


FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 216
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 216



FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 204
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 204
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
FORM TREE MID TERM TEST MARCH-2025
033/1 BOOK-KEEPING
Time: 3 Hours MARCH, 2025
Instructions
- This paper consists of three sections A, B and C with a total of 9 questions.
- Answer all questions in section A and B and only two (2) questions from section C.
- Section A carries twenty (20) marks, section B forty (40) marks and section C forty (40) marks.
- Non programmable calculators may be used.
- Cellular phones, and other authorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Write your examination number on every page of your Answer booklet(s).
SECTION A (20 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section
1. For each of the items (i)-(xv), choose the correct answer from among the given
Alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in the answer sheet provided
- If sales is 20,000 and profit make up is 25%, determine the amount of cost price
- 13,600
- 12,000
- 16,000
- 12,900
- 20,600
- Which book of prime entry records the sale or purchase of non-current Assets?
- General journal
- Sales journal
- Purchases journal
- Cash book
- Sales return day book
- If cash sale amount to Tshs 100,000/= paid direct into the bank account, the correct double entry will be to
- Debit sales account and credit cash account by sh.100, 000
- Debit cash account and credit bank account by sh.100, 000
- Debit bank account and credit sales account by sh.100, 000
- Debit bank account and credit cash account by sh.100, 000
- Debit sales account and credit bank account by sh.100, 000
- How much is to be reimbursed if a petty cashier has spent Tsh.189,00/=while his cash float is Tsh.200,000/=
- Tsh,11,000/=
- Tsh 389,000/=
- Tsh,189,000/=
- Tsh,200,000/=
- Tsh,21,000/=
- Working capital is a term meaning.
- The excess of current liabilities over current liabilities
- The excess of the current assets over the current liabilities
- the excess of the current assets over non-current liabilities
- The excess of current assets over non-current assets.
- The excess of non-current Assets over current liabilities
- Natasha and Ndengwe share profits and losses in the ratio 3:2. Their partnership recorded net profits of shs. 1,400, interest on capital shs. 420, partners’ salaries shs. 100 and drawings shs. 280, Determine Ndengwe’s share of the profits.
- TZS 840
- TZS 560
- TZS 464
- TZS 696
- TZS 506
- From the following categories of errors, identify the category of errors which affect only one account
- Casting errors
- Errors of principle
- Errors of omission.
- Errors of original entry.
- Errors of commission.
- In the business of C. Sangster, who owns a clothing store, which of the following is the capital expenditure?
- Fixtures and New Van bought
- Shop fixtures bought and wages of assistants
- Wages of assistants and new van bought
- Wages of assistants and Petrol for Van
- Fixtures and salaries.
- Manufacturing account is used to calculate:
- Production cost paid in the year
- Total cost of goods produced
- Production cost of goods completed
- Gross profit on goods sold
- Prime cost of goods manufactured
- Depreciation can be described as the : _______
- Amount spent to buy a non –current asset
- Salvage value of a non-current asset consumed during its period
- Cost of the non-current asset consumed during its period
- Amount of money spent replacing non-current asset
- Cost of old asset plus new assets purchased
- A bank reconciliation statement is a statement:
- Sent by bank when the account are overdrawn
- Drawn to verify cash book balance with the bank statement balance
- Drawn up by the bank to verify the cash book
- Sent by the bank to the customers when errors are made
- Sent by the bank customers to the friends.
- If two totals of trial balance do not agree, the difference must be entered in:
- A real account
- The trading accounts
- A nominal account
- The capital account
- A suspense account
- The accounting equation is expressed in the financial statement called:
- statement of financial position
- income statement
- expenditure statement
- reconciliation statement
- statement of change in equity
- If we take goods for own use, we should
- Debit drawings Account: Credit Purchase Account
- Debit Purchases Account: Credit Drawings Account
- Debit Drawings Account: Credit Inventory Account
- Debit Sales Account: Credit Inventory account
- debit inventory Account: Credit Drawing Account
- if a partnership maintains a fixed capital account, then the partner’s share
of profits is:
- Credited to the partner’s drawings account
- debited to the partner’s capital account
- credited to the partner’s capital account
- credited to the partner’s current account
- debited to the partner’s current account
2. For each of the items (i)-( v) match the narrations of bank reconciliation Items in column A with their corresponding names in column B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number in the answer sheet provided
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
|
|
SECTION B (40 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section.
3. In 1991 Mr. Chipepeto bought a motor car for the cost value of sh.8, 000,000/= with the aim of assisting him in business. But three years later he decided to dispose it for a book value of sh.6,700,000/=
- What is the term used to mean the difference between cost value and book value.
- Outline four reasons that could be the causes for him to dispose the car for less than the cost value.
4. The DSM Rotary club, has provided you with the following information:-
| As at 31st December | 2000 | 2001 |
| Subscription in arrears | 6400 | 8800 |
| Subscription in advance | 1200 | 3400 |
| Subscription during the year | - | 20,200 |
| Insurance expenses owing (in arrears) | 3700 | 2700 |
| Insurance expenses prepaid (in advance) | 4400 | 5200 |
| Insurance paid during the year | - | 16,800 |
Required: Prepare A Subscription account and Insurance account, clearly showing amounts to be transferred to income and expenditure accounts for year 2001.
5. Define the following terms
- Discount received
- Invoice
- Discount allowed
- Carriage inwards
- Carriage outwards
6. (a) Mr. Kyamba wants to start a business, but before commencement he needs to learn book keeping. Outline five objectives for him to study book keeping.
(b) Briefly explain three types of a cash book.
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer two questions only from this section.
7. Panguso& company limited own a manufacturing industry which had the following records for the year ended at 31st December 2007.
- Inventory at 1st January 2007:
- raw materials sh.760, 000
- Finished goods sh 360,000
- Purchases of raw material sh.420, 000
- Sales of finished goods sh.2, 490,000
- Factory Fuel & power sh.320, 000
- Royalty sh.500, 000
- Depreciation of works machine sh.88, 000
- Market value sh.1,800,670
- General office expense sh.10, 740
- Manufacturing wages sh.170, 000
- Inventory at 31 stDec 2007: raw material sh.900, 000
- Finished goods sh.580, 000
- Works in progress sh.734, 000
You are required to prepare
- Statement of manufacturing costs for the year ended at 31 stDec 2007
- Income statement for the year ended at 31.12.2007
8. XY Ltd provides for depreciation of its machinery at 20% per annum on cost; it charges for a full year in the year of purchase but no provision is made in year of sale/disposal.
Financial statements are prepared annually to 31th December. 2015
- January 1 Bought machine ‘A’ 10,000
- July 1 Bought machine ‘B’ 6,000
2016
- March 31 Bought machine ‘B’ 8,000
2017
- October 7 Sold machine ‘A’ – proceeds 5,500
- November 5 Bought machine ‘D’ 12,000
2018
- February 4 Sold machine ‘B’ – proceeds 3,000
- February 6 Bought machine ‘B’ 9,000
- October 11 Exchanged machine ‘D’ for machine valued at 7,000
Prepare;
- The machinery account for the period 1st January 2015 to 31st December 2018
- The accumulated provision for depreciation on machinery account, for the period 1st January 2015 to 31st December 2018.
9. The financial of the GGM trading company ended on 30th November 2014. You have been asked to prepare a total amount receivable and total amount payable for the draft final amounts. You are able to obtain the following information for the financial year the book of original entry.
| Sales | – Cash 344,890 – Credit 268,187 |
| Purchase | – Cash 14,440 – Credit 496,600 |
- Total receipts from customers 600,570
- Total payment to suppliers 503,970
- Discount allowed to credit customer 5,520
- Discount received from credit suppliers 3,510
- Refund given to cash customers 5,070
- Balance in sales ledger setoff against balance in the purchase ledger 700
- Bad debt written off 780
- Increase in the allowance for doubtful debts 900
- Credit note issued to credit customers 4,140
- Credit note received from credit suppliers 1,480
According to the audited financial statement for the previous year account receivable and account payable as to 1st December 2013 were 26,550 and 43,450 respectively
- Required;
Draw up the relevant total accounts entering end of year total for account receivable and account payable.
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 192
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 192
PRESIDENT OFFICE REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION
AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES
COMPETENCE BASED ASSESSMENT
FORM THREE
MID TERM EXAMS-AUG– 2023
062 BOOK KEEPING
Time: 2:30 Hours August, 2023
Instructions
- This paper consists of sections A, B and C with a total of nine (9) questions.
- Answer all the questions.
- Sections A carries fifteen (15) marks and B carries forty (40) marks and Section C carries forty-five (45) marks.
- All writings must be in blue or black ink.
- Non – programmable calculators may be used.
- All communication devices, programmable calculators and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet (s).
SECTION A (15 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section
- For each of the items (i) – (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter besides the item number in the answer booklet provided:
- How could purchases of a non- current assets by cheques affect the statement of financial position?
- By decreasing non-current assets account and decreasing bank account
- By increasing bank account and decreasing asset account
- By increasing non-current asset account and decreasing cash account
- By increasing cash account and decreasing asset account
- By increasing non-current asset account and decreasing bank account
- Amount of surplus in a statement of income and expenditure account indicates:
- Excess of income over expenditure
- Excess of cash received over credit sales
- Excess of expenditure over income
- Excess of gross profit over expenses
- Excess of expenses over net profit
- Government expenditures on items from which the government attains no value are called.
- Development expenditure.
- Recurrent expenditure.
- Capital expenditure.
- Revenue expenditure
- Nugatory expenditure.
- Which items would appear under non-current liabilities in the statement of financial position?
- TZS 700,000/= 5 years Loan from NBC.
- TZS 900,000/= of Credit purchases
- TZS 500,000/= paid for expenses
- TZS 600,000/= 10 months Loan from NMB
- TZS 800,000/= 6 months Loan from CRDB
- On 20th July, 2023, Mtumzima, a sole trader purchased a machinery for cash paying TZS 3,500,000/=. What would be a double entry for this transaction?
- Debit: Cash account, Credit: Machinery account
- Debit: Purchases account, Credit: Machinery
- Debit: Machinery account, Credit: Purchases account
- Debit: Machinery Account, Credit: Bank account
- Debit: Machinery account, Credit: Cash account
- At the beginning of Accounting year, Wini Charity Foundation had TZS 140,000/= as non-current Assets, TZS 50,000/= as current Assets and TZS 60,000/= as liabilities. What would be its opening Accumulated fund?
- TZS 190,000/=
- TZS 200,000/=
- TZS 110,000/=
- TZS 130,000/=
- TZS 250,000/=
- Which of the following best describes Non-current assets?
- Expensive items bought for the business
- Items having long life and not bought for resale
- Items which will not wear out quickly
- Items which do not add value to a business
- Items bought to be used by the business
- ______________ are the books under which the transactions are entered before being posted to their respective ledgers.
- Accounts
- Subsidiary books
- Cash books
- Ledger books
- Note books
- “A company does not include the value of skills gained by its employees from training programs in its financial records.” Which accounting concept is applied?
- Dual aspect concept
- Matching concept
- Dual Aspect concept
- Money measurement concept
- Business entity concept
- A firm bought a Motor van for TZS 5,000,000 which had a scrap value of TZS 500,000, and useful life of 5 years. What would be the depreciation charge if a straight line method is used?
- TZS 1,000,000
- TZS 1,100,000
- TZS 900,000
- TZS 100,000
- TZS 500,000
- Match the items in Column A with the responses in Column B by writing the letter of the correct responses below the corresponding item number in the table provided.
| Column A | Column B |
|
|
SECTION B (40 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
- Complete the following table by identifying the account to be credited and debited as well:
| S/N | Transactions | Account to be debited | Account to be credited |
| i | Cash paid to Rahima |
|
|
| ii | A payment of rent by cash |
|
|
| iii | Sales of goods to Mtumzima |
|
|
| iv | Cash received from Julius |
|
|
| v | Purchased goods for cash |
|
|
- Use the knowledge of accounting equation to fill in the gap in the following table
| S/N | ASSETS | CAPITAL | LIABILITIES |
| i | TZS 3,500,000 | TZS 1,700,000 | TZS __________ |
| ii | TZS ___________ | TZS 8,000,000 | TZS 4,100,000 |
| iii | TZS 4,900,000 | TZS _________ | TZS 2,100,500 |
| iv | TZS 25,600,000 | TZS 17,900,000 | TZS __________ |
| v | TZS ____________ | TZS 15,500,000 | TZS 3,400,000 |
- Briefly describe the meaning of the following terms as used in book keeping:
- Accrued expenses
- Book keeping
- Credit transaction
- Carriage outwards
- Trial balance
- Winfrida is a business woman who owns a Jewels shop in Arusha. She is also a customer of CRDB bank. Winfrida prefers to settle her debts using cheques. In the last month, she wrote a cheque to Onesmo, her creditor, for which the bank refused to settle it. In five points outline the reasons for this to happen.
SECTION C (45 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
- Mtumzima Transport Company with the financial year ending on 31st December, bought two motor vans on 1st January 2011, No 1 for TZS 18,000,000 and No 2 for TZS 15,000,000. It also buys another van, No. 3 on 1st July 2012, for TZS 19,000,000 and another No 4 on 1st October, 2013 for TZS 17,200,000 the van No 1 was sold for TZS 6,290,000 on 30th September 2014. It is a company’s policy to charge depreciation at 15% per annum using a straight line method for each month of ownership basis.
Required: Prepare for the year ended 31st December, 2011, 2012, 2013 and 2014.
- Motor van account
- Accumulated Provision for depreciation account
- Motor van disposal account
- The following information is available from the books for Ethan Wholesale Store on 1st September, 2021:
Balances in purchases ledger TZS 120,000 (CR)
Balances in sales ledger TZS 7,100 (CR)
Balances in purchases ledger TZS 4,800 (DR)
Balances in sales ledger TZS 163,100 (DR)
During September 2021:
Sales 140,000
Purchases 88,000
Returns inwards from debtors 55,000
Returns outwards from creditors 7,300
Receipts from debtors 91,300
Payments to creditors 76,700
Discount allowed 4,000
Discount received 2,200
Bad debts written off 3,800
Debtors cheque dishonored 7,500
Interest charged to debtors on overdue accounts 500
Sales ledger debit transferred to purchases Ledger 9,600
Notes:
- 10% sales and discount allowed relate cash transactions
- 5% of the goods bought during the month were destroyed by fire, the insurance company had agreed to pay adequate claim.
You are required to prepare:
- A sales ledger control account
- A purchases ledger control account
- Mtumzima Entreprises had the following assets and liabilities on the date shown:
01.01.2021 31.12.2021
Premises 14,500 14,500
Motor cars 2,800 1,800 Furniture 3,500 3,200
Stock in Trade 11,200 13,100
Trade debtors 10,900 11,400
Trade creditors 14,600 17,200
Cash at bank 1,330 3,980
Prepaid expenses 670 1,120
Accrued expenses 1,300 600
During 2021, Mtumzima withdrew TZS 3,000 per month from the business bank account for his personal use. On 4 July 2021 he sold his personal car for TZS 12,000 and paid the proceeds into the business bank account.
Required:
Calculate the net profit or loss made by Mtumzima for year ended 31st December, 2021.
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 149
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 149
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
FORM TREE MID TERM TEST MARCH-2023
033/1 BOOK-KEEPING
Time: 3 Hours MARCH, 2023
Instructions
- This paper consists of three sections A, B and C with a total of 9 questions.
- Answer all questions in section A and B and only two (2) questions from section C.
- Section A carries twenty (20) marks, section B forty (40) marks and section C forty (40) marks.
- Non programmable calculators may be used.
- Cellular phones, and other authorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Write your examination number on every page of your Answer booklet(s).
SECTION A (20 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section
1. for each of the items (i)-(xv), choose the correct answer from among the given
Alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in the answer sheet provided
- If sales is 20,000 and profit make up is 25%, determine the amount of cost price
- 13,600
- 12,000
- 16,000
- 12,900
- 20,600
- Which book of prime entry records the sale or purchase of non-current Assets?
- General journal
- Sales journal
- Purchases journal
- Cash book
- Sales return day book
- If cash sale amount to Tshs 100,000/= paid direct into the bank account, the correct double entry will be to
- Debit sales account and credit cash account by sh.100, 000
- Debit cash account and credit bank account by sh.100, 000
- Debit bank account and credit sales account by sh.100, 000
- Debit bank account and credit cash account by sh.100, 000
- Debit sales account and credit bank account by sh.100, 000
- How much is to be reimbursed if a petty cashier has spent Tsh.189,00/=while his cash float is Tsh.200,000/=
- Tsh,11,000/=
- Tsh 389,000/=
- Tsh,189,000/=
- Tsh,200,000/=
- Tsh,21,000/=
- Working capital is a term meaning.
- The excess of current liabilities over current liabilities
- The excess of the current assets over the current liabilities
- the excess of the current assets over non-current liabilities
- The excess of current assets over non-current assets.
- The excess of non-current Assets over current liabilities
- Natasha and Ndengwe share profits and losses in the ratio 3:2. Their partnership recorded net profits of shs. 1,400, interest on capital shs. 420, partners’ salaries shs. 100 and drawings shs. 280, Determine Ndengwe’s share of the profits.
- TZS 840
- TZS 560
- TZS 464
- TZS 696
- TZS 506
- From the following categories of errors, identify the category of errors which affect only one account
- Casting errors
- Errors of principle
- Errors of omission.
- Errors of original entry.
- Errors of commission.
- In the business of C. Sangster, who owns a clothing store, which of the following is the capital expenditure?
- Fixtures and New Van bought
- Shop fixtures bought and wages of assistants
- Wages of assistants and new van bought
- Wages of assistants and Petrol for Van
- Fixtures and salaries.
- Manufacturing account is used to calculate:
- Production cost paid in the year
- Total cost of goods produced
- Production cost of goods completed
- Gross profit on goods sold
- Prime cost of goods manufactured
- Depreciation can be described as the : _______
- Amount spent to buy a non –current asset
- Salvage value of a non-current asset consumed during its period
- Cost of the non-current asset consumed during its period
- Amount of money spent replacing non-current asset
- Cost of old asset plus new assets purchased
- A bank reconciliation statement is a statement:
- Sent by bank when the account are overdrawn
- Drawn to verify cash book balance with the bank statement balance
- Drawn up by the bank to verify the cash book
- Sent by the bank to the customers when errors are made
- Sent by the bank customers to the friends.
- If two totals of trial balance do not agree, the difference must be entered in:
- A real account
- The trading accounts
- A nominal account
- The capital account
- A suspense account
- The accounting equation is expressed in the financial statement called:
- statement of financial position
- income statement
- expenditure statement
- reconciliation statement
- statement of change in equity
- If we take goods for own use, we should
- Debit drawings Account: Credit Purchase Account
- Debit Purchases Account: Credit Drawings Account
- Debit Drawings Account: Credit Inventory Account
- Debit Sales Account: Credit Inventory account
- debit inventory Account: Credit Drawing Account
- if a partnership maintains a fixed capital account, then the partner’s share
of profits is:
- Credited to the partner’s drawings account
- debited to the partner’s capital account
- credited to the partner’s capital account
- credited to the partner’s current account
- debited to the partner’s current account
2. For each of the items (i)-( v) match the narrations of bank reconciliation Items in column A with their corresponding names in column B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number in the answer sheet provided
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
|
|
SECTION B (40 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section.
3. In 1991 Mr. Chipepeto bought a motor car for the cost value of sh.8, 000,000/= with the aim of assisting him in business. But three years later he decided to dispose it for a book value of sh.6,700,000/=
- What is the term used to mean the difference between cost value and book value.
- Outline four reasons that could be the causes for him to dispose the car for less than the cost value.
4. The DSM Rotary club, has provided you with the following information:-
| As at 31st December | 2000 | 2001 |
| Subscription in arrears | 6400 | 8800 |
| Subscription in advance | 1200 | 3400 |
| Subscription during the year | - | 20,200 |
| Insurance expenses owing (in arrears) | 3700 | 2700 |
| Insurance expenses prepaid (in advance) | 4400 | 5200 |
| Insurance paid during the year | - | 16,800 |
Required: Prepare A Subscription account and Insurance account, clearly showing amounts to be transferred to income and expenditure accounts for year 2001.
5. Define the following terms
- Discount received
- Invoice
- Discount allowed
- Carriage inwards
- Carriage outwards
6. (a) Mr. Kyamba wants to start a business, but before commencement he needs to learn book keeping. Outline five objectives for him to study book keeping.
(b) Briefly explain three types of a cash book.
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer two questions only from this section.
7. Panguso& company limited own a manufacturing industry which had the following records for the year ended at 31st December 2007.
- Inventory at 1st January 2007:
- raw materials sh.760, 000
- Finished goods sh 360,000
- Purchases of raw material sh.420, 000
- Sales of finished goods sh.2, 490,000
- Factory Fuel & power sh.320, 000
- Royalty sh.500, 000
- Depreciation of works machine sh.88, 000
- Market value sh.1,800,670
- General office expense sh.10, 740
- Manufacturing wages sh.170, 000
- Inventory at 31 stDec 2007: raw material sh.900, 000
- Finished goods sh.580, 000
- Works in progress sh.734, 000
You are required to prepare
- Statement of manufacturing costs for the year ended at 31 stDec 2007
- Income statement for the year ended at 31.12.2007
8. XY Ltd provides for depreciation of its machinery at 20% per annum on cost; it charges for a full year in the year of purchase but no provision is made in year of sale/disposal.
Financial statements are prepared annually to 31th December. 2015
- January 1 Bought machine ‘A’ 10,000
- July 1 Bought machine ‘B’ 6,000
2016
- March 31 Bought machine ‘B’ 8,000
2017
- October 7 Sold machine ‘A’ – proceeds 5,500
- November 5 Bought machine ‘D’ 12,000
2018
- February 4 Sold machine ‘B’ – proceeds 3,000
- February 6 Bought machine ‘B’ 9,000
- October 11 Exchanged machine ‘D’ for machine valued at 7,000
Prepare;
- The machinery account for the period 1st January 2015 to 31st December 2018
- The accumulated provision for depreciation on machinery account, for the period 1st January 2015 to 31st December 2018.
9. The financial of the GGM trading company ended on 30th November 2014. You have been asked to prepare a total amount receivable and total amount payable for the draft final amounts. You are able to obtain the following information for the financial year the book of original entry.
| Sales | – Cash 344,890 – Credit 268,187 |
| Purchase | – Cash 14,440 – Credit 496,600 |
- Total receipts from customers 600,570
- Total payment to suppliers 503,970
- Discount allowed to credit customer 5,520
- Discount received from credit suppliers 3,510
- Refund given to cash customers 5,070
- Balance in sales ledger setoff against balance in the purchase ledger 700
- Bad debt written off 780
- Increase in the allowance for doubtful debts 900
- Credit note issued to credit customers 4,140
- Credit note received from credit suppliers 1,480
According to the audited financial statement for the previous year account receivable and account payable as to 1st December 2013 were 26,550 and 43,450 respectively
- Required;
Draw up the relevant total accounts entering end of year total for account receivable and account payable.
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 122
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 122
THE PRESIDENT’S OFFICE MINISTRY OF EDUCATION, REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
COMPETENCY BASED SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES
BOOK KEEPING FORM THREE
Time: 2:30 Hours November, 2022
Instructions
- This paper consists of sections A, B and C with a total ofnine (9) questions.
- Answer all questions in sections A and B and two (2) questions from section C.
- Section A carries twenty (20) marks, section B forty (40) marks and section C carries forty (40) marks.
- All writings should be in blue or black ink pen and all drawings should be in pencil.
- Non programmable calculators may be used.
- Cellular phones, programmable calculators and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
SECTION A (20 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section
- For each of the items (i) – (xv), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter besides the item number in the answer booklet provided:
- How could a purchases of a non- current assets by cheques affect the statement of financial postion?
- By decreasing non-current assets account and decreasing bank account
- By increasing bank account and decreasing asset account
- By increasing non-current asset account and decreasing cash account
- By increasing cash account and decreasing asset account
- By increasing non-current asset account and decreasing bank account
- Which of the following errors would be disclosed by the Trial Balance?
- Credit sales of TZS 20,000/= entered in the books as TZS 2,000/=
- Cheque for TZS 65,000/= from R.James entered in R.James as TZS 59,000/=
- Cash sales TZS 100,000 were completely omitted in the books
- Selling expenses TZS 5,000 had been debited to sales Account.
- A purchase of goods worth TZS 2,500/= omitted from the books
- Which of the following depreciation methods uses the reduced value to compute the depreciation of non-current assets?
- Straight line method
- Sum of the years’ digit methods
- Diminishing balance method
- Unit of output method
- Revaluation method
- At the beginning of Accounting year, a club had TZS 14,000/= as non-current Assets, TZS 5,000/= as current Assets and TZS 5,000/= as liabilities. What would be its opening Accumulated fund?
- TZS 4,000/=
- TZS 14,000/=
- TZS 12,000/=
- TZS 24,000/=
- TZS 10,000/=
- Form three students were arguing on which primary and basic objective of preparing a trial balance is. Which of the following uses is the basic purpose of preparing a trial balance?
- A trial balance is used for internal control as back up document
- A trial balance is used as a tool for preparing financial statements
- A trial balance is used to check arithmetical accuracy of double entry
- A trial balance is used to present a list of balances at one place
- A trial balance is used to determine profit or loss of a business
- Which of the following are the examples of revenue expenditure?
- Purchases of goods and payment for electricity bill in cash
- Repair of van and petrol costs for van
- Buying machinery and paying for installation costs
- Electricity costs of using machinery and buying van
- Wages paid to the worker who operates a machinery
- Money contributed by individuals under non-profit marking organization is known as:
- Capital introduced
- Capital owed
- Capital employed
- Working capital
- Accumulated fund
- A firm bought a machine for TZS 16,000/=. It is expected to be used for 5 years then sold for TZS 1,000/=. What is the annual amount of depreciation if the straight-line method is used?
- TZS 3,200/=
- TZS 3,100/=
- TZS 3,750/=
- TZS 3,000/=
- TZS 6,000/=
- When business entity paid rent of TZS 800,000/=. The payment was recorded in the books as follows. Debit: “Bank” TZS 800,000/= and Credit: Rent TZS 800,000/=. What entries will be posted to rectify this error?
- Debit “Bank” TZS 800,000/= and credit “Rent” TZS 800,000/=
- Credit “Rent” TZS 800,000/= and credit “Bank” TZS 800,00/=
- Debit “Bank” TZS 800,000/= and Credit “Rent” TZS 1,600,000/=
- Debit “Rent” TZS 1,600,000/= and credit “Bank” TZS 1,600,000/=
- Debit “Bank” TZS 1,600,000/= and credit “Rent” TZS 1,600,000/=
- Baraka wants to start up a business dealing with Clothing Wholesale Store, but he does not have enough capital to commence his business. The following can be used as the sources of capital for his business EXCEPT:
- Money borrowed from bank
- Money saved for business start up
- Money saved for building a private house
- Cash received from the sales of shares
- Cash received from the sale of his private car
- Government expenditures on items from which the government attains no value are called.
- Development expenditure.
- Recurrent expenditure.
- Capital expenditure.
- Revenue expenditure
- Nugatory expenditure.
- A business owned by Esther had an opening and closing capital balances of TZS 57,000/= and TZS 64,300/= respectively. The drawings during the same year amounted to TZS 11,800/=. What was the amount of profit made by her business during that year?
- TZS 19,100/=
- TZS 16,600/=
- TZS 5,000/=
- TZS 19,600/=
- TZS 18,600/=
- Mtumzima Art Creators is a registered company dealing with production and supply of the artistic works. During October 2022, it Purchased machinery for cash costing TZS 35,000,000/=. What will be a double entry for this transaction?
- Debit Cash account, Credit Machinery account
- Debit Purchases account, Credit Machinery
- Debit machinery account, Credit Cash account
- Debit Purchases account , Credit cash account
- Debit purchases account, Credit machinery account
- What is the effect of TZS 500,000/= being added to Purchases instead of being added to a non-current asset?
- Net profit would be understated
- Net profit would be overstated
- Both Gross profit and Net profit would be understated
- Net profit would not be affected
- Gross profit would be affected
- Depreciation can be described as the
- Amount spent to buy a non-current asset.
- Salvage value of a non-current asset.
- Cost of the non-current asset consumed during its period.
- Amount of money spent replacing non-current asset.
- Cost of old assets plus new purchased.
- If the Assets of the business amounted to TZS 85,000/= and Owner’s Capital is TZS 60,000/= How much is the Liabilities of the business?
- TZS. 45,000/=
- TZS. 145,000/=
- TZS.25,000/=
- TZS.85,000/=
- TZS 60,000/=
- For each of the items (i) – (v), match the descriptions of correction of errors terms in Column A with their corresponding names in Column B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number in the answer sheet:
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| A. Error of complete reversal entries B. Error of compensating C. Error of commission D. Error of principle E. Error of original entry F. Error of omission G. Transposition error |
SECTION B (40 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section
- Briefly describe the meaning of the following terms as used in book keeping:
- Accrued expenses
- Book keeping
- Credit transaction
- Carriage outwards
- Net profit
- Upendo is a business woman who owns a Jewels shop in Arusha. She is also a customer of CRDB bank. Upendo prefers to settle her debts using cheques. In the last month, she wrote a cheque to Onesmo, her creditor, for which the bank refused to settle it. In five points outline the reasons for this to happen.
- On 31st December 2017, the cash book balance of ShedrackTraders was TZS 25,370/= where the bank statement showed a credit balance of TZS 25, 670/=. In comparing these two balances, the following were discovered;
- Cheques not yet presented for payment TZS 12,340/=
- Cheques paid into the bank but not yet credited by the bank account TZS 12,160/=
- Items shown in the bank statement but not yet entered in the cash book were as follows:
- Bank charges TZS 240/=
- Standing order TZS 460/=
- Dividends collected by the bank TZS 820/=
Required:
- Bring the cash book to date to show the correct cash book balance.
- Prepare a bank reconciliation statement starting with the adjusted cash book balance.
- Rule a petty cash book under the following headings: - Postage, stationery, Petrol, entertainment and ledger.
2020 TZS
March 12 Petty cashier received cash from main cashier…………………. 15,000
14. Paid postage………………………………………….. 500
16. Paid entertainment…………………………………… 3,000
18. Paid petrol…………………………………………….. 1,200
20. Paid B. Robert, a creditor……………………………… 4,000
25. Paid for stationery…………………………………… 1,700
29. The cashier reimbursed the petty cashier the amount spent in the period.
SECTION C (40 Marks)
Answer two (2) questions from this section.
- Mtumzima Transport Company with the financial year ending on 31st December, bought two motor vans on 1st January 2011, No 1 for TZS 18,000,000 and No 2 for TZS 15,000,000. It also buys another van, No. 3 on 1st July 2012, for TZS 19,000,000 and another No 4 on 1st October, 2013 for TZS 17,200,000 the van No 1 was sold for TZS 6,290,000 on 30th September 2014. It is a company’s policy to charge depreciation at 15% per annum using a straight line method for each month of ownership basis.
Required: Prepare for the year ended 31st December, 2011, 2012, 2013 and 2014.
- Motor van account
- Accumulated Provision for depreciation account
- Motor van disposal account
- The following trial balance has been extracted from the ledger of Julius, a sole trader.
Trial balance as at 31st May, 2022
| S/N | Name of account | DR | CR |
| 1 | Purchases and sales | 82,350 | 138,078 |
| 2 | Carriage | 5,144 | |
| 3 | Drawings | 7,800 | |
| 4 | Rent, rates and insurance | 6,622 | |
| 5 | Postage and stationery | 3,001 | |
| 6 | Advertising | 1,330 | |
| 7 | Salaries and wages | 26,420 | |
| 8 | Bad debts | 877 | |
| 9 | Allowance for doubtful debts | 130 | |
| 10 | Accounts receivables and payables | 12,120 | 6,471 |
| 11 | Cash in hand | 177 | |
| 12 | Cash at bank | 1,002 | |
| 13 | Inventory as at 1.6.2021 | 11,927 | |
| 14 | Equipment (at cost) | 58,000 | |
| 15 | Accumulated depreciation on equipment | 19,000 | |
| 16 | Capital | 53,091 |
The following additional information as at 31st May, 2022 is available:
- Rent is accrued by TZS 210/=
- Rates have been prepaid by TZS 880/=
- TZS 2,211 of carriage represent carriage on purchases
- Equipment is to be depreciated at 15% p.aon cost.
- The allowance for doubtful debts to be increased by TZS 40/=
- Inventory at the close of business has been valued at TZS 13,551/=
Required:
Prepare Julius’s Income statement for the year ending 31st May, 2022 and a Statement of financial position as at that date.
- The following information is available from the books for Abigail Wholesale Store on 1st September, 2021:
Balances in purchases ledger TZS 120,000 (CR)
Balances in sales ledger TZS 7,100 (CR)
Balances in purchases ledger TZS 4,800 (DR)
Balances in sales ledger TZS 163,100 (DR)
During September 2021:
Sales 140,000
Purchases 88,000
Returns inwards from debtors 55,000
Returns outwards from creditors 7,300
Receipts from debtors 91,300
Payments to creditors 76,700
Discount allowed 4,000
Discount received 2,200
Bad debts written off 3,800
Provision for bad debts increased by 600
Debtorscheque dishonored 7,500
Interest charged to debtors on overdue accounts 500
Sales ledger debit transferred to purchases Ledger 9,600
Notes:
- 10% sales and discount allowed relate cash transactions
- 5% of the goods bought during the month were destroyed by fire, the insurance company had agreed to pay adequate claim.
You are required to prepare:
- A sales ledger control account
- A purchases ledger control account
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 106
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 106
THE PRESIDENT’S OFFICE MINISTRY OF EDUCATION, REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
COMPETENCY BASED SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES
FORM THREE EXAMINATION
062 BOOK-KEEPING
![]() Time: 2:30 Hours Sept, 2022
Time: 2:30 Hours Sept, 2022
Instructions
- This paper consists of sections A, B and C with a total of nine (9) questions.
- Answer all questions in sections A and B and two (2) questions from section C.
- Section A carries twenty (20) marks, section B forty (40) marks and section C carries forty (40) marks.
- All writings should be in blue or black ink pen and all drawings should be in pencil.
- Non programmable calculators may be used.
- Cellular phones, programmable calculators and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
SECTION A (20 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section
- For each of the items (i) – (xv), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter besides the item number in the answer booklet provided:
- Mtumzima bought 5 items of TZS 800 each, and given allowance of 25% trade discount and 5% cash discount, if he could settle within the agreed credit period, how much was paid?
- TZS 2,850
- TZS 2,800
- TZS 2,600
- TZS 4,000
- TZS 3,000
- Mr. MRAMBA as a Petty cashier was given a desired cash float of TZS 100,000/= if TZS 72,000/= is spent by him, under imprest system of petty cash how much will be reimbursed?
- TZS 28,000/=
- TZS 172,000/=
- TZS 72,000/=
- TZS 70,000
- TZS 100,000/=
- The book value of an Asset after two years, using straight line method at 10% was TZS 10,000/=. What was the cost price of the Asset?
- TZS 20,000/=
- TZS15,000/=
- TZS 12,500/=
- TZS 10,000/=
- TZS 30,000/=
- Amount of surplus in a statement of income and expenditure account indicates:
- Excess of income over expenditure
- Excess of cash received over credit sales
- Excess of expenditure over income
- Excess of gross profit over expenses
- Excess of expenses over net profit
- Which of the following errors would be disclosed by the Trial Balance?
- Credit sales of TZS 20,000/= entered in the books as TZS 2,000/=
- Cheque for TZS 65,000/= from R.James entered in R.James as TZS 59,000/=
- Cash sales TZS 100,000 were completely omitted in the books
- Selling expenses TZS 5,000 had been debited to sales Account.
- A purchase of goods worth TZS 2,500/= omitted from the books
- Government expenditures on items from which the government attains no value are called.
- Development expenditure.
- Recurrent expenditure.
- Capital expenditure.
- Revenue expenditure
- Nugatory expenditure.
- What is the effect of TZS 500,000/= being added to Purchases instead of being added to a non-current asset?
- Net profit would be understated
- Net profit would be overstated
- Both Gross profit and Net profit would be understated
- Net profit would not be affected
- Gross profit would be affected
- At the beginning of Accounting year, a club had TZS 14,000/= as non-current Assets, TZS 5,000/= as current Assets and TZS 5,000/= as liabilities. What would be its opening Accumulated fund?
- TZS 4,000/=
- TZS 14,000/=
- TZS 12,000/=
- TZS 24,000/=
- TZS 10,000/=
- When the financial statements are prepared, the bad debts Account is closed by being transferred to: -
- Statement of financial position
- Provision for doubtful debts Account
- Income statement
- Statement of affairs
- Trading account
- When business entity paid rent of TZS 800,000/=. The payment was recorded in the books as follows. Debit: “Bank” TZS 800,000/= and Credit: Rent TZS 800,000/=. What entries will be posted to rectify this error?
- Debit “Bank” TZS 800,000/= and credit “Rent” TZS 800,000/=
- Credit “Rent” TZS 800,000/= and credit “Bank” TZS 800,00/=
- Debit “Bank” TZS 800,000/= and Credit “Rent” TZS 1,600,000/=
- Debit “Rent” TZS 1,600,000/= and credit “Bank” TZS 1,600,000/=
- Debit “Bank” TZS 1,600,000/= and credit “Rent” TZS 1,600,000/=
- A business had an opening and closing capital balances of TZS 57,000/= and TZS 64,300/= respectively. The drawings during the same year amounted to TZS 11,800/= What was the amount of profit made by the business during that year?
- TZS 19,100/=
- TZS 16,600/=
- TZS 5,000/=
- TZS 19,600/=
- TZS 18,600/=
- Gloria General store sold goods worth TZS 100,000/= to Joshua on credit and were neither recorded in sales account nor in Pearl’s personal account. This represents an error of:
- Error of commission.
- Error of omission.
- Error of original entry
- Error of principle.
- Error of complete reversal of entries.
- Jeff and Witness were arguing on the primary and basic reason of preparing a trial balance. As form three student taking business studies, what is the basic reason for writing up a trial balance among the following reasons?
- A trial balance issued for internal control as back up document.
- A trial balance is used as a tool for preparing financial statement.
- A trial balance is used to determine a reliable financial position
- A trial balance is used to present a list of balances at one place.
- A trial balance is used to check arithmetical accuracy of double entry.
- Which of the following are the examples of revenue expenditure?
- Purchases of goods and payment for electricity bill in cash
- Repair of van and petrol costs for van
- Buying machinery and paying for installation costs
- Electricity costs of using machinery and buying van
- Purchases of office equipment
- A firm bought a Motor van for TZS 50,000 which had a scrap value of TZS 5,000, and useful life of 5 years. What would be the depreciation charge if a straight line method is used?
- TZS 10,000
- TZS 11,000
- TZS 9,000
- TZS 1,000
- TZS 5,000
- Match the items in Column A with the responses in Column B by writing the letter of the correct responses below the corresponding item number in the table provided.
| Column A | Column B |
|
|
SECTION B (40 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
- Book keeping involves the recording on a daily basis of a company’s financial transactions whether on single entry system or double entry system and because of book keeping, companies are able to track all financial information on its books to make key operating, investing, and financing decisions. Outline five reasons stating why double entry system is better in book keeping.
- On 1st July, 2017 Mtumzima Company bought a machinery for TZS 18,000,000, and decided to sell it for TZS 12,000,000 after using it for four (04) years. In four (04) points describe briefly why the company decided to sell a machinery at a price lower than the original cost price.
- Prepaid rent at the beginning of the period was TZS 40,000/= and TZS 20,000/= was not paid last year. During the year payment of TZS 320,000/= was made with respect to rent. It was established that at the end of the period prepaid rent should be TZS 60,000/=. Compute the amount of Rent Expenses to be transferred to income statement.
- The following information relates with Star social club for the year ended 31st June 2020.
![]() 1.7.2019 31.6.2020
1.7.2019 31.6.2020
Subscription in arrears 4,500 3,200
Subscription received in advance 6,300 1,800
During the year, the subscriptions amounted to TZS. 120,000 were received from the club members.
Required:
Subscription account, showing the amount to be transferred to the statement of Income and expenditures for year ended 31st June, 2020.
SECTION C (40 Marks)
Answer two (2) questions from this section.
- SIJAFELI keeps his books on a single entries system. The following are the balances of Assets and Liabilities of his business for the year ended 31st December, 2017.
Receipts and Payments made for cash during the year were as follows:
Receipts from Debtors ______________________________________420,000
Payment to Creditors ______________________________________200,000
Carriage inwards ___________________________________________ 40,000
Drawings _________________________________________________120,000
Sundry Expenses __________________________________________140,000
Purchases of new furniture ___________________________________ 20,000
Other information:
There was a considerable amount of cash sales. Depreciate furniture at 10% on a closing balance.
From the information provided, prepare
- Accounts receivables and Accounts payables control Accounts
- Cash Account.
- Income statement for the year ended 31st December 2017
- Statement of financial position as at 31st December 2017
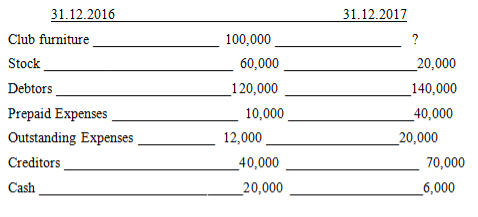
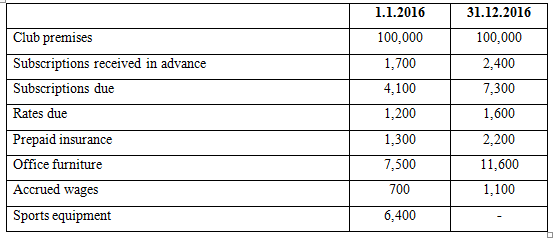
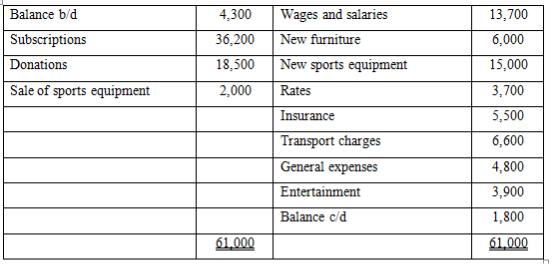
- MtumzimaSports Club, a non-profit making organization was looking for a form three student who is able to assist them in the preparations of various accounts and statements for payments. In their interview one of the questions was as follows: -
Assets and Liabilities:
Receipts and Payments Account
The following information were also available
- The sports equipment sold during the year had a book value of sh.3,500/=
- Depreciation on sports equipment was provided at 20% per year
Required:
- A statement of affairs as at 1.1.2016
- Subscription account
- A statement of Income and expenditure for the year ended at 31.12.2016
- A statement of financial position as at that date.
- The financial year of Collins Trading Company ended on 31.12.2017. You have been asked to prepare a Total Debtors Account and a Total Creditors Account in order to produce end-of-year figures for Debtors and Creditors for the draft financial statements.
You are able to obtain the following information for the financial year from the books oforiginal entry:
TZS
Sales made on Cash basis 782,500
Sales made on Credit 368,187
Purchases made on Cash basis 214,440
Purchases made on Credit 596,600
Total cash receipts from customers 300,570
Total cash payments to suppliers 503,970
Discounts allowed (all to credit customers) 5,520
Discounts received (all from credit suppliers) 3,510
Refunds given to cash customers 5,070
Balance in the sales ledger set off
against balance in the purchases ledger 700
Bad debts written off 780
Credit notes issued to credit customers 4,140
Credit notes received from credit suppliers 1,480
According to the audited financial statements for the previous year debtors and creditors as at 1.1.2017 were TZS 26,555 and TZS 43,450 respectively.
Required:
- Accounts receivables Control Account
- Accounts payables Control Account
Page 1 of 10
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 98
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 98
THE PRESIDENT’S OFFICE MINISTRY OF EDUCATION, LOCAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
BOOKEEPING- TERMINAL EXAMINATION-MAY
FORM THREE
TIME: 2½HRS 2020
NAME:______________________________CLASS:___________
INSTRUCTIONS
- Answer all questions
1. Choose the correct answer from the given alternatives write its letter beside the item number
(i) Which of the following is a liability?
- Debtor
- Loan from exim bank
- Building
- Prepaid expenses
(ii) The cash payment of T.shs 439,000 to Juma would appear as follows:
- Credit Juma account, credit cash account
- Debit Juma account, credit cash account
- Debit bank account, credit Juma account
- Debit cash account, credit Juma account
(iii) Which of the following are personal accounts?
- Building and machine
- Wages and salaries
- Account receivable and account payables
- Profits and loss
(iv)In the trial balance, accumulated provision for depreciation account is
- Shown as a credit item
- Not shown as it is part of depreciation
- Shown as a debit item
- Sometimes shown as a credit, sometimes as a debit
(v) Which of the following is not correct?
- Assets – capital=liabilities
- Liabilities + capital=assets
- Liabilities + Assets=capital
- Assets – liabilities =capital
(vi) Which of the following should be charged in the trading, profit and loss account(income statement)
- Office rent
- Work-in-progress
- Direct materials
- Carriage on raw materials
(vii) At the end of trading period, bad debt account is closed and transferred to the
- Balance sheet
- Profit and loss account
- Trading account
- Allowance for doubtful debits account
(viii) Revenue expenditure is
- The extra capital paid in buying non-current assets
- The extra purchase of goods for sale
- Money spent on selling fixed assets
- The cost inairred in running the business on a day to day basis
(ix) An allowance made on the date of sales in respect of the date of payment is
- Discount allowed
- Cash discount
- Trade discount
- Quantity discount
(x) If shs 1000/= was added to purchases instead of being added to a fixed asset
- Net profit only would be understated
- Net profit only would be overstated
- Both gross profit and net profit would be understated
- Both gross profit and net profit would be overstated
2. Match the following by choose the correct answer from column B and write its letter beside the item number in column A
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) An item is entered in the wrong class of account (ii) Where errors cancel each other (iii) Where transaction is completely omitted from the books (iv) Where correct accounts are used but each item is shown on the wrong side of an account (v) Where correct amount is entered in the wrong account (vi) Where incorrect amount is entered in the accounts (vii) Incorrectly adding up figures to give an answer which is less than it should be (viii) Used to set the amount which will make the trial balance to balance when is affected by errors (ix) When transaction is posted twice in along the correct principles of double entry system (x) Errors committed when dualistion aspect of a transaction is not followed |
|
SECTION B
3. Write short notes on the following
- Capital expenditure
- Bad debts
- Depreciation of non-current asset
- Manufacturing account
- Single entry system
4. Kibaha education centre had received house rent for 1982 amounting to sh. 72,000. Out of this amount shs. 4,000 related to the year ending December 1983.
Required:
Rent received account to show the amount transferred to the profit and loss account
SECTION C
5. Jangua started business on 1st January 1993. Purchases and disposals of machines over three years were as follows.
| machine | Date of purchase | Cost(shs) | Date of disposal | Disposal proceeds(shs) |
| MAI | 1Jan 1993 | 5000,000 | - | - |
| MB 2 | 1Jan 1993 | 2500,000 | 1 Jan 1995 | 900,000 |
| MC 3 | 1 Jan 1995 | 7000,000 | - | - |
The machines are depreciated on straight line method using rate of 20% per annum
Required:
- Machine account
- Provision for depreciation account
- Disposal of machines account
6. K owns a store, her records are incomplete. You have been called in to prepare her accounts.
Through investigation the following information was obtained
01.01.2013 31.12.2013
Stock 2,100 2,240
Trade creditors 960 1,000
Motor vans 1,200 1,000
Debtors 1,300 1,040
Rates pre-paid 80 96
Cash at bank 900 2,344
Additional information
Drawings during the year amounted to Tshs 120 per week
Legacy of Tsh.400 received on March 2013 had been paid into the business bank account
Required
- Statement of affairs at 1st January 2013
- Statement of affairs at 31st December 2013
- Statement of profit or loss for the year 2013
7. From the following prepare manufacturing, trading profit and loss account for the year ended 31.12.2013
Stock at 01.01.2013:
Raw materials 1,845,000
Work in progress 2,360,000
Finished goods 1,747,000
Purchases: raw materials 6,430,000
Carriage on raw materials 160,500
Direct labour 6,581,000
Office salaries 1,692,000
Rent 270,000
Office lighting and heating 576,000
Depreciation:
Works machinery 830,000
Office equipment 195,000
Sales 20,060,000
Factory fuel and power 592,000
Additional notes on 31.12.2013
Stock at 31.12.2013
Raw materials 2,021,000
Work-in-progress 1,739,000
Finished goods 2, 1488,500
Rent is to be apportioned as follows:
Factory (20) / (30)
Office (10) / (30)
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 19
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 19
THE PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND VOCATIONAL TRAINING
MID TERM EXAMIATIONS
024 BOOK-KEEPING FORM THREE
Duration: 2:30 Hours
INSTRUCTIONS.
- This paper consists of two sections A and B.
- Answer all questions in section A and only Four Questions in Section B
· All writing must be in blue or black ink except drawing which must be in pencil.
· Calculators, cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
· Write your Examination Number at the top right corner of every page.
· Show clearly all working for each question
- This paper consists of section A, B and C.
- Use pencil to draw all the account
- Attempt all the question
SECTION A (10 MARKS)
MULTIPLE CHOICE
Choose the correct answer from the alternatives given
1) Depreciation is
a) The salvage value of fixed assets
b) The amount spent to buy fixed assets
c) The part of cost of the fixed assets consumed during its period of use by the firm
d) The destroyed property
2) Which of the following is nominal account
a) Bank a/c b) Furniture and fittings c) Motor vehicles a/c
d) Motor vehicle running expenses
e) Bank overdraft
3) A firm bought a machine for shs. 50,000/= which had ascrap value of shs 5,000/= and
Useful life of 5 years. What would be the depreciation expenses if straight line method is used
a) shs. 10,000/= b) shs. 11,000/= c) shs. 9,000/=
d) shs. 5,000/= e) shs. 11,500/=
4. Which of the following is a liability
a) Premises b) We owe for goods d) Loan to Hamis
d) Cash at Bank e) Depreciation
5. Gross profit is
a) excess of sales over sales returns c) Cost of sales plus net profit
b) Sale less purchases d) Sales less cost of sales
6. Posting in book-keeping means
a) Making the first entry of double entry transactions
b) Entering items in a cash book
c) Making entries in different books
d) Making the second entry of double
7. When a customer returns goods previously sold to him, the shopkeeper will use a document
called
a) Invoice b) Credit note c) Pay-in-slip
d) Order note e) Debit note
8. Determine the amount of capital from the following: Premises shs. 20,000/= Loan to Shamir
Shs.17,000/= stock shs. 35,000/= Creditors shs. 5,000/= Loan from Kagose shs. 22,000/=
a) shs. 50,500/= b) shs. 54,000 c) shs. 48,000
d) shs. 45,500/= e) shs. 45,000/=
MATCHING ITEMS (10 MARKS)
9. Classify the following into nominal, real and personal account.
| Name of account | Classification |
| - Computer - Motor – van - Advertising - Return inward - Profit - Rent received - Television - Salaries - Building - Land - Transport - Rosemary |
|
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
10. Write short notes on the following
a) Double entry
b) Return inwards
c) Carriage inwards
d) Working capital
e) Journal
f) Contra entry
g) Imprest system.
11. Given the following transactions below
1990 January 1. Started business with capital shs. 5,000/=
1990 January 3. Bought goods for cash 1,500/=
1990 January 5. Paid wages in cash shs. 50/=
1990 January 7. Sold goods for cash shs. 3,000/=
1990 January 8. Bought calculator by cash shs. 420/=
1990 January 10. Paid transport by cash shs. 430/=
Required: Enter the above transaction in
- Cash account
- Ledger
- trial balance
SECTION C: (60 MARKS)
12. Enter the following transaction in the necessary ledgers
1st January 1951 – sold goods to Matatizo Tele on credit shs. 7,400/=
31st January 1951, Matatizo Tele paid his account by shs. 5,800/=
13. Given the following bank statement of Bahatisha Co. Ltd
| Date | particulars | folio | DR | CR | Balance |
| 1998 1-March 8-March 16-March 20-March 21-March 31-March 31-March 31-March |
Balance M. Tabu Cheque J. Bahari Cheque Traders credit Standing order Bank charges |
b/f |
1,220
2,080
490 280 |
2,440
3,330 570 |
51,97DR 53,190DR 50,750DR 52,830 DR 49,500DR 48,930DR 49,420DR 49,700DR |
The following extracted of a cash book is also available.
CASH BOOK (BANK COLUMN)
| Date | Particulars | Folio | Amount | Date | Particulars | Folio | Amount |
| 1998 3-March 21-March 31-March 31-March |
Mdendesi F Kulwa, A Hamis, s Balance |
c/d |
2,440 3,330 1,600 52,800 60,170 | 1998 1-March 6-March 30-March 30-March |
Balance M. Tabu J. Bakari J. Shoo |
b/f |
51,970 1,220 2,080 4,900_ 60,170
|
Required: Prepare the bank reconciliation statement as at 31st March 1998, starting with the
Balance as per cash book. (Do not adjust the cash book)
END
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 6
FORM THREE BKEEPING EXAM SERIES 6
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256







