conclusion could you make on that glass window?
- It is transparent material
- It is translucent
- It is opaque
- It is not cleaned
- It is black
- Mndeme was cooking ugali in a good conductor container, but she seems to use iron handle which is covered by plastic at its holding handle to hold cooking container. Why did she use plastic handle and not iron?
- Its good conductor of heat
- It reflects heat
- Its particles are dose to each other
- It is poor conductor of heat
- It is a good heat emitter
- Which of the following do not affect the rate of evaporation of water in a dam?
- Surface area
- Depth
- Humidity
- Barometric pressure
- Temperature
- Racing cars rarely get accidents despite their high speed because
- Have greater momentum
- Have big tyres with treads
- Have wide base and low center of gravity
- Exert greater frictional force
- Have less mass
- Retina in human eye has same function as which part of the lens camera.
- Shutter
- Diagram
- Film
- Convex lens
- Adjusting knob
- Which of the following factors influence friction between the surface of the road and tyres of a car moving with a constant speed?
- Weight and speed
- Nature of the surface and weight
- Surface area of the tyres and speed
- Acceleration and Nature of surface
- Speed and Nature of the surface
2. Match the following concept in List A with relevant description in List B by writing its letter beside the items number in sheet provided
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B (54 Marks)
3. (a) Students from Mwenge University were climbing Mt. Kilimanjaro, Suddenly one of them started experiencing nose bleeding
- Comment on why the student experienced nose bleeding
- Why do astronauts wear space suits
(b) The acceleration due to gravity on Jupiter in about 2.6 times that of earth. A spacecraft has weight of 24500N on earth
- What is the mass of space craft
- What would be its weight in Jupiter
4. (a)(i) What do you understand by the term specific heat capacity and specific latent heat of vaporization
(ii) Explain the factors that affect boiling point of water.
(b) What is the index of refraction for a certain medium if the light in air enters the medium at an angle of 30° and refracted at 22°C?
5. (a)Describe how a lens camera operates the same way as human eye. Give three points
(b) Briefly explain how conduction of heat can be applied in your daily life (Three reasons)
6. (a)Briefly explain why the doors of oven are made loosely fitting
(b) A steel bridge over a motor way is 20m at 0°C. How much longer is it at 20°C?
7. (a)Explain why a bat can fly in the dark without hilting objects
(b) A soldier standing in front of a vertical cliff fires a gun, he hears the echo after 3sec. On moving closer to the diff by 82.5m, he fires again, and hears the echo after 2.5 sec. Find
- The distance of the diff from initial position of the mars
- The speed of sound
8. (a)You read a newspaper because of the light that it reflects. Why do you not see even a faint image of yourself in a newspaper?
(b) Name factors on which the angle of deviation produced by a prism depend
SECTION C (30 Marks)
Answer any two questions
9. (a)A wire is Answer is carrying current is it charged?
(b)Explain the following
- A Kettle of water with steady supply of heats taken much longer time to boil dry it does to reach its boiling point.
- How does molecular theory of matter account for drop in temperature which results when for evaporation of volatile liquid occurs
(c)Why is a dull Black surface a better absorber of heat than a brightly polished surface?
10. (a) In which way does a wire carrying electric and placed between the poles of two magnets as shown in figure below tend to move? Explain your answer
(b)Explain any four (4) causes of power looses in a transformer that can reduce the efficiency of the transformer
(c)A 240V mains transformer has 1000 turns in its primary coil and it is designed to supply electrical energy to a 12V, 24W lamp. Determine the efficiency of the transformer if the current drawn from the 240V mains is 0.125A
11. (a)(i)State Ohms Law
(ii) How does Ohm’s law explain the fact that the resistance of a conductor depends on area of Cross-section of the conductor.
(b) (i)Explain why the path of lighting is not straight but zigzag
(ii)Two negative charges were brought together as shown below, re-draw a well diagram to show the magnetic field lines on how these two charges interact, remember to indicate neutral point.
(c) Study the circuit below and answer questions that follow.
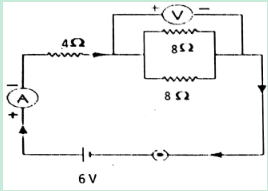
- Calculate the equivalent resistance
- What is the reading of Ammeter
- What is the reading of Voltmeter?
