THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL OF TANZANIA ADVANCED CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATIONS
131/1 PHYSICS 1
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
Time 3 Hours Year: 2016
Instructions
1. This paper consists of sections A and B with a total of ten (10) questions.
2. Answer all questions in section A and two (2) questions from section B.
3. Section A carries seventy (70) marks and Section B carries thirty (30) marks.
4. Marks for each question or part thereof are indicated.
5. Mathematical tables and non-programmable calculators may be used.
6. Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
7. Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
8. The following information may be useful:
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8m/sec2 .
Density of water, = 1000kg/m 3
Specific heat capacity of water = 4170J/kgK
Radius of the earth = 6.37 x 106m
Mass of the earth, = 6.0 x 10 24kg
Universal gravitational constant, G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2 kg-2
Stefan Boltzmann constant 6.67 x 10 -11 Nm2 kg-2
Heat of vaporization of water = 2256 x 10 3Jkg 1
Pie, = 3.14
1. (a) (i) Define the term dimension of a physical quantity.
(ii) The number of particles n crossing a unit area perpendicular to x-axis in a unit time is given as
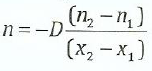
where ni and nz are the number of particles per unit volume for the values of Xl and X2 respectively. What are the dimension of diffusions constant D?
View Ans
(b) (i) Give two basic rules of dimensional analysis.
(ii) The frequency, f of a vibrating string depends upon the force applied, F the length, t of a string and the mass per unit length, g. Using dimension show how fis related to F, C and g.
View Ans
(c) (i) What is meant by least count of a measurement?
(ii) The period of oscillation of a simple pendulum is given by;
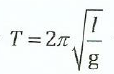
whereby 100 vibrations were taken to measure 200 seconds. If the least count for the time and length of a pendulum of 1m are 0.lsec. and Imm respectively, calculate the maximum percentage error in the measurement of g.
View Ans
2. (a) (i) Mention two characteristics of projectile motion.
(ii) If the range of the projectile is 120m and its time of flight is 4sec, determine the angle of projection and its initial velocity of projection assuming that the acceleration due to gravity g = 10ms-2
View Ans
(b) (i) State the principles on which the rocket propulsion is based.
(ii) A jet engine on a test bed takes in 40kg of air per second at a velocity of 100ms-1 and burns 0.8kg of fuel per second. After compression and heating the exhaust gases are ejected at 600ms-1 relative to the air craft. Calculate the thrust of the engine.
View Ans
(c) An object of mass 2kg is attached to the hook of a spring balance which is suspended vertically to the roof of a lift. What is the reading on the spring balance when the lift is:
(i) Going up with the rate of 0.2ms -2 ?
(ii) Going down with an acceleration of 0.1ms -2?
(iii) Ascending with uniform velocity of 0.15ms -1 ?
View Ans
3. (a) (i) Define the term inertia
(ii) Why is Newton's first law of motion called the law of inertia?
View Ans
(b) A jet of water from a fire hose is capable of reaching a height of 20m. If the cross-sectional area of the hose outlet is 4.0 x 10-4m 2, calculate the:
(i) Minimum speed of water from the hose (ii) mass of water leaving the hose each second. (ii) force on the hose due to the water jet.
View Ans
(c) A boy ties a string around a stone of mass 0.15kg and then whirls it in a horizontal circle at constant speed. If the period of rotation of the stone is 0.4sec and the length between the stone and boy's hand is 0.50m;
(i) Calculate the tension in the string
(ii) State one assumption taken to reach the answer in 3(c)(i).
View Ans
4. (a) What do you understand by the following terms?
(i) Damped oscillations.
(ii) Undamped oscillations.
View Ans
(b) (i) Sketch the waveform diagrams to represent the terms in 4 (a) (i).
(ii) Show that the total energy of a body executing S.H.M is independent of time.
View Ans
(c) A mass of 0.5kg connected to a light spring of force constant 20Nm-1 oscillates on a horizontal frictionless surface. If the amplitude of the motion is 3.0cm, calculate the:
(i) Maximum speed of the mass.
(ii) Kinetic energy of the system when the displacement is 2.0cm.
View Ans
5. (a) (i) What is meant by moment of inertia of a body?
(ii) List two factors on which the moment of inertia of a body depends.
View Ans
(b)(i) A thin sheet of aluminium of mass 0.032kg has a length of 0.25m and width of 0.1m. Find its moment of inertia on the plane about an axis parallel to the: length and passing through its centre of mass m.width and passing through the centre of mass m in its own plane.
View Ans
(c) (i) Define the term angular momentum.
(ii) A thin circular ring of mass M and radius r is rotating about its axis with constant angular velocity w1. If two objects each of mass m are attached gently at the ring, what will be the angular velocity of the rotating wheel?
View Ans
6. (a) (i)Mention one application of parking orbit.
(ii) Briefly explain how parking orbit of s satellite is achieved.
View Ans
(b) The earth satellite revolves in a circular orbit at a height of 300km above the earth's surface. Find the:
(i) velocity of the satellite. (ii) period of the satellite.
View Ans
(c) (i)Why are space rockets usually launched from west to east?
(ii) A spaceship is launched into a circular orbit close to the earth's surface. What  additional velocity has to be imparted to the spaceship in order to overcome the gravitational pull?
additional velocity has to be imparted to the spaceship in order to overcome the gravitational pull?
View Ans
SECTION B
7. (a) Briefly explain why:
(i) a body with large reflectivity is a poor emitter.
(ii) it would be too cold to live on the earth without its atmosphere.
View Ans
(b) (i) Identify two factors on which the coefficient of thermal conductivity of a material depends.
(ii) A brass boiler of base area 1.50 x10 1 m2 and thickness of 1.0cm boils water at the rate of 6.0kg/min when placed on a gas stove. Estimate the temperature of the part of the flame in contact with the boiler.
View Ans
(c) (i) Briefly describe the working principle of a thermocouple.
(ii) In a certain thermometer the e.m.f is given by:
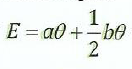
where Ø is the temperature of hot junction. If α 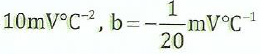 and the cold junction 20 is at O O C, calculate the neutral temperature.
and the cold junction 20 is at O O C, calculate the neutral temperature.
View Ans
8. What is meant by thermal radiation?
(ii) Briefly explain why forced convection is necessary for excess temperature less than 20K
View Ans
(b) (i) Why is the energy of thermal radiation less than that of visible light ?
(ii) A body with a surface area of 5.0cm2 and a temperature of 727 o c radiates 300 joules of energy in one minute. Calculate its emissivity.
View Ans
(c) (i)State Newtons's law of cooling.
(ii) A body cools from 70 0 C to 40 0 C in 5 minutes. If the temperature of the surrounding is IO O C, calculate the time it takes to cool from 50 0 C to 20 0 C.
View Ans
9. (i) Define the term junction as applied in electrical network. (ii) What is the physical significance of Kirchhoff's first law?
View Ans
(b) (i) Why is Kirchhoff's second law sometimes referred to as the voltage law?
View Ans
(ii) List down five points to be considered when applying Kirchhoff's second law in formulating analytical problems or equations.
(c) Study the circuit diagram in Figure 1 then answer the questions that follow:
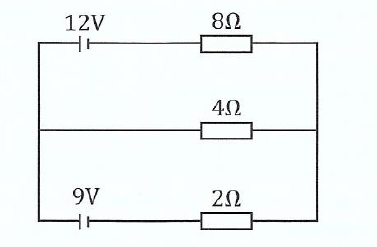
(i) How many loops are there in the circuit?
(ii) Find the current flowing through 20, 40 and 80 resistors.
View Ans
10. (a) What is meant by the following terms:
(i) Phase of alternating e.m.f
(ii) Root means square (r.m.s) value of alternating e.m.f.
View Ans
(b) An a.c circuit consists of a pure resistance of 100 is connected across an a.c supply of 230V, 50Hz. Calculate the:
(i) current flowing in the circuit. (ii) power dissipated.
View Ans
(c) A 25gF capacitor, a 0.1 OH inductor and a 250 resistor are connected in series with an a.c source whose e.m.fis given by E = 310sin314t volt. Determine the:
(i) frequency of the e.m.f.
(ii) net reactance of the circuit.
View Ans
SECTION C
11. (a)(i) What is the importance of doping as applied to semiconductors?
(ii) Distinguish between n-type and p-type semiconductors. Give three points.
View Ans
(b)(i) Why are transistors mostly used in common emitter arrangement?
(ii) When does a transistor amplifier work as an oscillator?
View Ans
(c )(i)Explain the use of an op-amp as a summing amplifier.
Figure 2 is an operational amplifier circuit where Rl=39kΩ, R = 4.7kΩ, R3 = 10kΩ and R4 = 2.7kΩ
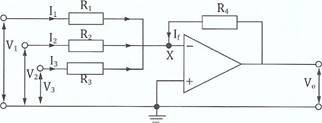
Calculate the output potential Vo given that the input voltage VI = 4.0V, V2 = 2.5V and V3 = 1.5V.
View Ans
12. (a) Name three electronic circuits in which multivibrators can be constructed.
View Ans
(b) (i) List down three types of multivibrators.
(ii) Briefly explain the applications of multivibrators listed in 12 (b) (i).
View Ans
(c) (i) Mention two characteristics of op-amps.
(ii) Briefly explain why op-amps are sometimes called differential amplifiers.
View Ans
13. (a) Discus the mode of action of each of the following sensors:
(i) Thermistor (TH)
(ii) Light Dependent Resistors (LDR).
View Ans
(b) Give symbols, expressions and truth tables for each of the following logic gates :
(i) NAND gate
(ii) Exclusive NOR gate.
View Ans
(c)(i) Why is NAND gate considered as a basic building block for a variety of logic circuits?
(ii) Produce a truth table for the gate shown in Figure 3 hence show that it behaves as NAND gate.
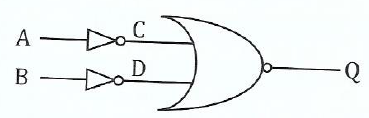
View Ans
14. (a) (i) What is meant by aerial environment? Give two examples.
(ii) Describe three ways at which the aerial environment is threatened.
View Ans
(b) (i) Briefly explain three major concepts on solar wind.
(ii)How do soil environmental components influence plants growth? Give four points.
View Ans
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256