THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL OF TANZANIA ADVANCED CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
132/1 CHEMISTRY 1
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
Time: 3 Hours Year: 2012
Instructions
1. This paper consists of sections A and B with a total of ten (10) questions.;
2. Answer all questions in section A and two (2) questions from section B.
;3. Each question carries ten (10) marks in section A and fifteen (15) marks in section B.
;4. Mathematical tables and non-programmable calculators may be used.;
5. Cellular phones and any unauthorised materials are not allowed in the examination room.;
6. Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
7.;;For calculations, you may use the following
Rydberg constant, RH;=;1.09678x 107m-1
Gas constant, R = 8.31JmoI-;1;K;-I;or 0.0082 atm mol-1;K;-I;dm3
GMV;;at s.t.p.;;;;22.4dm3
1 litre = 1 dm3;=1000cm3
At STP: Temperature = 273K, Pressure = 760mmHg
Planck constant, h=6.63x 10;-34;Js
Velocity of light, C = 3.0 x 108;m/s
Atomic masses H = 1, C = 12, N = 14, O-16, P-31, S=32, Cl=35.5, K=39, Mn=55, Fe=56![]()
1.;;;;;;;(a) Define mass spectrometer.
View Ans(c) Write the products of the following changes:;
(i) Alpha decay of;12;24;Mg and;84;Be
(ii) Beta decay of;146C and;3114Si
(d) If the wavelength of the first line in the Balmer series in a hydrogen spectrum is 6863 A0;, calculate the wavelength of the first line in the Lyman series in the same spectrum.
View Ans2.;;;The remains of an ancient firewood in a cave in Africa shows a146C decay rate of 3.1 counts per minute per gram of carbon. Assuming that the decay rate of;146C in a freshly cutwood is 13.6 counts per minute per gram of carbon, calculate the age of the remains, given the half-life of;146;C is 5730 years.
View Ans3.;;(a) Briefly explain the following terms:
(i) Reversible reaction
;(ii) Rate constant.
View Ans(b);;;;;;The reaction,;![]() ; attains its equilibrium at 470C. Study the reaction carefully and then answer the following questions:;
; attains its equilibrium at 470C. Study the reaction carefully and then answer the following questions:;
(i) State whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic.
(ii);;;;;How will the yield of HI be affected if:
•;;;;;;Pressure is increased?
•;;;;;;Temperature is increased?
•;;;;;;An inert gas is added?
(iii);;;Write the expression for the equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressures.
(iv);;;;At 47;0C, analysis of an equilibrium mixture of the gases yielded the following results:
PH2;=2.5x10-1;atm PI2;=1.6x10-1atm, and PHI;=4.0x10-1;atm. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction.
View Ans4.;;(a) State the following:
(i)Boyle's law
(ii);Charles' law
(iii)Dalton's law of partial pressures.
(b)A sample of PC15 weighing 2.69g was placed in a 1.00 litre flask and completely vaporized at a temperature of 2500C. The pressure observed at this temperature was 1 atmosphere.
The possibility exists that some of the PC15 may have dissociated according to equation;
![]()
;Calculate the partial pressures of PC15, PCI3;and C12;under the given experimental conditions.
View Ans5.(a)List four colligative properties of a solution.
View Ans(b);Considering that heptane and octane are liquids that form an ideal solution, answer the following questions:
(i)Give a mathematical expression for Raoult's vapour pressure law for a solution of two liquids and state each symbol used.
(ii)Under what conditions will a mixture of two liquids behave as an ideal solution?

6.(a)Briefly explain the following terms:
(i) Miscible liquids.;
(ii) Immiscible liquids.
;(iii) Partially miscible liquids.;
(iv) Partition law.
View Ans(b)10 grams of compound Q were dissolved in one litre of distilled water. When one litre of the solution formed was shaken with 100cm3;of ethoxyethane, 6 grams of compound Q were extracted. Calculate the amount of Q extracted from the solution residue after further shaking with 100cm;3;of ethoxyethane. Assume that the molecular state of the solute is the same in ethoxyethane and in water.
View Ans7.(a) Explain the following laboratory observations:
(i)When potassium permanganate is used in volumetric analysis it is acidified by using dilute sulphuric acid but not dilute hydrochloric acid or nitric acid.
(ii)Aqueous sodium hydroxide absorbs carbon dioxide readily but is never used to test the gas.
(b)0.50g of hydrated iron (Il) sulphate was dissolved in sulphuric acid and titrated against 0.1M aqueous potassium permanganate. Calculate the volume of potassium permanganate required to complete the titration.
View Ans8.Explain briefly the following facts:
(a) Nitric acid can be stored in aluminium tanks but not sulphuric acid or sodium hydroxide.
;(b) Galvanized iron sheets rust less rapidly than tinned iron sheets.
(c) Hydrogen gas can be used to reduce copper oxide but not zinc oxide.
(d) Sodium carbonate cannot precipitate lead carbonate from aqueous solution of lead ions.
(e) Calcium phosphate is soluble in dilute HCI but calcium sulphate is insoluble in dilute HCI.
View Ans9.(a)Briefly explain the term diagonal relationship.
View Ans(b);;Describe four similarities of lithium and magnesium.
View Ans(c) Describe the differences between graphite and diamond basing on the following;![]() properties:;
properties:;
(i) Hardness.
(ii)Electrical and thermal conductivity. (iii) Lubricating qualities.
View Ans10.Element X which exists in gaseous form is more reactive that Y which exists in liquid form,;![]() but the hydride of Y is a stronger acid than that of X. X does not disproportionate in water, while Y does. Although Y is not as reactive as X, it disproportionate in the cold and dilute or even in the hot and concentrated alkali while X does not. Both X and Y are the most electronegative elements in their respective periods. The reactive element X shows only negative oxidation state while Y shows negative and positive oxidation states. Basing on the given information:
but the hydride of Y is a stronger acid than that of X. X does not disproportionate in water, while Y does. Although Y is not as reactive as X, it disproportionate in the cold and dilute or even in the hot and concentrated alkali while X does not. Both X and Y are the most electronegative elements in their respective periods. The reactive element X shows only negative oxidation state while Y shows negative and positive oxidation states. Basing on the given information:
(a);Identify X and Y.
(b)Explain why X exists in gaseous form while Y is in liquid form.
(c) Give the equations of the reactions of X and Y with water, hot and concentrated alkali as well as cold and dilute alkali.
(d)Explain why X shows only negative oxidation state while Y shows both negative and positive oxidation states.
(e)Which one will displace the other in an aqueous solution of salts? Explain why.
View Ans11.(a) Name the following organic compounds according to IUPAC rules:
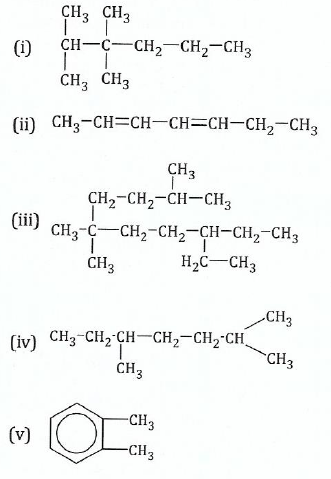
;(b)Write the structural formulae of the following:
(i)Cycloocta 1, 2, 5, 7-tetraene.
(ii)2, 2 dimenthyl 1, 3, 4 diethylheptane.
(iii)2-hydroxyl benzoic acid.
(iv)Butan 1, 2, 3, triol.
(v)Phenylethanone.
View Ans12.The following is a full structural formula of a certain organic molecule P. Study the structure and then answer the questions that follow:
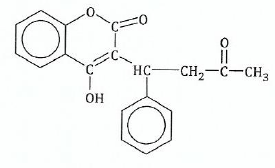
;(a)If the molecule gives a positive iodoform test:
(i)What are the reagents and conditions for the test?
(ii)Show on the formula which part of the molecule P gives the tri-iodomethane.
(b)Indicate on the formula the part of the molecule which will react with 2, 4-dinitrophenylhdrazine.
© Explain whether P would give a positive reaction with
(d) If molecule P reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide then:
(i)Name the group in P which is attacked by sodium hydroxide.;
View Ans(ii) Draw the structure of the product formed by the reaction.
View Ans7.(a) Explain the following laboratory observations:
(i)When potassium permanganate is used in volumetric analysis it is acidified by using dilute sulphuric acid but not dilute hydrochloric acid or nitric acid.
(ii)Aqueous sodium hydroxide absorbs carbon dioxide readily but is never used to test the gas.
(b)0.50g of hydrated iron (Il) sulphate was dissolved in sulphuric acid and titrated against 0.1M aqueous potassium permanganate. Calculate the volume of potassium permanganate required to complete the titration.
View Ans8.Explain briefly the following facts:
(a) Nitric acid can be stored in aluminium tanks but not sulphuric acid or sodium hydroxide.
;(b) Galvanized iron sheets rust less rapidly than tinned iron sheets.
(c) Hydrogen gas can be used to reduce copper oxide but not zinc oxide.
(d) Sodium carbonate cannot precipitate lead carbonate from aqueous solution of lead ions.
(e) Calcium phosphate is soluble in dilute HCI but calcium sulphate is insoluble in dilute HCI.
View Ans9.(a)Briefly explain the term diagonal relationship.
View Ans(b);;Describe four similarities of lithium and magnesium.
View Ans(c) Describe the differences between graphite and diamond basing on the following;![]() properties:;
properties:;
(i) Hardness.
(ii)Electrical and thermal conductivity. (iii) Lubricating qualities.
View Ans10.Element X which exists in gaseous form is more reactive that Y which exists in liquid form,;![]() but the hydride of Y is a stronger acid than that of X. X does not disproportionate in water, while Y does. Although Y is not as reactive as X, it disproportionate in the cold and dilute or even in the hot and concentrated alkali while X does not. Both X and Y are the most electronegative elements in their respective periods. The reactive element X shows only negative oxidation state while Y shows negative and positive oxidation states. Basing on the given information:
but the hydride of Y is a stronger acid than that of X. X does not disproportionate in water, while Y does. Although Y is not as reactive as X, it disproportionate in the cold and dilute or even in the hot and concentrated alkali while X does not. Both X and Y are the most electronegative elements in their respective periods. The reactive element X shows only negative oxidation state while Y shows negative and positive oxidation states. Basing on the given information:
(a);Identify X and Y.
(b)Explain why X exists in gaseous form while Y is in liquid form.
(c) Give the equations of the reactions of X and Y with water, hot and concentrated alkali as well as cold and dilute alkali.
(d)Explain why X shows only negative oxidation state while Y shows both negative and positive oxidation states.
(e)Which one will displace the other in an aqueous solution of salts? Explain why.
View Ans11.(a) Name the following organic compounds according to IUPAC rules:

;(b)Write the structural formulae of the following:
(i)Cycloocta 1, 2, 5, 7-tetraene.
(ii)2, 2 dimenthyl 1, 3, 4 diethylheptane.
(iii)2-hydroxyl benzoic acid.
(iv)Butan 1, 2, 3, triol.
(v)Phenylethanone.
View Ans12.The following is a full structural formula of a certain organic molecule P. Study the structure and then answer the questions that follow:

;(a)If the molecule gives a positive iodoform test:
(i)What are the reagents and conditions for the test?
(ii)Show on the formula which part of the molecule P gives the tri-iodomethane.
(b)Indicate on the formula the part of the molecule which will react with 2, 4-dinitrophenylhdrazine.
© Explain whether P would give a positive reaction with
(d) If molecule P reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide then:
(i)Name the group in P which is attacked by sodium hydroxide.;
View Ans(ii) Draw the structure of the product formed by the reaction.
View Ans13.(a) Write the reaction steps to show how to convert the following organic compounds:
(i)Benzophenone to diphenyl alcohol
(ii)Toluene to benzyl alcohol
(iii)Acetone to propyne
View Ans(iv)Propanal to I-phenyl-I-propanol
View Ans(b)Distinguish the following compounds:
(i);Phenol from chlorobenzene
(ii)Acetone from propyne
View Ans14.(a);![]() ;You are given the following compounds:
;You are given the following compounds:
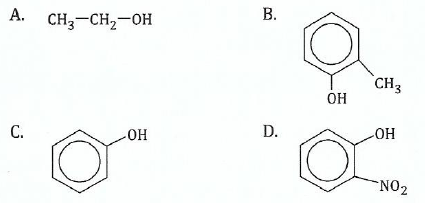
Arrange the given compounds in order of:
(i) Increasing acidity;
View Ans;(ii);;Increasing basic strength
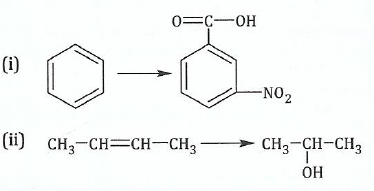
(b);;Outline how the following conversions can be achieved in more than four steps:
(c) Substance A is represented by a molecular formula C5H O. A undergoes oxidation with acidified potassium permanganate to give compound B which forms a crystalline derivative with 2, 4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine, but does not react with a mixture of iodine and sodium hydroxide.
(i);Write down the structural formulae of compounds A and B.
(ii)Show by means of an equation, how B reacts with 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine.
View AnsANSWER

Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania





