OFFICE OF THE PRESIDENT
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
SECONDARY EXAM SERIES
FORM ONE ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS-2024
PHYSICS
TIME 02:30 HRS NOV, 2024
Instructions
- This paper consists of three section A, B and C with a total of ten (10) questions.
- Answer ALL questions in the space provided.
- All writings must be in BLUE or BLACK ink except diagrams which must be in a pencil.
- Write your full name at the top right hand corner of every page.
- Where necessary you may use the following constants.
- Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s2
- Density of water = 1000 kg/m3
- Atmospheric pressure = 103360 Pa
SECTION A (15 Marks)
Answer ALL questions in this section
- For each of the items (i) to (x) choose the most correct answer from the given alternatives:
- People who study physics are known as
- Physician
 Scientists
Scientists- Physicists
- Philosophers
- Which of the following best describes a variable?
- A trend that shows an exponential relationship.
 Something whose value can change over multiple measurement
Something whose value can change over multiple measurement- A measure of how much a plot line changes along the y-axis
- Something that remains constant over multiple measurements.
- The mass of an object is changed if its
- State is changed
 amount of matter is reduced
amount of matter is reduced- Surface is reduced
- Volume is reduced
- The force acting on a stone falling from the roof of a house is an example of
- Falling force
 magnetic force
magnetic force- Force of gravity
- Electrostatic force.
- A falling object is pulled down by the earth. The earth is pulled up towards the object. Why doesn’t the earth move?
- Because the earth has only gravity.
 Because the earth has a very large mass and a small acceleration.
Because the earth has a very large mass and a small acceleration.- Because the earth has a very small mass and a large acceleration.
- Because air resistance gets in the way.
- The same body is immersed in liquid A and then in liquid B. The extent to which the body sinks in liquid A, What conclusion can be derived from such an observation?
 The density of liquid A is more than the density of liquid B.
The density of liquid A is more than the density of liquid B.- The density of liquid B is more than that of liquid A.
- The density of solid body is less than that of the liquid in both cases
- A student lowers an object in a liquid filled in a container. He finds that there is a maximum apparent loss in weight of the object when;
- It just touches the surface of the liquid.
 It is partially immersed and also touches the sides of the container.
It is partially immersed and also touches the sides of the container.- It is completely immersed in the liquid.
- It is partially immersed in the liquid.
- The sea water is denser than fresh water due to;
- Mixing of sand.
- Stagnation
 Mixing of salt
Mixing of salt- Evaporation.
 Pressure can be defined as;
Pressure can be defined as;
- The spread out of a force over the length.
- The concentration of a force on a surface area.
- The spread out of area.
- The product of a force and area.
- One Pascal is the pressure generated by;
- Force of 1 N on 1 m2
 Force of 1 kg on 1 m2
Force of 1 kg on 1 m2- Force of 1 N on 1000 cm2
- Force of 1 N on 1 cm2
- Match the item in column A with its corresponding item in column B. Then, write the letter of the correct response in the provided space.
| Column A | Column B |
|
|
| Column A | (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) | (v) |
| Column B |
|
|
|
|
|
SECTION B (70 Marks)
Answer ALL questions in this section
- (a) Some of the transport vessels that relay on the physics laws are
- _____________________________________________________________
- _____________________________________________________________
- _____________________________________________________________
- _____________________________________________________________
(b) Write any two applications of physics in each of the following areas
- Hospital;______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
- At home; _____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
- Entertainment;_________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
- (a) What are the warning signs?
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) Why it is necessary to wear gloves when giving First Aid to a bleeding person?
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(c) Outline three features of a good laboratory.
- ________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
- ____________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
- ____________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
- (a) The jaws of a Vernier caliper touch the inner wall of beaker without pressure.
The position of zero of Vernier scale on the main scale reads 3.4 cm. The 6th of
Vernier scale division coincides with the main scale division. Vernier constant
of caliper is 0.01 cm. Find actual internal diameter of beaker, when it is
observed that the Vernier scale has a zero error of -0.03 cm.
______________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) A rectangular block measures height 1.00 cm, width 2.50 cm and length
4.00 cm.
- What instrument was used to measure the sides of the rectangular block?
_____________________________________________________________
- Calculate the volume of the rectangular block.
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- (a) From the figures below identify the forces that are acting.


__________________________________________________________________
(b) If an object weighs 200 N on the earth. What would be its mass on the moon?
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- (a) If the volume of an object is increased while its mass is held constant, what
happens to its density?