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 157
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 157
THE PRESIDENT’S OFFICE MINISTRY OF EDUCATION, REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
COMPETENCY BASED SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES
PHYSICS FORM THREE
TIME: 3 HOURS NOVEMBER 2022
Instruction
- This paper consists of section A, B and C with a total of eleven [11] marks
- Answer all questions in section A and B and two [2] questions from section C
- Mathematical table and non – programmable calculator may be used
- Cellular phones are not allowed in the examination room
- Write your Examination number on every page of your answer sheet provided
- Where necessary the following constants may be used
- Acceleration due to gravity g = 10mls2
- Density of water, p= 1000 kg /m3or 1g/cm3
SECTION A [15 MARKS]
- For each of the items [i] – [x] choose the correct among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in the answer sheets provided.
- Which one among of the following is a factor on which up thrust exerted on a body by fluid depends:
- Volume of the fluid B. Mass of the fluid C. Viscosity of the fluid D. Density of the fluid E. Temperature of the fluid
- A layer of colour less water is carefully floated in a cylinder on top of blue copper sulphate solution after a time, the water becomes blue, because of?
- Liquid friction B. Density changes C. Diffusion
- Viscosity E. Pressure changes
- If the mass of copper over the volume of copper is 8.9g/cm3. Find the volume 89g of copper
- 10 -5 cm C. 10-5m3
- 0.1 cm3D. 100CM3E. 10cm3
- Aluminum is used in making motor engines, pistons and cylinders due to
- Its low density and high conductivity
- Low density and maximum pressure
- High density and varying mass
- Its high conductivity and high density
- Its heavy weight and low conductivity
- The acceleration of a moving body may be found from;
- The area under its velocity-time graph.
- The slope of the velocity-time graph.
- The area under its distance-time graph.
- The slope of the distance-time graph.
- The slope of the peak of its distance-time graph
- Oil is used as a lubricant in a machine because it has
- Low density
- High viscosity
- Low pressure
- High pressure
- Low viscosity
- When light is totally internally reflected from the boundary of a certain transparent material and air the critical angle is found to be 500 the speed of light in the material is
- 2.1 x 108m/s
- 2.2 x 108m/s
- 1.94 x 108m/s
D.2.3 x 108m/s
E. 3.0 x 108m/s
- Why buildings are constructed with wide foundation?
- Because of power
- In order to reduce pressure exerted by the building on the ground
- So as to build large house
- To increase pressure of the ground so as to maintain holding the house.
- To avoid earth quake
- The energy from the hot rocks within the earth is called.
- Tidal energy
- Water energy
- Cool- burning energy
- Biomass energy
- Geothermal energy
- A reference was a certain device to judge football game in 90 minutes at MKAPA arena, that device was:-
- Football C. Stop watch
- Tape measure D. 90 Minutes E. Line man

Section B [60 marks]
Answer all questions
- [a]. By using well labeled diagram, explain in short why the stem of the hydrometer is made thin and weighted with mercury or lead shorts? [06 marks]
[b]. A ship is made of steel and it is expected that it should sink in water. However it does not sink. At the same time a coin once dropped in water it will sink. How can you solve this contradiction so as to help a form one student who is totally confused? [04 marks]
- [a]. It has been found the efficiency of a pulley system is always less than 100%. Giving two reasons explain the secret behind. [04 marks]
[b]. A meter rule is pivoted at its mid-point. If two objects of weigh 1.0N and 2.0N are suspended at 30cm and 90cm respectively from one end, calculate the position
- [a]. State the laws of refraction of light
[b]. The diagram below shows a ray of light incident on a glass prism at an angle.
