THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
031/1 PHYSICS 1
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
TIME: 3 Hours 2006/10/13 a.m.
Instructions
1. This paper consists of sections A, B and C.
2. Answer all questions in section A and B, and two (2) questions from section C.
3. Cellular phones are not allowed in the examination room.
4. Electronic calculators are not allowed in the examination room.
5. Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
6. Whenever necessary use the following constants:
Acceleration due to gravity g = 9.8 m/s2
Specific heat capacity of water Cw = 4200 J/kg K
SECTION A (20 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
1. For each of the items (i) (x) choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number.
(i) Metals conduct heat better than nonmetals because:
- metals are good conductors of electricity
- metals have free electrons while nonmetals have not
- molecules of metals have higher velocity than that of nonmetals
- metals are normally of high specific heat capacity
- the crystalline structure of metals is more compact than that of nonmetals.
(ii) A metre rule is pivoted at point A as illustrated by the diagram below and balanced by a force of 2.5 N.
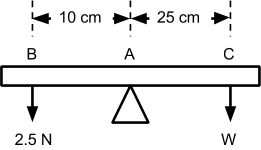 |
| Figure 1 |
The mass of the metre rule in kilogram is given by:
- 0.15
- 2.50
- 0.10
- 0.25
- 1.50
(iii) Which of the following will not affect the rate of evaporation of water in a dam?
- Surface area
- Depth
- Humidity
- Barometric pressure
- Temperature.
(iv) Aluminium has a specific heat capacity more than twice that of copper. Identical masses of aluminium and copper, both at 0°C are dropped together into a can of hot water. When the system has come to equilibrium
- aluminium is at a higher temperature than copper
- aluminium and copper are at the same temperature
- copper is at a higher temperature than aluminium
- temperature difference between the copper and aluminium depends on the amount of water in the can
- the temperatures of the copper and aluminium will be higher than that of water.
(v) In the diagram below (fig. 2) a beam of white light entering a triangular glass prism is refracted and dispersion of colour occurs.
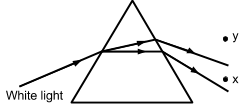 |
| Figure 2 |
A thermometer placed at Y records a rise in temperature from the radiation produced. The correct name for this radiation is
- ultra violet
- x-rays
- gamma rays
- infrared
- beta particles
(vi) A wire of uniform crosssectional area has a length of 10 m, a resistance of 2 ? and a resistivity of 2 x 10-7?m. The cross sectional area in m2 is:-
- 2 x 10-4
- 1 x 10-5
- 0.5 x 10-5
- 1 x 10-6
- 5 x 10-4
(vii) When the plastic pen is rubbed against dry hair, the pen attracts small pieces of paper. This means that the:
- hair becomes negatively charged
- hair becomes positively charged
- pen loses electrons
- hair gains electrons
- paper loses electrons.
(viii) Electric pressure is measured in
- current
- volts
- watts
- ampere
- force.
(ix) In the circuit diagram below (fig. 3) A, B, C and D are just positions and the switch is closed.
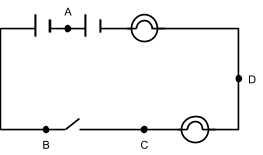 |
| Fig. 3 |
Choose the correct statement.
- The current at A will be different from the current at B
- The two lamps are wired in parallel
- The current reaches B before it reaches C
- With an extra lamp at D the current will be low
- With an extra lamp at A the batteries will run down immediately.
(x) The property which distinguishes longitudinal waves from transverse waves is the
- ability to be refracted
- need for a material medium
- relative directions of oscillations and propagation
- wavelength
- the speed of propagation.