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) The diameter of a solid metal sphere is measured using a micrometer screw gauge. Figure below shows an enlarged shaft of the micrometer screw gauge when taking measurement.

If the mass of the sphere is 0.45 g. What is the density of the metal used to make the sphere?
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- (a) A ship has a mass of 1000 tonnes and floats in seawater of density
1023.6 kg/m3. Calculate the amount of water displaced.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) Draw a well labelled diagram of a device used to determine relative density of
liquids.
- (a) Explain conditions for a body to float.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) Explain any two real life applications of law of floatation.
- ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
SECTION C (15 Marks)
- (a) Explain why buildings are constructed with wide foundations.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) Calculate the pressure exerted on a diver at a depth of 20 m below the surface
of water in a sea. Atmospheric pressure = 1.03 x 105 Pa,
density of water = 1000 kg/m3 g = 10 m/s2.
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(c ) A hydraulic press has pistons with areas of 0.02 m2 and 0.1 m2 , a car weighing
5000 N sits on platform mounted on the larger piston.
- How much force must be applied to small piston to lift the car? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- How far must smaller piston be pushed downward to raise the car 0.3 m2?
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 1 of 9
LEARNINGHUBTZ.CO.TZFORM ONE PHYSICS MODAL SERIES 26
OFFICE OF THE PRESIDENT
REGIONAL ADMINISTRATION AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT
SECONDARY EXAM SERIES
FORM ONE ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS-2024
PHYSICS
TIME 02:30 HRS NOV, 2024
Instructions
- This paper consists of three section A, B and C with a total of ten (10) questions.
- Answer ALL questions in the space provided.
- All writings must be in BLUE or BLACK ink except diagrams which must be in a pencil.
- Write your full name at the top right hand corner of every page.
- Where necessary you may use the following constants.
- Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s2
- Density of water = 1000 kg/m3
- Atmospheric pressure = 103360 Pa
SECTION A (15 Marks)
Answer ALL questions in this section
- For each of the items (i) to (x) choose the most correct answer from the given alternatives:
- People who study physics are known as
- Physician
- Scientists
- Physicists
- Philosophers
- Which of the following best describes a variable?
- A trend that shows an exponential relationship.
Something whose value can change over multiple measurement - A measure of how much a plot line changes along the y-axis
- Something that remains constant over multiple measurements.
- The mass of an object is changed if its
- State is changed
- amount of matter is reduced
- Surface is reduced
- Volume is reduced
- The force acting on a stone falling from the roof of a house is an example of
- Falling force
- magnetic force
- Force of gravity
- Electrostatic force.
- A falling object is pulled down by the earth. The earth is pulled up towards the object. Why doesn’t the earth move?
- Because the earth has only gravity.
Because the earth has a very large mass and a small acceleration. - Because the earth has a very small mass and a large acceleration.
- Because air resistance gets in the way.
- The same body is immersed in liquid A and then in liquid B. The extent to which the body sinks in liquid A, What conclusion can be derived from such an observation?
- The density of liquid A is more than the density of liquid B.
- The density of liquid B is more than that of liquid A.
- The density of solid body is less than that of the liquid in both cases
- A student lowers an object in a liquid filled in a container. He finds that there is a maximum apparent loss in weight of the object when;
- It just touches the surface of the liquid.
- It is partially immersed and also touches the sides of the container.
- It is completely immersed in the liquid.
- It is partially immersed in the liquid.
- The sea water is denser than fresh water due to;
- Mixing of sand.
- Stagnation
-
Mixing of salt - Evaporation.
- Pressure can be defined as;
- The spread out of a force over the length.
- The concentration of a force on a surface area.
- The spread out of area.
- The product of a force and area.
- One Pascal is the pressure generated by;
- Force of 1 N on 1 m2
- Force of 1 kg on 1 m2
- Force of 1 N on 1000 cm2
- Force of 1 N on 1 cm2
- Match the item in column A with its corresponding item in column B. Then, write the letter of the correct response in the provided space.
| Column A | Column B |
|
|
| Column A | (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) | (v) |
| Column B |
|
|
|
|
|
SECTION B (70 Marks)
Answer ALL questions in this section
- (a) Some of the transport vessels that relay on the physics laws are
- _____________________________________________________________
- _____________________________________________________________
- _____________________________________________________________
- _____________________________________________________________
(b) Write any two applications of physics in each of the following areas
- Hospital;______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
- At home; _____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
- Entertainment;_________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
- (a) What are the warning signs?
