THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
031/1 PHYSICS 1
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
TIME: 3 Hours Friday November 05, 2004 a.m.
Instructions
1. This paper consists of sections A, B and C.
2. Answer all questions in section A and B, and two (2) questions from section C.
3. Cellular phones are not allowed in the examination room.
4. Electronic calculators are not allowed in the examination room.
5. Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s). 6. Whenever necessary use the following constants:
Specific heat capacity of Aluminium,
CAL = 920 J kg1 K1
Specific latent heat of fusion of Aluminium LAL = 3.2×105 J kg1
Melting point of Aluminium = 660°C
SECTION A (20 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
1. For each of the items (i) (x) choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number.
(i) The movement of liquid from low to high concentration through a semipermeable membrane is called
- diffusion
- fusion
- osmosis
- osmotic pressure
- Brownian motion.
(ii) What would happen to the planets moving around the sun if the gravitational force suddenly disappeared?
- The planets would fuse together
- The planets would fly far away opposite to the sun’s direction
- The planets would move tangentially to their orbits in a straight line
- Some planets would fall onto other planets nearby
- Some of the planets would collide.
(iii) In a correctly fused plug, the cartridge fuse is connected between the
- neutral lead and live lead
- live lead and live pin
- neutral lead and earth lead
- live lead and earth pin
- positive lead and negative lead.
(iv) The weight of a body is 20 N in air, 15 N when totally immersed in water and 18 N when totally immersed in liquid L. What is the relative density of L?
- 5 N
- 0.4
- 0.4 N
- 2.5
- 0.5.
(v) A certain wave has a period of 0.2 sec and a wavelength of 60 cm. What is the velocity of the wave in cm/s?
- 30
- 0.30
- 12
- 3
- 300.0.
(vi) A convex mirror always forms
- real images only
- virtual images only
- inverted real images only
- magnified virtual images only
- real and virtual images depending on the position of the object.
(vii) One advantage of a leadacid accumulator is that
- its internal resistance is high
- no chemicals are used
- its e.m.f. is more than 15 V
- it can be recharged
- it supplies only a small current.
(viii) The unit of electric charge is
- ampere
- volta
- coulomb
- ohm
- ameter.
(ix) A wire carries a current i horizontally between the magnetic poles N and S which face each other on a table (see Fig. 1 below).
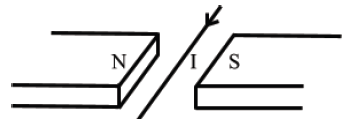 |
| Fig. 1 |
The direction of the force on the wire due to the magnet is
- from N to S
- from S to N
- opposite to the current direction
- vertically upwards
- in the direction of the current.
(x) Which of the following statements is not correct?
- The forbidden energy gap in conductors is very wide
- The majority charge carriers in ptype semiconductors are holes
- An integrated circuit (IC) has a combination of several resistors and transistors built out of the same crystal.
- Cathode rays consist of a beam of accelerated electrons
- Xrays are electromagnetic radiation of short wavelength.
2. Match the responses in list B with the words/phrases in list A by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number.
| List A | List B |
| (i) Hydrometer (ii) Greenhouse effect (iii) Translucent materials (iv) Y-rays (v) Nuclear fission (vi) Dynamos and generators (vii) Beats (viii) Magnetic lines of force (ix) P-type doping (x) Latent heat |
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
3. (a) (i) State the parallelogram of forces. (1 mark)
(ii) A metal sphere (Fig. 2) weighing 60 N is suspended from a beam by a thin string. What horizontal force must be applied to the weight to keep the string at an angle of 38° to the vertical? What is the tension in the string? (3 marks)
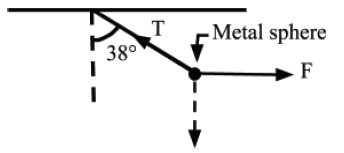
Fig. 2
View Ans(b) (i) State the principle of conservation of momentum. (1 mark)
(ii) Two cars of the same mass collide headon and become tangled so that they move on together. If the engines of both were stopped at the moment of impact and the speeds of the cars at impact were 120 m/s and 200 m/s, find the joint velocity immediately after collision. (3 marks)
View Ans(c) Draw a block and tackle pulley system with a velocity ratio of 4. (2 marks)
View Ans4. (a) A and B in Fig. 3 are two convex lenses correctly set up as a telescope to view a distant object as shown by the figure. One lens has a focal length of 5 cm and the other of 100 cm.
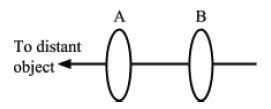
Fig. 3
(i) What is A called and what is its focal length? (½ mark)
(ii) How far from A is the first image of the distant object? (½ mark)
(iii) What is the name of B? (½ mark)
(iv) What acts as the ‘object’ for B and how far must B be from it if someone looking through the telescope is to see the final image at the same distance as the distant object? (1 mark)
(v) What is the distance between A and B with the telescope set up as in (iv)? (½ mark)
View Ans(b) Show by a ray diagram how a suitably placed eye sees an image of a point object which is placed
10 cm in front of a plane mirror. Show clearly the position of the image and give two reasons
why it is described as virtual. (4 marks)
View Ans(c) Calculate the critical angle for light emerging from glass of refractive index 1.55 into air. (3 marks)
View Ans5. (a) Explain the following concepts:
(i) Fundamental interval of a temperature scale (1 mark)
(ii) Apparent expansivity of water. (1 mark)
(iii) Anomalous expansion of water. (1 mark)
View Ans(b) Give one (1) reason for each of the following observations:
(i) Gas thermometers are more sensitive and accurate than liquid thermometers. (1 mark)
(ii) Alcohol in glass thermometers are commonly used in Arctic regions. (1 mark)
(iii) A house with thick walls is likely to be cooler during hot seasons. (1 mark)
View Ans(c) (i) Explain the observation that the level of liquid being heated in a vessel first falls before starting to rise. (2 marks)
(ii) Calculate the temperature of 50°C registered by a thermometer which has an ice point of 0° and steam point of 80°. (2 marks)
View Ans6. (a) Define capacitance of a capacitor and state the factors which affect capacitance. (4 marks)
View Ans(b) A capacitor is labelled with the capacitance value of 470µF and is charged to a potential difference of 10 V. Calculate the charge stored by the capacitor. (2 marks)
View Ans(c) After a long flight a plane may be charged.