2. Match the items in list A with responses in list B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number.
| List A | List B |
| (i) Internal resistance (ii) Short sighted person (iii) Thermistor (iv) Eddy current (v) Elasticity (vi) Thermopile (vii) Chromatic aberration (viii) Secondary colours (ix) Electrolysis (x) Isotopes |
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
3. (a) A rocket taking off vertically, pushes out 25 kg of exhaust gas every second at a velocity of 100 m/s. If the total mass of the rocket is 200 kg,
(i) what is the resultant upward force on the rocket? (2½ marks)
(ii) what is the upward acceleration of the rocket? (2 marks)
(b) Calculate the acceleration of the rocket in 3(a) above when it has burned off 100 kg of fuel. (3 marks)
View Ans(c) A simple weighing machine is made of a uniform bar 125 cm long and mass 5 kg and pivoted 2.5 cm from one end. Find the mass that must be suspended at the end of the long arm so as to balance a mass of 320 kg suspended at the end of the short arm. (2½ marks)
View Ans4. (a) State briefly:
(i) The cause of refraction of light when passing through transparent media. (1 mark)
(ii) Position of image in concave mirror, of a very distant object. (1 mark)
(iii) Cause for a blurred image in concave mirrors or convex lenses. (1 mark)
(b) Explain the following:
(i) Condition giving rise to critical angle and total internal reflection. (1½ mark)
(ii) Two principles in Physics used to make telescopes. (1½ mark)
View Ans(c) A telescope of 5.0 m diameter reflector of focal length 18.0 m is used to focus the image of the sun. using the distance of the sun from the earth and diameter of the sun as 1.5 x 1011 m and 1.4 x 109 m respectively, calculate the:
(i) position of the image of the sun. (2 marks)
(ii) diameter of the image of the sun. (2 marks)
View Ans5. (a) Define the following terms:
(i) Ampere (ii) Coulomb (iii) Volt (iv) Ohm (4 marks)
View Ans(b) (i) State Ohm’s law and two (2) of its limitations. (2 marks)
(ii) Determine the internal resistance of a cell and the value of R given that the p.d. of the cell in open circuit is 1.5 V, when connected to a 10 ? resistor its p.d. becomes 1.0 V, but when connected to a resistor of R ? the p.d. falls to 0.5 V (2 mark)
View Ans(c) A 200 g of liquid at 21°C is heated to 51°C by a current of 5 A at 6 V for 5.0 minutes. What is the specific heat capacity of the liquid? (2 marks)
View Ans6. (a) (i) Differentiate between heat and temperature. (2 marks)
(ii) With the aid of a sketch graph explain the importance of the anomalous expansion of water. (2 mark)
View Ans(b) Give reasons for the following
(i) A gap is left between two successive rails. (1 mark)
(ii) A glass tumbler breaks when hot liquid is poured. (1 mark)
(c) Define the coefficient of linear expansivity. (1 mark)
A copper pipe of length 100 cm at 15°C increases its length by 0.15% when a steam at 100°C passes through. Find the coefficient of linear expansivity of copper. (3 marks)
View Ans7. (a) A radioactive source is known to emit one type of radiation only i.e. ?, ? or ?. The source was placed in a holder as shown in fig. 4 below, first without a magnet and then a magnet was introduced. A detector was placed at positions 1, 2 and 3 and the count rates recorded in the table below.
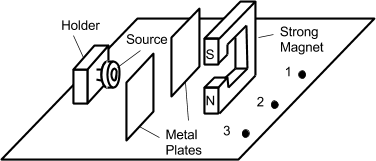 |
| Figure 4 |
| Counts per minute | ||
| Detector position | Magnet not present | Magnet present |
| 1 | 26 | 295 |
| 2 | 300 | 28 |
| 3 | 28 | 26 |
(i) What is the reason for placing the two metal plates in front of the source?
(ii) What is the value of the background counts per minute?
(iii) Define the background count. (3 marks)
(b) What is meant by the half-life of a radioactive element? (1 mark)
View Ans(c) A radioactive element has an initial count rate of 1200 counts per minute measured by a scale and this falls to 150 counts per minutes in 15 hours.
(i) Determine the half-life of the element. (3 marks)
(ii) If the initial number of atoms in another sample of this element is 3.0 x 1020, how many atoms will have decayed in 25 hours? (3 marks)
View Ans8. (a) (i) How does a conductor differ from a semiconductor in terms of energy levels?(2 marks)
(ii) By means of a well labelled diagram, describe the electric and magnetic effects on the cathode beam deflection in a c.r.o. (3 marks)
View Ans(b) (i) What is a diode? (1 mark)
(ii) Make a sketch of the output voltage against time for half-wave rectification. explain why the output flows in pulses. (2 marks)
View Ans(c) Describe and explain how a full-wave rectification is achieved by using two diodes. (2 marks)
View AnsSECTION C (20 marks)
Answer any two (2) questions from this section
9. (a) What do you understand by the following terms
(i) Triple point of water. (1 mark)
(ii) Specific latent heat of fusion. (1 mark)
(b) State three (3) differences between evaporation and boiling. (3 marks)
View Ans(c) A tin contains water at 290 K and is heated at a constant rate. It is observed that the water reaches boiling point after 2 minutes and after further 12 minutes it is completely boiled away. Calculate the specific latent heat of steam. (5 marks)
View Ans10. (a) Explain the meaning of
(i) Magnetic induction. (1 mark)
(ii) Magnetic screening. (1 mark)
(b) Draw a circuit diagram of an electric bell and explain how it works. (4 marks)
View Ans(c) (i) Draw the symbols for PNP and NPN transistors. (2 mark)
(ii) Sketch the simple circuit for NPN transistor amplifier. (2 marks)
View Ans11. (a) (i) Distinguish between speed and velocity. (2 marks)
(ii) Define uniform velocity and uniform acceleration. (2 marks)
View Ans(b) Sketch the diagram of a body which starts from rest and accelerates uniformly for sometimes to a constant velocity and then maintains this velocity for a certain period of time before decelerating uniformly to a stop. (2 marks)
View Ans(c) A car moving with a uniform velocity of 100 m/s is decelerated at 2.5 m/s2 to a stop. Calculate
(i) The time taken for the car to stop. (2 marks)
(ii) The distance traveled by the car before it is brought to rest. (2 marks)
View AnsANSWER

Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania