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) Why it is necessary to wear gloves when giving First Aid to a bleeding person?
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(c) Outline three features of a good laboratory.
- ________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
- ____________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
- ____________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
- (a) The jaws of a Vernier caliper touch the inner wall of beaker without pressure.
The position of zero of Vernier scale on the main scale reads 3.4 cm. The 6th of
Vernier scale division coincides with the main scale division. Vernier constant
of caliper is 0.01 cm. Find actual internal diameter of beaker, when it is
observed that the Vernier scale has a zero error of -0.03 cm.
______________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) A rectangular block measures height 1.00 cm, width 2.50 cm and length
4.00 cm.
- What instrument was used to measure the sides of the rectangular block?
_____________________________________________________________
- Calculate the volume of the rectangular block.
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- (a) From the figures below identify the forces that are acting.


__________________________________________________________________
(b) If an object weighs 200 N on the earth. What would be its mass on the moon?
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- (a) If the volume of an object is increased while its mass is held constant, what
happens to its density?
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) The diameter of a solid metal sphere is measured using a micrometer screw gauge. Figure below shows an enlarged shaft of the micrometer screw gauge when taking measurement.

If the mass of the sphere is 0.45 g. What is the density of the metal used to make the sphere?
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- (a) A ship has a mass of 1000 tonnes and floats in seawater of density
1023.6 kg/m3. Calculate the amount of water displaced.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) Draw a well labelled diagram of a device used to determine relative density of
liquids.
- (a) Explain conditions for a body to float.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) Explain any two real life applications of law of floatation.
- ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
SECTION C (15 Marks)
- (a) Explain why buildings are constructed with wide foundations.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) Calculate the pressure exerted on a diver at a depth of 20 m below the surface
of water in a sea. Atmospheric pressure = 1.03 x 105 Pa,
density of water = 1000 kg/m3 g = 10 m/s2.
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(c ) A hydraulic press has pistons with areas of 0.02 m2 and 0.1 m2 , a car weighing
5000 N sits on platform mounted on the larger piston.
- How much force must be applied to small piston to lift the car? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- How far must smaller piston be pushed downward to raise the car 0.3 m2?
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 1 of 9
LEARNINGHUBTZ.CO.TZFORM ONE PHYSICS MODAL SERIES 24
LEARNING HUB TANZANIA
PHYSICS EXAMINATION FORM ONE
ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS.
NAME ..CLASS .TIME: 2:30HRS
INSTRUCTIONS:-
INSTRUCTIONS
- Answer all questions in section A and B and TWO questions in section C.
- (i) A body of mass 50 kg has a weight of;
- 50 N B. 500N C. 0.5N D. 1000
(ii) A piece of silver has a volume of 300cm3 and density of 10.5g/cm3. Calculate its
mass;
- 315g B. 500N C. 0.5N D. 1000N
(iii) Two types of Mechanical Energy are;
- Electricity and magnetism
- Nuclear and potential energy
- Potential and kinetic energy
- Nuclear and solar energy
(iv) The ratio of density of substance to the density of water is;
- Relative density
- pressure
- Acceleration
- Mass
(v) Which of the following is not a form of energy?
- Weight B. Light C. Sound D. Magnetism
(vi) The normal human body temperature is 98.6°F.
- 37°C B. 42°C C. 30°C D. 27°C
(vii) The law of floatation states that;
- The mass of a floating body is equal to that weight of the fluid displaced
- A floating body displaces a fluid of its own volume
- Its weight is equal to its volume
- The weight of a floating body is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced
(viii) The Atmospheric pressure at sea level is 76cm Hg or about;
- 100 Pa B. 100,000Pa C. 1000Pa D. 5000Pa
(ix) The pressure due to a water column of depth 20m, of density 100kg/m3 is;
- 200kPa B. 200Pa C. 2000Pa D. 20Pa
(x) The atmospheric pressure at Mount Kilimanjaro is;
- Higher than the atmospheric pressure at Dar es salaam
- Less than the atmospheric pressure at Dar es salaam
- Less or equal to the atmosphere pressure at Dar es salaam
- Equal to the atmospheric pressure at Dar es salaam
- Match each item in List A with the correct responses in List B by writing its letter below the number of the corresponding item.
| LIST A | LIST B |
| (i) pascals principle (laws) (ii) Pressure in liquids (iii) Measure relative density of liquid. (iv) A spring balance (v) Force pump, suction pump lift pump bicycle pump, syringe. |
|
| i | ii | iii | iv | v | vi | vii | viii | ix | x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SECTION B:60 marks
- Fill in the gaps provided of the;
(i) .. is the weight of a body when it is immersed in a fluid.