(i) What causes the charge? (2 marks)
(ii) Why are passengers in the plane not charged, but an attendant who immediately opens the door from outside after the landing of plane is at risk? (2 marks)
View Ans7. (a) (i) Give two (2) properties that distinguish beta particles from gamma rays. (2 marks)
(ii) Differentiate between xrays and white light. (2 marks)
View Ans(b) (i) What do you understand by the term “half life of a radioactive substance”? (1 mark)
(ii) A radioactive element has a halflife of 1600 years. What will the fraction of its original mass which has decayed after 6400 years be? (2½ marks)
View Ans(c) Find the value of a, b, c, and d
(i) 2 1834 Po → 2 0892 Pb + A ba (1 mark)
(ii) 20892 Po → cdBi + e −01 (1 mark)
(iii) What is A in equation 7 (c) (i) above? (½ mark)
View Ans8. (a) (i) Name two (2) semiconductors which are widely used in electronics. (1 mark)
(ii) Give an illustration of a pn junction diode and its symbol. (2 marks)
(iii) How does a junction diode work? (2 marks)
(iv) Study the circuit diagrams in Fig. 7 (l and m) carefully. Which of the two circuits will light a bulb. (1 mark)
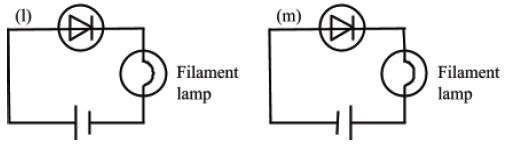 |
| Fig. 4 |
| (b) The semiconductor diode can be used as a rectifier as used in the circuit below? Fig. 5. |
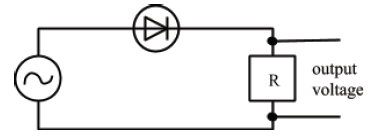 Fig. 5 |
(i) What does the term rectification mean? (1 mark)
(ii) The rectification described by the circuit in Fig. 5 above, is half wave rectification. Sketch its waveform which would be seen on a suitably adjusted CRO and explain why the output voltage is so rectified.
View AnsSECTION C (20 marks)
Answer two (2) questions from this section
9. (a) Explain the following terms:(4 marks)
(i) Saturated vapour. (1 mark)
(ii) Unsaturated vapour. (1 mark)
(iii) Dew point. (1 mark)
View Ans(b) The table below gives the results of an experiment to determine the saturation vapour pressure of water at various temperatures. Plot a graph of these results. Use the graph to deduce the:(1½ mark)
(i) vapour pressure of water in a room where the dew point is 8°C. (½ mark)
(ii) boiling point of water at a pressure of 120 mm Hg. (½ mark)
| Temperature (°C) | 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| Vapour pressure (mm Hg) | 4.6 | 9.2 | 17.5 | 31.8 | 55.3 | 92.5 | 149.4 |
(c) Distinguish between heat (thermal) capacity and specific heat capacity. (1 mark)
(d) A block of aluminium, 500 g at 20°C was heated in a furnace until it just melted.
(i) Find the total quantity of heat required. (2 marks)
(ii) If in this process the furnace consumed 100 litres of gas of calorific value 16800 J/litre, find its efficiency. (1½ marks)
View Ans10. (a) List down two (2) factors that affect the magnitude of induced e.m.f. in a moving coil galvanometer. (1 mark)
View Ans(b) (i) State the laws of electromagnetic induction. (2 marks)
(ii) Explain how eddy currents are produced.
(iii) How can eddy currents be minimized? (3 marks)
View Ans(c) A moving coil galvanometer of 30 ? resistance which carries a maximum current of 15mA can be converted into an ammeter.
(i) How can the galvanometer be made to give ampere readings? (1 mark)
(ii) If the device is to give a 1.5 A full scale deflection (f.s.d.), what value of resistance will be required? (3 marks)
View Ans11. (a) Explain briefly the following:
(i) Thermionic emission (1 mark)
(ii) The production of a stream of electrons in a cathode ray oscilloscope (c.r.o.). (1 mark)
(iii) The principle of the transistor. (1 mark)
View Ans(b) What method in devices using the thermionic emission principle ensures that the electrons produced:
(i) do not accumulate at the source? (1 mark)
(ii) reach their target undeviate? (1 mark)
(iii) travel without meeting other forms of particles on their way to the target? (1 mark)
View Ans(c) Using block diagrams for n p n transistor, show how a transistor can be used in a simple circuit as:
(i) an amplifier. (2 marks)
(ii) a switch. (2 marks)
View AnsANSWER

Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania