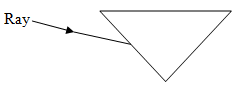
Complete the diagram to show as it emerges from the other side [05marks]
[c]. Sketch a ray diagram to show the formation of a solar ellipse [03marks]
- [a]. Give one difference and one similarity between a fuse and a circuit – breaker [04 marks]
[b]. A cell supplies a current of 0.6A through a 2? coil and a current of 0.2Athrough a752? coil. Calculate the e.m.f and internal resistance of the cell [06marks]
- [a]. Explain on the basic of conservation of linear momentum, how a fish propels itself forward by swishing its tail back and forth [04 marks]
[b]. A block and tackle system of 5 pulley is used to raise of 490N steadily through a is then 1800 J. calculate the efficiency of the system and efforts applied[06 marks]
- (a) Explain four (4) factors affecting resistance of a conductor. (6 marks)
(b) Describe two (2) defects of simple cell(4 marks)
Section C [25 marks]
Answer two [2] question form this section
- When a simple pendulum displaced at a small angle swings to and fro, in this motion potential energy and kinetic energy changes by alternating each other. With the aid of diagram verify the alternation of these energies.(8.5 marks)
(b) A 50kg girl runs up a staircase of 50 steps each step is 15cm in height in 5s. Find Work doneagainst gravity by the girl and Power she use to run(4 marks)
10. (a) A drum at station A is connected to a wire string at station B. A man at A beats the drum while another person at B places his ear at the wire and hears two sounds separated by the time interval of 0.5 seconds. If the velocity of sound in the wire string is 5280m/s. How far apart are the two men. (5 marks)
(b) How long will it take a 240V, 3000W electric immersion heater to raise the temperature of 150 litres of water in a well lagged copper tank of mass 20kg from 15? to 70?. Also find the cost at 5 shillings per kwh. (5 marks)
11. (a).A plane mirror and concave mirror both they produce an image from the given object. Draw the diagram to represent the formation of image in each case (for the concave mirror consider an object to be at the center of curvature, (C). Hence show two similarities and two differences of images formed. ( 6 marks)
(b) Explain the formation of mirage (4 marks)
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 112
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 112
THE PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION, REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES
ANNUAL EXAMINATION
FORM THREE-NOVEMBER 2021
PHYSICS 1
Instructions
l. This paper consists of sections A, B and C with a total of eleven (11) questions.
2. Answer all questions in sections A and B and two (2) questions from section C.
3. Section A carries fifteen (15) marks, section B sixty (60) marks and section C carries twenty five (25) marks.
4. Cellular phones and any unauthorised materials are not allowed in the examination room.
5. Non-Programmable calculators may be used.
6. Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
- Where necessary the following constants may be used:
(i)Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s2 or 10 N/kg
(ii)Specific heat capacity of mercury is 1395 J/kg°C
(iii) 1g of water is equivalent to 1 cm3
(iv) Pi = 3.14.
SECTION A (30 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
1. For each of the items (i) - (x), choose the correct answer among the given alternatives and write its letter besides the item number in the answer booklet provided.
(i)The correct formula to find the elastic force constant (k) of a spring is
- Tension/extension
- mass/extension
- extension/mass
- extension/tension
- tension/mass
(ii) Why is oil used as a lubricant?
- It has low density.
- It is highly viscous.
- It is flammable.
- it is inflammable
- It is less viscous.

(iii)Which one is a characteristic of a plane mirror?
- It forms image which is real and opaque.
- It forms an image which is larger than the object.
- It forms an image which is real and laterally inverted
- It forms an image which has the same size as the object.
- It forms an image which is smaller in size than the object.
(iv) In a light experiment, the results showed that less light was transmitted and the image was distorted. Which type of material was used?
- A translucent material
- An opaque material
- A luminous material
- A transparent material
- A non-luminous material
(v) What quantity of heat is required to raise the temperature of 25 kg sample of mercury from 20°C to 30°C?
- 1,743,750J
- 348,750J
- 345,750J
- 413,750J
- 1,550,750J
(vi) Why is Mercury preferred in clinical thermometers as a thermometric of a liquid to water and alcohol?
- It is denser than other liquids.
- It is opaque and does not need colouring.
- It is more sensitive to temperature.
- It is active and does not wet the glass.
- It is a poor conductor of heat.
(vii) Which of the following is an example of a scalar quantity?
- Electric current
- Force
- Velocity
- Displacement
- Acceleration
(viii)What role does the iris play in the human eye?
- To hold the lens in position.
- To prevent internal reflection.
- To control the size of the pupil.
- To control the thickness of the lens.
- To protect the eye from light.
(ix) A launderer was thinking about a proper day for washing and drying clothes. Which day would he prefer most among the following?
- Dry day
- Hot day
- Windy day
- Still day
- Cold day
(x) What will be the resistivity of a wire 2 metres long with a cross-sectional area of 0.50 mm2 and a resistance of 2.20?
- 5.5 x 10-7 ?m
- 6.5 xlO-7?m
- 2.3 x 10-7 ?m
- 1.1 x 10-6?m
- 5.5 x 10-6?m.
2. Match the items in List A with responses in List B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number in the answer booklet provided.
| LIST A | LIST B |
| (i) Materials that can strongly be magnetized. (ii) Substance which are made up of soft iron. (iii) Materials that cannot be affected by magnets. (iv) Objects which are made up of steel. (v) Groups of magnetic dipoles arranged themselves in a magnetized object.
|
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
3. (a) Briefly explain why hydrometer
(i) is weighed with lead shots.