(ii) is the descent or decline of an object to the lower levels in a liquid.
(iii) Submarines, hot air balloons, ships hydrometers are the applications of the Archimedes principle and law of ..
(iv) When a body is immersed in a fluid the upwards push that the fluid exerts on the body .. or buoyance.
(v) Mathematically force can be defines as . times
(vi) The two types of barometers are .. and .
(vii) Nails, sports shoes, razor blades, knives, high healed shoes and a bucket with thin handle have a small contact area causing pressure.
(viii) Pressure below the surface of Lake Victoria increases with ..
(ix) Matter is anything
(x) Relative density of a substance is the ratio density (10 marks)
- (a) Define work
(b) Calculate the work done by a force of 50N acting on a body through a distance (displacement) of 10 m. (10 marks)
- (a) Define the term density
(b) A piece of silver metal has a mass 4kg and a density of 10.5g/cm3. Find its volume;
(10 marks)
- (a) Define the terms;
(i) Mass ..
(ii) Weight .
(b) Calculate the weight of an Astronout whose mass is 60 kg on the surface of the moon
if the gravitational acceleration of the moon g = 2m/sec2. (10 marks)
- (a) Define the terms;
(i) Power
(ii) Energy and state their SI units .
(iii) An electric heater used 450,000J of energy in 5 minutes. Calculate its power;
(10 marks)
- The Pascals principle (or law) states that if pressure is applied at any point in an enclosed fluid it is transmitted equally in all directions. In a hydraulic press, the small piston has an area of 200m2 and the large piston has an area of 4000m2. The force applied on the small piston is 100N.
Calculate;
(i) The force at the large piston
(ii) The pressure at both pistons (10 marks)
SECTION C 25 marks
9. (a) What is a force?
(b) Mention and shortly describe the 5 types of force.
(c) Write the SI of unit of Force?
(d) What is the weight of the body of the moon whose mass is 20kg?
10. (a) State the Archimedes principle.
(b) What is the apparent weight?
(c) What is apparent loss?
(d) What is the weight in air?
(e) State the low of floatation.
11. (a) When a body of density 0.5kg/m3 is immersed in water, it displaces the volume of 0.2m3.
Find the apparent loss in weight if the weight of a body inside the water is measured 0.8N.
(b) What is Upthrust?
(c) (i) Differentiate between weight in air and upthrust.
(ii) Compare between weight in air and upthrust.
LEARNINGHUBTZ.CO.TZ Page 1
LEARNINGHUBTZ.CO.TZFORM ONE PHYSICS MODAL SERIES 14
LEARNING HUB TANZANIA
PHYSICS EXAMINATION FORM ONE
ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS.
NAME………………………………………..CLASS……………………………………………….TIME: 2:30HRS
INSTRUCTIONS:-
INSTRUCTIONS
- Answer all questions in section A and B and TWO questions in section C.
- (i) A body of mass 50 kg has a weight of;
- 50 N B. 500N C. 0.5N D. 1000
(ii) A piece of silver has a volume of 300cm3 and density of 10.5g/cm3. Calculate its
mass;
- 315g B. 500N C. 0.5N D. 1000N
(iii) Two types of Mechanical Energy are;
- Electricity and magnetism
- Nuclear and potential energy
- Potential and kinetic energy
- Nuclear and solar energy
(iv) The ratio of density of substance to the density of water is;
- Relative density
- pressure
- Acceleration
- Mass
(v) Which of the following is not a form of energy?
- Weight B. Light C. Sound D. Magnetism
(vi) The normal human body temperature is 98.6°F.
- 37°C B. 42°C C. 30°C D. 27°C
(vii) The law of floatation states that;
- The mass of a floating body is equal to that weight of the fluid displaced
- A floating body displaces a fluid of its own volume
- Its weight is equal to its volume
- The weight of a floating body is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced
(viii) The Atmospheric pressure at sea level is 76cm Hg or about;
- 100 Pa B. 100,000Pa C. 1000Pa D. 5000Pa
(ix) The pressure due to a water column of depth 20m, of density 100kg/m3 is;
- 200kPa B. 200Pa C. 2000Pa D. 20Pa
(x) The atmospheric pressure at Mount Kilimanjaro is;
- Higher than the atmospheric pressure at Dar es salaam
- Less than the atmospheric pressure at Dar es salaam
- Less or equal to the atmosphere pressure at Dar es salaam
- Equal to the atmospheric pressure at Dar es salaam
- Match each item in List A with the correct responses in List B by writing its letter below the number of the corresponding item.
| LIST A | LIST B |
| (i) pascals principle (laws) (ii) Pressure in liquids (iii) Measure relative density of liquid. (iv) A spring balance (v) Force pump, suction pump lift pump bicycle pump, syringe. |
|
| i | ii | iii | iv | v | vi | vii | viii | ix | x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SECTION B:60 marks
- Fill in the gaps provided of the;
(i) ………………………….. is the weight of a body when it is immersed in a fluid.
(ii) …………………………… is the descent or decline of an object to the lower levels in a liquid.
(iii) Submarines, hot air balloons, ships hydrometers are the applications of the Archimedes principle and law of ………………………..
(iv) When a body is immersed in a fluid the upwards push that the fluid exerts on the body ………………………….. or buoyance.
(v) Mathematically force can be defines as …………………. times …………………
(vi) The two types of barometers are …………………….. and ……………………….
(vii) Nails, sports shoes, razor blades, knives, high healed shoes and a bucket with thin handle have a small contact area causing …………………… pressure.
(viii) Pressure below the surface of Lake Victoria increases with ………………………..
(ix) Matter is anything ………………………………………………………………
(x) Relative density of a substance is the ratio density ………………………………(10 marks)
- (a) Define work ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) Calculate the work done by a force of 50N acting on a body through a distance (displacement) of 10 m. (10 marks)
- (a) Define the term density ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) A piece of silver metal has a mass 4kg and a density of 10.5g/cm3. Find its volume;
(10 marks)
- (a) Define the terms;
(i) Mass ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) Weight …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) Calculate the weight of an Astronout whose mass is 60 kg on the surface of the moon
if the gravitational acceleration of the moon g = 2m/sec2. (10 marks)
- (a) Define the terms;
(i) Power ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) Energy and state their SI units ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iii) An electric heater used 450,000J of energy in 5 minutes. Calculate its power;
(10 marks)
- The Pascal’s principle (or law) states that if pressure is applied at any point in an enclosed fluid it is transmitted equally in all directions. In a hydraulic press, the small piston has an area of 200m2 and the large piston has an area of 4000m2. The force applied on the small piston is 100N.
Calculate;
(i) The force at the large piston
(ii) The pressure at both pistons (10 marks)
SECTION C 25 marks
9. (a) What is a force?
(b) Mention and shortly describe the 5 types of force.
(c) Write the SI of unit of Force?
(d) What is the weight of the body of the moon whose mass is 20kg?
10. (a) State the Archimedes’ principle.
(b) What is the apparent weight?
(c) What is apparent loss?
(d) What is the weight in air?
(e) State the low of floatation.
11. (a) When a body of density 0.5kg/m3 is immersed in water, it displaces the volume of 0.2m3.
Find the apparent loss in weight if the weight of a body inside the water is measured 0.8N.
(b) What is Upthrust?
(c) (i) Differentiate between weight in air and upthrust.
(ii) Compare between weight in air and upthrust.
LEARNINGHUBTZ.CO.TZ Page 1
LEARNINGHUBTZ.CO.TZFORM ONE PHYSICS MODAL SERIES 13
LEARNING HUB TANZANIA
PHYSICS EXAMINATION FORM ONE
ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS.
NAME………………………………………..CLASS……………………………………………….TIME: 2:30HRS
INSTRUCTIONS:-
- This paper consists of sections A, B and C
- Answer all questions
- All answers must be clearly, neatly and systematically written
- The following constants may be used: Acceleration due to gravity g = 10m/s2, or 10N/Kg
SECTION A.
- Choose the most correct answer from among the given alternatives and write its letter against the item number in the space provided.
(i) Pressure in liquids depends on
- Area and density
- Volume and density
- Depth and density [ ]
- Mass and depth
(ii) An image that is formed in a plane mirror is always
- Smaller than the object
- Larger than the object
- The same size as the object [ ]
- Real image
(iii) A stone of mass 500g is lifted through a height of 2meter, the potential energy gained by the stone is ……….. (use g = 10N/kg)
- 1000J
- 40J
- 70J [ ]
- 10J
(iv) A force of 25N is used to move an object through a distance of 1.5m in one minute. The power dissipated by force is
- 37.5W
- 0.625W
- 37.5J [ ]
- 0.625J
(v) A body of mass 150kg moving with a velocity of 2m/sec. possesses kinetic energy equal to
- 150J
- 300J
- 450J [ ]
- 600J
(vi) Liquid A has a density of 1.03g/cm3 and liquid B has a density of 0.97g/cm3 a hydrometer sinks
- More in B than in A
- More in A than in B
- Equally in both liquids A and B [ ]
- None of the above
(vii) The pressure or air inside a car tyre increases if the car stands for sometime in full sunlight. According to kinetic theory this is due to an increase inside the tyre of
- The size of air molecules
- The number of air molecules
- The speed of air molecules [ ]
- the average distance between the air molecules
(viii) A stone of mass 5kg is pulled to a height of 2cm above the ground. The work done against the pull of gravity is
- 10J
- 100J
- 1000J [ ]
- 10000J
(ix) A relative density bottle has a mass of 18.50g when empty 54.50g when filled with water and 38.30g when filled with a second liquid. The density of second liquid is
- 1.8g/cm3
- 0.18g/cm3
- 0.055g/cm3 [ ]
- 0.56g/cm3
(x) According to the scientific definition of work, pushing on rock accomplishes no work unless there is
- A net force
- An opposing force [ ]
- Movement in the same direction as the direction of force
- Movement
(xi) The force of friction between layers of a liquid is called
- Surface tension
- Strain
- Viscosity
- Electricity
(xii) Which of the following devices work by the help of atmospheric pressure
- Bicycle pumps and hydraulic press
- Lift pumps and hydrometers
- Flushing tanks and syringes [ ]
- Lactometers and thermometers
(xiii) The density of a block with dimensions 0.24m x 0.08m x 0.20m and a mass of 2.4kg is
- 1.6 x 10-3 kg/m3
- 6.25 x 102 kg/m3
- 2.4 kg/m3 [ ]
- 0.500 x 103 kg/m3
(xiv) Which of the alternatives below comprises only of elastic type of force?
- Tension force, adhesive force, repulsive force
- Attractive force, repulsive force, buoyancy
- Cohesive force, adhesive force, surface tension [ ]
- Tensional force, Compressional force, shear force
(xv) Fluid particles are said to be in a random vigorous motion which has a lot of collisions this motion is referred to as
- Brownian motion
- Diffusion
- Capillarity [ ]
- Osmosis
(xvi) The ability of a material to be deformed under a stress and regain its original shape when the stress is over is
- Capillarity
- Surface tension
- Meniscus [ ]
- Elasticity
(xvii) What name refers to the movement of water molecules from their region of high concentration through a semi permiable membrane?
- Brownian motion
- Diffusion
- Capillarity [ ]
- Osmosis
(xviii) Which of the following units is commonly used in a manometer?
- Newton per square meter
- Millibars
- Atmospheres [ ]
- Millimeters of mercury
(xix) The difference between pressure in solids and liquids in that
- Pressure in solids is constant while that in liquids change with area of constant
- Pressure in solids is dependent on the area of constant while liquid pressure is independent of the area of constant [ ]
- Solid pressure change with height while liquid pressure is independent of height
- Liquid pressure is independent on height while solid pressure depends on both height and area of constant.
(xx) What is your understanding of the term “hypothesis”?
- The problem to be researched on
- A researchers intelligent guess
- An opinion [ ]
- An ideal
- Match the items in list A with the response in list B by writing the letter of the correct response beside the item number in the table provided below
List A.
(i) Temperature
(ii) Beam balance
(iii) Micrometer screw gauge
(iv) Kgm/sec2
(v) Chemical energy
(vi) Plastic deformation
(vii) Blotting paper
(viii) Hooke’s law
(ix) Surface tension
(x) Law of flotation
List B.
- Beyond elastic limit
- Unit of force
- Capillarity action
- Form of potential energy
- An instrument used for measuring length to the accuracy of 0.001cm
- Extension of a spring is proportional to the applied force
- A floating body displaces its own weight of fluid
- Measures mass
- Measures temperature
- Degree of coldness or hotness of a body
- The force that cause the surface of liquid to behave as an elastic sheet
- The force that caused depression or attraction
- An instrument used for measuring length to the accuracy of 0.01cm
| i | ii | iii | iv | v | vi | vii | viii | ix | x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SECTION B.
Answer question 3 – 7 by filling the correct answers in the space provide
- (a) When taking any measurement there may be some error in the reading. Mention three common examples of errors
(i) ___________________________________
(ii) ___________________________________
(iii) ___________________________________
(b) Explain the following observations:
(i) A nail made of iron sinks into water while a ship made of iron and steel floats
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(ii) an object’s weight on earth is greater than the object’s weight on the moon _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- (a) Define the terms below and give examples
(i) Physical quantity ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(ii) Fundamental quantity ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(iii) Derived quantity ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) (i) A form one boy has a weight of 500N on a spring balance. What is his mass on a
beam balance? (take g = 10N/kg)
(ii) Explain why the weight of an astronaut of mass 65kg is 650N on earth but it change to 130N on the moon while the mass remains at 65kg __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- (a) State
(i) The Archimedes principle ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(ii) The law of flotation ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) Define:
(i) surface tension ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(ii) Diffusion ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(iii) Cohesion ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- (a) (i) Define the mass of a body and state its SI unit ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(ii) Define density of a substance and state its SI unit __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(i) Find the mass of 100cm3 of wood with the density of 0.9g/cm3 ______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) (i) density of mercury is 13.6g/cm3 find the volume of 408g of mercury __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(ii) distinguish between density and relative density and state SI unit of relative density __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- (a) (i) What is meant by saying that one liquid is more viscous than other liquid? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(ii) what is meant by the viscosity of liquid? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) (i) Pressure is defined as ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(ii) Proof that pressure P = hdg ________________________________________________________________________
(iii) a car of mass 1000kg is travelling at a velocity of 15m/sec. what is its kinetic energy? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
SECTION C.
Answer all questions from this section
- (a) Define
(i) Force
(ii) Energy
(iii) Work
(iv) Power
(b) A lorry has a mass of 1000kg moving at a velocity of 20m/sec. knocks a wall.
Calculate the energy transferred to the wall
(c) A body of mass 42 lifts his body up a distance of 25cm in 2sec. what is his bicepts
power? (g = 10N/kg)
- (a) (i) Name devices that are used for measuring pressure
(ii) State Pascal’s principles
(iii) The pistons of a hydraulic press have their areas given as 3.0 x 10-4m2 and 2.0 x 10-2m2 respectively. If the smaller piston pushed down with a force of 120N. What is the force required to push the larger piston?
(b) A rectangular tank measures 5m by 3m at its base. It contains water to a height of 3m. Calculate the pressure on the base of the tank given that the density of water is 1000kg/m3 and g = 10N/kg.
LEARNINGHUBTZ.CO.TZ Page 1
LEARNINGHUBTZ.CO.TZFORM ONE PHYSICS MODAL SERIES 6
LEARNING HUB TANZANIA
PHYSICS EXAMINATION FORM ONE
MODEL EXAMINATIONS.
NAME………………………………………..CLASS……………………………………….TIME: 2:30HRS
INSTRUCTIONS
- Whenever necessary use the following constants;
(i) Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10m/s2
(ii) Density of water = 1g/cm or 1000kg/m3
- All answers must be written in the answer sheets provided. NOT IN THE QUESTIONS PAPER.
SECTION A:
- For each of the items (i) – (x), choose the correct answer among the given alternatives and write its letter;
(i) The study of matter in relation to energy is called;
- Chemistry
- Physicits
- Biology
- Physics
(ii) The force which cause tear and wear between machine parts is known as;
- Friction
- Tensional
- Repulsive
- Magnetic
(iii) As one goes far away from the earth, the density of air;
- Becomes bigger
- becomes less
- Remains constant
- Greater than its weight
(iv) Ferry boat floats in sea water because its density is;
- Greater than that of water
- Smaller than that of water
- The same as its weight
- Greater than its weight
(v) Study figure below;
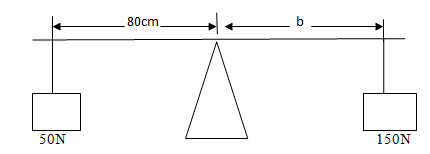
How far from the pivot must the 150g mass be placed for the system to be in
equilibrium?
- 16.7m B. 17.6cm C. 36.6cm D. 26.7cm.
(vi) A patient who is to get an injection when a nurse applies a small force to push a needle feels much pain on his skin due to;
- Very high pressure
- Very low pressure
- Blunt of the needle lip
- Small applied force
(vii) The suspended magnetic needle always comes to rest with its axis in a vertical plane called;
- Geographical meridian
- Magnetic meridian
- Geographical declination
- Magnetic declination
(viii) As the angle between two plane mirrors increases, the number of images formed;
- Decreases B. Increases C. Remains constant D. Goes to infinity
(ix) Which of the following materials do not allow light to pass through?
- Glass B. Tinted glass C. Clear plastics D. Human bodies
(x) To view distant objects which are out of direct vision we normally use;
- Telescope B. Microscope C. Periscope D. Slid projector
(xi) The process by which water soaks through the cell of rice and beans is called;
- Capillarity B. Cohesion C. Diffusion D. Osmosis
SECTION B: 70 Marks
- Match each item in list A with a correct response in List B by writing its letter below the number of the corresponding item in the table provided;
| LIST A | LIST B |
| (i) Measures the net change in position. (ii) Rate of change of distance (iii) Rate of change of velocity. (iv) Motion under the effects of gravity. (v) Measures the rate at which position changes. |
|
SECTION B 60 Marks
- Complete each of the following statements by writing the correct answer in the space provided.
(i) The product of mass and velocity of a body is called ………………………………
(ii) Claw hammer and pair of scissors are in which class of lever? ……………………
(iii) Weight has the same SI unit as …………………………………………..
(iv) An instrument used to measure pressure of a gas is known as …………………..
(v) The tendency of a liquid to rise in narrow tubes is called. …………………… (10 marks)
- (a) Define the following terms as applied in measurements and give two examples;
(i) Fundamental quantities.
(ii) Derived quantities
(b) Figure below shows graduated cylinder containing water before and after a store is
immersed,
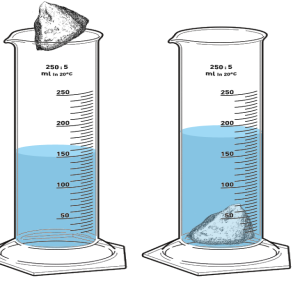
If the mass of the stone is 50g, calculate the;
(i) Volume of the stone
(ii) Density of the stone
- (a) (i) List two characteristics of images formed by plane mirrors;
(ii) Give reasons why the sky appears blue during a clear sunny day.
(b) Draw the diagram of each of the following;
(i) Parallel rays of light
(ii) Divergent rays of light
(iii) Convergent rays of light.
- (a) Define the following terms as used in physics and give its SI Unit;
(i) Work (ii) Energy
(b) A man lifts a load of 20 kg through a height of 4m in 10 seconds. Calculate the;
(i) Work done (ii) Power developed the man (10marks)
- (a) (i) State the Principle of moments.
(ii) A uniform half metre rule is freely pivoted at the 20cm mark and it balances
horizontally when a body of mass 30g is hung at 5cm mark from one end.
Calculate the mass of the rule.
(b) (i) What is meant by equilibrium?
(ii) List three applications of equilibrium in daily life. (10marks)
- (a) Define the following terms;
(i) Inertia (b) Impulse
(b) (i) Give two examples where impulse and momentum play an important role.
(ii) A tennis ball of mass 120g moving at a speed of 10m/s was brought to rest by one
player in 0.02 seconds. Calculate the average force applied by the player. (10marks)
SECTION C 25 MARKS
- (a) (i) What is the function of rheostat in an electric circuit?
(ii) List four factors that affect the resistance of a conductor.
(b) Study the circuit diagram in figure below then answer the questions that follow;
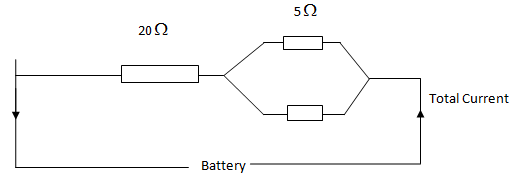
If the current flowing in 5![]() resistor is 2A; Calculate the;
resistor is 2A; Calculate the;
(i) Current flowing in 10![]() resistor
resistor
(ii) Potential difference (p.d) across the 20![]() resistor.
resistor.
- (a) (i) Define the term pressure and give its SI unit.
(ii) Why are dams constructed thicker at the bottom that at the top?
(b) (i) List three applications of hydraulic press.
(ii) A hydraulic brake has a force of 1000N applied to a piston whose area is 50cm2.
Calculate the pressure transmitted throughout the liquid.
LEARNINGHUBTZ.CO.TZ Page 1
LEARNINGHUBTZ.CO.TZFORM ONE PHYSICS MODAL SERIES 5
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
 For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256
For Call,Sms&WhatsApp: 255769929722 / 255754805256






