

FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 213
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 213
THE PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATIVE AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
FORM THREE MID TERM EXAMINANTIONS AUG/SEPT-2024
PHYSICS
PHYSICS FORM THREE
Where necessary use the following constants
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10m/s2
Density of water = 1g/cm3/ 1000kg/m3
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS IN THIS SECTION
SECTION A (16 Marks)
Answer all question in this section
(i) A car is initially at rest on a flat road. The driver applies a force on the accelerator, and the car starts moving forward. Which of the following correctly explains this situation?
- The applied force causes the car to overcome inertia and accelerate.
- The applied force increases the car's weight, causing it to move forward due to gravitational force.
- The applied force interacts with the car's fuel, generating a combustion force that propels the car forward.
- The applied force acts as a magnetic force, enabling the car to move forward through electrostatic interactions.
- The applied force causes the friction between the car and the road to decrease, allowing the car to move forward.
(ii) In a wind turbine, which factor affects the amount of electricity generated the most?
- Wind speed
- Blade length
- Wind direction
- Turbine weight
- Turbine height
(iii) Sam is measuring the temperature of a cup of hot coffee using two different thermometers. The first thermometer has a resolution of 1°C, while the second thermometer has a resolution of 0.1°C. If the temperature of the coffee is 65.6°C, which thermometer will provide a more accurate measurement?
- The first thermometer
- The second thermometer
- Both thermometers will provide equally accurate measurements
- None of the thermometers will provide an accurate measurement
- It is impossible to determine which thermometer is more accurate
(iv) A person sitting on a plastic chair gets up and experiences a small electric shock. What is the most likely cause of this shock?
- Static electricity buildup
- Friction between the chair and the person's clothes
- Transfer of charges between the person and the chair
- Electromagnetic induction due to nearby electrical appliances
- Gravity acting on the person's body
(v) Heat would be lost in the thermos flask if the walls of the glass container were not coated with silver. Which process contributes to this kind of heat loss?
- Radiation
- Conduction
- Convection
- Absorption
- Transmission
(vi) In a light experiment, observing an object through a certain material showed that less light was transmitted and the image was distorted. Which type of material was used
- A translucent material
- An opaque material
- A luminous material
- A transparent material
- A non-luminous material
(vii) A body is said to be in equilibrium if
- It moves with uniform speed
- The net force acting on it is zero
- The upward and downward forces are equal
- Its center of gravity is low positioned
- Its center of gravity is high
(viii) What happens when a liquid changes into gaseous state?
- Some surface molecules absorb latent heat of vaporization and escape
- It gives its own latent heat that can be used to heat up the surrounding
- The potential and kinetic energies of the molecules increase
- The molecules attractive forces to one another increases and their average kinetic energy decreases
- There is no adhesive force between molecules.
(ix) A red tie was viewed by using light from a torch which was blue. The colour that was seen was black. What happened to the blue colour from a torch when it met with red tie?
- Reflection
- Absorption
- Transmission
- Refraction
- Diffraction
(x) Ntanguye was cooking ugali in a good conducting container, but she seems to use iron handle which is covered by plastic at its holding handle to hold a cooking container. Why did she use plastic handle and not iron?
- It is good conductor of heat
- Its particles are closely to each other
- It reflects heat
- It is a poor conductor of heat
- It is a good heat emitter
2. Match the property of the mirror in list A with their corresponding mirrors in list B, by writing the letter of the correct response beside the corresponding item number
| LISTA | LIST B |
| (i) Has wide field of view (ii) Used as shaving mirrors (iii) Forms laterally inverted images (iv) They have spherical shape (v) Are used in periscope (vi) Are used in car head light |
|
SECTION B
3. (a) A car starts from rest and accelerates uniformly for 10 seconds, reaching a final velocity of 30 m/s. It then maintains this velocity for another 5 seconds before coming to a stop. Determine the total distance covered by the car during this time by using equations of uniformly accelerated motion.
(b) A rectangular block of iron has a mass of 2.5 kg and dimensions 10 cm x 5 cm x 3 cm. Determine the density (in kg/m³) and relative density of the iron block.
4. (a) During a scuba diving session, a diver descends into the ocean. As the diver goes deeper, does the pressure on their body increase or decrease? Explain your answer.
(b) In a collision between two objects, object A with a mass of 5 kg and object B with a mass of 3 kg, object A was initially at rest, and object B was moving with an initial velocity of 10 m/s . After the collision, object A gained a velocity of 4 m/s in the opposite direction. Calculate the velocity of object B after the collision.
5. (a) Briefly explain how does the transfer of thermal energy occur in a metal spoon that has been placed in a pot of boiling water?
(b) A 2 kg block of aluminum is initially at a temperature of 20°C. If 20,000 J of thermal energy is added to the block, what will be its final temperature?
6.(a) Explain why does a solid weigh more in air than when immersed in a liquid? (04 marks)
- By using a help of diagram explain what happen to the two parallel straight conductors when current is moving in the same direction and in opposite direction. (04 marks)
- A block of wood of mass 5kg is placed on a rough inclined plane, at 60° to the horizontal. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the wood and the plane is 0.3, determine the acceleration of the wood down the plane. (05 marks)
7. (a) NYAMWERU was at home cultivating. He had two hoes, sharp and blunt hoe. Blunt hoe was not cutting well as how sharp hoe did. Explain to him why sharp hoe cuts well than blunt hoe. (03 marks)
(b) A cube of sides 2cm is completely submerged in water so that the bottom of the cube is at a depth of 10cm. find:
- Difference in pressure between bottom and top of the cube. (3.5 marks)
- Different of force between bottom and top of the cube. (2.5 marks)
8. (a) Form one students from Mzumbe secondary school visited Kilimanjaro Mountain. When climbing the Mountain to high altitude, one of the students got the problem of nose bleeding.
i. Comment on why student got such problem?( 02 marks)
ii. Why astronauts wear space suits?(02 marks)
(b) The acceleration due to gravity on Jupiter is about 2.6 times that on the earth. A spacecraft has a weight of 24500 N on earth.
(i) What is the mass of the spacecraft?(03 marks)
(ii) What would be its weight on Jupiter?(03 marks)
9. (a) Mr. Samwel put the coin on a card placed over the mouth of a bottle. When the card is flicked away with the figure the coin drops neatly into the bottle.
(i) Which law demonstrated by Mr.Samwel?(01 mark)
(ii) State the law identified in (i) above(02 marks)
(b) A screw jack has a screw pitch of 5mm and the effort arm 16 cm
(i) State two forms of energy in which the energy supplied to the screw jack is finally converted to (2 marks).
(ii) Determine the percentage efficiency of this screw jack, if it needs an effort of 30N to lift a load of 750N. (04 marks)
10. (a) Describe how a lens camera operates the same as human eye. Give three points (06 marks)
(b) Briefly explain how conduction of heat can be applied in your daily life(three reasons)(04 marks)
SECTION C
11. (a) An ice forms at the top of ocean and other water bodies during freezing condition but not at the bottom. Identify the name given to this phenomenon and the significance of this phenomenon. Hence draw the graph of density against temperature that leading to the phenomenon. (05 marks)
(b) The specific heat capacity of water is 42003/kg/c what does this statement mean?, If a student of mass 50kg wanted to take a bath mixed 4kg of water at 80°C with 6kg of water at 20°C. What is the final volume and final temperature of the water (4 marks)
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 182
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 182
PRESIDENT’S OFFICE REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
COMPETENCY BASED EXAMS
SECONDARY EXAMINATION SERIES
FORM THREE MID TERM-2 EXAMINATION
031 PHYSICS
TIME : 3HRS AUG,2023
INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper consists of section A, B, and C with a total of eleven (11) questions
- Answer all questions in section A and B and any two (2) questions from section C
- Show clearly your work
- Section A carries fifteen (15)marks, section B sixty (60) marks and section C carries twenty five (25) marks
- All writing should be in blue or black pen except for diagrams that must be drawn in pencil.
- Non-programmable calculator may be used
- Cellular phones and any unauthorized materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Write your examination number on each page of your answer sheet(s)
- Where necessary, use the following constants
- Acceleration due to gravity(g) = 10m/s2
- Density of water = 1g/cm3 or 1000kg/m3
SECTION A (15 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section
- For each of the following items (i-x) choose the correct answer from the among the given alternative and write its letter beside the item number in your answer sheet
i. Which property of a concave mirrors is suitable for a dentist to consider when selecting concave mirrors for repairing dental related activities?
- The one that produce diminished images
- The one with wide field of view
- The one which produce virtual and erect image
- The one which produce larger magnification
- The one in which objects and images are seen clearly
ii. Why is mercury preferred in clinical thermometer as a thermo metric liquid as compared to water and alcohol?
- Its denser than other liquids
- It is opaque and does not need colouring
- It is more sensitive to temperature
- It is active and does not net the glass
- It is poor conductor of heat
iii. When a plastic pen is rubbed against a dry hair, the pen attracts small pieces of paper. This means that
- Hair becomes negatively charged
- Hair becomes positively charged
- Pen loses electrons
- Paper loses electrons
- Hair gains electrons
iv. Which of the following statements is correct when the resistance “R” if a wire is measured using an ammeter, voltmeter and Rheostat?
- The ammeter is in parallel with R
- The voltmeter is in series with R
- A graph of V against I has a gradient equal to R
- A graph of I against V has a gradient equal to R
- The Rheostat is in parallel with R
v. A form three student wishes t check the upper fixed point and the lower fixed point on Celsius scale thermometer. The student has four beakers namely P, Q R and S
P- Contains a mixture of boiling salt solution
Q- Contains a mixture of ice and water
R- Contains a mixture of ice and salt
S- Contains boiling water
Which beaker should a student use to check the fixed points?
- P and R
- P and S
- Q and S
- Q and R
- S and R
vi. Refractive index of glass block cannot be evaluated from the following relation-
- sin i to sin r
- velocity of light in air to velocity of light in glass
- real depth to apparent depth
- Velocity of light in glass to the velocity of light in air
- A and C
vii. A force prevents a body from sliding is called?
- Compression force
- stretching force
- Frictional force
- restoring force
- Repulsion force
viii. A stone is thrown from the top of a building 45m high at a speed of 12m/s. How long does it take to reach the ground?
- 15 sec
- 5 sec
- 3sec
- 8sec
- 2.03sec
ix. Racing cars rarely gets accident despite their high speed because they-
- Have greater momentum
- Have big tyres with big treads
- Have wide base and low centre of gravity
- Have less mass
- Exert greater frictional force
x. “Extension of material is proportional to force applied” where is this statement belongs?
- Dalton atomic theory
- Archimedes principle
- Charles law
- Hook’s law
- Newton’s law
2. Match the items in list A response to list B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the items number in your answer booklet provided
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B (60 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section
3. a)i) A form three students from a certain school was unable to know the rules of locating an image by using converging mirror. List three rules that will help the students to locate an image when an object is placed in front of converging mirror perpendicular to its principal axis.
ii) A concave mirror is used to form an image of a pencil with the same size as a pencil’s objects. By using a well labeled diagram show the position of the image and state its characteristics.
b) A ray of light is travelling from air to water make an angle of incidence of 60o given that the refractive index of water is 4/3, what is the angle of refraction of the ray of light?
4. a)i) What is the turning effect of a force?
ii) How can the moment of a force be increased considerably in practical life? Give two examples.
b) i) Briefly explain why the handle of a door is near to its outside edge?
ii) A uniform meter ruler AB is pivoted at a distance of 80cm from end B. If 20g mass hang at end B. At what distance from end A must 100g mass hang on a meter rule in order to balance the rule horizontally? (Neglect the mass of the rule).
5. a) i) Distinguish between light spectrum and dispersion of light.
ii) Briefly describe how a light ray passes through an equilateral glass prism.
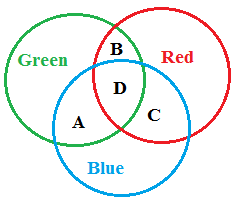
b) Figure below represents three primary colours combined together and answer the questions that follow
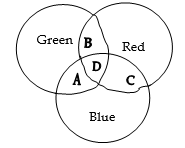
- Identify the colours represented by A, B C and D.
- What general name is given to the colours obtained by mixing two primary colours
- Name the colour produced as a result of mixing three primary colours.
6. a) Suppose you are given a bar magnet whose poles are not located. Briefly explain how you can determine which end of a bar is the North pole in the laboratory.
b) Explain the meaning of magnetic shielding.
c) Draw the following diagram.
- Arrangement of atoms or magnetic domains in a non-magnetic materials.
- Arrangement of atoms or magnetic domains in a magnetic iron bar.
7. a) State the relationship between pressure, force and area.
b) Explain why one feels not comfortable when he/she lift a bucket of water by its handle made of thin metal. What will be the pressure experienced if the handle is made of thicker metal?
c) The mss of the cube is 120kg, if it measures 50cm x30cm x20cm, what is maximum pressure that it can exert?
8. a) A positively charged rod is brought near body A and B if body A is at a distance of 1cm and body B is a distance of 3cm, which of the two bodies will be attracted more?
b) i) What happens when two positively charged bodies brought into contact?
ii) Explain why a pieces of paper attracted by a plastic charged pen after few seconds fell off?
SECTION C (25 MARKS)
Answer any two questions from this section
9. a) A resistor of 4? is connected in series with two bulbs of 3? and 6? connected in parallel. If two cell (battery) of 3V is connected across the circuit.
i) Draw the circuit diagram to show the arrangement.
ii) What is the P.D across the 3? bulb?
b) What is the advantage of parallel arrangement of a bulbs over series arrangement during electric installation at home.
10. a) i) State the law of flotation.
ii) Mention two conditions that can make an object to float.
b)i) Why hydrometer contain a large number below and small number above.
ii) Draw a well labeled diagram of Hydrometer.
c) A body weight 0.8N in air and 0.5N when completely immersed in water. Calculate,
- The relative density of a body.
- The density of a body
11. a) Car A is moving with a velocity of 20m/s while car B is moving with a velocity of 30m/s. Calculate the velocity of car B relative to car A if,
- They are moving in the same direction
- They are moving in the opposite directions
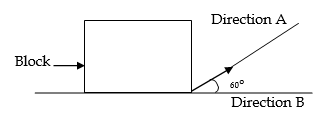
b) i) What is resolution of a force?
ii) Figure below shows a block being pulled along a horizontal surface. If a force of 20N is applied in direction of A at an angle of 60o. What is the resolved part of the force in direction B?
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 146
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 146
THE PRESIDENT’S OFFICE
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATIVE AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
FORM THREE EXAMINATIONS SEPT 2022
NEW NECTA FORMAT
PHYSICS
PHYSICS FORM THREE
Where necessary use the following constants
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10m/s2
Density of water = 1g/cm3/ 1000kg/m3
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS IN THIS SECTION
- (a)For each of the items (i) – (x) choose the correct answer among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number.
- A force F newton’s gives a mass of 2kg an acceleration of 4m/s2. A force of 3F newton will give a mass of 8kg an acceleration in m/s2 of?
- 1
- 3
- 6
- 12
- 24
- A Uniform beam XY is pivoted at one end X and a vertically upward force of 4N at Y keeps the beam horizontal. The weight of the beam in Newton’s is
- 8
- 6
- 4
- 2
- 1
- In the process of charging by induction in static electricity
- A conducter is rubbed with an insulator
- A charge is produced by friction
- Negative and positive charges are separated
- A positive charge induces a positive charge
- Electrons are sprayed into an object.
- In a single rope 4-pulley system, the mechanical advantage is less than 4 because
- The effort may vary
- The load is raised
- The upper pulleys do not move
- Friction acts on the pulleys
- The weight of the pulleys may be neglected
- Which of the following are non-renewable energy sources
- Wave energy
- Biofuels
- Fossil fuels
- Radiant energy
- Geothermal
- An airship is floating stationary high above the ground in this case
- Up thrust = airship weight
- Air temperature inside the ship = Air temperature outside the ship
- Air density outside the ship is greater than air density inside
- Air density outside the ship is less than air density inside the ship
- The air up thrust is greater, than the air weight
- Which of the following describe the particles in a sold at room temperature
- Close together and vibrate
- Close together and moving around at random
- For apart and moving at random
- Close together and stationary
- Far apart and stationary
- The relationship between the local length (f) and radius of conture of a concave mirror (r)is that
- f=2r
- f =r
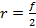
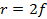
- When two cars A and B are morap in the same direction; the velocity of A relative to B is given by
- VAB=VA – VB
- VAB = VAB – VA
- VAB = VA + VB
- None of the above
- The following work on the principle of total internal reflection except
- Prism Pens copes
- fibre optic cable
- mirage
- mirror pens cope
- Match the items in List A with a response in List B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B (60 MARKS)
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS IN THIS SECTION
- (a)With the aid of a ray diagram, explain why a concave mirror is used as a shaving mirror
(b)A convex mirror of focal length 15cm is used to produce an image an object placed 20cm from the pole of the mirror
Find the position and nature of the image formed
- (a)How is absolute velocity different from Relative velocity
(b)A bird is plying at 80/km/hr. due East relative to the air. A wind is blowing at 30km/hr in the north East direction as seen from the ground. What is the velocity of the bird relative to the observer on the ground?
(c) Identify three ways of reducing friction force acting on a body
- (a)Explain why it is not possible for you to push a car when you are seated inside it
(b)A uniform beam of mass 50kg and length 6m is supported by two vertical strings at A and B such that each pant is 0.5m from each end A mass of 40kg is also hung at m from A. Find the tension in the strings at points A and B
- (a)(i)Draw a well labelled diagram of a hydrometer
(ii) Explain the important of the following on a hydrometer
- Narrow stem
- Wide bulb
(b) A cube of side 10cm and mass 400g floats in water
- What fraction of the cube is under the water
- What is the extra force that must be exerted on the cube such that it is completely submerged in the water
- (a)With a clear diagram show how a prism can be used to produce a spectrum when white light falls on its
(b)A compound microscope has objective lens of focal length 8cm and eyepiece lens of focal length 4cm the distance between the lenses is 28cm. the lens is adjusted such that the final image is at infinity
- Calculate the position of the object from the objective lens
- What is the angular magnification of the lens
- (a)Explain the importance of anomalous expansion of water to marine organision
(b)A wheel and exle has wheel radius of 20cm and axle radius of 5cm. The efficiency of the machine is 90%
- What is the velocity of the machine
- What is the effort required to raise a load of 2000N
SECTION C
ATTEMPT ANY TWO QUESTIONS IN THIS SECTION
- (a)Explain why during the installation of electrical wires that transmit electricity from one place to another the wires are left sagging and not tight
(b)The figure below shows a bimetallic strip having two metals invar and brass. (Brass has a higher linear expansitivity than invar)
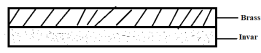
Explain how the bar will bend if it is heated to a higher temperature than room temperature
(c) A telegraph wire has a length of 30m and is made of metal of linear expansitivity 0.00002/K
Find the change in length from a hot day temperature 30°C to a very cold day - 5°C
- (a)What are the laws that govern friction force
(b)Explain why coefficient of Kinetic friction is always smaller than coefficient of state friction
(c)Three forces act on a body as shown below
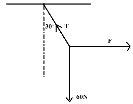
Find the value of T and F
- (a)Explain the appearance of a blue shirt with red spots when viewed through
- Blue light
- Red light
- Green light
(b)Convex mirrors are always used as driving mirrors. With the aid of a diagram explain why these kinds of mirrors are used in this case
(c)What is the maximum magnification produced by a convex lens of local length 5cm.
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 95
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 95
THE PRESIDENT'S OFFICE
MINISTRY OF REGIONAL GOVERNMENT AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
MID TERM EXAMINATION
PHYSICSFORM-3
2021- AUG/SEPT
TIME: 2:30 HRS
Instructions
- This paper consists of sections A, B and C with a total of eleven (11) questions.
- Answer all questions in sections A and B and two (2) questions from section C.
- Cellular phones and any unauthorised materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Non-programmable calculators may be used.
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
- Where necessary the following constants may be used:
- Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s 2
- Density of water = I .0 g/cm3
- Pie= 3.14.
- Coefficient of linear expansivity of the brick 1.2 x 10 -5K -1
- Speed of light in air = 3 x 108 m/s.
- Speed of sound in air = 340 m/s.
SECTION A (15 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
1. For each of the items (i) - (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in the answer booklet provided.
(i) A bar of copper is heated from 293 K to 333 K. Identify a false statement among the following:
- Its density will increase slightly
- Its length will increase slightly
- Its electrical conduction will decrease slightly
- Its mass will not change
- Its weight will remain unchanged.
(ii) Which among the following is not a property of magnetic lines of force due to a bar magnet?
- They have a direction from North Pole to South pole outside the magnet
- They do not exist inside the magnet
- They have a direction from South pole to North pole inside the magnet
- They tend to be close inside the magnet but are wider apart outside the magnet
- They form complete loops.
(iii) When an object moves around a horizontal circle of centre O with a constant speed, its acceleration will be
- zero
- towards the centre
- away from the centre
- along the tangent to the circle
- along the direction of rotation.
(iv) The image formed by plane mirrors are always
- real, magnified and laterally inverted
- virtual, laterally inverted and same in size
- magnified, virtual and erect
- laterally inverted, same in size and real
- erect, real and magnified.
(v) The battery in the circuit shown in the following diagram has an e.m.f. of 2 V and negligible internal resistance.
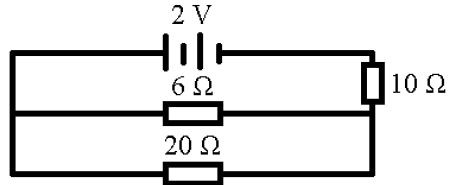
What will be the current flowing in the 6 ? resistor?
- 0.15 A
- 0.64 A
- 1.42 A
- 0.10 A
- 0.33 A
(vi) A body is said to be in equilibrium IF
- it moves with uniform speed
- the net force acting on it is zero
- the upward and downward forces are equal
- its centre of gravity is low positioned
- its centre of gravity is high.
(vii) Tow forces of 5 N and 8 N are acting at the same point and are inclined at an angle of 45° to each other. What will be their resultant force?
- 11.2 N
- 12 N
- 22.4
- 1.2 N
- 1.12 N
(viii) A solid metal cube has each side doubled to make a solid cube of the same metal eight times bigger in volume. The ration of resistivity of the new cube to resistivity of the old cube is
- 8:1
- 6:1
- 1:1
- 1:6
- 1:8
(ix) A green card with red flowers when viewed in a red light will appear:
- completely red
- completely yellow
- completely green
- yellow with red flowers
- green with red flowers.
(x) Colours are produced when white light passes through glass prism because
- light waves interfere
- glass prism colours the light
- in glass different colours travel at different speeds
- different colours are filtered
- diffraction of light occurs.
2. Match the following items.
| List A | List B |
| (i) Ability to oppose flow of current (ii) Path around which electrons can flow (iii) Wire with high potential difference relative to other wires in a cable (iv) Wire dipped into ground near home to protect appliances (v) Work done by moving unit of electricity from one point to another |
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
3. (a) In a light experiment, a narrow beam of light directed onto a glass prism leaves the prism and falls on a white screen. Draw a labelled diagram to show the experimental set-up and observation seen on a screen.
(b) Explain two ways in which lens cameras differ from human eye.
4. (a) Briefly explain why hydrometer
(i) is weighed with lead shots.
(ii) has a narrow stem.
(b) A piece of rubber of volume 100 cm3 and the density of 0.45 g/cm3 floats in water. Calculate:
(i) The volume of rubber that partially immersed in water.
(ii) The force required to immerse the rubber completely.
5. (a) List four factors which affect the rate of evaporation of liquids.
(b) (i) Define relative humidity.
(ii) Calculate the relative humidity given that the reading on dry bulb hydrometer is 24°C and the wet bulb temperature reading is 16°C.
6. (a) (i) What peculiar property does the effort has in all classes of levers?
(ii) A metre rule of weight 1.0 N is supported horizontally on two knife edges each placed 10.0 cm from its ends. If the weight of 1.5 N is placed at its mid-point, calculate the reaction at the supports.
(b) (i) State the law of floatation.
(ii) Find the fraction of the cork that partially immersed when a piece of cork of density 0.25 g/cm3and a mass of 20 g floats in water.
7. (a) Write down the second and third equations of motion in a straight line.
(b) Explain the following terms as they are applied in motion in a straight line:
- Velocity.
- Retardation.
(c)A stone is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of 50 m/s.
(i) Calculate the time that the stone will take to return back to the thrower.
(ii) What will be the maximum height reached?
8. Three resistors of 2 ?, 4 ? and 6 ? are connected in series to a battery of e.m.r 24 V and have negligible internal resistance.
(a) Draw the circuit diagram including the battery, ammeter, switch and the three resistors.
(b) Find the current flowing in the circuit drawn in 8 (a) above.
(c) Find the potential difference at the ends of each resistor in 8 (a).
SECTION C (25 Marks)
Answer two (2) questions from this section
9. (a) A beaker containing ice is heated from -5°C to 0°C and then from 0°C to 15°C. With the aid of a diagram, explain the variation of density with temperature.
(b) A brick at 20°C has a dimension of 30 cm, 18 cm and 10 cm for length, width and height respectively. If a brick is heated to a new temperature of 150°C, calculate the new dimensions.
10.(a) State two conditions for a body to be in equilibrium.
(b) Distinguish between centre of mass and centre of gravity.
(c) A uniform metre rule AB is balanced horizontally on a knife edge placed 5cm from B with a mass of 60g at B. Find the mass of the ruler.
11. (a) Define the word coulomb.
(b) States Ohms law.
(c) Two resistors of 30 and 60 are connected in parallel to a 3V battery.
(i)Draw the schematic diagram.
(ii)Find the effective resistance of the circuit.
(iii)Calculate the current passing through the 60 resistor.
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 62
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 62
THE PRESIDENT'S OFFICE
MINISTRY OF REGIONAL GOVERNMENT AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
AUGUST-SEPTEMBER EXAMINATION SERIES
PHYSICS FORM-3
2020
TIME: 2:30 HRS
Instructions
- This paper consists of sections A, B and C with a total of eleven (11) questions.
- Answer all questions in sections A and B and two (2) questions from section C.
- Cellular phones and any unauthorised materials are not allowed in the examination room.
- Non-programmable calculators may be used.
- Write your Examination Number on every page of your answer booklet(s).
- Where necessary the following constants may be used:
- Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s 2
- Density of water = I .0 g/cm 3
- Pie= 3.14.
- Coefficient of linear expansivity of the brick 1.2 x 10 -5 K -1
- Speed of light in air = 3 x 108 m/s.
- Speed of sound in air = 340 m/s.
SECTION A (15 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
1. For each of the items (i) - (x), choose the correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter beside the item number in the answer booklet provided.
(i) Which pairs of instruments would you use to correctly measure the diameter of a small ball bearing?
- Measuring tape and vernier caliper
- Slide rule and micrometer screw gauge
- Vernier caliper and slide rule
- Micrometer screw gauge and vernier caliper
- Metre rule and micrometer screw gauge
(ii) When the sun shines on the dark-coloured driving wheel of a car, the wheel feels warm. Why?
- It is because the sun warms the car by induction.
- It is because the sun gives energy to the wheel by convection.
- It is because the sun radiates thermal energy to the wheel.
- It is because the sun radiates heat to the glass windows.
- It is because the sun conducts thermal •energy to the wheel.
(iii)Which one is a characteristic of a plane mirror?
- It forms image which is real and opaque.
- It forms an image which is larger than the object.
- It forms an image which is real and laterally inverted
- It forms an image which has the same size as the object.
- It forms an image which is smaller in size than the object.
(iv)What role does the iris play in the human eye?
- To hold the lens in position.
- To prevent internal reflection.
- To control the size of the pupil.
- To control the thickness of the lens.
- To protect the eye from light.
(v) The correct arrangement of metals in ascending order of their linear expansivities is?
- Iron, Copper, Invar, Brass and Nickel
- Nickel, Brass, Invar, Copper and Iron
- Brass, Copper, Nickel, Iron and Invar
- Invar, Iron, Nickel, Copper and Brass.
- Nickel, Brass, Iron, Invar and Copper.
(vi) The suspended magnetic needle always comes to rest with its axis in a vertical plane called?
- Geographic meridian
- Magnetic meridian
- Geographic declination
- Magnetic declination
- Geographic North Pole.
(vii) Which of the following is the correct weight of a body of mass 48 g when placed on the moon surface?
- 0.48 N
- 4.8 N
- 0.80 N
- 0.048 N
- 80.0 N.
(viii) A car moving at steady speed has a frictional force on its surface whose size depends on its
- speed and surface area
- speed
- surface area
- weight
- wheels speed.
(ix) The image formed by plane mirrors are always
- real, magnified and laterally inverted
- virtual, laterally inverted and same in size
- magnified, virtual and erect
- laterally inverted, same in size and real
- erect, real and magnified.
(x)Lenz’s law can be applied to predict the
- magnitude of back e.m.f. in a circuit
- magnitude of induced current in a circuit
- direction of applied e.m.f. across the circuit
- direction of induced e.m.f. in a circuit
- direction of the applied e.m.f. within a circuit.
2. Match the items in List A with responses in List B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number in the answer booklet provided.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
3. (a) Why a bubble of air increases in volume as it rises from the bottom of a pond of water to the surface? Briefly explain.
(b) A half meter rule AB is freely pivoted at 18 cm from end A and balances horizontally when a body of mass 35 g is hung 48 cm from end B. Calculate the mass of the rule.
4. (a) Briefly explain why hydrometer
(i) is weighed with lead shots.
(ii) has a narrow stem.
(b) A piece of rubber of volume 100 cm3 and the density of 0.45 g/cm3 floats in water. Calculate:
(i) The volume of rubber that partially immersed in water.
(ii) The force required to immerse the rubber completely.
5. (a) Give two examples which illustrate the rectilinear propagation of light.
(b) (i) The refractive index of light passing from water to air is 3/4. Calculate the critical angle. (ii) Outline two differences between primary and secondary rainbows.
6. (a) (i) What is the essential of kinetic theory of matter?
(ii) Sketch a graph showing how force applied in a stretched string varies with its extension.
(b) (i) State Hooke’s law.
(ii) List two applications of gamma rays.
7. (a) (i) Define turning effect of force and give its SI unit.
(ii) How the moment of force can be increased considerably in practical life? Give two examples.
(b) (i) List two factors that affect stability of a body
(ii) Briefly explain why the handle of a door is near its outside edge?
8. (a) (i) Distinguish between light spectrum and dispersion of light.
(ii) Briefly describe how a light ray passes through an equilateral glass prism.
(b) Study Figure 1 which represents three primary colours combines together and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the colours represented by the letters A, B, C and D.
- What general name is given to the colours obtained by mixing two primary colours?
- Name the colour produced as a result of mixing three primary colours.
SECTION C (25 Marks)
Answer two ( 2) question from this section.
9. (a) (i) What is meant by the term thermal expansion?
(ii) Mention two applications of thermal expansion of solids.
(b) (i) List three areas where bimetallic strips are used.
(ii) Why a bimetal strip made of brass and invar is curved outside with brass?
(c) Describe how simple fire alarm system operates.
10. (a) (i) Distinguish between primary and secondary cells, giving one example of each.
(ii) Identify two defects of a simple cell.
(b) (i) Explain why lead – acid accumulators are used in car batteries rather than dry cells?
(ii) A cell of unknown e.m.f, E and internal resistance 2? is connected to a 5? resistance. If the terminal p.d, V is 1.0V. Calculate the e.m.f, E of a cell.
(c) (i) List two devices that are important when checking electrical faults in domestic appliances.
(ii) Briefly explain why a very high voltage is necessary when transmitting electrical energy from power station?
11. (a) (i) What is meant by impulse of a force?
(ii) Briefly explain why seat-belts are designed to stretch in a collision.
(b) i) Define momentum.
- The cork of a bottle of mass 4 g is ejected with a velocity of 10 m/s in 0.1 second. Find the force exerted on the bottle.
(c)A car of mass 2000 kg is travelling along a straight road at a constant velocity of 10 m/s developing 3.0 kilowatts. If the engine of the car is switched off:
- Calculate the energy lost by the car in coming to rest
- Briefly explain the energy changes in the process stated in (c) above.
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 30
FORM THREE PHYSICS EXAM SERIES 30
Hub App
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256







