THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL OF TANZANIA
CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
033/1 BIOLOGY 1 (For Both School and Private Candidates)
Time: 3 Hours Wednesday, 07th November 2018 a.m.
Instructions
-
This paper consists of sections A, B and C with a total of thirteen (13) questions.
-
Answer all questions in sections A and B and one (1) question from section C.
-
Except for diagrams that must be drawn in pencil, all writing should be in blue or black ink.
-
Calculators, cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
-
Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
SECTION A (20 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
For each of the items (i) - (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in the answer booklet.
(i) Mitosis normally takes place in
- reproductive cells
- animal cells only
- blood plasma
- plant cells only
- somatic cells.
(ii) Which of the following is the symptom of the disease caused by lack of protein in children?
- Anemia
- Swollen head
- Breeding
- Pale and thin hair
- Sneezing.
(iii) flow many gametes are produced from one cell during meiosis?
- Eight
- Two
- Four
- Six
- Ten.
(iv) Which of the following is the excretory organ in human?
- Mouth
- Kidney
- Pancreas
- Stomach
- Anus.
(v) Which of the following hormones stimulates seed germination in plants?
- Gibberellins
- Auxin
- Cytokinins
- Abscisic acid
- Ethene.
(vi) A joint which allows rotation in all planes is called
- suture
- ball and socket
- pivot
- ligament
- hinge.
(vii) In which environmental condition the loss of water vapour from plants is mostly favourable?
- Hot and Windy day
- A saturated atmosphere
- Cool and dry atmosphere
- Windy day
- Hot day.
(viii) The function of the bright coloured petals in flowers is
- to store nectarines
- to hold sepals in position
- to produce colour of the flower
- to receive pollen grain
- to attract insects for pollination.
(ix) The function of hydrochloric acid in food testing experiment is
- to decolourise food sample
- to test reducing sugar
- to oxidize the food sample
- to neutralize sugary foods
- to hydrolyze complex to simple sugar.
(x) The interaction between two species in which both organisms benefit is known as
- ectoparasite
- parasitism
- commensalisms
- mutualism
- endoparasite.
2. Match the phrases in List A with the responses in List B by writing the letter of the correct response from List B beside the item number of List A in your answer booklet.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
All questions carry 8 marks except question three (3) and seven (7) which carry 6 marks each.
3. (a) Differentiate the term "Biological apparatus" from "Biology Laboratory".
(b) Briefly explain why the following substances are dangerous?
-
Toxic substances
-
Highly flammable
-
Corrosive substances
-
Radioactive substances.
4. (a) Give the meaning the following terms as used iri Biology:
-
Blood transfusion.
-
Blood compatibility.
(b) (i) State two advantages of blood transfusion.
(ii) Outline four precautions to be taken during blood transfusion.
5. (a) Explain the distinctive features of the Division Filicinophyta.
(b) Draw a well labeled diagram of a fern plant.
6. (a) Describe the stages of human post-natal growth and development.
(b) What do you understand by a term "primary growth" in plants?
7. (a) Briefly explain the process of menstruation in human being.
(b) Mention two types of the common disorders of human reproductive system.
8. (a) List any four macro-elements in plant nutrition.
(b) Explain the causes of any three common disorders and diseases of the human digestive system.
9. (a) A newly married couple expects a baby. Using a genetic cross, work out the probability of their first born child being a boy.
(b) Give the meaning of the following terminologies as used in genetics:
(i) Sex linked genes
(ii) Sex determination
(iii) Phenotype.
10. (a) Give the meaning of the following Biological terms as used in the ecosystem:
-
Biotic components
-
Abiotic components
-
Food chain
-
Food web.
(b) Construct a feeding relationship which accommodates the following organisms:
Grasses, Goat, Sheep, Shrubs and Man.
SECTION C (20 Marks)
Answer one (1) question from this section.
-
Elaborate four causes and five preventive measures of drug abuse.
-
With the aid of a well labelled diagram, describe the urinary system and explain the process of urine formation in human beings.
-
Describe four evidences of organic evolution.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
033/1 BIOLOGY 1
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
Time: 3 Hours Wednesday, 01stNovember 2017 a.m.
Instructions
- This paper consists of sections A, B and C with a total of thirteen (13) questions.
- Answer all questions in sections A and B and one (1) question from section C.
- Except for diagrams that must be drawn in pencil, all writing should be in blue or black ink.
- Calculators, cellular phones and any unauthorised materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
SECTION A (20 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
1. For each of the items (i) - (x), choose the correct answer among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in the answer booklet provided.
(i) Goitre is a deficiency disease caused by lack of which element in the diet?
- Carbohydrate
- Iodine
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin C
- Protein.
(ii) Tongue rollers in genetics is an example of
- gametogenesis
- continuous variation
- swallowing
- lubricating food
- discontinuous variation.
(iii)Which food substance is investigated in the biuret test procedur?
- Carbohydrate
- Lipids
- Protein
- Starch
- Reducing sugar.
(iv) The product of anaerobic respiration process in animals is
- lactic acid
- carbondioxide
- alcohol
- water
- oxygen.
(v) A phylum consisting of species with jointed appendages and exoskeleton is known as
- Chordata
- Anelida
- Arthropoda
- Platyhelminthesis
- Nematoda.
(vi) Which part of the flower receives pollen grain during pollination?
- Petal
- Stigma
- Stamen
- Style
- Ovary.
(vii) A rapid growth in plants is mainly taking place in
- leaves
- cambium
- roots
- shoots and root tips
- stem.
(viii) Which of the following is NOT a component of First Aid Kit?
- Razor blade
- Panadol
- Bandage
- Soap
- Microscope.
(ix) Which disease spread rapidly as a result of poor waste disposal?
- Anemia
- AIDS
- Cholera
- Leukemia
- Small pox.
(x) A voluntary muscle that is capable of relaxing continuously and do not fatigue easily is known as
- skeletal muscle
- biceps
- triceps
- cardiac muscle
- smooth muscle.
2. Match the phrases in List A with the responses in ListB by writing the letter of the correct response from List B beside the item number of List A in your answer booklet provided.
| LIST A | LIST B |
| (i) A disease casued by flatworms known as schistosome. (ii) A disease caused by a protozoan called trypanosoma. (iii)A tropical disease caused by plasmodiun. (iv) A water bone disease casued by entamoeba histolystica. (v)An outbreak disease caused by vibrio cholerae. (vi)A sexually transmitted disease caused by bacteria known as treponema palladium. (vii)A communicable disease casued by salmonella typhii. (viii) A sexually transmitted disease caused by bacteria known as Neisseria gonorrhoea. (ix) A viral infection disease caused by HIV. (x) A disease caused by micobacterium tuberculosis. |
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
All questions carry 8 marks except question eight (8) and nine (9) which carry 6 marks each.
3. (a) Why schools should have a Biology laboratory? Give a reason.
(b) State six laboratory rules.
4. (a) State two principles of waste disposal.
(b) Suggest three proper ways of waste disposal in the community.
5. (a) (i) What do you understand by the term respiration?
(ii) Name the two types of respiration.
(b) Explain how gaseous exchange occurs across the aveolus.
6. (a) Differentiate complete dominance from incomplete dominance.
(b) In a laboratory experiment, tall pea plants were crossed wiht dwarf pea plants. F1 plants were then selfed to produce F2 generation.
(i) Using appropriate symbols, work out a genetic cross for F 1 generation.
(ii) Give the phenotypic and genotypic ratio of F1 generation.
7.(a) Explain the process of fertilization in flowering plants.
(b) Briefly explain how you would identify an insect pollinated flower.
8. (a) Name three type of muscles found in mammals.
(b) Briefly explain how muscles are adapted to their role. Give three points.
9. (a) List any two types of blood cells.
(b) Give two differences between arteries and vein.
10. (a) With examples, state the meaning of “abiotic” and “biotic” factors of the environment.
(b) (i) Differentiate the terms “food chain” from a “trophic level”.
(ii) Construct a food chain by using organisms named in the following list: Grass, Bacteria, Lions and Zebra.
SECTION C (20 Marks)
Answer one (1) question from this section.
11. Describe the types of macronutrients needed in human body. In each type identify the source and function of food substances in human body.
12. With the aid of illustrations, discuss the stages of mitosis.
13. With the aid of a well labelled diagram, describe the structure of bacteria and give three advantages and disadvantages of bacteria in daily life.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
033/1 BIOLOGY 1
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
Time: 3 Hours Thursday, 03 rd November 2016 a.m.
Instructions
-
This paper consists of sections A, B and C.
-
Answer all questions in sections A and B and one (1) question from section C.
-
Except for diagrams that must be drawn in pencil, all writings should be in blue or black ink.
-
Calculators and cellular phones are not allowed in the examination room.
-
Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
SECTION A (20 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
-
For each of the items (i) - (x), choose the correct answer among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in the answer booklet provided.
(i)Caridac muscle can be found in which part of the animal body?
- Skull
- Heart
- Small intestine
- Limbs
- Head.
(ii)The kidney in animals is mainly responsible for
- excretion
- digestion
- transportation
- respiration
- absorption.
(iii) The aim of experiment in the scientific investigation is to
- identify the problem
- test the hypothesis
- confirm the problem
- predict the results
- collect data.
(iv) The main product of anaerobic respiration process in plants is
- uric acid
- lactic acid
- alcohol
- water
- oxygen.
(v) Which of the following parasitic organisms is typicall ectoparasite?
- Tick
- Tapeworm
- Plasmodium
- Round worm
- Lichen.
(vi) Which of the following is a seed bearing plant?
- Liverwort
- Prothallus
- Fern
- Sisal
- Moses.
(vii) A part of an onion bulb which is important for vegetative propagation is
- scale leaves
- foliage leaves
- terminal buds
- roots
- stem.
(viii) Which of the following is NOT a component of blood?
- Erythrocyte
- Platelets
- Leucocyte
- Plasma
- Vein.
(x) Which food substance can be tested by using iodine solution?
- Protein
- Starch
- Carbohydrate
- Non reducing sugar
- Reducing sugar.
(x) The offspring produced by mating the F1 generation is konwn as
- F3 generation
- F1 products
- F2 generation
- New generation
- Genetic generation.
2. Match the phrases in List A with the responses in List B by writing the letter of the correct response from List B beside the item number of List A in the answer booklet provided.
| LIST A | LIST B |
| (i) External appearence of a given characteristic as a result of influence by a gene. (ii) Genetic disorder characterised by failure of blood clotting. (iii) A sudden genetic change which can be inherited. (iv)Characteristics that can pass on from parent to offspring through sexual reproduction. (v) The possession of the characteristics which are different from those of the parents and other offspring. (vi) A gene that influences characteristics over another gene when in heterozygous state. (vii) A cross between individuals with homozygous parents. (viii) A unit of inheritance which determins a specific characteristic. (ix) Genetic makeup of a given gene which determines a given characteristic. (x) A disorder resulting from lack of melanin pigments |
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
-
(a) Give the meaning of the term “laboratory.”
(b) Describe three warning sign found on the laboratory containers.
-
(a) State three basic principles of waste disposal.
(b) Why poor waste disposal at home is said to cause adverse effects?
-
(a) Briefly explain the following terms:
-
Trophic level.
-
Food chain.
-
Food web.
-
-
(b)With example, briefly explain how the following interactions of living organism take place.
-
Predation
-
Parasitism.
-
-
(a) Define the terms “classification” and “Taxonomy”.
(b) (i) List the types of classification systems.
(ii) Give two differences between the classification systems you have listed in (b)(i).
-
(a) (i) Name three types of muscles found in mammals.
(ii) Which one of the muscle named in (a)(i) is a voluntary muscle?
(b)Briefly explain the functions of the following component of the skeleton:
-
Skull
-
Ribs
-
Vertebral column
-
Pelvic girdle.
-
-
(a) (i) What are the raw materials for photosynthesis?
(ii) List two products of photosynthesis.
(b) State how the ileum is adapted for absorption function.
-
(a) Explain how anaerobic respiration is applied in a real life situation.
(b)List the organs responsible for gaseous exchange in the following organisms:
-
Goat
-
Grasshopper
-
Frog
-
Tilapia.
-
-
(a) Give the meaning of the following terms:
-
Vegetative propagation.
-
Gamete.
-
-
(b) Explain the merits and demerits of asexual reproduction in plants.
SECTION C (20 Marks)
Answer one (1) question from this section.
-
With the aid of a well labelled diagram, describe the internal part of the mammalian heart.
-
Explain how mammals regulate their internal body temperature in response to external environmental changes.
-
Write a descriptive report which you can use to educate the community about the mode of transmission, symptoms and prevention measure of malaria in Tanzania.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
033/1 BIOLOGY 1
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
TIME: 3 HOURS Wednesday, 04 th November 2015 a.m.
INSTRUCTIONS
-
This paper consists of three sections A, B and C.
-
Answer all questions from sections A and B and one (1) question from section C.
-
Except for diagrams that must be drawn in pencil, all writing should be done using a blue or black pen.
-
Calculators and cellular phones are not allowed in the examination room.
-
Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
SECTION A (20 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section.
1. For each of the items (i) – (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in the answer booklet provided.
(i) Bowmans capsule is found in which of the following organs?
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Kidney
- Spleen
- Heart
(ii) Which of the following processes is involved in the regulation of body temperature in human beings?
- Urination
- Painting
- Deamination
- Sweating
- Detoxification
(iii) A structure that allows air to enter the trachea and prevents food from entering the wind pipe is known as
- glottis
- tongue
- soft plate
- mouth
- epiglottis
(iv) Study the following sequence of organisms: Grass ? Rabbit ? Wolves ? Fleas
The sequence is an example of
- food web
- ecosystem
- a pyramid
- food chain
- abiotic
(v) Lipase enzymes are mainly contained in which digestive secretions?
- Hydrochloric acid
- Gastric juice
- Saliva
- Intestinal juice
- Pancreatic juice
(vi) A person who is admitted in the hospital after an operation will most likely be fed on food rich in:
- vitamin C
- vitamin A
- protein
- lipids
- water
(vi) Which of the following is a vector of sleeping sickness?
- House fly
- Mosquito
- Tsetse-fly
- Tick
- Cockroach
(vii) The outer most living structure that identifies a plant cell is the presence of
- cytoplasm
- vacuole
- cell wall
- nuclear membrane
- cell membrane
(x) One of the most distinctive features used to place organisms in the Kingdom Fungi is the presence of
- gill structures
- hyphae
- cellulose
- cap
- exoskeleton
(x) Which of the following represent the organisms with homologous structures?
- Wings of Birds and Butterfly
- Forelimbs of Bird and Bat
- Tail of Rat and Scorpion
- Sting of Honey bee and Mosquito
- Beak of Duck and Hen
2. Match the phrases in List A with the responses in List B by writing the letter of the correct response from List B beside the item number of List A in your answer booklet.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question carries 8 marks except question three and eight which carry 6 marks each.
-
(a) What do you understand by the following terms:
-
Biology
-
Zoology
-
(b) Why is it important to study Biology? Give four reasons.
-
(a) What do you understand by the term “First Aid”?
(b) State how you would render First Aid to a person who has been shocked by electric current.
-
(a) Define the terms “digestion” and “feeding” as used in Biology.
(b) Explain why during digestion the food is:
-
Alkaline when in the mouth.
-
Acidic when in the stomach.
-
Alkaline when in the ileum.
-
-
(a) List any three characteristics of the Phylum Arthropoda.
(b) (i) Mention the Classes of the Phylum Arthropoda
(ii) Name one representative member for each Class you have mentioned in 6(b)(i).
-
The diagram in Figure 1 represents an eye of a human being. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
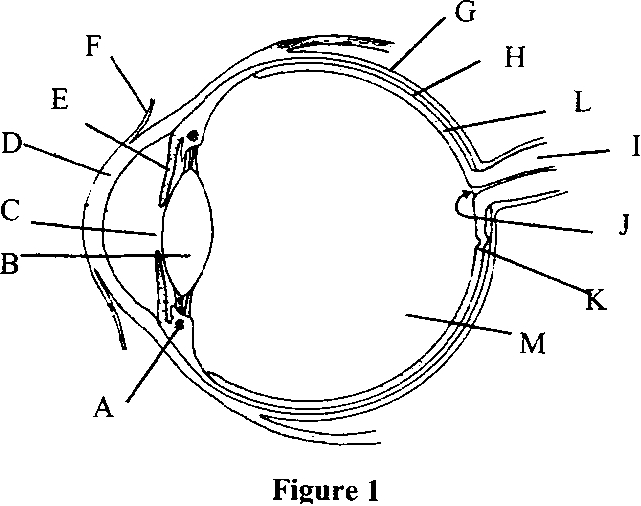
(a)Name the labeled parts A – L.
(b) What will happen in part C if someone suddenly faces:
-
the dim light.
-
bright light.
-
-
(a) Define the term “gene” and “genetics”.
(b) Give two differences between Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic Acid (RNA).
-
(a) Give the long meaning of the following abbreviation terms:
-
HIV
-
STIs
-
Tds
-
(b) Briefly explain any two ways through which HIV is transmitted from one person to another.
-
(a) Define the term “osmoregulation”.
(b) Briefly explain the mechanisms of regulating sugar level in the blood.
SECTION C (20 Marks)
Answer one (1) question from this section.
-
Explain how parts of the mammalian heart are adapted to their function.
-
Describe the symptoms of a person who is infected by Vibrio cholera and suggest six prevention measures and treatment for a cholera outbreak.
-
Explain the functions of the major components of the human skeleton and their adaptations.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
033/1 BIOLOGY 1
(For Both School and Private Candidates)
TIME: 3 HOURS Wednesday, 05 th November 2014 a.m.
INSTRUCTIONS
-
This paper consists of three sections A, B and C.
-
Answer all questions from sections A and B and one (1) question from section C.
-
Except for diagrams that must be drawn in pencil, all writings should be in blue or black ink.
-
Calculators and cellular phones are not allowed in the examination room.
-
Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
SECTION A (20 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section.
1.. For each of the items (i) – (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in your answer booklet.
(i)A term which best describes a condition of a plant cell that has lost too much water is
- haemolysis
- turgidity
- creanation
- plasmolysis
- osmosis
(ii) Bowmans capsule in the kidney functions as a
- filter
- sanction
- transmitter
- sponge pump
- absorber
(iii) A structure which controls the body balance in humans is located in the
- outer ear
- eardrum
- inner ear
- middle ear
- inner membrane
(iv) The main product of photosynthesis process is
- sunlight
- carbohydrate energy
- carbon dioxide
- water
- oxygen
(v) Species with cellulose in their cells are formally placed in
- Kingdom Monera
- Kingdom Animalia
- Kingdom Fungi
- Kingdom Plantae
- Kingdom Protista
(vi) Fertilization process is defined as
- formation of new cells
- union of an egg and sperm
- implantation of a zygote
- fusion of eggs in the uterus
- cell division in the oviduct
(vii) Mutual interaction between two species is described by which of the following characteristic
- Both live as parasite
- Both may be harmed
- Both benefit and flourish
- One is harmed and the other benefits
- Both neither benefits for is harmed
(viii) One of the characteristics used to identify producers in the ecosystem is
- feeding on ready-made food
- growing in fertile soil
- feeding on other organisms
- making their own food
- adding organic matter in the soil
(ix) The role of the optimum temperature in cellular activities is to
- change the chemical reactions
- balance the equilibrium of the reactions
- destroy many enzymes at once
- speed up the rate of chemical reaction
- create favourable environment for enzymes
(x) Rise of body temperature in the human body is corrected mainly by
- Dilating the skin arteries and sweating
- Constricting the skin arteries and shivering
- Dilating the skin veins and sweating
- Constricting the skin veins and shivering
- Dilating of arteries and shivering
2. Match the responses in List B with the phrases in List A by writing the letter of the correct response from List B beside the item number of List A in your answer booklet.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question carries 8 marks except question five and six which carry 6 marks each.
3. (a) State three actions which take place in the human body in response to each of the following conditions:
-
When the temperature of the surroundings is low.
-
When the body temperature rises due to increase in the surrounding temperature.
(b) Briefly explain why people look pale when they feel cold.
4. (a) Give the meaning of the following terms and identify two examples for each:
-
Waste
-
An accident
(b) Elaborate four procedures of giving First Aid to a person who has been injured in a bus accident and has severe bleeding.
5. (a) What do you understand by the following terms:
-
Evolution
-
Acquired characteristics
(b) Outline merits and demerits of Lamercks theory of evolution.
6. (a) Explain the functions of the vascular system in plants
(b) State three importance of transportation of materials in living things.
7. (a) In the experiment conducted on single factor inheritance, individuals which were male homozygous tall married a female who was homozygous dwarf. The gene for tall was dominant over dwarf. Use the crosses to find out the possibility of the phenotypic results and the ratio in the first filial generation.
(b) Give the meaning of the following:
-
Test cross
-
Back cross
-
Trait
8. (a) Define the following terms:
-
Meiosis
-
Mitosis
-
Growth
(b) (i) Explain the significance of mitosis in growth
(ii) State three factors affecting growth in humans.
9. (a) Draw a large and neat labelled diagram of the villus found in the digestive system.
(b) (i) Name the digestive juice which is produced by the liver.
(ii) State the function of the substances contained in the digestive juice named in b (i).
10. (a) Differentiate the following:
-
Breathing and respiration
-
Inhalation and exhalation
(b) Briefly describe the following phenomenon:
-
A person breathes more when running fast.
-
The ribs move outwards and upwards while the diaphragm flattened when air enters the lungs.
SECTION C (20 Marks)
Answer one (1) question from this section.
-
Explain any four effects of irresponsible sexual behaviour and suggest five ways of eradicating those behaviours in the community.
-
Describe how malaria parasites are transmitted, the sign developed to the host and give four ways which can help in combating malaria in the country.
-
Explain two differences between artificial and natural classification systems and indicate the two merits and demerits for each system..
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
033/1 BIOLOGY 1
(For School Candidates Only)
TIME: 3 HOURS Thursday, 07 th November 2013 a.m.
INSTRUCTIONS
-
This paper consists of three sections A, B and C.
-
Answer all questions from sections A and B and one (1) question from section C.
-
Except for diagrams that must be drawn in pencil, all writing should be done using a blue or black pen.
-
Calculators and cellular phones are not allowed in the examination room.
-
Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
SECTION A (20 MARKS)
1. For each of the items (i) – (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number.
(i) Animals which are able to maintain fairly constant body temperature are described as
- poikilothermic
- hydrostatic
- sympathetic
- symbiotic
- homoiothermic
(ii) Night blindness in the human body is avoided by eating
- oranges
- carrot
- red
- green vegetables meat
- chicken
(iii) A blood vessel which conveys deoxygenated blood away from the heart is called
- capillaries
- artery
- vein
- pulmonary vein
- pulmonary artery
(iv) The function of cones in the human eye is to
- sense light
- sense colour
- cover the eye
- reflect light
- protect the eye
(v) A term used to identify an individual animal having both male and female sex organs is
- unisexual
- hermaphrodite
- asexual
- dioecious
- monoecious
(vi) Which of the following structures is a site of respiration?
- Chloroplast
- Ribosome
- Nuclear
- Nucleic acid
- Mitochondrion
(vii) The structures found in bacteria are A plasmid, flagella and cilia
- cytoplasm, cilia and pastids
- cell wall, plasmid and flagella
- cell membrane,
- flagella and hairs
- plasmid, capsule and cilia
(viii) The by products in the photosynthesis process are
- carbohydrate and water
- carbon dioxide and oxygen
- oxygen and water
- carbohydrate and carbon dioxide
- oxygen and air
(ix) The factors which contribute to the spread of dental cavities in human being include
- prolonged exposure to cold water
- prolonged exposure
- prolonged exposure to warm water
- prolonged exposure to bitter food to hard water
- prolonged exposure to sugary foodstuff
(x) The main feature observed in prokaryotic is that they
- have genetic materials not enclosed by nuclear membrane
- have genetic material enclosed by nuclear membrane
- have no genetic material in their nuclear
- have more than one nucleic acid in their nuclear
- have genetic material enclosed by two membranes
2. Match the responses in List B with the phrases in List A by writing the letter of the correct response from List B beside the item number of List A in your answer booklet. Each choice in column B may be used once, more than once or not at all.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.Each question carries 8 marks except question three (3) and six (6) which carry 6 marks each.
3. (a) What do you understand by the term “Botany”?
(b) Briefly explain five characteristic of living things.
4. (a) State the conditions necessary for seed germination and briefly describe how they facilitate germination.
(b) Differentiate epigeal germination from hypogeal germination.
5. (a) Define the term “irritability.”
(b) Describe the neuronic pathway taken by reflex actions in human being.
6. (a) Give the meaning of osmosis and diffusion.
(b) Briefly explain how the following illustrates osmosis.
-
Shrinking of a cell when immersed in a high concentrated solution.
-
Bursting of red blood cell when immersed in dilute solution.
7. (a) Name and explain any four theories of the origin of life.
(b) Outline two ideas of Darwin theory.
8. (a) What is the meaning of the terms:
-
Digestion
-
Malnutrition
-
Balanced diet
-
Nutritional disorder
(b) Outline four types of nutritional deficiency disorders in human beings.
9. (a) Give the meaning of the following:
-
Continuous and discontinuous variations.
-
Inherited and acquired variations.
(b) Briefly explain how mutation and nutritional factors cause variation among organisms.
10. (a) Explain two factors affecting gaseous exchange in animals.
(b) Why does a fish die when taken out of water to land while a frog survives in both water and on land?
SECTION C (20 Marks)
Answer one (1) question from this section.
11. Give four common accidents at home and school, for each case explain the causes and three prevention measures.
12. Explain four ways of transmission, symptoms and treatment of HIV/AIDS.
13. Describe four similarities and seven differences between insect and wind pollinated flowers.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 033/1 BIOLOGY 1
TIME: 3 HOURS Thursday, 11 th October 2012a.m.
INSTRUCTIONS
-
This paper consists of three sections A, B and C.
-
Answer all questions from sections A and B and one (1) question from section C.
-
Read each question carefully before you start answering it.
-
Except for diagrams that must be drawn in pencil, all writing should be done using a blue or black pen.
-
Calculators are not allowed in the examination room.
-
Cellular phones are not allowed in the examination room.
-
Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
SECTION A (20 MARKS)
1. For each of the items (i) – (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number.
(i)The joint in the human body which allows movement in all directions is known as
- pivot
- hinge
- double hinge
- ball
- peg and socket and socket
(ii)Which of the following is a metabolic waste product?
- Tears
- Saliva
- Mucus
- Faeces
- Urine
(iii) The following are examples of water-borne diseases:
- malaria and bilharzia
- yellow fever and typhoid
- diarrhoea and malaria
- cholera and plaque
- cholera and typhoid
(iv)One of the distinctive features of kingdom Fungi is possession of:
- plasma membrane
- cytoplasm
- chitin materials
- cell membrane
- cellulose material
(v)The regions of most active growth in plants are found mainly in the
- axillary buds and flowered
- stems and leaves
- stems and root hairs
- leaves and flowers
- stem and root apices
(vi) A grasshopper ventilates its gaseous exchange surfaces by
- moving the diaphragm
- beating of cilia
- rhythmic body movement
- opening of spiracles
- moving its rib cage
(vii) The taxonomic category of organisms belonging to the same class but not the same family is:
- Species
- Genus
- Order
- Phylum
- Kingdom
(viii) The breakdown of glycogen into glucose in the body is due to the action of:
- insulin
- adrenaline
- secretion
- glucagon
- gastric
(ix) The function of sunlight energy in the human skin is the stimulate the synthesis of
- vitamin A
- vitamin C
- vitamin D
- vitamin K
- vitamin B
(x)A rise in the temperature of a human body is corrected by
- construction of the skin arteries and sweating
- construction of the skin arteries and shivering
- dilation of the skin arteries and sweating
- dilation of the skin arteries and shivering
- shivering and sweating
2. Match the responses in List B with the phrases in List A by writing the letter of the correct response from List B beside the item number of List A in your answer booklet. Each choice in column B may be used once, more than once or not at all.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
All questions carry 8 marks except for question five and six which carry 6 marks each.
3. (a) Outline four features which distinguish a Biology Laboratory from other school facilities.
(b) Outline four steps involved in using a microscope.
4. (a) Define the following terms as used in Biology:
-
First Aid kit
-
Risks
-
An accident
-
Poisoning
(b) Outline four procedures of giving First Aid to a person who has been stung by a bee.
5(a) Describe the following ecological terms:
-
Decomposers
-
Producers
-
Parasites
(b) With example, briefly explain how comparative embryology supports the idea of organic evolution.
6. (a) Outline three factors affecting transpiration.
(b) State three significance of transpiration.
7. (a) The laboratory technician at Mtakuja secondary school performed an experiment with the aim of proving the Mendelian experiment on single factor inheritance for a coat colour in mice. In the experiment, pure-breed (homozygous) black fur mouse (male) was mated with a pure-breed brown fur mouse (female). The gene for black fur colour was dominant over the gene for brown fur colour. Use crosses to show the possibilities of the results in the first filial generation.
(b) Explain the meaning of the following:
-
Gene
-
Recessive
-
Phenotype
8. (a) Define the following terms:
-
Growth
-
Intercalary growth
(b) Briefly explain three factors that affect growth and development in humans.
9. The diagram in Figure 1 is the alimentary canal of a human being. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
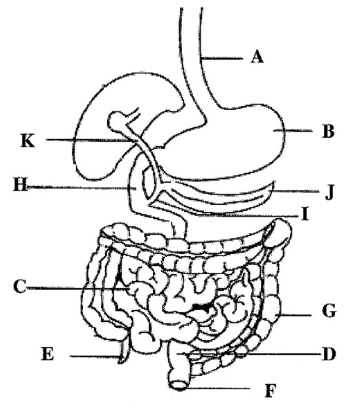
(a) Name the parts labelled A – K.
(b)(i) Name the digestive juice which is produced in organ labelled B.
(ii) Mention the substances contained in the digestive juice named in (b) (i) above.
10. (a) Briefly explain three importance of movement in plants and animals.
(b) State any five functions of the skeleton.
SECTION C (20 Marks)
Answer one (1) question from this section.
11. Describe the mechanism of breathing in human beings. Diagrams are not necessary.
12. Elaborate the causes of drug abuse to young people and advise the Tanzanian Government on the ways of combating drug abuse in the country.
13. Explain five factors which contribute to irresponsible sexual behavior among young people and their effect in the community.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 033/1 BIOLOGY 1
TIME: 3 HOURS Wednesday, 05 th October 2011 a.m.
INSTRUCTIONS
-
This paper consists of three sections A, B and C.
-
Answer all questions from sections A and B and one (1) question from section C.
-
Read each question carefully before you start answering it.
-
Except for diagrams that must be drawn in pencil, all writings should be in blue/black ink or ball point pen.
-
Calculators are not allowed in the examination room.
-
Cellular phones are not allowed in the examination room.
-
Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
SECTION A (20 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section, each question carries 10 marks.
1. For each of the items (i) – (x) choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number.
(i) How many gametes are produced from one cell during meiosis?
- Two
- Four
- Six
- Eight
- Ten
(ii) Which of the following is not an excretory product in plants?
- Tannins
- Carbon Dioxide
- Urea
- Calcium oxalate
- Latex
(iii) Why are skeletal muscles usually found in opposing pairs?
- One muscle alone cannot extend a joint
- Muscles can only work by contraction
- One muscle alone cannot flex a joint
- Paired muscles are stronger
- Muscles normally work in antagonistic fashion
(iv) Which of the following bests defines allergy?
- Body reaction to antigen
- Body reaction against a specific drug
- Body reaction against a diseasecausing microorganism
- Accumulation of mucus caused by inhaling dust particles
- Formation of rash caused by eating specific foods
(v) When students were conducting private study at night, lights went off completely. Which of the following changes occurred in the eyes of the students?
- The lens became thicker
- The pupil became larger
- The ciliary muscle relaxed
- The lids close
- The eyes opened wider
(vi) Select the item that indicates the best match in vitamindeficiency:
- Vitamin A dry scaly skin
- Vitamin B loss of appetite and yawning
- Vitamin C anemia and high blood pressure
- Vitamin D soft deformed bones
- Vitamin K poor night vision
(vii) Which of the following is formed immediately after fertilization?
- Placenta
- An embryo
- A foetus
- Amniotic fluid
- A zygote
(viii) The human ovary secretes hormones known as:
- Oestrogen and testosterone
- Progesterone and testosterone
- Oestrogen and lactogen
- Oestrogen and progesterone
- Follicle stimulating hormone and progesterone
(ix) The offspring of crosses between red flowered and white flowered plants were always found to be pink. This is an example of:
- Crossing over
- Mutation
- Co-dominance
- Incomplete dominance
- Natural selection
(x) At early stages of development of the human zygote which organ develops first?
- Liver
- Heart
- Kidney
- Eyes
- Notochord
2. Match the responses in List B with the phrases in List A by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
3. (a) Identify structures found in plant cells only.
(b) Describe the functions of each structure identified in 3(a) above.
4. (a) (i) What do you understand by the term peristalsis?
(ii) Suppose the peristalsis stops. What problems would and animal face?
(b) Describe the kind of food which should be added to a meal in order to improve peristalsis.
5. (a) Define the term “irritability” in living organisms.
(b) How does each of the aspects below illustrate the phenomena in 5(a) above?
-
Germinating seeds
-
A potted hibiscus plant growing near a window
-
A zebra sniffing the air with a predator nearby.
6. (a) With example, explain the meaning of the following:
-
Renewable natural resource?
-
Nonrenewable natural resource?
(b) (i) What is the importance of recycling of the resources?
(ii) Name the carbon cycle processes which are likely to affect the oxygen concentration in the atmosphere.
7. (a) Name two types of girdles found in the skeletal system.
(b) (i) Describe the three main functions of limb girdles.
(ii) State the type of joint formed at the girdles.
8. Figure 1 is a diagram of a plant root. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
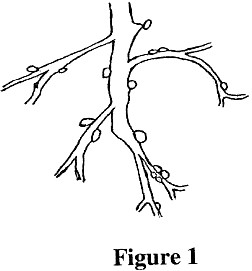
(i) Name a group of plant represented by the diagram in Figure 1.
(ii) Give any two examples of plants which can be found in a group of plants mentioned in (a)(i)?
(iii) Name the organisms which inhabit the swellings on the root.
(iv) What is the relationship existing between the plant and the organism mentioned in (a)(iii)?
-
Name the bacteria which does the following:
-
Changes nitrates into nitrites;
-
Converts ammonia into nitrites;
-
Change nitrites into nitrates.
-
9. (a) Mention any four laboratory safety rules.
(b) Some of the chemicals and apparatus used in Biology are harmful/dangerous. In what way are the following substances harmful/dangerous?
-
Toxic substances
-
Highly flammable substances
-
Corrosive substances
-
Radioactive substances
-
Biohazards
10. (a) (i) List the five kingdoms into which orgamisms are placed.
(ii) List the distinctive features of members of the kingdom to which a malaria vector belongs.
(b) (i) Identify by using common name, two types of flatworm found in the alimentary canal of a living organism.
(ii) To which kingdom does organism in (b)(i) belong?
SECTION C (20 Marks)
Answer one (1) question from this section.
11. Write an essay on transportation in plants using the following guidelines:
-
Meaning of transportation
-
The importance of transpiration
-
The adaptation of features which enable plants to reduce water loss
12. With the aid of a diagram, describe the structure and function of blood tissue.
13. (a) State the function of the following parts of the brain:
-
Medulla oblongata
-
Hypothalamus
-
Cerebellum
-
Cerebrum
(b) (i) Define the term “drug use”
-
Explain three effects of drug abuse
-
Explain two ways in which drug abuse can be controlled
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
033/1 BIOLOGY
(For School Candidates Only)
Time: 3 Hours Wednesday, 6 th October 2010 a.m.
Instructions
-
This paper consists of sections A, B and C.
-
Answer all questions in sections A and B and one (1) question from section C.
-
Read each question carefully before you start answering it.
-
Except for diagrams that must be drawn in pencil all writings should be in blue/black ink or ball point pen.
-
Calculators are not allowed in the examination room.
-
Cellular phones are not allowed in the examination room.
-
Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
SECTION A (20 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section.
1. For each of the items (i) – (x) choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number.
(i) Which of the following is common to both plants and animals?
- Respiration
- Digestion
- An excretory system
- Chloroplasts
- Starch grains
(ii) A flower which possesses both stamens and carpels is said to be
- Unisexual
- Hermaphrodite
- Monoecious
- Zygomorphic
- Polymorphic
(iii) Useful substances are retained in the kidney by
- Filtration
- Osmosis
- Selective reabsorption
- Osmo-regulation
- Diffusion
(iv) The Monera are also referred to as Prokaryotes. This means having:
- No nucleus
- Membrane bounded organelles
- Simple structures
- Reduced nucleus
- Circular nucleus
(v) Which of the following is a characteristic of wind-pollinated flowers?
- They have large brightly coloured petals
- They produce a small number of pollen grains
- They have small anthers situated inside the flower
- They do not have nectarines
- They have large, sticky or spiky pollen grains
(vi) Food is moved along the oesophagus by a process known as:
- Assimilation
- Chewing
- Egestion
- Peristalsis
- Churning
(vii) Reptiles differ from birds because:
- Reptiles do not lay eggs while birds do
- Reptiles have a backbone while birds do not
- Reptiles have scales while birds do not
- Reptiles are cold blooded while birds are warm blooded
- Reptiles have moist skin while birds have dry skin
(viii) Removal of predators in the ecosystem will result in:
- Decrease in the number of producers
- Increase in the number of producers
- Decrease in the number of prey
- An increase in the number of decomposers
- No significant change
(ix) A bean plant can either bear terminal or axial flowers. When a terminal flowered plant (T) is pollinated with an axial flowered plant (t), the offspring produced were 200 terminal flowered and 210 axial flowered. Which of the following represents the genotypes of the parents?
- TT x Tt
- Tt x Tt
- TT x tt
- Tt x tt
- T x t
(x) What does selective breeding mean?
- Only pure stock should be inbred
- The parents are chosen to produce desired offspring
- The encouragement of out breeding
- The parents are chosen carefully
- The offspring are like parents
2. Match the responses in List B with the phrases in List A by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
3. (a) For each of the following processes, state the site of the process, the raw materials, important products and by-products.
-
Photosynthesis
-
Aerobic respiration
(b) Give reasons why it is healthier tobreath through the nose than through the mouth.
4. (a) Explain what is meant by the following terms:
-
Heterotrophic nutrition
-
Autotrophic nutrition
(b) The diagram below (Figure 1) shows the external structure of a leaf.

-
Name the parts labeled A, B and C.
-
What is the function of the part labeled C.
-
What features of the external structure show that a leaf is adapted for photosynthesis.
5. (a) Some insects are harmful and some are useful to man. Argue for this statement by giving three examples for each.
(b) In what way are earthworms important to farmers?
6. (a) (i) Define the term tropism.
(ii) State the biological importance of hydrotropism and phototropism.
(b) How is accommodation brought about in the human eye?
7. (a) Explain the functions of the following parts of a compound microscope.
-
Stage
-
Eyepiece
(b) Name four (4) human diseases caused by viruses.
8. (a) Maduda on her way to school came across a rattle-snake on the path coming right towards her. In no time she found herself up a tree.
-
What gave her the ability to climb the tree so quickly?
-
Identify the different processes that went on in her body during this incidence.
9. (a) Define the following terms as used in Biology:
-
Ecology
-
Environment
-
Community
-
Ecosystem
(b) (i) State the difference between natural and artificial ecosystems. Give one example for each case.
(ii) Explain why food webs are more representative of feeding relationships than food chains.
10. (a) Explain the following:
-
Acquired characters are not inherited.
-
Ecological pyramids taper towards the apex.
-
Walls of ventricles are thicker than those of auricles.
-
Rate of heart beat increases when one is frightened.
(b) Write down three (3) differences between mitosis and meiosis.
SECTION C (20 Marks)
Answer one (1) question from this section.
11. Genetics is a branch of Biology dealing with heredity. How can this field of Biology be applied to everyday life?
12. The brain is the largest portion of the nervous system and very important for controlling activities in the body. With the aid of a diagram, describe the functions of the different parts of the human brain. Explain why only humans are said to be intelligent.
13. Write an essay on birth control methods which do the following:
-
Suppress the formation and/or release of gametes.
-
Prevent the union of gametes in fertilization.
-
Prevent the implantation of fertilized egg.
VIEW MARKING SCHEME

Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania






