View Ans
(c);;;;;;The following constants have been determined for hydrosulphuric acid at 25;0;C.
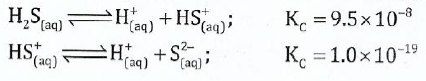
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at the same temperature:
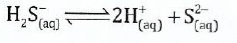
View Ans
5.;;(a) 60cm;3;of a certain gas was collected at 60;0;C and;1.05 X 105Nm-2;. Calculate the volume of the gas at stp.
View Ans
(b);;;;;When 0.5dm;3;of 02 and 1.0dm;3;of C02 were mixed at 27;0;C, the total pressure in the vessel was found to be 1.2atm. calculate:
(i);;;;;;;Partial pressure of each gas
(ii);;;;;The mass of each gas
View Ans
6.;;;;;;;;;(a) Give ant four differences between a positive and a negative non-ideal solutions.
View Ans
(b);;;;;Equal moles (0.5 moles) of benzene and toluene were mixed to form an ideal solution. Calculate the fraction of benzene and toluene in the second vapour given that P}nz = 95.1mmHg and =28.4mmHg
View Ans
SECTION B
7.;;(a) 0.01M aqueous solution of 92.5% NaCl is dissociated at 180C. Calculate the osmotic pressure(n) of this solution at the given temperature.
View Ans
(b);;;;;When 5.8g of acetic acid (CH3C02H) was dissolved in 90g of benzene (C6H6) the freezing point depression was found to be 3.80C. Calculate the degree of association of acetic acid in benzene, given that acetic acid dimerizes in benzene and Kf =5.1;0C mol-I kg
View Ans
8.;;(a) State Hess's law of constant heat summation.
View Ans
(b);;;(i) Give the difference between the standard bond dissociation energy and the standard heat of formation of a substance.
(ii);;;;;;Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction;
2NH3;; ;;;2(g) +3H2(g) given
;;;2(g) +3H2(g) given
that:;;;;;
View Ans
9.;;(a) Giving examples, briefly explain each of the following:
;(i) Hydrogen bonding;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
(ii) Coordinate bond
(iii) Van der Waal forces
View Ans
(b);;;;;For each of the following pairs of substances, predict which substance has a higher melting point, and give reason for each choice you make. (i) CH3CH3 and CH30H C02 and H2
(iii);;;;HCI and H20;;;;;(iv) Al and Mg (v) Si and Na
View Ans
(c);;Describe the hybridization of beryllium in beryllium chloride (BeC12).
View Ans
10.;;;;;(a);;Distinguish between the following: (i) atomic number from mass number (ii) a photon from a quanta.
View Ans
(b);;;;;A photon was absorbed by a hydrogen atom in its ground state and the electron was promoted to the fifth orbit. When the excited atom returned to its ground state, visible radiation and other quanta were emitted.
(i);;;;;;;Briefly explain the transitions made by the electron for the excited atom to return to its ground state.
(ii);;;;;Calculate the wavelength of a photon emitted during a transition from the n1
= 5 state to the n2 = 2 state in the hydrogen atom given that AE = 2.18x10-38
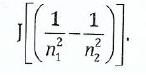
View Ans
;
SECTION C
11.;;;;;(a);Briefly explain each of the following as applied in organic reactions
(i) Positive inductive effect. (ii) Negative inductive effect (iii) Mesomeric effect (iv) Stearic factors
View Ans
(b);;;;;;Explain each of the following observations:
(i)Addition reactions in benzene need high energy.
(ii) Nucleophilic substitution reactions in benzene are not possible.
(iii);;;Methly group when attached to benzene ring direct another incoming group to ortho or para position.
(iv);;;;Nitro group when attached to benzene ring direct another incoming group to meta position.
View Ans
12.;;;;;Give the mechanism for the following:
(a);;;;;;;Sulphonation of benzene
View Ans
(b);;;;;;Chlorination of benzene
View Ans
13.;;;;;(a) Write the mechanism ofthe following substitution reaction, indicating clearly the nucleophile, substrate and the leaving group:
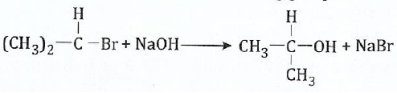
View Ans
;(b);;;;;;Carry out the following conversions:
(i);;;;;;;;Propane to I-chloropane.
(ii);;;;;;Propane to propene
View Ans
(c);;;;;;;Complete the following reactions and name the organic product formed.
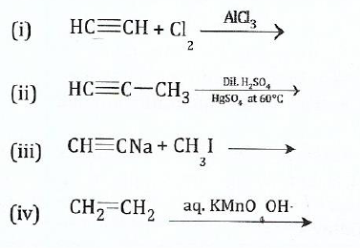
View Ans
14. (a) Write the open structures of five isomers of the compound C5H7Cl and their corresponding IUPAC names.
View Ans
(b);;;;;;Arrange the following compounds in the order of increasing acidity and reason(s) for your arrangement:
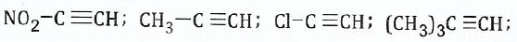
View Ans
;(c);;;;;;Suggest suitable tests to distinguish the following compounds:;
(i);;Propyne and propene
(ii);;;2-methylpent-2-ene and 3-methlpent-2-ene
(iii);But-2-yne and butane
;
View Ans
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256