THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL OF TANZANIA CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
HISTORY
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
Time: 3 Hours Year: 2005
SECTION A
1. For each of the items (i) — (x) choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number.
(i) Students of History should understand the fact that:
A. Africa had no development at all before the coming of the missionaries.
B. The coming of traders in Africa by the 19 th century was a blessing to African handicraft industries.
C.Africa had its own economic and technological achievements before the 15th century.
D.Changes in African societies were independent of the contact with Asia and Europe by the 20th century.
E.The present development problems are a result of colonialism only.
Choose Answer :(ii)The feudal lords and traders in the East African coast reacted against the Portuguese invasion because they:
A. Wanted to expand clove plantation.
B.Wanted to protect their economic and political interests.
C.Wanted to safeguard their serfs.
D.Were racists.
E.Feared to lose their slaves.
Choose Answer :(iii)Which of the following is the best description of Homohabilis?
A. The early man
B. The modern man
C. The thinking man
D. The erect man
E. Man the tool-maker
Choose Answer :(iv)The United Nations' agency responsible for literacy is:
A. UNESCO
B. UNDP
C. UNEP
D. IFAD
E. UNICEF
Choose Answer :(v)The British colonial rule in East Africa constructed the Uganda railway in order to:
A. Attract more European settlers to Kenya.
B. Compete with the Imperial German East African rule.
C. Provide cheap means of transport for East African people.
D.Gain easy access to resources surrounding the interlacustrine area.
E.Facilitate transportation of suppressive soldiers against the rebel Bunganda Empire.
Choose Answer :(vi)What did the emergence of Mau Mau in Kenya indicate?
A.The settlers were in full control of the country.
B.Kenyans were prepared to sacrifice their lives for liberation of their land.
C. Jomo Kenyatta was the likely person to lead independent Kenya.
D.There was disunity among the Africans in their opposition to British rule.
E.The direct rule system as applied in Kenya did not function.
Choose Answer :(vii)The Moresby treaty was not successful to the abolition of slave trade because it:
A.was not against slave trade.
B.was anti-slavery but not anti slave trade.
C. faced strong opposition from Americans.
D.confined itself to slave trade within East Africa.
E.did not consider economic well-being of African chiefs.
Choose Answer :(viii) One of the problems facing the African Unity is colonial legacy. This is because:
A.Colonialism preserved and emphasized the separation of each colony.
B. Indirect rule introduced by the British facilitated interstate hatred.
C. The Portuguese policy of assimilation discouraged unity.
D.Colonialism encouraged growth of apartheid in all settler colonies.
E.Territorial size of African states as created by colonialists is not even.
Choose Answer :(ix) In many colonies peasant agriculture was preferred by the colonial state because:
A.it was cheap and peasants produced for both the metropole and themselves.
B.settlers were arrogant and conformists.
C.peasants were able to acquire capital loans from colonial banks and pay on time.
D.it was easy to inject new production techniques among peasants.
E.it enabled the colonial states to bring about development among the rural peasants.
Choose Answer :(x) The former East African Community was formed primarily to:
A.Bring about East African Federation.
B.Put to an end to hostility between Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda.
C.Share the resource of the three member states.
D.Promote Kiswahili in the East African countries.
E.Strengthen economic cooperation between Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda.
Choose Answer :2.(a) Match the phrases in List A with the responses in List B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number.
LIST A
(i) Hehe chiefdom
(ii) The Battle of Isandhlwana
(iii) Ubugabire
(iv) The International African Association
(v) Liberia and Sierra Leone
LIST B
A.Former West African Colonies.
B.Launched by King Leopold to spearhead the colonization of the Congo.
C.An example of militarized centralized state in South-Central Tanzania by the 19 th Century.
D.Title of the Tutsi leader in Burundi and Rwanda. E. Afro-Boer confrontation in South Africa.
F. African resistance against the colonization of Zulu Empire.
G.An exploitative relation between the cattle owning Tutsi and Hutu agriculturalists.
H.Settlements of freed slaves.
I.The former OAU human rights agency.
J.A monument of African resistance against British colonialism.
View Ans(b) Arrange the following statements in a chronological order
(i) Thus, between Egypt and neighbours, wars over scarce resources became common.
(ii)The production of surplus needed additional labour in order to assist families to cope with the increased amount of work.
(iii)The collapse of communalism in Egypt did not only lead to the ![]() formation of the state but also to production of surplus products.
formation of the state but also to production of surplus products.
(iv) The most reliable source of the additional labour force was war which provided captives who could be made to work for the captors.
(v) At first the war captives were either adopted or killed, but with the demand for additional labour, they started being used as slaves.
View AnsSECTION B
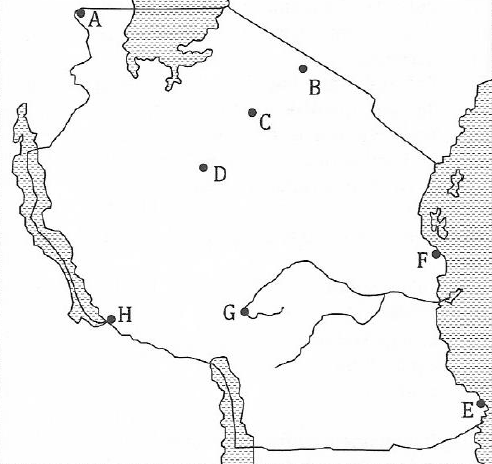
3.(a) The map below locates the most famous historical sites in Tanzania labelled A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H. Name five (5) of them.
(b) Match the dates in Column I with the corresponding historical events in Column Il by writing the letter of the correct event beside the number of the date.
| COLUMN I | COLUMN II |
| (i) 1919 (ii) 1957 (iii) 1963 (iv) 1964 (v) 1975 | A. The actual armed struggle began in Mozambique when FRELIMO guerrillas crossed into Niasa and Carbo Delgado Provinces. B.Tanganyika got her independence. C. The Berlin Conference. D. The Independence of Ghana under Kwame Nkrumah. E. End of German colonial rule in East Africa. F. End of British colonial rule in Zanzibar. G. Civil war erupted in Angola. H. The Portuguese colonized Mozambique. I. Tanganyika became a German mandate colony. J. Maji Maji resistance against German colonial economy ended. |
4.Under each of the sentences (i) — (x) below there are five statements. One of the statements wrongly explains the sentence. Identify the wrong statement and write the letter of the statement beside the sentence number.
(i) Africa and the Middle East are related both geographically and historically. A. Out of the 22 members of the Arab League, nine are in Africa.
B.Slaves from Africa worked in big plantations established by the Berbers.
C.The Arab states have had commercial, religious, cultural and economic ties with the African continent from ancient times.
D.Trans-Saharan trade served as a major link between the Ovo regions.
E.In East Africa pre-colonial trade link with Middle East evolved prosperous coastal city states.
(ii)The major European activities in Africa between the 15th and 19th centuries were:
A. Colonization
B. Trade
C. Evangelization
D.Exploration
E. Tourism
(iii)After independence African countries were confronted by various political, economic and social challenges including how to:
A. Contain political strife and coup d'états.
B. Conform to the OAU and UNO Charters.
C. Exploit and redistribute resources and land.
D.Maintain national sovereignty and integrity.
E.Correct international boundaries set by the colonial powers.
(iv)The following statements explain about the coming of the Whites in South Africa:
A.The first whites to settle at the Cape of South Africa came from Holland in 1652.
B.The coming of the whites in South Africa should be seen in the light of the economic development in Europe in the 16th and 17th centuries.
C.The period between the 16th and 17th centuries was marked by the rise of monopoly capitalism in Europe.
D.In the 16th and 17th centuries trade within and outside Europe was crucial in the development of European economies.
E.In this period the principal concern of the European nations was to accumulate wealth in the form of gold, silver and spices.
(v) The Independence of Ghana strengthened African confidence.
A. Kwame Nkrumah played a leading role in the continent-wide struggle for independence.
B. In April 1958, Nkrumah called the first conference of Independent African States.
C. In the first Conference of Independent African States the heads of states of independent Africa took a common stand against colonialism.
D. South African regime under W.P. Botha walked out of the first Conference of Independent African States.
E. The first Conference of independent African States laid the foundation for the formation of the Organization of African Unity.
(vi) Colonialism created the conditions of neo-colonialism.
A.Economically, the structures set emphasized on primary sector.
B.The industrial sector was the smallest of all. C. Rich Africans were not accommodated.
D.Revolutionary nationalist leaders were eliminated.
E.The African petty-bourgeoisie as a class was created to serve the big capitalists.
(vii)The following statements explain about the slave owning societies in East Africa by 1850.
A. Usually slaves could not marry or acquire wealth.
B. Slaves were people who had become attached to chiefs' courts.
C. Slaves were men so controversial that their kinsmen disowned them.
D. Slaves were prisoners of war.
E. Examples of societies which owned slaves were Kerewe and Sambaa.
(viii)The Berlin Conference was an imperialist conference which:
A. legalized the partition of African countries among European imperialist powers.
B. influenced penetration of European missionaries and explorers in the ![]() interior of Africa.
interior of Africa.
C. resolved inter-imperialist conflicts over Africa.
D. declared the Nile, Niger and Congo River basins as free zones.
E. declared abolition of slave trade in the European territories.
(ix)The indirect rule system:
A. was introduced and enforced by Lord Fredrick Lugard.
B. made most of African chiefs the main colonial administrative instruments.
C. helped the colonial officials to collect taxes easily from the local people.
D. was more effective in German colonies than in the French West African colonies.
E. was introduced first in Northern Nigeria among the Islamic emirates.
(x) The following are the main functions of the Moran in the Maasai society:
A. Protect the whole society.
B. Protect livestock against enemies and wild animals
C.Trade with neighbouring societies in order to accumulate more livestock.
D. Raid neighbouring communities for the purpose of increasing the number of their herds.
E. Travel far with the herds in search for water and pastures.
View AnsSECTION C
5.Account for the rapid expansion of slave trade in East Africa during the 19 th century.
View Ans6.What brought about the Chimurenga war in Southern Rhodesia in 1896 — 1897?
View Ans7.Show the role played by Islam in the formation and transformation of states in pre-colonial West Africa.
View Ans8.Describe briefly the common characteristics of settler and plantation agriculture in colonial Africa.
View Ans9.Why did the Portuguese colonies in Africa engage in armed struggle to liberate themselves?
View Ans10.Discuss the role played by the Organization of Africa Unity (OAU) in the decolonization of Africa.
View AnsANSWER

Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania





