THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL OF TANZANIA ADVANCED CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATIONS
131/1 PHYSICS 1
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
Time 3 Hours Year: 2017
Instructions
1. This paper consists of sections A and B with a total of ten (10) questions.
2. Answer all questions in section A and two (2) questions from section B.
3. Section A carries seventy (70) marks and Section B carries thirty (30) marks.
4. Marks for each question or part thereof are indicated.
5. Mathematical tables and non-programmable calculators may be used.
6. Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
7. Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
8. The following information may be useful:
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s 2
Ratio of specific heat capacities, y 1.4
Density of water p = 1000 kg/m 3
Mass of electron, Me = 9.1 x 10 -31 kg
Gravitation constant, G = 6.7 x 10 -11 kg-I m g s-2
Electronic charge, e = 1.6 x 10 -19 C Pi, 3.14
1. (a) Give the meaning of the following terms as used in error analysis:
(i) Absolute error (ii) Relative error.
View Ans
(b) The force 'F' acting on an object of mass 'm' travelling at velocity 'V' in a circle of radius 'r'

(i) Fractional error
(ii) Percentage error in the measurement of force
View Ans
(c) Show how you will record the reading of force, 'F' in part (b)
View Ans
2. (a) (i) Define the term dimensions of a physical quantity. (ii) Identify two uses of dimensional equations.
View Ans
(b) (i) What is the basic requirement for a physical relation to be correct? List two quantities whose dimension is [ML2 T-1].
View Ans
(c) (i) The frequency 'f' of vibration of a stretched string depends on the tension 'F', the length 'l' and the mass per unit length g of the string. Derive the formula relating the physical quantities by the method of dimensions.
(ii) Use dimensional analysis to prove the correctness of the 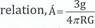 where p
where p
= density of the earth, g = acceleration due to gravity, R radius of the earth and G = gravitational constant.
View Ans
3. (a)(i) Why does the kinetic energy of an earth satellite change in the elliptical orbit? (ii) Give two factors which determine whether a planet has an atmosphere or not.
View Ans
(b) A spacecraft is launched from the earth to the moon. If the mass of the earth is 81 times that of the and the distance from the centre of the earth to that of the moon is about 4.0 x 105 km;
(i) Draw a sketch showing how the gravitational force on the spacecraft varies during its journey.
(ii) Calculate the distance from the center of the earth where the resultant gravitational force becomes zero.
View Ans
4. (a) (i) Justify the statement that ‘if no external torque acts on a body, its angular velocity will not be conserved
(ii) A car is moving with a speed of 30 ms-I on a circular track of radius 500 m. If its speed is increasing at the rate of 2 me; find its resultant linear acceleration.
View Ans
(b) An object of mass 1 kg is attached to the lower end of a string 1 m long whose upper end is fixed and made to rotate in a horizontal circle of radius 0.6 m. If the circular speed of the mass is constant, find the:
(i) Tension in the string (ii) Period of motion.
View Ans
5. (a) A 75 kg hunter fires a bullet of mass 10 g with a velocity of 400 ms4 from a gun of mass 5 kg. Calculate the:
(i) Recoil velocity of the gun.
(ii) Velocity acquired by the hunter during firing.
View Ans
(b) A jumbo jet travelling horizontally at 50 ms 0-1 at a height of 500 m from sea level drops a luggage of food to a disaster area.
(i) At what horizontal distance from the target should the luggage be dropped? (ii) Find the velocity of the luggage as it hits the ground.
View Ans
6. (a) The equation of simple harmonic motion is given as x = 6 sin 10 Tit+ 8 cos 10 lit, where x is in centimeter and t in second. Determine the: (i) Amplitude
(ii) Initial phase of motion
View Ans
(b) (i) Show that the total energy of a body executing simple harmonic motion is independent of time.
(ii) Find the periodic time of a cubical body of side 0. 2 m and mass 0.004 kg floating in water then pressed and released such that it oscillates vertically.
View Ans
p style='margin-right:0in;margin-left:0in;font-size:15px;font-family:"Calibri","sans-serif";margin-top:0in;margin-bottom:10.0pt;line-height:normal;text-align:center;'>SECTION B 7. (a) (i) Give a common example of adiabatic process.
(ii) What happens to the internal energy of a gas during adiabatic expansion?
View Ans
(b) Amass of an ideal gas of volume 400 cm3 at 288 K expands adiabatically. If its temperature falls to 273 K;
(i) Find the new volume of the gas.
(ii) Calculate the final volume of the gas if it is then compressed isothermally until the pressure returns to its original value.
View Ans
8. (a) State the following according to heat exchange:
(i) Prevost's theory
(ii) Wien's displacement law.
View Ans
(b) Briefly explain why:
(i) Steam pipes are wrapped with insulating materials:
(ii) Stainless steel cooking pans fitted with extra copper at the bottom are more preferred:
View Ans
(c) The value of the property X of a certain substance is given by:
X = X + 0.50 + 2 x 10-4 Ø2, where Ø is the temperature in degree celsius. What would be the Celsius the temperature defined by the property X which corresponds to a temperature of 50 oc on this gas thermometer scale?
View Ans
9. (a) (i) What is the advantage of using a greater length of potentiometer wire?
(ii) Why is Wheatstone bridge not suitable for measuring very high resistance?
View Ans
(b) Study the circuit diagram in Figure 1 then answer the questions the follow:
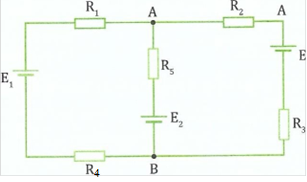
Figure 1
If the value of RI = R2 = R3 = 1.0 0, R 5 = 2 0, E2 = E3 = 4 V, El = 2. 0 V, calculate the: (i) Current flowing through the circuit (ii) Potential difference, Vab.
View Ans
10. (a) (i) List two factors on which the resistivity of a material depends.
(ii) A wire of resistivity, P is stretched to double its length. What will be its new resistivity? Give reason for your answer.
View Ans
(b) (i) Why should a high voltage supply have high internal resistance?
(ii) Justify the statement that 'it is not possible to verify Ohm's law by using a filament lamp'.
View Ans
(C) A potential difference of 4V is connected to a uniform resistance wire of length 3.0 m and cross-sectional area 9 x 10-9, when a current of 0.2 A is flowing in the wire. Find the; (i) Resistivity of the wire
(ii) Conductivity of the wire
View Ans
SECTION C
11. (a) Briefly explain the function of the following:
(i) Oscilloscope
(ii) Op-amps
View Ans
(b) Study Figure 2 then construct a truth table showing the output P, Q and R.
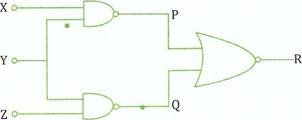
Figure 2
View Ans
(c )(i) List three basic elements of communication system
(ii) Explain the advantage of using optical fibre systems rather than coaxial cable system in telecommunication processes.
View Ans
12. (a)(i) Define the term semiconductor
(ii) Give three examples of semiconductor materials.
View Ans
(b) (i) Outline two factors on which electrical conductivity of a pure semiconductor depends.
(ii) How does the forbidden energy gap of an intrinsic semiconductor vary with increase in temperature?
View Ans
(c) Figure 3 is a circuit diagram containing an ideal diode
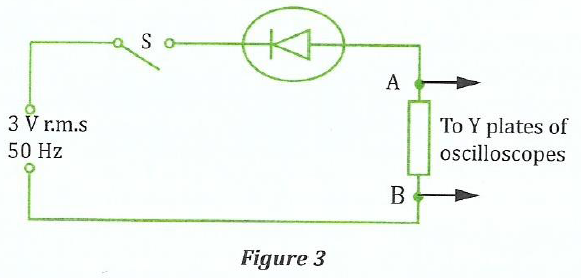
Calculate
(i) The peak voltage
(ii) The period
View Ans
13. (a) Explain the meaning of the following terms:
(i) P-type semiconductor
(ii) N -type semiconductor
View Ans
(b) (i) List three types of transistor configurations.
(ii) Why is the collector of a transistor made wider than emitter and base?
View Ans
(c ) A change of 100 PLA in the base current produces a change of 3 mA in the collector current.
Calculate:
(i) The current amplification factor, ß (ii) The current gain, ct
View Ans
14.(a) (i) State three sources of heat energy within the interior of the earth.
(ii) Discuss two advantages of windbreaks to plant environment.
View Ans
(b) Briefly explain the major causes of the following types of environmental pollution:
(i) Water pollution
(ii) Air pollution
View Ans
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256