(ii) has a narrow stem.
(b) A piece of rubber of volume 100 cm3 and the density of 0.45 g/cm3 floats in water. Calculate:
(i) The volume of rubber that partially immersed in water.
(ii) The force required to immerse the rubber completely.
4. (a) List four factors which affect the rate of evaporation of liquids.
(b) (i) Define relative humidity.
(ii) Calculate the relative humidity given that the reading on dry bulb hydrometer is 24°C and the wet bulb temperature reading is 16°C.
(c) With the aid of a sketched graph, explain how temperature affects the saturated vapour pressure of water.
5. (a) Briefly explain why hydrometer
(i) is weighed with lead shots.
(ii) has a narrow stem.
(b) A piece of rubber of volume 100 cm3 and the density of 0.45 g/cm3 floats in water. Calculate:
(i) The volume of rubber that partially immersed in water.
(ii) The force required to immerse the rubber completely.
6. (a) How does the increase of length and cross-section area of a conductor affect its resistance?
(b) (i) State the function of a circuit breaker in a wiring system.
(ii) Determine the ratio of resistance of wire A to that of wire B which are made up of the same material such that wire A has half the length and twice the diameter of wire B.
7. (a) Give two examples which illustrate the rectilinear propagation of light.
(b) (i) The refractive index of light passing from water to air is 3/4. Calculate the critical angle. (ii) Outline two differences between primary and secondary rainbows.
(c) In Figure 1, identify the names of colours labeled A, B, C, D, E, F and G.
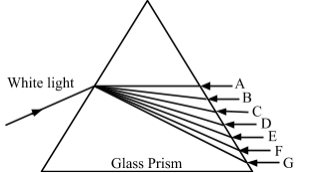
11. (a) Mention two practical examples in our daily life in which the principle of conservation of energy is applied.
(b)(i) What is a simple pendulum.
(ii) Describe the energy changes that take place when a simple pendulum swings from one side to another.
(c)Name a machine or an apparatus used to change the following forms of energy.
- Heat energy to mechanical energy.
- Mechanical energy to electrical energy.
- Electrical energy to sound energy.
- Sound energy to electrical energy.
- Heat energy to electrical energy.
SECTION C (25 Marks)
Answer two (2) questions from this section
9. (a) State the following rules:
(i) Cork screw rule.
(ii) Dynamo rule.
(b) (i) Give one structural difference between A.C. and D.C. generators.
(ii) Mention one application of induction coil.
(c) Figure 2 shows a transformer used to step down power. Assuming that there are no power losses, what will be the ammeter reading on the output part?
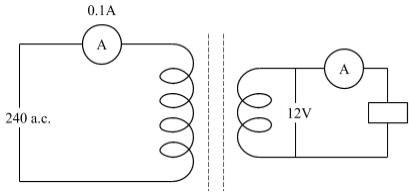
10. (a) (i) What is meant by the term thermal expansion?
(ii) Mention two applications of thermal expansion of solids.
(b) (i) List three areas where bimetallic strips are used.
(ii) Why a bimetal strip made of brass and invar is curved outside with brass?
(c) Describe how simple fire alarm system operates.
11.(a) (i) What are sustainable energy sources?
(ii) State four applications of energy generated from water.
(b)(i) Define geothermal energy.
(ii)Briefly explain how geothermal energy can be harnessed.
(c)(i) What is a windmill?
(ii)Mention three disadvantages of energy caused by wind. (iii) Does wind itself possess energy? Explain.
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 71
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 71
THE OFFICE OF THE PRESIDENT
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
PHYSICS EXAMINATION FORM THREE
ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS.
NAME………………………………………..CLASS……………………………………………….TIME:2:30HRS
Instructions:
- This paper consists of two (2) questions. Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries twenty five (25) marks.
- Qualitative Analysis Guide Sheet authorized by NECTA and non – programmable calculators may be used.
- Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s)
- Where necessary the following constants may be used:
(i)Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10m/s2.
(ii)Density of water = 1.0g/cm3.
(iii)Pie, ![]() = 3.14.
= 3.14.
(iv)Coefficient of linear expansivity of the brick = 1.2 ![]() 10-5 K-1.
10-5 K-1.
(v)Speed of light in air = 3 ![]() 108 m/s.
108 m/s.
(vi)Speed of sound in air = 340 m/s
SECTION A (15 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
1. For each of the items (i) – (x) choose correct answer from among the given alternatives and write
its letter beside the item number;
(i) The direction of the heat flow between two bodies is determined by;
- The direction of the wind
- The mass of the body
- The temperature difference of the two bodies
- The coefficiency of cubical
- Expensivity
(ii) A rectangular wooden block of density 0.8g/cm3 has dimensions 0.5m x 0.8m x 6m. Whatmaximum pressure will it exert on the ground?
- 48000N/m2 B. 4000N/m2 C. 2.4N/m2 D. 19200N/m2 E. 400N/m2
(iii) Racing cars rarely get accidents despite their high speed because they;
- Have greater momentum
- have big tyres with big treads
- Have wide bases and low centre of gravity
- exert greater frictional force
- have less mass
(iv) When a bus starts or stops moving, passengers tend to be jerked forward or backwards. This is due to;
- Newtons 1st law motion
- Newtons 2nd law of motion
- Newton 3rd law of motion
- Newton universal law of gravitation
(v) In a uniform rod 1.0m long of mass 100g is supported horizontally on two knife edges placed 10.0cm from its ends, the reaction at the support when a 150g mass is placed at the midpoint of rod will be;
A. 250GB. 125NC. 1.25ND. 125KN
(vi) The SI unit of momentum is;
- Ns B. Kgm51 C. KG/m D. Js
(vii) The area under a speed against time graph represents;
- Displacement B. Velocity C. Distance D. Acceleration
(viii) If the refractive index of water is 4/3, then the critical angle of water – interface is;
- 48°35 B. 45° C. 42° D. 36°51
(ix) In concave lens parallel rays are;
- Converged
- Diverged
- Brought to focus at the centre of curvature
- transmitted parallel
(x) If a bottle capable of holding 200g of a liquid of density, 800kg/m3 is allowed to hold 160g of
sand of density 3200kg/m3 then the mass of water needed to fill the bottle is;
- 200g B. 40g C. 90g D. 150g
2. Match the items in LIST A with responses in LIST B by writing the letter of the correct responses.
| LIST A | LIST B |
| (i)Surface tension effect (ii)Maximum displacement of pendulum bob. (iii)Cooling by evaporation (iv)Thermopile (v)Impulse |
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
3. (a) State the law of floatation
(b) A piece of a cork with volume 100cm3 is floating on water. If the density of cork is 0.25g/cm3,
(i) Calculate the volume of cork immersed in the water;
(ii) Calculate the force needed to immerse the cork completely (Assume mass of 1g = 0.01N).
4. (a) Define energy
(b) A ball of mass 0.2kg is dropped from a height 20M. On impact with the ground it loses 30J of
energy. Calculate the height it reaches on the rebound.
5. (a) What is meant by the terms;
(i) Heat capacity
(ii) Specific heat capacity
(b) Explain very briefly how heat losses have been presented in the vacuum flask.
6. (a) State the principle of moments
(b) A heavy mental boom AB of mass 25kg is supported at its ends. The beam carries a mass of 150kg
of a distance of 0.75m from end A. If the beam is 2m long, determine the thrust at support A and B.
7.(a) Define the following terms related to friction;
(i) Limiting friction
(ii) Normal reaction
(b) What is the normal reaction of body of mass 10kg placed on an inclined place of angle 30°
8. (a) Why a bubble of air increases in volume as it rises from the bottom of a pond of water to the surface? Briefly explain.
(b) A half meter rule AB is freely pivoted at 18 cm from end A and balances horizontally when a body of mass 35g is hung 48 cm from end B. Calculate the mass of the rule.
SECTION C (25 Marks)
Answer two (2) questions from this section.
9. (a) Electrical energy is distributed in all parts of Tanzania by the National grid system which transmits alternating current at a very high voltage. Explain why is it necessary to have a very high voltage?
(b) A generator producing a varying current from 0 to 10 A was allowed to flow in a coil of magnetic field. After a time interval the current was observed to be 4 A. Describe how back e.m.f. was induced in a self – induction.
- (a) Mention any two differences between boiling and evaporation
(b) Calculate the quantity of heat required to melt 4kg of ice and to raise the temperature of water formed to 100°C
- (a) (i) State Boyle’s law and Charles’ law
(ii) Write down the ideals gas equation
(iii) What does the term STD means?
(b) At a temperature of 50°C and a pressure of 74cm Hg the volume of a gas is 300cm3. Calculate the volume of the gas at STP.
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 36
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 36
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256







