Chapter 01 : Introduction to History
| Introduction History is among important subjects which many nations choose for their young generation to study. The reason for such a choice is that history enables citizens to raise their self-awareness and be aware of the world around them. It enables citizens to study different aspects of their society to understand how it came to be the way it is and how those aspects impact the world. This will help them become responsible for themselves, others and their nation. In this chapter; you will learn about the meaning of history, the importance of studying history, and the relationships between history and other related subjects. You will also learn about the sources of historical information. The competencies developed will enable you to use and value sources of historical information. |
| Think History and sources of historical information |
Meaning of History
History is a study of events and processes that happened in the past, and which might influence the present. These events and processes are about social, political, and economic developments of people and society. Studying history enables us to answer the following questions ,among others:
(a)What events happened in the past?
(b)When did they happen?
(c)Why did they happen?
(d)Who took part in those events?
(e)How did the events happen?
(f)How did they affect people's lives?
In this case, not all events are historical. Therefore, historical events have special qualities.
Qualities of historical events
Historical events have specific qualities that differentiate them from non-historical events. For an event to be termed as historical, it must have unique qualities such as the following
Significance
A historical event must have a significant impact on shaping the course of history in a particular society.Historical events can have a significant impact on politics, education,and economies,such as trade,industries and agriculture.A good example is the Maji Maji War of 1905-1907.
Long-term effects
A historical event possesses long-term effects on the society in which it occurred. Some of the event,are the Berlin Conference of 1884-1885,the Slave Trade,and the independence.These events can influence or shape such a society.
Diyersity
Historical events are diverse and cover a wide range of topics.These topics may include social,political,economic,scientific and military events.
Context
A historical event happens within a specific historical context or place influenced by various factors such as political,social,economic and technological conditions.
Interpretation
Historical events are subject to interpretation by historians. Historians can come up with different perspectives and narratives that can lead to debates and interpretations on the causes, effects and significance of an event.
Educative
Historical events provide essential lessons for future generations. By studying the past, societies learn from both the successes and failures, enabling them to make informed decisions in the present and future. For example, resistance to colonial imposition on Africa had lessons to modern nationalist leaders.
Time
A historical event must have time in which it happened. It is time which specifies one event from another. Indeed, it is time which justifies the occurrence of an event.
Ways of dating historical events
Historians divide time into days,weeks,months,years,decades,generations,centuries, millennia, periods and ages. A decade is a period of ten years. A generation is a period for children to grow into adulthood and have their own children. This period is commonly 30 years. A century is a period of 100 years. A millennium is a period of 1,000 years. Age is a period during which a particular historical phenomenon dominates. It may cover several years, centuries or millennia. Known ages in History include the Stone Age, the Iron Age, the Industrial Age, the Nuclear Age, and the Digital Age. A period is determined by one continuous event lasting for some years. Examples include the period of long-distance trade in East Africa, the period of the trade, and the period of colonial rule in Africa.
Time division in History
A starting point for time division in History has been chosen.The starting time is known as year zero.The period from zero onwards is called the Common Era(CE). Previously,this period was known as Anno Domino(AD),which meant years after the birth of Jesus Christ.The period before year zero is called Before Common Era (BCE),previously known as Before Christ (BC).For example,the ruler of the Roman Empire,Julius Caesar,died in 44BCE.
Dating historical events
There are four main ways of determining dates.These are recalling events,language studies,carbon 14,and Potassium-argon.
Recalling events : In this method,one has to remember important events.Examples of such events are famines,wars,droughts,eclipses of the sun or moon,volcanic eruptions,floods,epidemics,arrival of strangers,age groups,births and deaths.This method is useful in studying societies which did not keep written records.
Language studies: Dates can also be determined by studying languages.For example, foreign names of crops,animals and food have been introduced into Kiswahili.Thus, by determining when those names and words started being used in a particular society, one can tell the origin of those names and words and determine when foreigners came, and the inhabitants began to grow such crops.Other concepts might emerge almost simultaneously,such as karafuu,coffee or cotton plantations.
Carbon-14 dating: This is a scientific method of determining dates.It is used to determine the dates for the remains of plants and animals that died many years ago. Carbon 14 is a carbon element that plants and other living organisms absorb.When living organisms die,carbon 14 starts decreasing from their bodies at a constant rate. In laboratories,scientists measure the amount of carbon 14 that has remained in a particular plant or animal to find out the number of years that have passed since the plant or animal died.
Potassium-argon: Archaeological materials can be dated using another scientific method known as Potassium-argon.This technique dates archaeological remains associated with inorganic materials,particularly volcanic rocks or ash,that were formed millions of years ago.
Ordering historical events
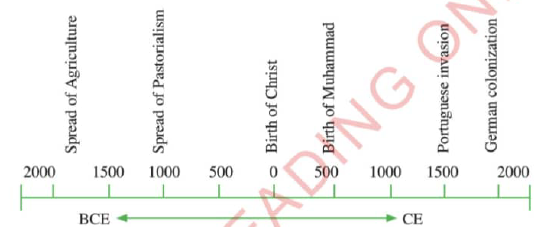
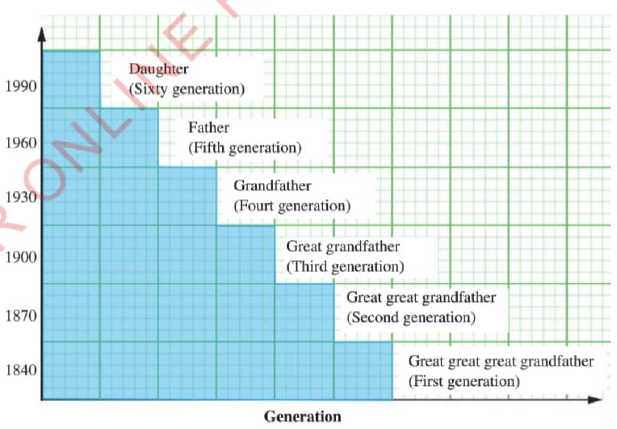
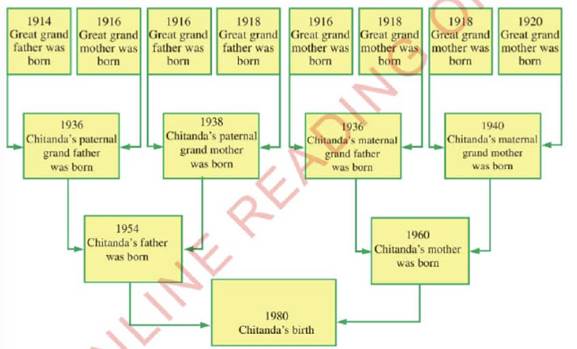
Historians use illustrations such as timelines,time graphs,family trees,and time charts to show how historical events followed each other.Figures 1.1,1.2,1.3 and 1.4 indicate timelines,time graphs,family tree,and time charts,respectively.
|
Figure 1.1:Timeline |
|
Figure 1.2 : Time-graph |
| Period CE | Historical event |
| 1500 | Beginning of Ntemi systems or organisation |
| 1698 | End of Portuguese rule on the East African coast |
| 1741 | Mombasa Arabs established their sheikhdom |
| 1840 | Seyyid Said moved his capital from Muscat to Zanzibar |
|
Figure 1.4 : Family tree |
| Activity1.1 Design a three-generation family tree,to show how the family tree can help you understand your generation. |
Importance of studying History
History is about people's efforts to use and change their environments for their socio- economic and political needs.There is a connection between people's past actions and their present life.In other words,we are what we are today because of past events.
The importance of studying history includes the following:
Understanding our origins
History enables us to understand our societies and their origins.It gives us a sense of belonging to our community.In this way,History influences us to love our country and its people as well as neighbouring countries and their people.Studying History also helps us to know how and why our present societies differ from those of the past. When we study History,we learn how people obtained their livelihoods and dealt with challenges in the past.For example,we learn how people obtained food,protected themselves from enemies,treated the sick and worshipped.Therefore,History helps us to understand how people used their knowledge,skills and experiences to manage their environment.
Promoting tolerance
History is like a raised stage from which we can clearly see people's past lives. It shows us their actions,courage,wisdom,and unity. In this way,we understand the culture and behaviour of other people.We also learn to respect and tolerate the differences among people and societies.We realise that our ethnic groups,beliefs, customs,and traditions may differ from those of others.History teaches us to tolerate those differences.
Learning from past actions
History teaches us that the actions of one person may affect others.For example,our ancestors discovered crop cultivation and animal husbandry.These activities continue to benefit people up to now.Others discovered fire and iron tools,which are also being used today.We also learn that the activities we do today may be helpful or harmful to others in the future.People are always influenced by what others did in the past. History shows that what happens in one society at one time may later positively or negatively affect other societies.
Encouraging the search for evidence
History is based on information collected from different sources.When we get a piece of information,we should ask questions about its source,whether it is trusted, and whether the information might have been distorted.Finally,we should judge and conclude.In this way,we learn that,for every issue,there are various sources of information.We also learn that,for every problem,there may be several causes, effects and solutions.
Appreciating other people's culture
History helps us to know that people develop their culture depending on their environments and contacts.Through such contacts,they come to understand the ways of life of other people.Therefore,by studying History,people learn and appreciate the cultures of other people in the world.
Promoting patriotism
History plays a critical role in promoting patriotism.Patriotism means the love of one's society or nation,and the willingness to defend it.History promotes this love and willingness because it teaches how the past and present generations offered their lives to build the nation and defend it from internal and external enemies.It teaches how anation started and how it changed over time Moreove,History acknowledges men and women who played important roles in building thenation as national heroes and heroines.Through History,learners develop an appreciation of the memory and identity of their nation.History is,therefore,critical in making people know their nation,love it,and be ready to defend or even die for it.It is difficult for people who do not know their nation's history to be proud of or ready to die for it.
| Activity1.2 Study the following illustration,then write a paragraph on the importance of studying History.
|
Exercise 1.1
1.“Studying history wastes time because the subject deals with past events as opposed to contemporary life."Explain.
2.Provide reasons on the argument that the history of our ancestors is our history.
| Activity 1.3 Read different reliable digital and non-digital sources to identify the relationship between history and other subjects. |
Relationship between history and other subjects
History relates to some subjects,including Geography,Mathematics,Biology,and Languages such as Kiswahili,English and Arabic.History also relates to Music and Theatre Arts
History and Geography
History relates to Geography because both deal with the theories concerning the world and human beings.While History deals with the origin of human beings,Geography deals with the origin of the universe,where historical events occur,and human beings study them.Another relationship is that historical events occurred in certain geographical environments that favoured human beings.For example,the remains of human civilisation suggest that civilisations flourished around the environments that supported survival,primarily river valleys and forests.Since then,human beings have occupied such places.
History and Mathematics
History has a close relationship with Mathematics as Mathematics is used for determining the chronology and sequence of historical events.We use graphs,charts and timelines to explain historical events.Mathematics is also used to determine the time in which events happened,the dates,and the arrangement of those events chronologically.In this case,History uses the knowledge of Mathematics to verify the events that happened in the past.
History and Biology
The evolution theory used to study the origin of human beings in History is also used in Biology to study the origin and existence of varieties of species.Therefore,History has close relationship with Biology.This relationship allows further investigation of human existence.
History and Language (Kiswahili,English,A rabic and others)
History helps to study the origin,development and changes that have taken place in human languages over time.History facilitates languages to spread from one place to another,through various actions/events.Spread of languages helps historians to trace regional migration of people and their impacts on new regions.
History and Music
History traces origin,development and influence of music throughout the human existence.Music serves not only as a historical artefact but also as a vehicle for transmitting historical narratives.In this case,music becomes a narrator of the past and a channel through which History finds its meaning and spreads across time.
History and Theatre Arts
History and Theatre Arts are closely related subjects that complement each other.As History offers historical perspectives and narratives,Theatre Arts brings emotional depth,sympathy,and artistic explanations to historical events,enhancing our understanding of the past and its relevance to the present.
Concept of sources of historical information
Historical knowledge is obtained through the examination of sources of historical information.One can obtain historical information from either primary or secondary sources.Primary sources are original materials that provide first-hand information or direct evidence on a particular event.Primary sources are materials created by individuals directly involved in such events.Such materials include memos,diaries, letters,artefacts,photographs,interviews,speeches,autobiographies,and official records.In addition,secondary sources are a product of primary sources.They are created by people who were not directly involved in the original events.Secondary sources analyse,interpret or comment on primary sources.Secondary source materials include books,reviewed articles,dissertations,articles in news papers and academic papers.
There are various sources for obtaining historical information.These include oral sources,historical sites,written records,museums,archives,archaeology,historical linguistics,ethnographic records,and anthropology.However,it is important to remember that none of these sources is self-sufficient.Each of them may be used together with other sources.
Oral sources
These are sources of historical information by word of mouth.There are two types of oral sources,namely oral traditions and oral testimonies.
Oral traditions
These are sources of historical information transmitted from one generation to another by word of mouth. They consist of memorized stories, tales ,riddles,narratives,poems, proverbs,jokes,songs,and prayers.The information given in oral traditions can be presented differently by different people.For example,one Rwandese oral tradition says the Hutu fell from heaven and met the Tutsi on earth.Another tradition holds that the Hutu and Tutsi are brothers.These two oral traditions refer to one event: the origin of the Hutu and Tutsi.They,however,present different views on the same event.In many African societies,there were professionals or official storytellers and poets.They used their skills to explain why and how important events occurred in the past.Oral traditions are still used today in research and writing History.
Oral testimonies
These are narrations of the past provided by people who witnessed the event or the process being examined.They provide information on events or processes within the living memory of the narrators.For example,soldiers who participated in the Tanzania-Uganda War of 1978-1979 can provide valuable testimonies about the war. In general,oral traditions and oral testimonies have one similarity. They are both transmitted orally. The difference between them is that the information provided in oral traditions is about the distant past, while that provided in oral testimonies is about the recent past.
Functions of oral traditions and oral testimonies
Oral traditions and oral testimonies transmit knowledge about cultural beliefs, traditional values, skills and rituals from one generation to another. They provide education on the past to both literate and non-literate people. Oral traditions and oral testimonies also encourage people to appreciate and preserve their culture. Furthermore,they both entertain people during various cultural activities such as weddings, crop harvesting, initiation ceremonies and rituals.
Advantages of oral traditions and testimonies
Oral traditions and oral testimonies provide helpful information on past events and processes, where other sources are unavailable. Oral traditions and oral testimonies can also be obtained from both literate and non-literate people. In addition ,non-literatepeople can access historical information easily.
Furthermore, oral traditions and oral testimonies allow historians to capture the point of view of the local people from whom traditions have been collected Similarly, they express experiences, emotions and feelings about historical events. This is because one can see emotions and feelings of a narrator.
Limitations of oral traditions and oral testimonies
Oral traditions and oral testimonies are not always accurate. Sometimes, informants omit essential information due to memory loss because of age or distance in time. They may also give differing accounts of the same historical events or provide exaggerated information.
Another limitation of oral traditions and oral testimonies is that they can capture events from only a few past generations because traditions only have partial information about the remote past due to memory loss.
These limitations sometimes make oral traditions and oral testimonies unreal.There are two ways of improving the reliability of oral traditions and oral testimonies.The first is to collect several narratives on the same event or historical process.This can help historians discover and avoid distortion in oral information.The second way is to discuss with other people who know such traditions or testimonies.After the discussion,compare their different views.Then,draw your conclusions based on the findings.
Written records
Written records are documents that provide historical information.They include letters, maps,magazines,legal documents,newspapers,reports and minutes of meetings. These records are found in archives,libraries,museums,offices and on the internet. They are also found in individual people's homes as well as in religious institutions such as churches and mosques.Some of the written records are found in the form of books written a long time ago.An example of such books is The Periplus of the Erythrean Sea that was written by a Greek trader in the first century CE.Another example of such books is Ptolemy's Geography written in the second century CE. These books describe the coastal people of East Africa and their trading activities. They also tell us about the beauty of the environments and cultures of people in cities such as Kilwa.
In the history of Africa,we have written documents in Arabic,Portuguese,Spanish, English and French languages,most of which are from the 15 Century CE.These documents tell us about people,geography,culture and interactions of people of different regions in Africa.
Historians read various written records to get information about the past.Some of them contain pictures,tables,maps,and figures.These illustrations add meaning and information about the events being reported.
Functions of written records
Written records provide historical information about past events and processes,such as the Maji Maji War,First World War,Second World War and European colonialism in Africa.They also help to keep historical information for long periods.Similarly, they help historians to write about the past such that it can be read and understood as history.During colonialism,written documents were used to promote achievements of colonialism as new civilisation.
Advantages of written records
Written records have various advantages.The following are some of those advantages:
Written records are easier to obtain and use compared to other sources such as archaeological.It is also easier to identify distortions in them.In addition,written records may last for a long time if well kept.Likewise,they may be reliable sources of information when honestly recorded and written.Furthermore,they can be written and translated into different languages such as Kiswahili,Spanish,Arabic,and English. Therefore,people in different parts of the world can use them to write history.Lastly, written records are usually well organised and logically presented.Therefore,it is easy to find relevant information from them,accordingly,historians can use them to write history
Limitations of written records
Written records have various limitations,including the following:
None of them contains all the detailed information on a given topic.One cannot learn everything from a single written source.Therefore,one must read other sources of information to fill gaps.
Written records are also not always reliable.Some of them may contain wrong or distorted information.They may also promote political,ethnic,religious or personal interests.For this reason,written sources must be used with great caution.In addition, during calamities or disasters,written records can be destroyed or lost.Such calamities can be fire,floods,earthquakes and wars.Therefore,special skills and facilities are required to keep them safe.
Lastly,written records can only be written by literate people.People who are unable to read and write cannot use written records for any purpose.
Exercise 1.2
1.How will you use oral traditions and testimonies to get valid and reliable historical information?
2.Differentiate written sources from oral sources.
Historical sites
These are places where remains of past human activities and cultures are found.
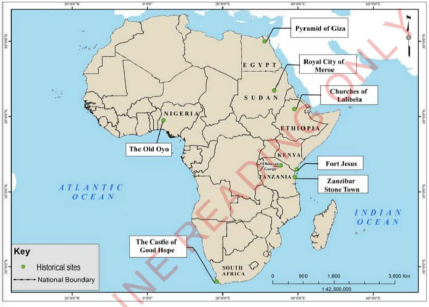
They include remnants of ancient settlements such as buildings,dwelling caves and ruins from which various economic activities,drawings and paintings can be observed. Famous historical sites in Africa include Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania, the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt, the Castte of Good Hope in South Africa, the Royal City of Meroe in Sudan, Churches of Lalibela in Ethiopia, Zanzibar Stone Town, Fort jesus in Mombasa-Kenya and the Old Oyo in Nigeria. Figure 1.5 shows some of these historical sites in Africa.
|
Figure 1.5 shows some of site Africa |
Functions of historical sites
Historical sites provide information on past human activities. They also provide proof of the level of knowledge and skills of people in the past. Such knowledge and skills include rock paintings, architecture, ironwork, irrigation systems, hunting tools and food gathering routes. In addition, historical sites act as places of entertainment for interested people. Furthermore, they are used as sources of income through tourism.
Advantages of historical sites
Historical sites preserve evidence of ancient history as they contain different types of ancient information. For example, they show styles of buildings, utensils, working tools and settlement patterns. Some of the old buildings retain their original functions up to now
Historical sites are also places for preserving ancient objects. These are protected areas with important historical objects. Historians study and interpret the historical objects found at the site and write the history of the people around the site. In Tanzania, these sites are conserved and maintained by trained personnel under the National Museum of Tanzania.
Furthermore, some of the historical sites atract local and foreign tourists. These ourists get ideas about the past by looking at ancient structures.
Likewise, historical sites are important for historical research. Researchers obtain useful information for doing research and writing history. In this regard, they use historical sites to complement information collected from other sources of history.
Limitations of historical sites
Historical sites are likely to be destroyed or damaged. Some of them disappear entirely due to natural and human factors. Natural factors include rainfall, earthquakes, wind, the sun's heat and foods. Human factors include wars, construction of various infrastructure, vandalism, grazing, and farming. In addition, some historical sites are located in remote areas that are difficult and expensive to visit by road and other means of transportation.
Furthermore, historical sites are costly in terms of preservation and management. Professionals or experts should manage these sites.
Museums
Museums are buildings in which historical objects are kept. For example, we find cultural objects related to religious beliefs and ceremonies in museums. We also find collections of animal and plant fossils. Good examples of animal fossils are shells and bones. Moreover, there are political objects such as crowns, regalia, objects used during nationalist struggles and drums which are kept in museums. Economic objects such as coins, minerals, and cowries as well as technological objects such as stone tools, iron tools, canoes, and clothing are also kept in museums. Furthermore, museums keep remains of artwork, such as rock paintings, drawings, sculptures, pottery and basketry. There are two types of objects housed in museums. The first type consists of artefacts, including stone and iron tools. The second type consists of ecofacts, which include human, animal and plant remains. Many countries have national, regional, district and even village museums. For example, in Tanzania, there is the National Museum and House of Culture, the Village Museum in Dar es Salaam, and the House of Wonders in Zanzibar (Beit al-Ajaib). Other museums in Africa include the Genocide Memorial (Kigali, Rwanda), the Robben Island (Soub Africa), the Apartheid Museum (Johannesburg, South Africa), the National Museum of Ethiopia, the Egyptian Museum, and the Ghana National Museum. Figure 1.6 shows some famous museums in Africa.
 |
Functions of museums
Museums keep a wide variety of historical and cultural materials under one roof. These consist of objects rich in information that benefit the present and future generations. Furthermore, national museums keep historical objects from all over the country. They make them available for viewing and learning by the public.
Museums preserve national heritage and historical information.
Similarly, museums provide education to people about different cultures. In addition, they are a source of entertainment. People can visit museums for leisure.
Likewise, museums are used as sources of income through fees paid by tourists. Local and international tourists visit museums to view various cultural objects and learn from the past.
Advantages of museums
Museums are used for preserving the culture of the respective society. In addition, artefacts preserved in museums are not borrowed for whatever purpose, a condition that increases their security.
Museums provide employment opportunities.They employ both professionals and other workers.Professional employees include conservators,curators,and attendants. Another advantage of a museum is entertainment.Most museums entertain peoplewho visit them.
Limitations of museums
Museums are very expensive to construct and maintain.A large space is needed to build a museum.Moreover,trained personnel is needed to run museums.All these are costly.
In addition,some museum objects can be destroyed by fire,moisture,heat,dust, insects,and rats.For example,the pages of an old book may turn yellow and tear easily due to moisture and heat.Therefore,much care is needed in museums to keep the materials in good condition.
Moreover,individual researchers are not allowed to take out the materials kept in a museum for gathering historical information.Instead,they have to visit museums several times for research purposes.This can be costly and time-consuming.
Similarly,some historical remains cannot be preserved in museums due to their nature and size.Such remains include huge commercial ships,ruins of houses,and graves. Furthermore,not every person can afford to visit museums due to cost,distance and restrictions.
| Activity 1.4 Read various reliable online and library sources on historical information to differentiate historical sites from museums. |
Archives
Archives are places where documents and old written records are kept and maintained. These documents come from both public and private institutions.They include missionaries' and travellers' records,reports,photographs,some of the old books, colonial records,post-colonial records and files.
The documents are preserved carefully to be used for a long time.Some of them are available for use by the public,while others are confidential.National,regional, district and village archives are located in various places.The best-known public archives in Tanzania are the Tanzania National Archives located in Dar es Salaam and the Zanzibar Institute of Archives and Records.The zonal centres include the National Records Centre in Dodoma,the Mbeya Records Centre,the Arusha Records Centre,and the Mwanza Records Centre.There are also church archives like the Moravian Church Archives in Rungwe District and the Benedictine Fathers Archives in Peramiho.These archives keep pre-colonial,colonial and post-colonial records. Currently,we can access archival information in two main ways:manual and digital. Manual archives provide written records in hard copy by visiting the respective archives.Digital archives provide written records in soft form by accessing online archives.
It is important to note that one can only access either manual or digital archives after getting an official permit from the respective institution.
Functions of archives
Archives are used to preserve historical information for public use.Some of the archival records are confidential,but they may later be opened for public use. In addition,archives are the most important shelters for historical information.These shelters are specifically designed to reduce the possibility of damage to the materials stored in them from threats such as fire,thieves,pests,and excessive heat and moisture. Likewise,archives provide conducive environment for the retrieval of information from written sources of various kinds.
Advantages of archives
Archives preserve past and recent documents.Documents in the archives contain information from both recent and distant past.Using these documents,one can trace the continuity of the historical facts or processes over time.
In addition,archives consistently organise information that can easily be located or traced by researchers.Furthermore,the materials in archives can be quite detailed, providing in-depth information about people,places,time and events.
Limitations of archives
Documents housed in the archives may be destroyed if not well preserved.In addition, archives are expensive to establish and run.It is costly to set up archives because they involve constructing special buildings.Furthermore,they need special facilities, skilled personnel and trusted people.There may not be sufficient funds to meet the costs of these requirements.
Archives apply strict regulations for users to follow.Thus,it may make it difficult for users to obtain and use the records or documents at their own pace.Moreover, some records are confidential and cannot be available to every researcher.Similarly, researchers cannot immediately access new documents with restricted information. They can be released for use after 30 years,subject to negotiation with the creator of the document Likewise,documents may be lost or misplaced in the archives.In such cases, researchers will not get all the information they need.
| Exercise 1.3 With vivid examples,briefly explain how Tanzanians can benefit from museums. |
Archaeology
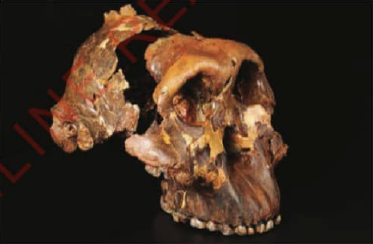
Archaeology is the study of past human activities through material remains.Such remains include pottery,hoes,utensils,bows,arrows,animal bones,seeds,ancient buildings,irrigation canals,and iron-smelting furnaces.These remains are also called archaeological materials.A person who studies archaeology is called an archaeologist.Such people include Dr Louis Leakey and his wife,Dr Mary Leakey.
These archaeologists worked at the Olduvai Gorge in north-eastern Tanzania in Arusha Region.They discovered the oldest human skull in 1959.They named the skull Zinjanthropus boisei.The skull is kept in the National Museum and House of Culture in Dar es Salaam.Figure 1.7 shows the skull of Zinjanthropus boisei.
|
Figure 1.7:The skull of Zinjanthropus boisei |
Another example of an archaeologist is Professor Felix Chami,a Tanzanian scholar who has conducted extensive archaeological studies along the coast of East Africa.
Moreover,archaeological sites are places in which material remains of past human activities are found.In these sites,material remains may be found either above or under the ground,while some are found in caves.
Archaeologists use survey and excavation methods to discover archaeological materials.Using the survey method,archaeologists walk randomly or systematically around the area to find archaeological materials on the earth's surface.Conversely, excavation is used to obtain archaeological materials. Excavation refers to systematic digging and removing of soil layers to obtain material remains. Excavators use special equipment such as trowels, picks, shovels, and hoes. During excavation, archaeologists record all objects or buildings found.
Archaeologists study and interpret the material remains to explain the relationship between them. For example, the discovery of human bones associated with stone tools may help archaeologists explain the culture of the people living in a particular place. These archaeologists can also understand how those material remains were made and used. The information gathered is used to write the history of those who lived there. That is why archaeology is regarded as one of the sources of History.
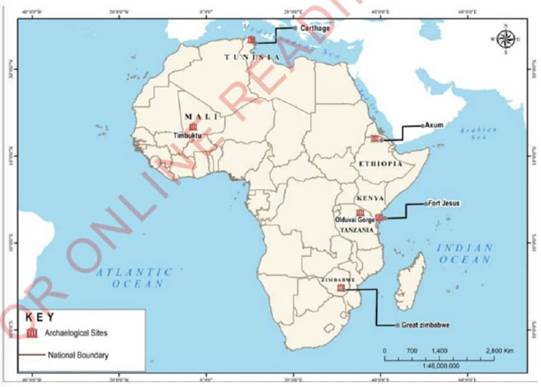
Some of the famous archaeological sites in Africa are Olduvai Gorge(Arusha)-Tanzania, Great Zimbabwe (Zimbabwe), Timbuktu (Mali) and Fort Jesus (Mombasa Kenya), Carthage (Tunisia),andAxum(Ethiopia).Figure 1.8 shows some famous archaeological sites in Africa.
|
Figure 1.8: Some famous archaeological sites in Africa |
Functions of archaeology
Archaeology provides evidence of material remains used by ancient people. Examples of such remains are hoes, axes, arrows, and spears.
It enables archaeologists and historians to reconstruct past events using evidence from actual objects.For example,past settlement patterns can be reconstructed from excavated remains.Furthermore,it provides historical knowledge about the past.
Advantages of archaeology
Archaeology is based on actual material objects.It uses material remains of objects made and used in the past.Therefore,it can describe people's past cultures more reliably than other sources.
In addition,archaeology contributes to History from its scientific methods.Forexample, historians can benefit from the carbon 14 dating technique,which archaeologists use. Therefore,historians cooperate with archaeologists to date historical events and processes.Furthermore,archaeologists excavate some materials and keep them in museums for future generations.Equally significant,archaeological excavation has been instrumental in uncovering new findings or evidence in History.One example is the discovery of human footprint in 2016 at Laetoli Tanzania.
Limitations of archaeology
Some of the material remains cannot be recovered if damaged.Not all cultural remains survive long in the ground.Plants and some bones,when buried,decay quickly.
Therefore,some material remains that could tell about the past cannot be found for study. Archaeological research requires large funding for purchasing excavation equipment, to and from the sites,camping facilities,storage,as well as caring facilities.
The money required to meet these costs may not be available. In addition,archaeological work is a long process that involves surveying,excavating the site to get the remains,and analysing the materials in laboratories.Therefore, archaeological work takes a long time.
Similarly,many archaeological sites are in remote areas.Some sites are found in yery remote areas which cannot be reached easily.Sometimes,it becomes difficult for archaeologists to locate such sites.
Furthermore,shortage of personnel and equipment is another limitation of archaeology. Archaeological excavations require highly trained people.However,such people are not always readily available.
Historical linguistics
Historical linguistics is one of the methods of obtaining historical information by studying languages and their change over time.Through this method,the origin of people can be traced by studying their languages.By so doing,historical linguists and historians discover past human migrations and interactions.They can even tell when contact between specific groups of people occurred.For example,Arabic words such as shukrani, shikamoo, madrasa, karafuu and Alhamis in Kiswahili reveal contacts between Arabs and Swahili people that occurred along the coast of East Africa before colonialism.The most significant period of the contact can be determined by looking at when many Arabic words were introduced into Kiswahili.
Anthropology
Anthropology is a discipline that studies cultural practices and patterns of human societies.In particular,it studies human societies regarding their origin,development, customs,beliefs,and taboos.People who study these items are called anthropologists.
They travel around the world to study and record the cultures of existing societies. Anthropologists use fieldwork method by staying in such societies for relatively long periods.Through a deep examination of the existing societies,anthropologists give various historical information on matters of such societies.This information enables historians to reconstruct the past.
Ethnographic records
Ethnographic information was created by people who stayed in societies other than their own and made intensive observation.Such information include written records and images recorded on tapes and films.Europeans who travelled across the African Continent for various reasons during the pre-colonial and colonial times made most of these records.They recorded information on subjects such as cultural practices and customs observed during their stay on the continent.
| Activity 1.5 Identify any historical event of your interest and suggest various sources of historical information that you can use to study that event.Provide reasons for each source you will use. |
www.learninghubtz.co.tz
Revision exercise 1
1.Write TRUE for a true statement and FALSE for incorrect statement.Rewrite the incorrect statements so that they are TRUE.
(a)The purpose of learning history is to enable Africans to understand how European nations colonised and exploited them. .
(b)Historically significant events have a lasting impact on societies, shaping their values,beliefs and institutions. .
(c)Carbon-14 dating is among the methods for determining the age of historical artifacts.
(d)A timeline is a visual representation of chronological events organised in a linear order. .
(e)A time graph represents various historical data like political,social and economic data. .
2.Explain how History can promote patriotism among citizens.
3.Suppose the East African Community wanted to preserve some historical objects in one of its member state's museums,and you are appointed to advise the community.Prepare a speech about using the museum as a place for preserving historical objects.
4.Match sources of historical information in Column A with their corresponding meaning in Column B
| Column A | Answer | Column B |
| (i)Oral sources |
| |
| (ii)Historical sites | ||
| (iii)Written records | ||
| (iv)Archives | ||
| (v)Museums | ||
| (vi)Archaeology | ||
| (vii)Historical linguistics | ||
| (viii)Anthropology | ||
| (ix)Ethnographic records |
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
WHATSAPP US NOW FOR ANY QUERY
App Ya Learning Hub Tanzania