THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL OF TANZANIA CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
013 GEOGRAPHY
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
Time: 3 Hours Tuesday, 06th November 2018 p.m.
Instructions
- This paper consists of sections A, B, C and D with a total of twelve (12) questions.
- Answer all questions in section A, B and C and one (1) question from each part of section D.
- Map extract of Ilonga (Sheet 265/2) is provided.
- Calculators, cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
PHYSICAL AND MATHEMATICAL GEOGRAPHY
1. For each of the items (i) (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter besides the item number in the answer booklet provided.
(i) Which of the following instrument is used to measure maximum and minimum temperature?
- Barometer
- Thermometer
- Anemometer
- Sixs thermometer
- Hydrometer.
(ii) Which among the following is an extrusive volcanic feature?
- Crater
- Laccolith
- Batholith
- Sills
- Dykes.
(iii) One of the factors for soil formation is
- organic matters
- mineral matters.
- time.
- water.
- air.
(iv) The layer of the atmosphere which is nearer to the earths surface is called
- troposphere
- stratosphere
- hydrosphere
- mesosphere
- thermosphere.
(v) Which among the following is a heavenly body that possesses and transmits its own light?
- Moon
- Sun
- Earth
- Astreroid
- Planet.
(vi) A region which consists of thick forests, tree dwellers and people who engage in cultivation of rubber, cocoa, bananas and oil palms is known as
- Tropical savanna
- Tropical monsoon
- Polar climate
- Mediterranean
- Equatorial.
(vii) An instrument used to determine Magnetic North is called
- Stevenson screen.
- Compass.
- Thermometer.
- Hygrometer
- Barometer.
(viii)Which of the following is not a process for chemical weathering?
- Carbonation
- Saltation
- Hydrolysis
- Hydration
- Oxidation.
(ix) Which among the following features are produced by wave erosion?
- A Geo, wave cut platform and stack
- Blow hole, sea arch and levee
- Sea arch, beach and stump
- Beach, spit and bars.
- Tombolo, meander and cliff.
(x) If the scale of a map is 1:50,000, what will be the actual ground distance of a river with 18cm on a map?
- 9 km
- 2 km
- 4 km
- 8 km
- 1 km.
2. Match the process involved in the formation of rocks in with the type of rock in List B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number in the answer booklet provided.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
3. (a) Describe the following terms:
- Distributaries.
- Lagoon.
- Levee.
(b) Delta is formed under different conditions. Outline three conditions necessary for its formation.
SECTION B (27 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
APPLICATION OF STATISTICS, INTRODUCTION TO RESEARCH AND
ELEMENTARY SURVEYING
- Carefully study the following statistical graph showing coffee production (in tonnes) in Tanzania, from 2011 to 2014 and answer the questions that follows
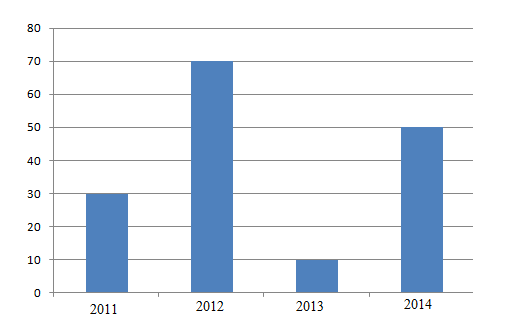
- Describe the type of statistical graph used.
- Analyse the five procedures involved in constructing such a statistical graph.
- Giving two points, comment on the differences in coffee production shown in the graph.
- Give three advantages of presenting data by using the type of graph described in 4(a).
- (a) Give three differences between interview and observation. (b) Outline four merits of library research.
- Explain five importance of survey in daily life.
SECTION C (28 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
MAP READING AND PHOTOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
7. Study the map extract of Ilonga (Sheet 265/2) and answer the following questions:
- By using square method, determine the area North western of Luhombero river from grid reference 570963 to 644034.
- With evidence from the map, name six symbols which have been used to inteprete a given map.
- Give the direction of Iputi to Ilonga.
- Describe the settlement pattern of the mapped area.
- Giving evidences, mention five possible economic activities which might take place in the mapped area.
8. Study the following photograph and answer the questions that follow:

- Giving two reasons, name the type of photograph.
- Suggest the type of settlement pattern and give one factor that has influenced it.
- Suggest two economic activities that might be taking place in the area.
- Provide three advantages of photographs over maps.
SECTION D (20 Marks)
Answer one (1) question from each part.
PART I: REGIONAL FOCAL STUDIES
- Explain five factors which influence the distribution of natural forests in the world.
- Analyse five ways of promoting textile industry in Tanzania.
PART II: ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES, POPULATION AND SETTLEMENTS
- Describe seven problems associated with rapid urbanization.
- Examine seven effects of climatic change in the world.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
013 GEOGRAPHY
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
Time: 3 Hours Monday, 30thOctober 2017 p.m.
Instructions
- This paper consists of sections A, B, C and D with a total of twelve (12) questions.
- Answer all questions in sections A, B and C and one (1) question from each part of section D.
- Map extract of Arusha (Sheet 55/3) is provided.
- Credit will be given for the use of relevant diagrams.
- Calculators, cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s)
SECTIONA(25Marks)
Answer all questions in this section
PHYSICAL AND MATHEMATICAL GEOGRAPHY
For each of the items (i) - (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item(s) number in the answer booklet(s) provided.
(i) The luminous body which provides energy to the solar system is
- Sun
- Earth
- Moon
- Planet
- Satellite.
(ii) The earth’s layer which consists of sial and sima is called
- lithosphere
- hydrosphere
- stratosphere
- atmosphere
- thermosphere.
(iii) Which of the following is the process of wearing down the rock surface by wind where the load becomes cutting tools?
- Deflation
- Attrition
- Abrasion
- Corrasion
- Hydration.
(iv) The renewed power of erosion of a river is called.
- river capture
- river erosion
- river rejuvenation
- river meanders
- river basin.
(v)Prediction of the state of atmosphere in a region for 24 to 48 hours is known as
- weather elements
- weather report
- weather instrument
- weather station
- weather forecasting
(vi) The process through which rain water enters the ground is called
- Evaporation
- Infiltration
- Transpiration
- Condensation
- Percolation.
(vii) The process of changing granite to gneiss rock is known as
- sedimentation
- vulcanism
- denudation
- metamophism
- exfoliation.
(viii) Which of the following is another name for Savanna climate in Africa
- Tropical maritime.
- Warm temperature maritime.
- Tropical grassland.
- Warm temperature desert.
- Cool temperate western margin.
(ix)The process of peeling off and falling of rock mass is called
- disintegration
- weathering
- mass wasting
- erosion
- exfoliation.
(x)Which of the following are features of ocean floor?
- Basin, Ocean deep and Cliff.
- Trench, Continental shelf and Stump
- Trench, Ridge and Ocean deep.
- Ocean deep, Continental shelf and Drumlin.
- Basin, Continental shelf and Tombolo.
2. Match the items in List A with the responses in List B by writing the letter of the corresponding response besides the item number in the answer booklet(s) provided.
| LIST A | LIST B |
| (i) Removal of loose materials from the rocks by the force of moving water. (ii) Fine and light particles moved by wind. (iii) Dissolved soluble minerals which are found in rocks by flowing river water. (iv) Tearing away of blocks of rocks which have become frozen into the sides or bottom of a glacier. (v) Swash carries pebbles and other rock fragments from the shore of the ocean. |
|
3. (a) Define the term soil.
(b) Briefly explain four importance of soil to human life.
(c) Mention three sources of soil nutrients.
APPLICATION OF STATISTICS, INTRODUCTION TO RESEARCH AND ELEMENTARY SURVEYING
4. (a) Define compound bar graph.
(b) Study carefully the table below on hypothetical data about cash crops production (in ‘000 tonnes) in East Africa in the year 2000, then answer the questions that follow. Find this
| Country | Crops |
| |
| Coffee | Tea | Cotton | |
| Kenya | 2200 | 2000 | 1800 |
| Uganda | 1700 | 700 | 800 |
| Tanzania | 1300 | 1900 | 2300 |
(i) Draw compound bar graphs to represent the data provided.
(ii) Outline four merits of using compound bar graph.
5.(a) Describe the following research terms:
- Population.
- Random sampling.
- Literature review.
(b) (i) Define secondary data.
(ii) Give four merits of secondary data.
6. (a) Describe plane table survey.
(b) Explain five importance of plane table survey.
SECTION C (28 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
MAP READING AND PHOTOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
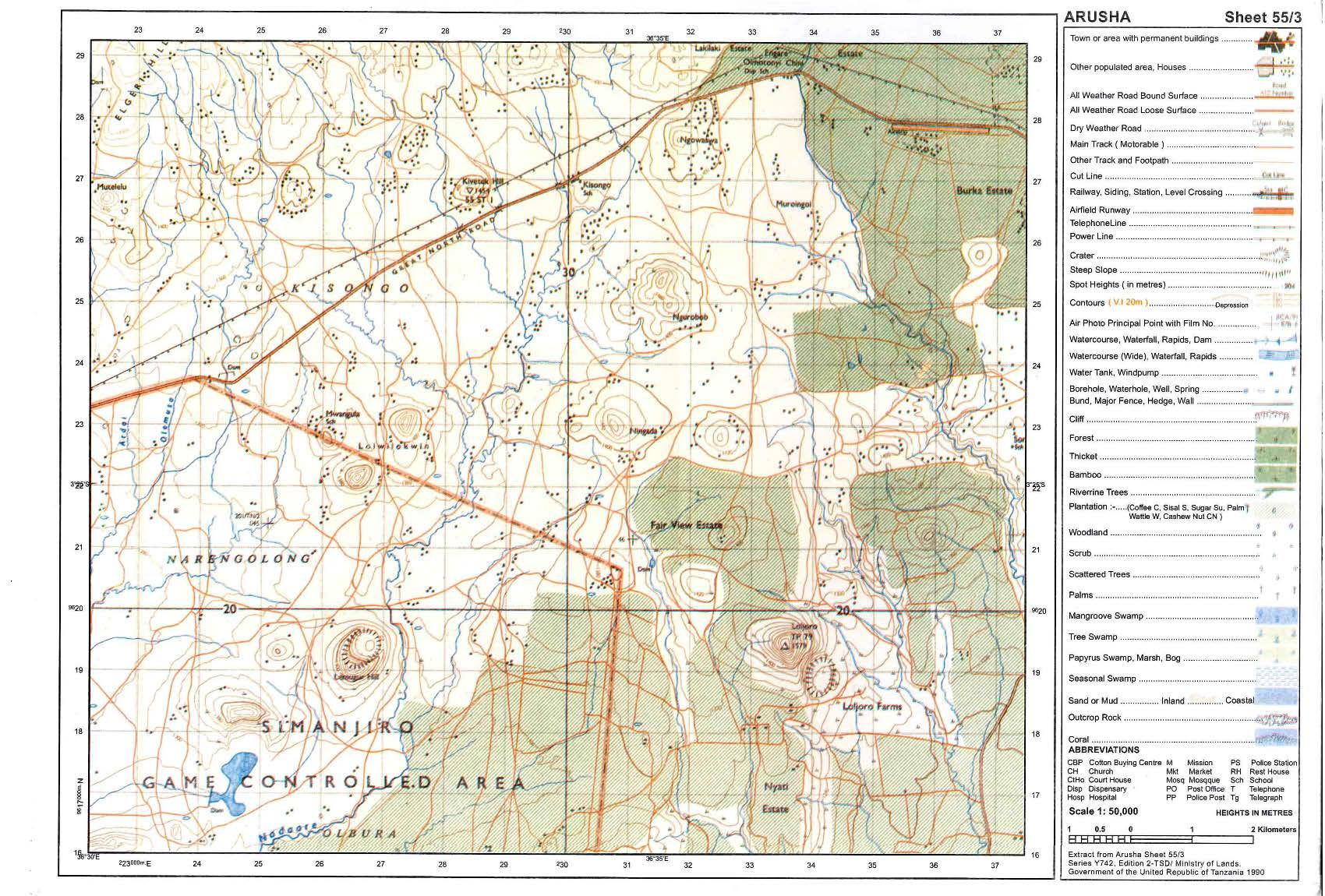
7. Carefully study the map extract of Arusha (Sheet 55/3) provided then answers the questions that follow.
- Describe the relief of the mapped area.
- Giving evidences, mention the major means of transport shown in a map.
- Change the scale of the map into a statement scale.
- Measure the length of the road from grid reference 378314 to grid reference 480276 in kilometres.
- With evidence from the map, identify three social services which are found in this area.
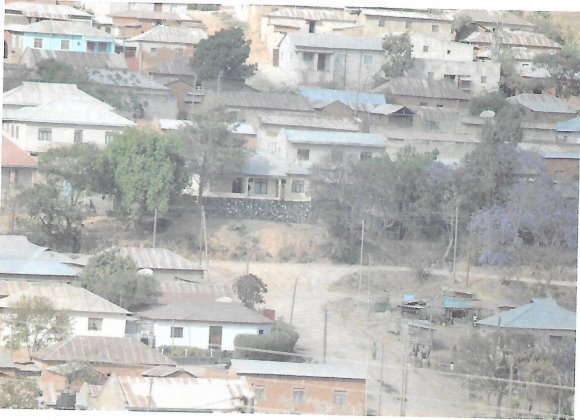
8. Study carefully photograph provided then answer the questions that follows.

(a) Suggest the title of the photograph.
(b) (i)Name the type of forest seen in the photograph.
(ii) Give two characteristics of the forest named in (i).
(c) Outline three ways of interpreting the photograph given.
(d) (i) Identify the product in the middle ground of the photograph.
(ii) Give two uses of the product in the middle ground of the photograph.
SECTION D (20 MARKS)
Answer one (1) question from each part.
PART 1: REGIONAL FOCAL STUDIES
9. Explain seven ways of improving tourism industry in Tanzania.
10.Elaborate seven ways of managing industrial pollutants to the environment.
PART II: ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES, POPULATION AND SETTLEMENTS
11. Describe five uses of population data to a country.
12. Explain six problems associated with expansion of cities in Tanzania.
THE U NITED R EPUBLIC O F TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CERTIFICATE O F S ECONDARY E DUCATION E XAMINATION
013 G EOGRAPHY
(For B oth S chool a nd P rivate Candidates)
Time:3 Hours Wednesday, 02nd November 2016 p.m.
Instructions
1. This paper consists of sections A, B, C and D.
2. Answer all questions in sections A, B and C and one (1) question from each part of section D.
3. Map extract of Hanang (Sheet 84/4) is provided.
4. Calculators and Cellular phones are not allowed in the examination room.
5. Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s)
SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
PHYSICAL AND MATHEMATICAL GEOGRAPHY
1. For e ach o f the i tems ( i) - ( x), c hoose t he correct answer from among the g iven a lternatives and write its letter in the a nswer booklet provided.
(i) The speed of the earth quake waves i n t he earth is c hanged at a line called
- Mohorovic discontinuity
- Gutenberg discontinuity
- Tectonics
- Tectonics
- Isostatic.
(ii) Liverpool team scored a goal at 5.00 pm in England (15° W). At what time the goal was scored in Dar es Salaam (45° E)?
- 1.00 p.m
- 7.00 p.m
- 9.45 p.m
- 9.00 p.m
- 6.30 a.m.
(iii) The sun is overhead attropic of Capricorn every year on
- 22nd December
- 21st March
- 23rd September
- 21st June
- 24th March.
(iv)Day reaches its maximum length on 21st June in
- Southern hemisphere
- Northern Hemisphere
- Arctic Circle
- Polar region
- Tropic of Capricorn.
(v) Which of the following planets have small celestial bodies in orbit a round them?
- Mercury, Jupiter and Uranus
- Pluto, Earth a nd Mars
- Earth, Jupiter and Saturn
- Mercury, Venus and Earth
- Venus, Earth and Saturn.
(vi) Deposition of soil materials removed from one horizon to another is called
- Convex sided
- Concave sided
- Gentle sided resistance
- Steep sided resistant
- Steep sided non resistance.
(vii) The excessive strong wind blowing across an extensive ocean surface is called
- Tsunami
- Ocean currents
- Storm s urge
- Hurricane
- Wind.
(ix) Rainfall that occurs when the air moves towards a hill or a mountain is called
- cyclonic
- orographic
- convectional
- showers
- typhoon.
(x) Mountains can be classified on the basis o f
- their importance
- their s urrounding
- their c omposition
- their formation
- their height.
(x) A channel diverging from the main river a nd flowing into the sea or a lake by a separate mouth is called
- tributary
- stream
- distributary
- river basin
- water shade.
2. Match the items in L ist A with the responses in List B by writing the letter of the correct response b esides t he i tem number i n t he answer b ooklet provided.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
3. (a) Describe discordant drainage s ystem.
(b) Explain the process of river transport and describe four ways in which a river transports its load.
SECTION B (27 Marks)
Answer allquestions this section.
APPLICATION OF STATISTICS, INTRODUCTION TO RESEARCH AND ELEMENTARY SURVEYING
4. (a) (i) Define simple d ivided c ircle.
(ii) Give four m erits of u sing s imple d ivided c ircle.
(b) Carefully study the bar graph presented below showing production of crops i n t onnes (“000”) from Ujamaa village in 2010, and then answers t he questions that follow.
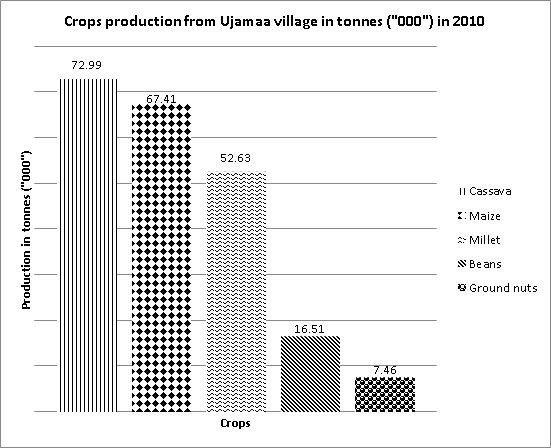
(i) Draw the above bar graph to a simple divided circle by showing all the procedures.
(ii) Give two possible factors for variation of crops production in the above bar graph provided.
5. (a) Point out four objectives of doing research in Tanzania.
(b) Describe the following terms as used in research:
(i) Case study
(ii) Feasibility s tudy.
(iii) Participatory observation.
(iv) Research hypothesis.
(v) Research problem.
6. (a) Explain two major forms of measurements in land surveying.
(b) (i) Define leveling.
(ii) Explain four significances of leveling.
SECTION C (28 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
MAP READING AND PHOTOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
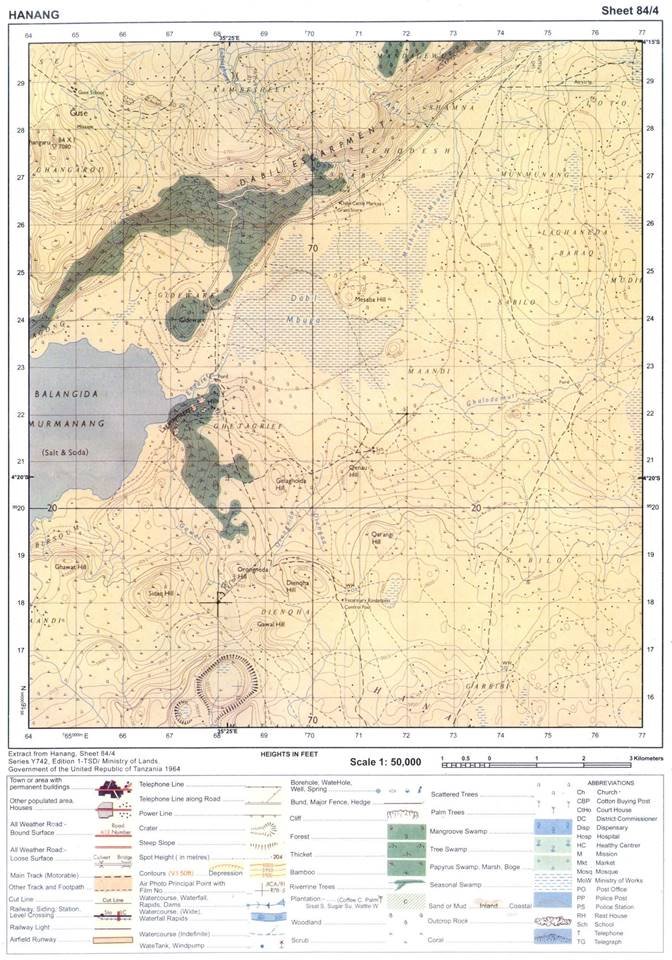
7. Carefully study the map extract of Hanang (Sheet 84/4) provided and answer the following questions:
(a) Express the map scale as a statement.
(b) Find the bearing of grid reference 720220 to 680180.
(c) Giving three evidences from the map, suggest the climate of the mapped area.
(d) Suggest with evidence, five major economic activities which might take place in the area.
(e) Give four supportive contents of a topographical map provided.
(f) Mention three factors which affected the contents of the map given.
8. Study the photograph provided below and then answer the questions that follows:
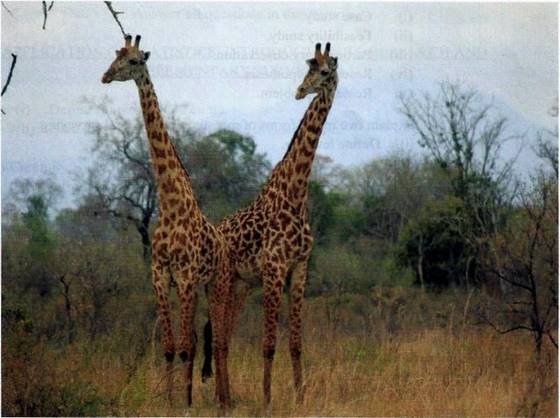

(a) Name the type of photograph.
(b) Give three characteristics of the type of photograph in (a) above.
(c) Explain four possible factors which may cause the loss of biodiversity in the photograph.
(d) Give two economic importance of the area.
(e) In three points, describe the importance of the vegetation shown in the area.
SECTION D (20 Marks)
Answer one(1) question from each part.
PART 1: REGIONAL FOCAL STUDIES
9. Evaluate six factors that determine exploitation of minerals in a country.
10. Explain six factors that hinder development of river transportation in Africa.
PARTII: ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES, POPULATION AND SETTLEMENTS
11. Describe five measures to control floods to the environment.
12. Analyse eight problems associated with growth of urban settlement.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
013 GEOGRAPHY
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
Time: 3 Hours Thursday, 05thNovember 2015 a.m.
Instructions
1. This paper consists of sections A, B, C and D.
2. Answer all questions in sections A, B and C and one (1) question from each part of section D.
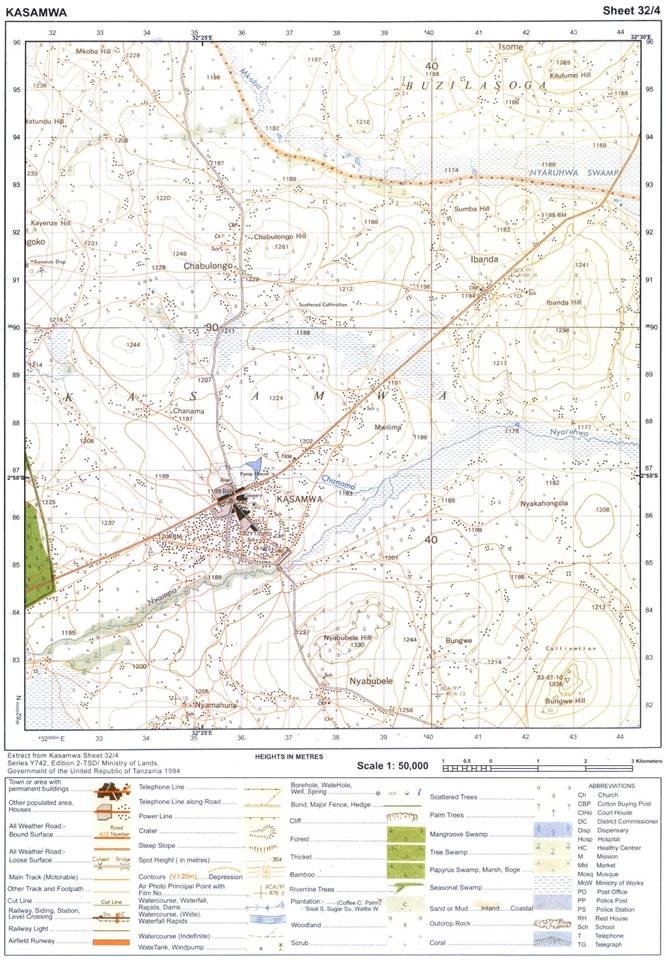
3. Map extract of Kasamwa (sheet 32/4) is provided.
4. Credit will be given for the use of relevant diagrams.
5. Calculators and Cellular phones are not allowed in the examination room.
6. Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s)
SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
PHYSICAL AND MATHEMATICAL GEOGRAPHY
1. For each of the items (i) (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter in the answer booklet provided.
(i) Autumn, winter, spring and summer are the result of
- monsoon
- lunar eclipse
- rotation
- revolution
- tides.
(ii) A large part of the Southern Hemisphere is covered by
- land mass
- volcanoes
- water mass
- dark clouds E ice.
(iii) The shallow part of the sea that stretches out from the coast is called
- Continental shelf
- Continental slope
- Ocean ridge
- Ocean trench
- Island.
(iv) Which of the following is not a factor influencing temperature of a place?
- Aspect.
- Ocean current.
- Altitude.
- Eclipse.
- Length of a day.
(v) The sideways erosion which widens the V-shaped valley is known as
- vertical erosion
- lateral erosion
- headward erosion
- hydraulic action
- attrition.
(vi) Deposition of soil materials removed from one horizon to another is called
- illuviation
- weathering
- eluviation
- organic sorting
- leaching.
(vii) Which of the following results to vertical movements within the earth’s crust?
- Earthquake, faulting and volcanic eruptions.
- Block mountains, raised beaches and broad basins.
- Volcanic eruptions, rock fall and asymmetric folds.
- Fold mountains, basins and asymmetrical folds.
- Emerged coasts, over folds and faulting.
(viii) Which among the following features is the impact of water action in the desert?
- Yardang
- Gullies
- Badlands
- Sinkholes
- Rock pedestals.
(ix) An active state of decomposition caused by soil microorganism is called
- organic matter
- soil water
- mineral matter
- soil air
- soil components.
(x) Which of the following is associated with magnitude of an earthquake?
- Richter scale
- Seismography
- Focus
- Epicenter
- Tsunami.
2. Match the items in List A with the responses in List B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number in the answer booklet provided.
| LIST A | LIST B |
| (i) Residues that have decomposed and mixed with soil mass. (ii) Status of soil with respect to amount of elements necessary for plants growth. (iii) Removal of materials from surface of land. (iv) Vertical section of the soil to the underlying rocks. (v) Fineness and coarseness of soil particles. |
|
3. With the aid of a well labeled diagram, describe the internal structure of the earth.
SECTION B (27 Marks)
Answer all questions this section.
APPLICATION OF STATISTICS, INTRODUCTION TO RESEARCH AND ELEMENTARY SURVEYING
4. Study the following data showing the production of Irish Potatoes in a thousand (“000”) tones in three villages in Tanzania from 2000 to 2002, then answer the questions that follow:
| YEAR | Potato production (“000”) | ||
| Sunga | Mwaligulu | Mpera | |
| 2000 | 20 | 15 | 5 |
| 2001 | 40 | 15 | 10 |
| 2002 | 50 | 20 | 10 |
(a) Construct a compound bar graph to show the production of Irish potatoes in the three villages.
(b) Give three advantages and two disadvantages of the compound bar graph.
(c) Suggest any other methods which could be used to present the data provided in the table.
5. (a) What is an interview?
(b) Analyze five things to be adhered to for a researcher to have a successful interview.
6. (a) (i) Define chain survey.
(ii) Give four principles of chain survey.
(b) Give one reason for each of the following:
(i) Ranging pole has a pointed metal end.
(ii) Note book is important during field study.
(iii) Back bearings are taken during compass survey.
(iv) During surveying, measurements are called back by the booker.
SECTION C (28 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
MAP READING AND PHOTOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
7. Study the map extract of Kasamwa (sheet 32/4), then answer the questions that follow:
(a) Identify two ways that have been used to show relief on the map.
(b) Draw a relief section to connect Nyabubele Hill at 383834 and Bungwe Hill at 430825.
(c) Identify the length of the all weather road in km from grid reference 315844 to 443940.
(d) Find the bearings of Chabulongo Hill at 367917 to a school at Nyamahuna 349818.
8. Carefully study the photograph given below then answer the questions that follow:

(a) Name the type of photograph.
(b) Describe the relief of the area.
(c) Giving two reasons, describe the scale of production of the crop in the photograph.
(d) Explain two uses of the crop in the photograph.
(e) Describe three conditions necessary for the production of the crop.
SECTION D (20 Marks)
Answer one (1) question from each part.
PART 1: REGIONAL FOCAL STUDIES
9. Describe six contributions of cash crops production ot the economy of United States of America.
10. Analyse six potentials of the Rufiji river basin.
PART II: ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES, POPULATION AND SETTLEMENT
11. Give five reasons for decreasing death rates in many parts of the world.
12. With the aid of examples, describe six factors affecting growth of settlements in Africa.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA
NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
013 GEOGRAPHY
(For School Candidates Only)
Time: 3 Hours Monday, 04?th?November 2013 a.m.
![]()
Instructions
1. This paper consists of sections A, B, C and D.
2. Answer ?all? questions in sections A, B and C and ?one (1) que?stion from each part of section D.
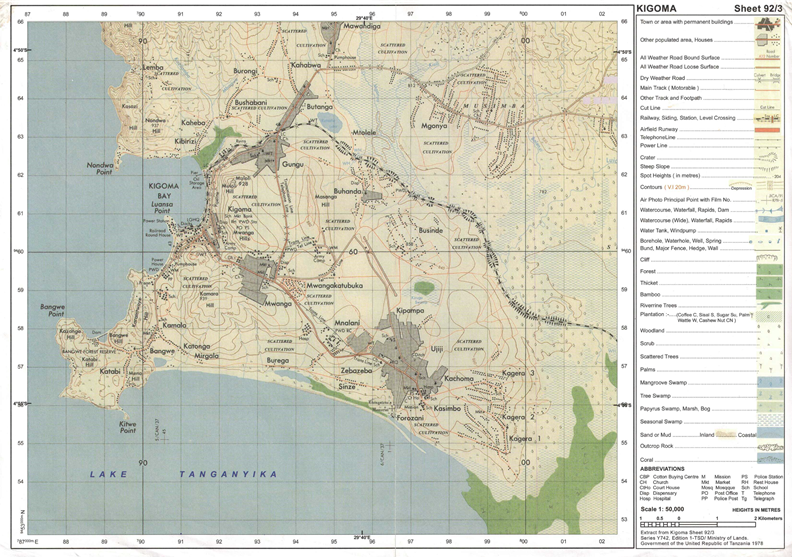
3. Map extract of Kigoma (Series Y742 sheet 92/3) is provided.
4. Credit will be given for the use of relevant sketch maps and diagrams.
5. Calculators and cellular phones are ?not? allowed in the examination room.
6. Write your ?Examination Number? on every page of your answer booklet(s)
SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer ?all? questions in this section.
PHYSICAL AND MATHEMATICAL GEOGRAPHY
1. For each of the items (i) - (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number.
(i A cirque is
A an arm-chair shaped depression on a glaciated lowland area
B an arm-chair shaped depression on the sides of a glaciated mountain
C an arm-chair shaped depression in the desert areas
D an arm-chair shaped valley in glaciated areas
E an arm-chair shaped depression on the plateau.
(ii) A geyser can be described as
A a hot spring
B an explosion of volcanic vapour
C a fountain of superheated water and steam
D a thermal stream E a pool of hot water.
(iii) Which one of the following conditions is important for the growth of coral reefs?
A Warm and muddy river water
B Warm and muddy sea water
C Warm and clear sea water
D Warm and clear tape water
E Warm and clear river water.
(iv) A time accepted throughout a time zone of 15° longitude is known as
A local time
B noon time
C greenwich mean time
D sun time
E standard time.
(v) Which sequence of the following processes is necessary for the formation of rainfall?
A Condensation, cooling and evaporation
B Evaporation, cooling and condensation
C Evaporation, sedimentation and cooling
D Evaporation, condensation and cooling
E Evaporation, cooling and sedimentation.
(vi) Which of the following instruments is used to measure pressure?
A Wet and dry bulb thermometer
B Aneroid barometer
C Anemometer
D Rain gauge
E Hygrometer.
(vii) Faulting may lead to the formation of
A rift valleys B moraines C ox-bow lakes D boulder clays E yardangs.
(viii) Which of the following statements is true to an equatorial region?
A It has a small annual range of temperature
B It has four rainfall maxima
C It experiences temperatures below 20°C
D It has a high annual range of temperature
E It is found between 15° and 30° north and south of the equator.
(ix) The earth’s crust is also known as
A atmosphere
B hydrosphere
C mantle
D lithosphere
E troposphere.
(x) What is the compass bearing of WNW?
A 270°
B 337°
C 315°
D 327°
E 292°
2. Match the items in ?List A? with the responses in ?List B by w?riting the letter of the correct response beside the item number.
| List A |
| List B |
| (i) A tidal wave formed as a result of an earthquake or volcanic eruption. (ii) Denser rocks that form the ocean floor. (iii) A force that causes the bending of the earth’s crust. (iv) Intrusive volcanic feature formed horizontally along the bedding plane. (v) Formed when two caves on opposite sides of headland join up. | A B C D E F G | Compression Dyke Sial Ocean currents Faulting Arch Sima |
|
| H | Tsunami |
|
| I | Stack |
|
| J | Sill |
3. With the aid of diagram, explain any five features formed by wave deposition.
SECTION B (27 Marks)
Answer ?all ?questions this section.
APPLICATION OF STATISTICS, INTRODUCTION TO RESEARCH AND ELEMENTARY SURVEYING
4. (a) Explain the meaning of the standard deviation.
(b) Study the following data showing the age of the Primary School pupils at Tumaini Primary School and answer the questions that follow: 15, 8, 7, 6, 12, 5, 14 and 13.
(i) Determine the range and median of the age of the pupils.
(ii) Calculate the standard deviation.
5. (a) What is research?
(b) Explain four benefits of conducting research.
6. (a) Explain the best steps required in order to conduct an accurate chain survey.
(b) What are the five good booking methods used in chain survey?
SECTION C (28 Marks)
Answer ?all? questions in this section.
MAP READING AND PHOTOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
7. Study the printed map extract of Kigoma (Series Y742 sheet 92/3), then answer the following questions:
(a) By using the vertical scale of 1cm to 20m, draw a cross section from grid reference 91057 to grid reference 932620 and determine its Vertical Exaggeration (V.E).
(b) With vivid evidence from the map, mention the major types of transport shown in the area.
(c) Apart from fishing activities, use concrete evidence to name other economic activities taking place in the area.
(d) In which hemisphere is the mapped area located? Give evidence for your answer.
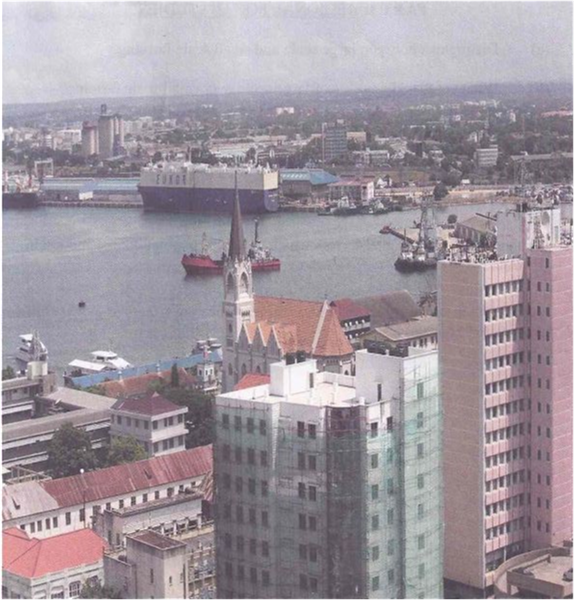
8. Study the photograph given below and then answer the questions that follow:

(a) Identify the type of photograph. Give concrete evidence
(b) By providing evidence from the photograph, describe the relief of the area.
(c) Explain three possible factors which have contributed to the growth of this town.
(d) Apart from providing shade, explain any other three advantages of the vegetation shown on the photograph.
SECTION D (20 Marks)
Answer ?one (1)? question from each part.
PART 1: ?REGIONAL FOCAL STUDIES
9. Explain six factors which account for the development of car manufacturing industry in Japan.
10. Describe six problems facing railway transportation in East Africa.
PART II:? ?ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES, POPULATION AND SETTLEMENT
11. Elaborate ?six? importance of Mount Kilimanjaro to Tanzania.
12. Examine six effects of environmental pollution in African cities.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
013 GEOGRAPHY
(For School Candidates Only)
Time: 3 Hours Wednesday, 10thOctober 2012a.m.
Instructions
1. This paper consists of sections A, B, C and D.
2. Answer all questions in sections A, B and C and one (1) question from each part of section D.
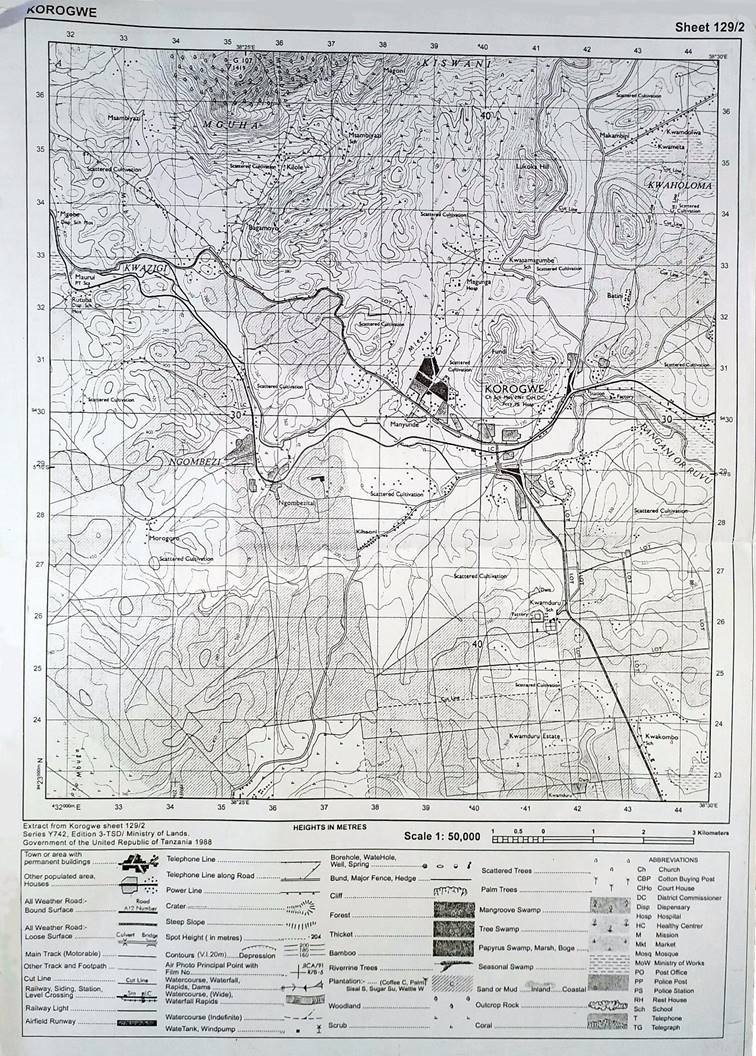
3. Map extract of Korogwe (Series Y742 sheet 129/2) is provided.
4. Credit will be given for the use of relevant sketch maps and diagrams.
5. Calculators and cellular phones are not allowed in the examination room.
6. Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s)
SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
PHYSICAL AND MATHEMATICAL GEOGRAPHY
1. For each of the items (i) - (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number.
(i) The outer layers of the earth include:
- Atmosphere, Lithosphere and Troposphere
- Atmosphere, Troposphere and Biosphere
- Atmosphere, Hydrosphere and Biosphere
- Atmosphere, Lithosphere and Biosphere
- Atmosphere, Hydrosphere and Lithosphere.
(ii) Which of the following is the effect of mass wasting?
- Frost action
- Interlocking spur
- Rock fall
- Exfoliation
- Rock disintegration.
(iii) The columns of clay capped by boulders formed due to rain action are known as:
- soil creep
- gullies
- land slide
- earth pillars
- cuesta
(iv) Which of the following features is formed by river erosion?
- pot hole
- ox bow lake
- delta
- flood plain
- lagoon.
(v) Rotation of the earth results to:
- elliptical orbit
- change of seasons
- day and night
- leap year
- standard time.
(vi) __________ are good examples of fold mountains in Africa.
- Uluguru and Oldoinyo Lengai
- Jos and Karoo
- Elgon and Kilimanjaro
- Atlas and Cape Ranges
- Udzungwa and Kilimanjaro.
(vii) Which one of the following is a process of wind erosion?
- Abrasion
- Corrosion
- Hydrolysis
- Exfoliation
- Attrition.
(viii) A great circle is a circle on a globe whose plane:
- passes through the centre of the globe
- has the shortest distance between two points
- is perpendicular with the globe
- marks a line of longitude
- marks a line of latitude.
(ix) The intensity of an earthquake is measured by:
- epicentre
- seismograph
- richter scale
- chronometer
- mercalli scale.
(x) Soil texture refers to:
- arrangement of soil particle
- size of individual soil particles
- soil catena
- soil PH
- grained structure.
2. Match the items in List A with the responses in List B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number.
| LIST A | LIST B |
| (i) The earth’s zone which is made up of nickel and iron. (ii) A wall like feature formed when a mass of magma cuts across the bedding plane. (iii) The upper most layer of the earth. (iv) A sheet of magma which lies along the bedding plane. (v) Magma which reaches the earth’s surface and solidifies to form extrusive features. |
|
3. (a) What is an earthquake?
(b) Briefly explain five effects of earthquakes.
(c) Describe four ways of reducing the risks of earthquakes.
SECTION B (27 Marks) Answer all questions this section.
APPLICATION OF STATISTICS, INTRODUCTION TO RESEARCH AND
ELEMENTARY SURVEYING
4. Carefully study the hypothetical data presented below showing the export of crops from Tanzania.
The Export of Crops in Tonnes
| Year | Cloves | Sisal | Cotton |
| 1990 | 4000 | 3500 | 7000 |
| 1991 | 2500 | 2000 | 4500 |
| 1992 | 3500 | 1500 | 6000 |
| 1993 | 6000 | 1000 | 8500 |
| 1994 | 6500 | 1500 | 9000 |
(a) Present the data using compound bar graph.
(b) Explain two advantages and disadvantages of compound bar graph.
5. (a) What is meant by sampling techniques as used in research?
(b) Briefly explain the following concepts as they are applied in sampling:
(i) A sample
(ii) Random sampling
(iii) Systematic sampling
(iv) Stratified sampling
(c) Outline the procedures of conducting an interview.
6. (a) (i) Define the term levelling survey.
(ii) Sate four benefits of levelling survey.
(b) Explain essential equipments used in levelling surveying.
SECTION C (28 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
MAP READING AND PHOTOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
7. Study the printed map extract of Korogwe (Series Y742 sheet 129/2), then answer the following questions:
(a) Describe the relief of the mapped area.
(b) Calculate the area of the whole map of Korogwe in Km2 by using grid squares.
(c) Examine the settlement patterns of the area.
(d) Express the scale of the map into statement scale.
8. (a) Name three types of geographical photographs.
(b) Specify the type of geographical photograph which is:
(i) taken horizontally on the ground.
(ii) used in map making.
(c) Explain five differences between the photograph you have mentioned in (b) (ii) above and topographical maps.
SECTION D (20 Marks)
Answer one (1) question from each part.
PART 1: REGIONAL FOCAL STUDIES
9. By using concrete examples, explain five negative effects of tourism in East Africa.
10. Elaborate eight reasons indicating why the transportation sector is important to the economy of Tanzania.
PART II: ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES, POPULATION AND SETTLEMENT
11. Explain eight environmental problems related to the rapid population growth.
12. (a) Describe five objectives of conducting census in a country.
(b) Explain three limitations of census in African countries.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA
NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
013 GEOGRAPHY
(For School Candidates Only)
Time: 3 Hours Tuesday, 4th O ctober 2011 a.m
Instructions
1. This paper consists of sections A, B, C and D.
2. Answer all questions in sections A, B and C and one (1) question from each part of section D.
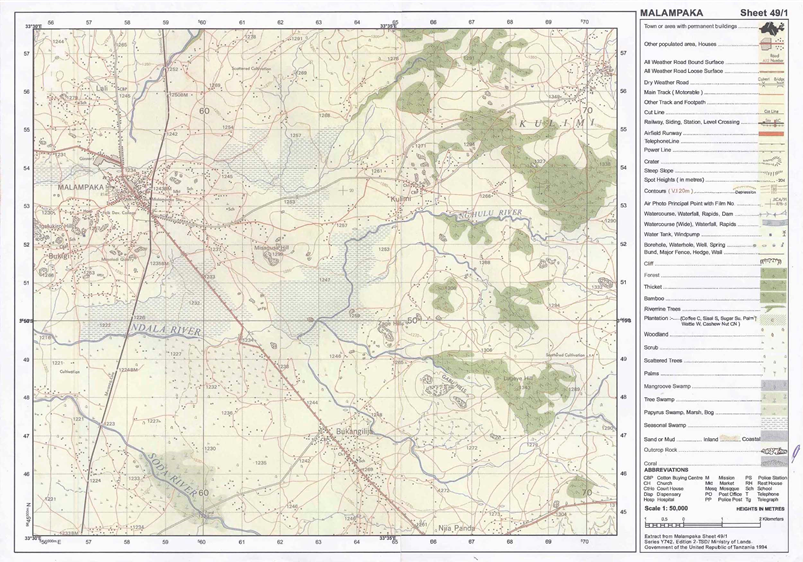
3. Map extract of Malampaka (sheet 49/1) is provided.
4. Credit will be given for the use of relevant sketch maps and diagrams.
5. Calculators and cellular phones are not allowed in the examination room.
6. Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s)
SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
PHYSICAL AND MATHEMATICAL GEOGRAPHY
1. For each of the items (i) - (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number.
(i) One of the following features is a characteristic of coniferous forests:
- Trees are made up of hard wood
- Trees occur in stands
- Trees favour high temperatures
- Trees have broad leaves
- Trees grow in a few years.
(ii) The Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) means
- a region of low pressure
- a region of doldrums
- a region of high pressure
- a sub-tropical high pressure belt
- a region with high speed winds.
(iii) Rias often provide natural harbour because they are
- found along the sub-merged coast.
- mainly found in Europe where the sea is shallow
- deep outlets of water along the coast
- not deep, ships can approach ports easily
- similar to lagoons but have shallow depths.
(iv) If the local time at town X (30°E 45°N) is 5.00 p.m. Monday, what will the time be at town Y (15°W 50°S)?
- 2 a.m. Monday
- 8 p.m. Monday
- 2 p.m. Monday
- 3 p.m. Monday
- 2 p.m. Sunday.
(v) The following are instruments used in chain and tape survey:
- Barometer, pegs, notebook, compass
- Tape measure, chain, cross staff, anemometer
- Chain, arrows, ranging poles, altimeter
- Arrows, ranging poles, pegs, chain
- Cross staff, notebook, chain and plane table.
(vi) When the river flows in its long profile it performs the following geological activities:
- Moves fast and can carry everything on the earth’s surface
- Erodes, transports and deposits weathered materials
- Meanders and forms ox-bow lakes throughout the profile
- Does three functions such as abrasion, solution and attrition
- Acts as agent of weathering and erosion along the profile.
(vii) If the location of a point on a map is given by grid reference 365490, then
- 365 are Degrees
- 365 are Longitudes
- 490 are Northings
- 490 are Eastings
- 365 are Northings
(viii) The following are the elements of weather:
- Soils, clouds, dew, humidity, rainfall
- Fog, barometer, humidity, pressure, air mass
- Clouds, sunshine, pressure, humidity, thermometer
- Pressure, clouds, sunshine, humidity, winds
- Pressure, humidity, soils, fog.
(ix) Which one of the following is not an outcome of the rotation of the earth on its own axis?
- Deflection of winds and ocean currents
- Difference of one hour between two meridians 15° apart
- Day and night
- Seasons of the year
- Sunrise and sunset.
(x) Landforms formed by vulcanicity can be divided into
- Many parts according to the nature of lava
- Sills, dykes, valleys and earthquakes only
- Volcanic mountains and sills only
- Extrusive and intrusive features
- Batholiths, dykes and volcano only.
2. Match the items in List A with the responses in List B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number.
| LIST A | LIST B |
| (i) Earth’s zone which is rich in Nickel and iron. (ii) Erosional feature which is always formed in the young/upper stage of the river valley. (iii) Consists of a huge canopy which limits the undergrowth. (iv) The feel of coarseness or softness of the individual soil particles. (v) A planet in the solar system with the longest orbit around the sun. |
|
3. Soils may differ from one area but they share almost the same components.
Describe the composition of the soil.
SECTION B (27 Marks)
Answer all questions this section.
APPLICATION OF STATISTICS, INTRODUCTION TO RESEARCH AND ELEMENTARY SURVEYING
4. Data in the following table show the enrolment of Form One students at Mji Mpya Secondary School from 2006 to 2010. Carefully study them and answer the questions that follow.
| Year | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
| Number of students | 220 | 200 | 150 | 180 | 205 |
(a) Present the data by using simple bar graph.
(b) Comment on the trend of the enrolment.
(c) Explain the advantages of the method you have used in (a) above.
5. (a) What is hypothesis formulation?
(b) Explain four importance of hypothesis in research.
6. Form three students at Nguvumali secondary school would like to conduct a simple chain survey around their school compound and measure the height of the big gully near the headmaster’s office. Describe the significance of survey in Tanzania
SECTION C (28 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
MAP READING AND PHOTOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
7. Carefully study the map extract of Malampaka (sheet 49/1) provided and answer the following questions:
(a) Calculate the area covered by seasonal swamps in Km2.
(b) Explain the distribution of natural vegetation.
(c) How long in kilometres is river Ng’hulu from grid reference 625496 to grid reference 700522?
(d) Identify any three ways which have been used to represent relief in the area.
(e) Through giving evidence, explain any four economic activities that might be taking place in the area.
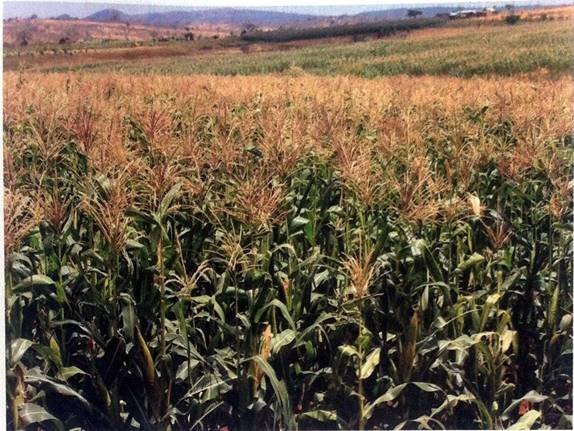
8. Carefully study the following photograph and answer the questions that follow.

(a) Such the type of the photograph by giving two reasons.
(b) Suggest any four economic activities that might be taking place in the area shown on the photograph.
(c) Comment on the nature of the settlement pattern as it is portrayed on the photograph.
(d) Explain the relief of the area.
SECTION D (20 Marks)
Answer one (1) question from each part.
PART 1: REGIONAL FOCAL STUDIES
9. (a) Distinguish between large scale and small scale farming.
(b) What are the advantages of large scale over small scale farming?
10. “Oil as an economic resource has improved the living standards of the people of Libya”. Discuss.
PART II: ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES, POPULATION AND SETTLEMENT
11. Explain the environmental factors which influence population distribution in Tanzania.
12. Suggest the measures to be taken in order to reduce the effects of global climate change at national level.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
013 GEOGRAPHY
(For School Candidates Only)
Time: 3 Hours Tuesday, 5th O ctober 2010 a.m.
Instructions
1. This paper consists of sections A, B, C and D.
2. Answer all questions in sections A, B and C and one (1) question from each part of section D.
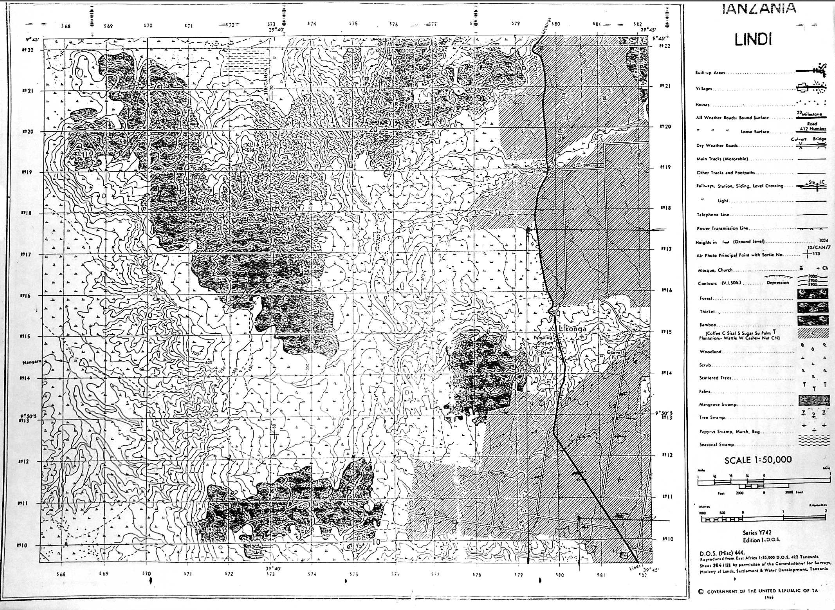
3. Map extract of LINDI is provided.
4. Credit will be given for the use of relevant sketch maps and diagrams.
5. Calculators and cellular phones are not allowed in the examination room.
6. Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s)
SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
PHYSICAL AND MATHEMATICAL GEOGRAPHY
1. For each of the items (i) (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number.
(i) Crater lakes are most likely to be formed in
- areas of fold mountains
- intensively faulted areas
- downwarped areas
- regions where subsidence is taking place
- areas of active vulcanicity.
(ii) Which one of the following is not associated with earthquakes?
- Body waves
- Geyser
- Richter scale
- Seismograph
- Focus.
(iii) If the time at town X 15°E is 12.00 noon, what could be the longitude of town Y if it is 8.00 a.m?
- 15°W
- 30°E
- 45°W
- 30°W
- 45°E
(iv) Which one of the following, by origin and composition is not a form of igneous rocks?
- Sill
- Gypsum
- Lava plain
- Volcano
- Granite.
(v) One of the following features is a product of weathering:
- Earth pillar
- Gully
- Lilly
- Hot springs
- Soil creep.
(vi) The process of river erosion where fragments are worn out during collision against each other is termed as
- hydraulic action
- attrition
- abrasion
- corrosion
- hydrolysis.
(vii) A scale of 4 cm representing 18 km on the ground will be represented by representative fraction (R.F) scale as
- 1 : 900000
- 1 : 1800000
- 1 : 450000
- 2 : 900000
- 1 ? 10,000
(viii) Which one of the following owes its origin to deflation?
- Qattara depression
- Lake turkana
- Tekekitarn
- Lake Chad
- Lake Victoria.
(ix) The presence of paired terraces on both sides of a river valley indicates that
- river capture has taken place
- lateral erosion is dominant
- sea level has risen
- rejuvenation has taken place
- truncated spurs have retreated.
(x) A good example of intrusive igneous rocks is
- gneiss
- basalt
- gabbro
- marble
- imestone.
2. Match the items in List A with the responses in List B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number.
| LIST A | LIST B |
| (i) Saucershaped structure of permeable rock layer lying between two impermeable rocks (ii) A process by which wind transport loose materials (iii) Part of the land that lies between high water and low water (iv) A volcano made of viscous lava (v) One of the components of soil |
|
3. (a) What is meant by marine erosion?
(b) Describe four (4) processes which are involved in marine erosion.
SECTION B (27 Marks)
Answer all questions this section.
APPLICATION OF STATISTICS, INTRODUCTION TO RESEARCH AND ELEMENTARY SURVEYING
4. Carefully study the data in the table below showing importation of motor vehicles from Europe in 2009, and answer the questions that follow:
| Name of Motor Vehicle | Number of Motor Vehicle |
| JEEP | 430 |
| BENZ | 192 |
| BMW | 108 |
| RIMOUSSENE | 70 |
(a) Draw a divided circle to represent the data.
(b) Show the disadvantages of the method you have used in (a) above.
5. Hypothesis formulation can be used in both qualitative and quantitative research. Examine the problems faced in hypothesis formulation
6. The chairman of Mivumoni village advised his village mates to use simple chain survey in order to get the right measurements of their farms. Show the merits and demerits of simple chain survey.
SECTION C (28 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
MAP READING AND PHOTOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
7. Carefully study the map Extract of LINDI provided, and then answer the following questions.
(a) Explain the possible reasons for the uneven population distribution in the area.
(b) How long in Kilometers is the LindiNachingwea allweather road (bound surface).
(c) Giving two evidence from the map, name the type of climate experienced in this area.
(d) How big in Km2 is the area covered by the forest south of grid line 160?
8. Carefully study the photograph provided below and then answer the questions that follow.
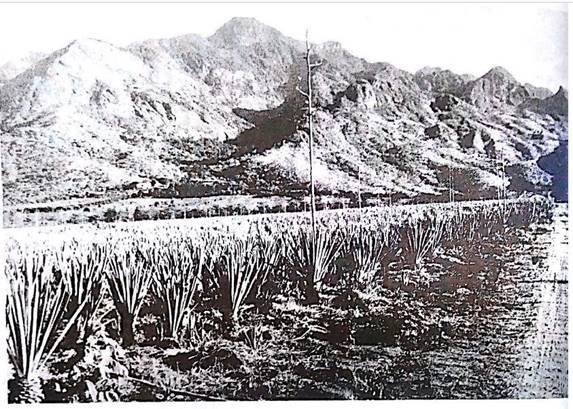

(a) Name the crop shown in the photograph.
(b) Mention the natural conditions which favour the growth of the crop
(c) Tanzania is very famous in growing the crop mentioned in (a) above. Name the regions of Tanzania which grow the crop at commercial level.
(d) With concrete evidence, explain the scale of production as shown on the photograph.
SECTION D (20 Marks)
Answer one (1) question from each part.
PART 1: REGIONAL FOCAL STUDIES
9. In order to achieve economic development, transport and communication are inevitable. Describe the significance of transportation in developing countries.
10. Discuss the reasons for the low level of industrial development in SubSaharan Africa.
PART II: ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES, POPULATION AND SETTLEMENT
11. Examine the best ways which can ensure a sustainable use of forestry resources.
12. How does rapid population explosion affect small scale agriculture?
VIEW MARKING SCHEME

Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania






